c语言指针进阶版
系列文章目录
1.字符指针
2.数组指针
3.指针数组
4.数组传参和指针传参
5.函数指针
6.函数指针数组与指向函数指针数组的指针
7.回调函数(通过计算器的实现来体会)
8.qsort库函数的实现。
9.指针和数组面试题的解析
前言
为啥指针需要进阶那是因为指针是c语言的灵活它可以->变量/->结构体/->函数/->数组/->文件.非常灵活方便,因而写此文章提升能力。
一、字符指针
-
Example 1
int main()
{
char ch = 'r';
char* pc = &ch;
printf("%c", *pc);
return 0;
}这边需要注意输出的时候*不能漏。
-
Example 2
通过结果进行对比,让我们明白了数组str1与str2的地址不同。因此不一样,而str3与str4是取得字符串的地址因此一样。
二、指针数组
强调: 类型 (*字母)[ ]
- //解释:ar先和*结合,说明p是一个指针变量,然后指着指向的是一个大小为10个整型的数组。所以ar一个指针,指向一个数组,叫数组指针。
- //这里要注意:[]的优先级要高于*号的,所以必须加上()来保证ar先和*结合
-
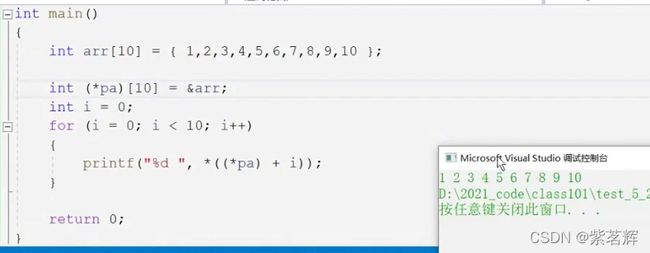
Example 1:
*()是解引用将
指针pa中的地址解析出来。
- Example 2:
&数组名vs数组名
&arr取出的是首元素地址。
通过冒泡排序进行举例
挖掉parr3[10],剩下的就是这个数组里面的东西。
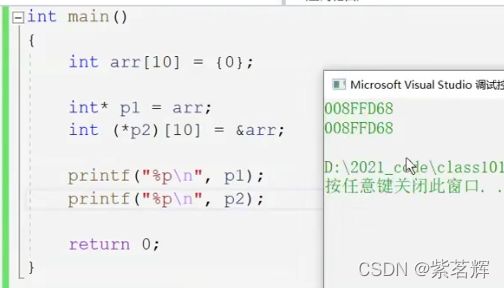
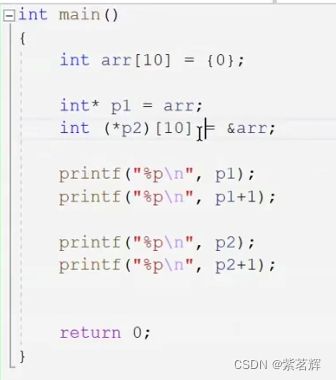
三、数组指针
Parr就是数组arr的指针。 Parr是指针名去掉后就是指针类型 ![]() 指向的是10个元素int类型。
指向的是10个元素int类型。
正常来说数组名是数组首元素的地址,但有两个例外:
1.sizeof(数组名)——数组名表示整个数组,计算的是整个数组的大小,单位是字节。
2.数组名——数组名表示整个数组,取出的是整个数组的地址。
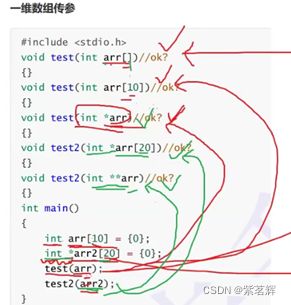
四、数组传参和指针传参
一级指针传参。
二级指针传参。
五、函数指针与指针函数
函数指针
nt (*) ()类型是函数指针
2种写法。底下的写法是上面的简化版,由于函数名就是函数的入口地址,所以把&,*这个步骤省略。
通过2个代码理解
代码1:
里面那个void (*)()是函数指针类型。吧0强制转换为函数指针类型。(如果里面加p , void (*p)()就变成了函数指针变量了)这步操作将0转化为函数的地址。由于无参所以void类型。然后将其括号起来加上解引用符*(void (*)())0在整体括号起来
(*(void (*)())0)();由于无参所以无法传参也是空着的。
代码2:
Signal是函数名signal后面()里面的是函数参数类型。
还可以这样简化。
指针函数
是指返回指针的函数
六、函数指针数组
通过以下例题进行实战了解:
计算器实现:
普通版本:
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int Sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
int Mul(int x, int y)
{
return x * y;
}
int Rem(int x, int y)
{
return x/ y;
}
void menu()
{
printf("*********************\n");
printf("**** 1.Add 2.Sub ****\n");
printf("**** 3.Mul 4.Rem ****\n");
printf("********0.Exit*******\n");
}
int main()
{
int input = 0;
do
{
menu();
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
int result = 0;
printf("请选择:>");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case 0:
printf("退出程序\n");
break;
case 1:
printf("输入x,y>:");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
result=Add(x,y);
printf("result=%d\n", result);
break;
case 2:
printf("输入x,y\n");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
result = Sub(x, y);
printf("result=%d\n", result);
break;
case 3:
printf("输入x,y>:");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
result = Mul(x, y);
printf("result=%d\n", result);
break;
case 4:
printf("输入x,y\n");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
result = Rem(x, y);
printf("result=%d\n", result);
break;
default:
printf("并无此功能,请重新选择功能!\n");
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
加强版二:
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int Sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
