【Java】认识String类
目录
String是什么?
字符串比较
理解字符串不可变
字符、字节、字符串
字符与字符串的相互转换
字节与字符串
字符串常见操作
字符串比较
字符串查找
字符串替换
字符串拆分
字符串截取
其他操作方法
StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder
小结
String是什么?
Sring是字符串类型
它是引用数据类型,不是基本数据类型。
用双引号("")引起来的都是字符串,例如:"a","菜","abcde","123",这些都是字符串。
字符串是一种不可变对象,它的内容不能改变。
创建字符串三种方法:
//方法一
String str1="abcdef";
//方法二
String str2=new String("ghijk");
//方法三(相当于将字符数组转为字符串)
char[] ch={'t','b','g'};
String str3=new String(ch);
举个例子:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//方法一
String str1="abcdef";
//方法二
String str2=new String("ghijk");
//方法三
char[] ch={'t','b','g'};
String str3=new String(ch);
System.out.println(str1);
System.out.println(str2);
System.out.println(str3);
}
}
运行结果:
字符串比较
public static void main(String[] args) {
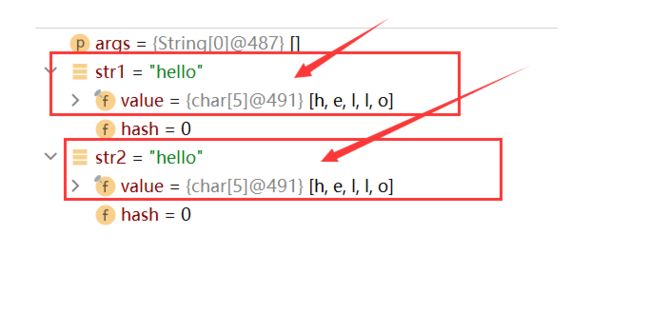
String str1="hello";
String str2=new String("hello");
System.out.println(str1==str2);
System.out.println("=================");
String str3="hello";
String str4="hello";
System.out.println(str3==str4);
System.out.println("=================");
String str5=new String("hello");
String str6=new String("hell0");
System.out.println(str5==str6);
}
//执行结果:
//false
//true
//false注意:
因为String是引用类型,这里的(str1==str2)比较的是他们引用的对象的地址,而不是比较他们的内容。
那么为什么运行结果是这样子的呢?
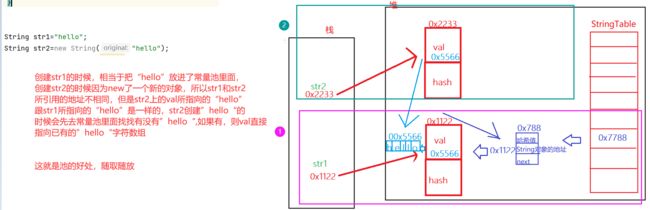
这时候我们得提到一个概念--->池。
" 池 " 是编程中的一种常见的 , 重要的提升效率的方式 , 我们会在未来的学习中遇到各种 " 内存池 ", " 线程池 ", " 数据库连接池 " ....
这里主要了解是字符串常量池。那什么是字符串常量池呢?
字符串常量池:主要存放字符串常量,本质上是一个哈希表(String Table)。
接下来我们再来看看上面的字符串比较。
String str1="hello";
String str2=new String("hello");
我们可以看到str1的val和str2的val所存放字符数组是一样的,说明他俩所指向"hello"是同一个。
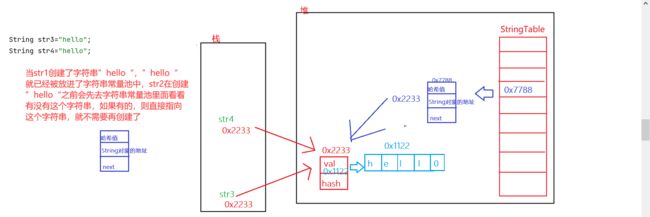
String str3="hello";
String str4="hello";
String str5=new String("hello");
String str6=new String("hello");
同上,因为str5new了一个对象,str6又new了一个对象,他们所引用的对象的地址肯定不一样。
以上都是比较的都是地址,那么内容该怎么比较呢?
