二维矩形件排样算法之最低水平线算法实现
最低水平线算法的简单实现(Python)
二维矩形排样算法众多,最早的有BL算法、下台阶算法、最低水平线算法等,其中最低水平线算法及其优化算法应用较多,是与智能优化算法(遗传算法、模拟退火算法等)结合的较多的算法,本文利用python对最低水平线算法做了实现
问题描述
矩形件优化排样问题就是在给定的矩形板材上排放一系列矩形零件,且矩形板材的宽度为一定值,高度方向无限延伸,所有零件采用正交排放的方式,被排放的零件之间不能有重叠,且零件必须全部排放在板材内部,要求找到一个最优排样方案使得板材的利用率最高。
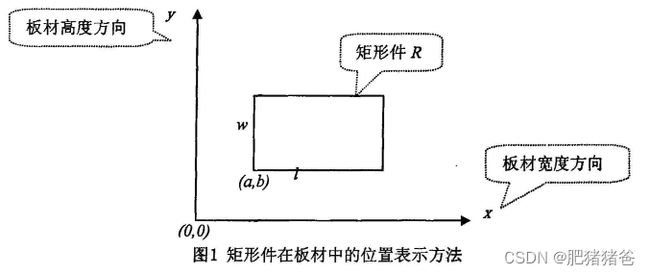
为了方便对问题进行描述,不妨设矩形板材的宽度 W W W为一定值,高度 H H H不限,待排零件总数为 n n n,矩形件集为 ( R 1 , R 2 , . . . , R n ) (R_1,R_2,...,R_n) (R1,R2,...,Rn),第 i i i个矩形件 R i R_i Ri的长为 l i l_i li,宽为 w i w_i wi。以板材的左下角为原点,宽度方向为x轴,高度方向为y轴建立直角坐标系。每一个被排入的零件在板材中的具体位置用其在坐标系中最左、最上、最右、最下四个坐标值表示,即 R e c t ( l e f t , t o p , r i g h t , b o t t o m ) Rect(left,top,right,bottom) Rect(left,top,right,bottom)。如下图所示,矩形件 R R R的长为 l l l,宽为 w w w,左下角坐标值为 ( a , b ) (a,b) (a,b),则可以用 R ( a , b + w , a + l , b ) R(a,b+w,a+l,b) R(a,b+w,a+l,b)来表示矩形件 R R R在板材中的位置。
将指定规格和数量的矩形零件排入矩形板材内,排完后板材在高度方向上使用的越少其利用率越高,问题的目标函数如式1。

其中 H m a x H_{max} Hmax为排样完成后所用板材的最大高度,目标函数 f ( x ) f(x) f(x)实际为板材的利用率。
最低水平线法
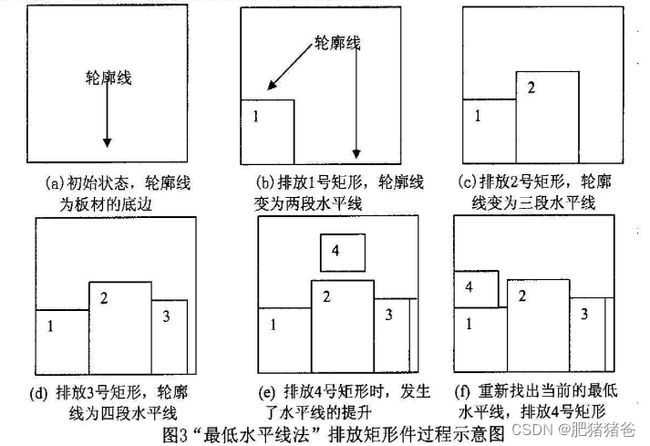
近年来贾志欣等人提出的最低水平线法受到了理论界的广泛关注,众多学者对其加以改进应用,都取得了较好的排样效果。最低水平线法是一种不断更新水平线集的排样算法,其基本思想就是在水平线集中选择高度最低的那条,将要排放的零件排放在最低水平线上并更新水平线集,如果最低水平线宽度不够,排放不下当前要排的零件,则搜索与最低水平线左右两边相邻的水平线,选择高度低的一条,将最低水平线提升至该高度,判断更新后的最低水平线能否排入该零件,若依然排不下则继续执行提升水平线的操作,直至该零件能排入为止。其具体步骤如下:
(1)初始化水平线集,初始状态下水平线集中只有一条水平线,为坐标系中板材最底部的边;
(2)选择要排入的零件;
(3)从水平线集中的选取最低的那条水平线,如果最低水平线不止一条则选取最靠左边的那条。如果被选中的水平线的宽度大于要排入的矩形零件的长度,执行步骤(4),否则执行步骤(5);
(4)将该零件排放在最低水平线的最左端,更新水平线集,转步骤(6);
(5)选择与最低水平线相邻且高度较低的一段水平线,将最低水平线提升与该水平线平齐,更新水平线集,转向执行步骤(3);
(6)判断所有零件是否排样完毕,若排放完毕则排样结束,否则转向执行步骤(2)。
本文令水平线集为 L i n e L i s t LineList LineList,每一条水平线由其在坐标系中的起始点和终点横坐标及它们共同的纵坐标三个变量表示,即 L i n e ( o r i g i n , e n d , h e i g h t ) Line(origin,end,height) Line(origin,end,height),图2 所示为一个最低水平线法的排样过程,初始时刻水平线集中只有一条水平线 L i n e L i s t { ( 0 , W , 0 ) } LineList\{(0,W,0)\} LineList{(0,W,0)},将零件1排放在该水平线上,并相应的更新水平线集,此时零件1的位置为 R 1 ( 0 , w 1 , l 1 , 0 ) R_1(0,w_1,l_1,0) R1(0,w1,l1,0),水平线集为 L i n e L i s t { ( 0 , l 1 , w 1 ) , ( l 1 , W , 0 ) ) } LineList\{(0,l_1,w_1),(l_1,W,0))\} LineList{(0,l1,w1),(l1,W,0))},从水平线集中选取高度最低的一段,比较其与零件2的宽度,如图(b)所示,最低水平线宽度大于零件2的宽度,于是将零件2排放在最低水平线上,零件2的位置为 