int Mul(int x, int y)
{
return x * y;
}
int Rem(int x, int y)
{
return x / y;
}
void menu()
{
printf("*********************\n");
printf("**** 1.Add 2.Sub ****\n");
printf("**** 3.Mul 4.Rem ****\n");
printf("********0.Exit*******\n");
}
int main()
{
int input = 0;
do
{
menu();
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
int result = 0;
int (*pfArr[5])(int, int) = { NULL,Add ,Sub,Mul,Rem };
printf("请选择:>");
scanf("%d", &input);
if (input >= 1 && input <= 4)
{
printf("输入x,y>:");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
result = (pfArr[input])(x, y);
printf("result=%d\n", result);
}
else if (input == 0)
{
printf("退出程序\n");
}
else
{
printf("选择错误,请重新选择\n");
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
究极进化三:
这个就是将选择的程序。进行调过去比方说Mul将除法调过去然后进行输入最后将值带入除法计算然后得出答案。
void menu()
{
printf("*********************\n");
printf("**** 1.Add 2.Sub ****\n");
printf("**** 3.Mul 4.Rem ****\n");
printf("********0.Exit*******\n");
}
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int Sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
int Mul(int x, int y)
{
return x * y;
}
int Rem(int x, int y)
{
return x / y;
}
void tmd(int(*nmd)(int, int))
{
int x;
int y;
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
int rep = nmd(x, y);
printf("rep=%d\n", rep);
}
int main()
{
int input = 0;
do
{
menu();
printf("请选择效果");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch(input)
{
case 1:
tmd(Add);
break;
case 2:
tmd(Sub);
break;
case 3:
tmd(Mul);
break;
case 4:
tmd(Rem);
break;
case 0:
printf("退出计算器\n");
break;
default:
printf("选择错误,请重新选择\n");
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}通过计算器的实现我们可以清楚明白函数指针数组的实现。
关于回调函数在究极版中有出现所以请自己领悟体会。
八、qsort库函数的实现。
base表示的是元素的地址,num表示的是元素的个数,size表示的是宽度,由咋们使用者自己选择类型实现。最后一个是排序的实现调用。
咋们通过以下例题进行深入实践了解:
进行数组排序:
int cmp(const* e1, const* e2)
{
return *(int *)e1 - *(int *)e2;
}
void print_arr(int* arr, int sz)
{
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%d",*(arr+i));
}
}
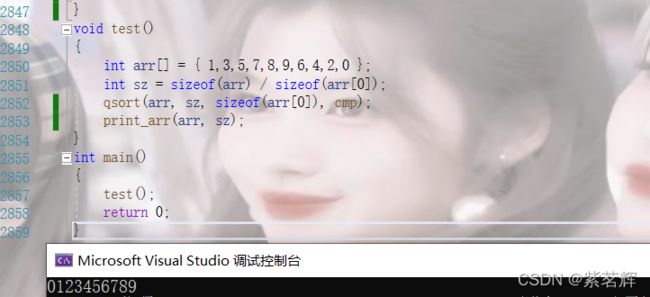
void test()
{
int arr[] = { 1,3,5,7,8,9,6,4,2,0 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
qsort(arr, sz, sizeof(arr[0]), cmp);
print_arr(arr, sz);
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}对学生年龄成绩姓名进行排序:
姓名:
struct Stu
{
char name[20];
int age;
float score;
};
void cmpname(const void* e1,const void* e2)
{
return strcmp(((struct Stu*)e1)->name, ((struct Stu*)e2)->name);
}
void printstu(struct Stu *arr, int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
printf("%s %d %.f\n", arr[i].name, arr[i].age, arr[i].score);
}
}
void test()
{