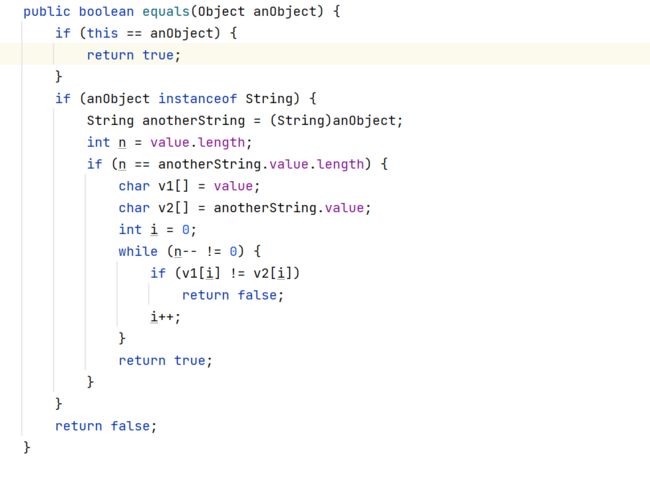
可以用equals来比较两个字符串的内容是否相等,接下来我们先看看它的源码:
怎么用?举个例子:
String str1="hello";
String str2=new String("hello");
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));
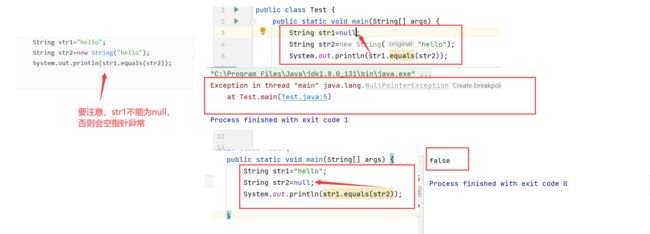
//执行结果 true需要注意:
equals前面的字符串在这里就是str1不能为null!!!
注意:
String str3=null;//代表的是str3不指向任何对象
String str4="";//代表的是str4指向的对象为空理解字符串不可变
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1="hello";
str1=str1+"world";
System.out.println(str1);
}
//打印结果 helloworld看上面代码,一看,欸,str1内容通过拼接改变了欸,其实str1本身是没有改变的,普通的字符串拼接会被优化成StringBuilder对象,str1拼接其实是通过new StringBuilder创建了一个新的对象,这个新的对象里面进行拼接,所以str1本身是没有改变的。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1="hello";
//StringBuilder stringBuilder=new StringBuilder();
//stringBuilder.append(str1);
str1=str1+"world";
//stringBuilder.append("world");
System.out.println(str1);
//System.out.println(stringBuilder.toString);
}
}但是如果我们非要改变它,可以用反射,但是这里不过多介绍,后续会再说。
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
String str="hello";
// 获取 String 类中的 value 字段. 这个 value 和 String 源码中的 value 是匹配的.
Field valueField = String.class.getDeclaredField("value");
// 将这个字段的访问属性设为 true
valueField.setAccessible(true);
// 把 str 中的 value 属性获取到.
char[] value = (char[]) valueField.get(str);
// 修改 value 的值
value[0] = 'g';
System.out.println(str);
// 执行结果
//gello
}字符、字节、字符串
字符与字符串的相互转换
字符数组--->字符串
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] ch={'a','b','c'};
String str=new String(ch);//将整个字符数组转为字符串
String str1=new String(ch,1,2);//将字符数组部分转为字符串
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(str1);
}
//执行结果
//abc
//bc字符串-->字符/字符数组
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="helllo";
System.out.println(str.charAt(2));//获取某个下标的字符
// 将字符串变为字符数组
char[] data = str.toCharArray() ;
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
System.out.print(data[i]+" ");
}
}
//执行结果
//l
//h e l l o字节与字符串
//字符串转字节数组
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="abcde";
byte[] data=str.getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
System.out.print(data[i]+" ");
}
//字节数组转字符串
System.out.println("============");
String str1=new String(data);
String str2=new String(data,1,2);//字节数组部分转字符串,这里是从下标为1开始转,长度为2
System.out.println(str1);
System.out.println(str2);
}
//打印结果
//97 98 99 100 101
//============
//abcde
//bc
字符串常见操作
字符串比较
equals(内容比较,区分大小写)
equalsIgnoreCase(不区分大小写的比较)
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1="Hello";
String str2="hello";
boolean flag=str1.equals(str2);//区分大小写的比较
boolean flag1=str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str2);//不区分大小写的比较
System.out.println(flag);
System.out.println(flag1);
}
//执行结果
//false
//truecompareTo:比较两个字符串大小,返回类型为int类型
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("A".compareTo("a"));
System.out.println("a".compareTo("A"));
System.out.println("A".compareTo("A"));
System.out.println("AC".compareTo("AB"));
}
//执行结果
//-32
//32
//0
//1字符串查找
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1="hello";
//contains:是否包含某个字符串,返回类型boolean
boolean flag=str1.contains("h");
System.out.println(flag);//true
System.out.println(str1.contains("a"));//false
//indexOf:查找某个字符串所在指定下标,如果不存在返回-1
//也可以从指定下标位置开始查找
System.out.println(str1.indexOf("o"));//4
System.out.println(str1.indexOf("b"));//-1
System.out.println(str1.indexOf("l",0));//2
System.out.println(str1.indexOf("lo",2));//3
System.out.println(str1.indexOf("a",0));//-1
//lastIndexOf:从后往前找,是否找到某个字符串,找到返回该下标,找不到返回-1
System.out.println(str1.lastIndexOf("o"));4