R 2 ( l 1 , w 2 , l 1 + l 2 , 0 ) R_2(l_1,w_2,l_1+l_2,0) R2(l1,w2,l1+l2,0),再排零件3,此时的最低水平线集为 L i n e L i s t { ( 0 , l 1 , w 1 ) , ( l 1 , l 1 + l 2 , w 2 ) , ( l 1 + l 2 , W , 0 ) } LineList\{(0,l_1,w_1) ,(l_1,l_1+l_2,w_2),(l_1+l_2,W,0)\} LineList{(0,l1,w1),(l1,l1+l2,w2),(l1+l2,W,0)},但最低水平线宽度小于零件3的宽度,因此将该水平线提升至与其相邻的且高度较低的那段水平线的高度,如图(d)所示,更新后的水平线集为 L i n e L i s t { ( 0 , l 1 , w 1 ) , ( l 1 , W , w 2 ) } LineList\{(0,l_1,w_1),(l_1,W,w_2)\} LineList{(0,l1,w1),(l1,W,w2)},再选择高度最低的那条排入零件3,依次类推。图(f)为最终排样结果。
代码如下,所需的依赖包有 matplotlib 和 numpy
import copy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 水平线类(起始x位置,终止x位置,高度)
class OutLine:
def __init__(self, origin, end, height):
self.origin = origin
self.end = end
self.height = height
def __str__(self):
return "OutLine:origin:{}, end:{}, height:{}".format(self.origin, self.end, self.height)
# 矩形物品类(宽度,高度,编号)
class Product:
def __init__(self, w, h, num=0):
self.w = w
self.h = h
self.num = num
def __str__(self):
return "product:w:{}, h:{}, num:{}".format(self.w, self.h, self.num)
@staticmethod
def by_num(num, data):
_l = [d for d in data if d.num == num]
return _l[0] if len(_l) > 0 else None
# 布局类
class RectLayout:
def __init__(self, line_list=[]):
self.line_list = line_list
# 初始化水平线集合(起始x位置,终止x位置,高度)
def init_line_list(self, origin, end, height):
self.line_list.append(OutLine(origin, end, height))
# 提升最低水平线
def enhance_line(self, index):
if len(self.line_list) > 1:
# 获取高度较低的相邻水平线索引,并更新水平线集
neighbor_idx = 0
if index == 0:
neighbor_idx = 1
elif index + 1 == len(self.line_list):
neighbor_idx = index - 1
else:
# 左边相邻水平线
left_neighbor = self.line_list[index - 1]
# 右边相邻水平线
right_neighbor = self.line_list[index + 1]
# 选择高度较低的相邻水平线,左右相邻水平线高度相同时,选择左边相邻的水平线
if left_neighbor.height < right_neighbor.height:
neighbor_idx = index - 1
elif left_neighbor.height == right_neighbor.height:
if left_neighbor.origin < right_neighbor.origin:
neighbor_idx = index - 1
else:
neighbor_idx = index + 1
else:
neighbor_idx = index + 1
# 选中的高度较低的相邻水平线
old = self.line_list[neighbor_idx]