struct Stu arr[] = { {"wuwu",19,46.5f},{"lele",16,50.5f},{"huihui",17,53.6f}};
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
qsort(arr, size, sizeof(arr[0]), cmpname);
printstu(arr, size);
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}年龄:
struct Stu
{
char name[20];
int age;
float score;
};
void cmpname(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return ((struct Stu*)e1)->age-((struct Stu*)e2)->age;
}
void printstu(struct Stu* arr, int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
printf("%s %d %.f\n", arr[i].name, arr[i].age, arr[i].score);
}
}
void test()
{
struct Stu arr[] = { {"wuwu",19,46.5f},{"lele",16,50.5f},{"huihui",17,53.6f} };
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
qsort(arr, size, sizeof(arr[0]), cmpname);
printstu(arr, size);
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}成绩:
struct Stu
{
char name[20];
int age;
float score;
};
void cmpscore(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
if (((struct Stu*)e1)->score > ((struct Stu*)e2)->score)
{
return 1;
}
else if (((struct Stu*)e1)->score < ((struct Stu*)e2)->score)
{
return -1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
void printstu(struct Stu* arr, int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
printf("%s %d %.f\n", arr[i].name, arr[i].age, arr[i].score);
}
}
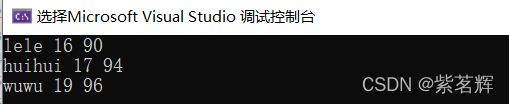
void test()
{
struct Stu arr[] = { {"wuwu",19,96.5f},{"lele",16,90.5f},{"huihui",17,93.6f} };
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
qsort(arr, size, sizeof(arr[0]), cmpscore);
printstu(arr, size);
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}我们通过冒泡排序进行实现。
由于时间原因直接上加强版冒泡:
void Smp(char* base1, char* base2, int width)
{
for (int i = 0; i < width; i++)
{
char tmp = *base1;
*base1 = *base2;
*base2 = tmp;
base1++;
base2++;
}
}
void bubble_s(void* base, int size, int width, int (*cmp)(const void* e1, const void* e2))
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < size-1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size-i - 1; j++)
{
if (cmp((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width) > 0)
{//2个元素进行交换
Smp((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width, width);
}
}
}
}
void printbubble(int arr[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
printf("%d", arr[i]);
}
}
int cmpint(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return *(int*)e1 - *(int*)e2;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 9,2,6,3,5,4,7,8,1,0 };
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
bubble_s(arr, size, sizeof(arr[0]), cmpint);
printbubble(arr, size);
return 0;
}总结
成为强者。