System.out.println(str1.lastIndexOf("c"));//-1
//lastIndexOf:也可以从指定下标从后往前找某个字符串
System.out.println(str1.lastIndexOf("h",2));//0
System.out.println(str1.lastIndexOf("l",2));//2
//startsWith:某个下标位置对应的字符串是否是这个字符串或者判断是否以这个字符串开头
System.out.println(str1.startsWith("h",0));//true
System.out.println(str1.startsWith("h",1));//false
System.out.println(str1.startsWith("e",0));//false
System.out.println(str1.startsWith("e",1));//true
System.out.println(str1.startsWith("he"));//true
//endsWith:判断是否以这个字符串结尾
System.out.println(str1.endsWith("o"));//true
System.out.println(str1.endsWith("l"));//false
}字符串替换
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1="hello";
System.out.println(str1.replaceAll("l","_"));//替换所有指定内容
System.out.println(str1.replaceFirst("l","_"));//替换首个内容
}
//执行结果
//he_ _o
//he_lo字符串拆分
将字符串全部拆分
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1="hello world hello everybody";
String[] result=str1.split(" ");//按照空格拆分
for (String s:result) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
//执行结果
//hello
//world
//hello
//everybody将字符串部分拆分
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1="hello world hello everybody";
String[] result=str1.split(" ",2);
for (String s:result) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
//执行结果
//hello
//world hello everybody拆分时,有些特殊字符作为分割符可能无法正确切分,需要加上转义。
注意:
String str = "192.168.1.1" ;
String[] result = str.split("\\.") ; //"."需要加上\\转义
for(String s: result) {
System.out.println(s);
}
//执行结果
//192
//168
//1
//1 public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1="hello@world hello&everybody";
String[] result=str1.split("@| |&");//多个分隔符可用|隔开
for (String s:result) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
//执行结果
//hello
//world
//hello
//everybody多次拆分:
String str = "name=zhangsan&age=18" ;
String[] result = str.split("&") ;
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
String[] temp = result[i].split("=") ;
System.out.println(temp[0]+" "+temp[1]);
}
//打印结果
//name zhangsan
//age 18字符串截取
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1="hello world";
System.out.println(str1.substring(1));//从指定位置截取到结尾
System.out.println(str1.substring(1,7));//截取部分内容,左闭右开
}
//执行结果
//ello world
//ello w其他操作方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1=" hello world hello ";
//trim:去掉左右空格保留中间空格
System.out.println("ok"+str1.trim()+"ok");//okhello world hellook
//toUpperCase:字符串转大写
System.out.println(str1.toUpperCase());//HELLO WORLD HELLO
String str2="HELLO";
//toLowerCase:字符串转小写
System.out.println(str2.toLowerCase());//hello
//concat:字符串拼接
System.out.println(str2.concat(" WORLD"));//HELLO WORLD
//判断字符串是否为空(长度是否为0)
System.out.println("hello".isEmpty());//false
System.out.println("".isEmpty());//true
}StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcdef";
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
sb.append(str);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
sb.append(i);
}
str = sb.toString();
System.out.println(str);
}
如果这里用的是String的话,在循环里面会创建多个对象,但是StringBuffer不会,所以这种时候用StringBuffer就更节省空间。我们可以看下图StringBuffer的源码,他返回的是对该对象的引用,而String返回的new的新的对象。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="abcdef";
//String-->StringBuffer/StringBuilder
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();
sb.append(str);//利用append()方法
//StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer(str);构造方法
//StringBuffer/StringBuilder-->String
String str2=sb.toString();//调用toString()方法
}小结
以上就是今天的内容了,有什么问题欢迎大家在评论区留言✌✌✌