# 更新相邻水平线
if neighbor_idx < index:
self.line_list[neighbor_idx] = OutLine(old.origin, old.end + self.line_width(index), old.height)
else:
self.line_list[neighbor_idx] = OutLine(old.origin - self.line_width(index), old.end, old.height)
# 删除当前水平线
del self.line_list[index]
# 按位置更新水平线
def update_line_list(self, index, new_line):
self.line_list[index] = new_line
# 按位置插入水平线(插在某索引位置后面)
def insert_line_list(self, index, new_line):
new_lists = []
if len(self.line_list) == index + 1:
new_lists = self.line_list + [new_line]
else:
new_lists = self.line_list[:index + 1] + [new_line] + self.line_list[index + 1:]
self.line_list = new_lists
# 计算水平线宽度
def line_width(self, index):
line = self.line_list[index]
return line.end - line.origin
# 找出最低水平线(如果最低水平线不止一条则选取最左边的那条)
def find_lowest_line(self):
# 最低高度
lowest = min([_l.height for _l in self.line_list])
# 最低高度时,最小开始横坐标
origin = min([_l.origin for _l in self.line_list if _l.height == lowest])
for _idx, _line in enumerate(self.line_list):
if _line.height == lowest and _line.origin == origin:
return _line, _idx
return None, None
# 清空水平线集合
def empty_line_list(self):
self.line_list.clear()
# 计算最高水平线高度,即所用板材最大高度
def cal_high_line(self):
max_height = max([ll.height for ll in self.line_list])
return max_height
# 主方法
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 板材宽度
container_width = 10
# 矩形物品数量
item_num = 25
# 初始化矩形物品尺寸,也可以随机生成
# item_sizes = np.random.randint(1, 8, size=(item_num, 2)).tolist()
item_sizes = [[3, 1], [4, 4], [1, 1], [2, 3], [2, 4], [3, 4], [1, 4], [2, 2], [3, 3], [3, 1], [4, 2], [3, 1],
[3, 1], [3, 2], [4, 2], [1, 2], [1, 3], [3, 4], [2, 3], [1, 1], [2, 1], [3, 2], [4, 3], [3, 2],
[4, 3]]
# 按面积对矩形物品尺寸排序
_item_sizes = sorted(item_sizes, key=lambda x: x[0] * x[1], reverse=True)
print(_item_sizes)
# 排样序号
ran = [i + 1 for i in range(item_num)]
print(ran)
# 矩形物品列表
products = []
for idx in range(item_num):
products.append(Product(_item_sizes[idx][0], _item_sizes[idx][1], ran[idx]))
# 初始化布局类
layout = RectLayout()
# 初始化水平线集
layout.init_line_list(0, container_width, 0)
# 最终位置结果[[矩形件编号,左下角横坐标,左下角纵坐标], ...]
result_pos = []
_products = copy.deepcopy(products)
while _products:
# 取出首部矩形件
pro = _products[0]
# 最低水平线及其索引
lowest_line, lowest_idx = layout.find_lowest_line()
# 可用长度
available_width = layout.line_width(lowest_idx)
if lowest_line is None and lowest_idx is None:
exit(0)
if available_width >= pro.w:
# 对矩形件排样
result_pos.append([pro.num, lowest_line.origin, lowest_line.height])
# 更新水平线集
new_line1 = OutLine(lowest_line.origin, lowest_line.origin + pro.w, lowest_line.height + pro.h)
new_line2 = OutLine(lowest_line.origin + pro.w, lowest_line.origin + available_width, lowest_line.height)
layout.update_line_list(lowest_idx, new_line1)
if available_width - pro.w > 0:
layout.insert_line_list(lowest_idx, new_line2)
# 剔除已经排样的物品
_products.pop(0)
else:
# 最低水平线宽度小于要排样矩形宽度,提升最低水平线
layout.enhance_line(lowest_idx)
# 计算最大排样高度
container_height = layout.cal_high_line()
# 计算板材利用率
used_area = 0
for pos in result_pos:
_p = Product.by_num(pos[0], products)
used_area += _p.w * _p.h
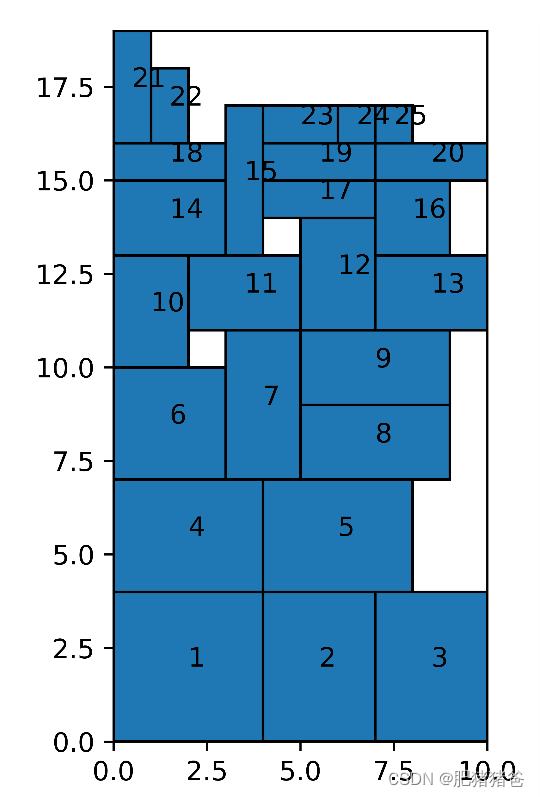
print("used_area: {}".format(used_area))
print("ratio: {}%".format(round((used_area * 100) / (container_width * container_height), 3)))
# 绘制排样布局
fig = plt.figure()
plt.xlim(0, container_width)
plt.ylim(0, container_height)
plt.axis("off")
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, aspect='equal')
ax.set_xlim(0, container_width)
ax.set_ylim(0, container_height)
for pos in result_pos:
pro = Product.by_num(pos[0], products)
ax.add_patch(
plt.Rectangle(
(pos[1], pos[2]), # 矩形左下角
pro.w, # 长
pro.h, # 宽
alpha=1,
edgecolor='black',
linewidth=1
)
)
# 物品编号
ax.text(pos[1] + pro.w / 2, pos[2] + pro.h / 2, "{}".format(pos[0]), transform=ax.transData)
# plt.show()
plt.savefig('lowest_horizontal_line.png', dpi=800)
代码托管在gitee,项目持续更新
本文参考了合肥工业大学硕士论文《启发式算法在矩形件优化排样中的应用》和广西师范大学硕士论文《矩形件下料优化排样的遗传算法》
下一篇文章将分析最低水平线算法的缺点,并讲解最低水平线搜索算法,尽情期待
作者这水平有限,有不足之处欢迎留言指正