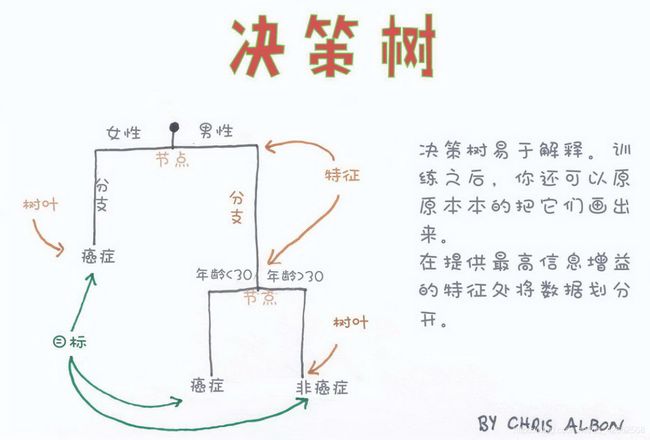
模式识别与机器学习作业——决策树(Python实现)
Decision Tree
- Homework 4
-
- Report:
-
- ID3
- CART
- Code:
-
- ID3
- Cart
- Reference:
Homework 4
Report:
ID3
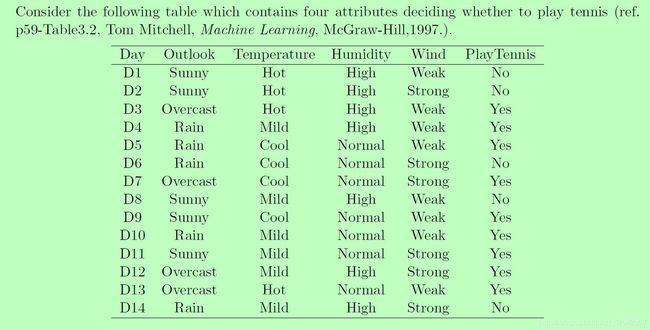
(a) (20 points) Build a decision tree based on the this table using I D 3 ID3 ID3 algorithm (Please use the entropy impurity).
The result:(based on I D 3 ID3 ID3)
CART
(b) Build a decision tree based on the this table using C A R T CART CART algorithm (Please use the G i n i Gini Gini impurity).

The result:(based on C a r t Cart Cart)
© Compare the results of (a) and (b), and explain the major difference between I D 3 ID3 ID3 and C A R T CART CART.
| Generating decision tree | pruning | |
|---|---|---|
| I D 3 ID3 ID3 | When the I D 3 ID3 ID3 algorithm generates a decision tree, the feature with the largest information gain and all its possible values are picked up at each layer to divide the data set, so I D 3 ID3 ID3 generation is not necessarily a binary tree. | The pruning of I D 3 ID3 ID3 is performed by comparing the changes of the loss function of a branch before and after being pruned |
| C A R T CART CART | When C A R T CART CART spans the tree, iterates through all possible values of each feature, calculates the maximum or minimum G i n i Gini Gini coefficient (classification) or mean square error (regression) and its value, and divides the data set according to whether it is equal to this value. Therefore, the decision tree derived by C A R T CART CART is a binary tree. The nature of regression tree is also the idea of classification. | C A R T CART CART uses a non-fixed ‘regularization parameter’, and gradually increases (or decreases) the value to obtain multiple pruned subtrees, and selects the optimal subtree through cross-validation. |
Code:
ID3
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from math import log
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
dataset = pd.read_csv('data.csv')
dataset = dataset.iloc[:,1:]
dataset
| Outlook | Temperature | Humidity | Wind | PlayTennis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Sunny | Hot | High | Weak | No |
| 1 | Sunny | Hot | High | Strong | No |
| 2 | Overcast | Hot | High | Weak | Yes |
| 3 | Rain | Mild | High | Weak | Yes |
| 4 | Rain | Cool | Normal | Weak | Yes |
| 5 | Rain | Cool | Normal | Strong | No |
| 6 | Overcast | Cool | Normal | Strong | Yes |
| 7 | Sunny | Mild | High | Weak | No |
| 8 | Sunny | Cool | Normal | Weak | Yes |
| 9 | Rain | Mild | Normal | Weak | Yes |
| 10 | Sunny | Mild | Normal | Strong | Yes |
| 11 | Overcast | Mild | High | Strong | Yes |
| 12 | Overcast | Hot | Normal | Weak | Yes |
| 13 | Rain | Mild | High | Strong | No |
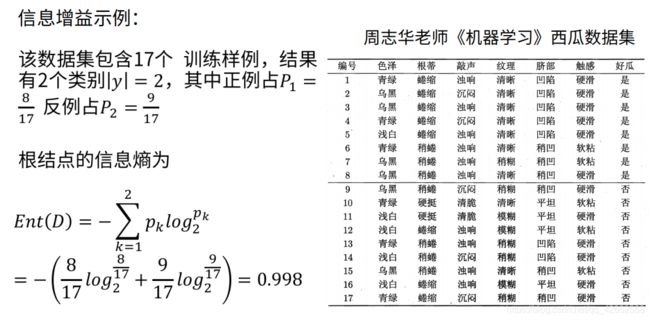
# 计算熵
def calc_ent(datasets):
data_length = len(datasets)
label_count = {}
for i in range(data_length):
label = datasets[i][-1]
if label not in label_count:
label_count[label] = 0
label_count[label] += 1
ent = -sum([(p / data_length) * log(p / data_length, 2)
for p in label_count.values()])
return ent
calc_ent(dataset['PlayTennis'].tolist())
0.9402859586706309
# 根据某一特征划分数据
def split_dataframe(data, col):
unique_values = data[col].unique()
result_dict = {elem : pd.DataFrame for elem in unique_values}
for key in result_dict.keys():
result_dict[key] = data[:][data[col] == key]
return result_dict
data_split = split_dataframe(dataset, 'Outlook')
for item, value in data_split.items():
print(item, value)
Sunny Outlook Temperature Humidity Wind PlayTennis
0 Sunny Hot High Weak No
1 Sunny Hot High Strong No
7 Sunny Mild High Weak No
8 Sunny Cool Normal Weak Yes
10 Sunny Mild Normal Strong Yes
Overcast Outlook Temperature Humidity Wind PlayTennis
2 Overcast Hot High Weak Yes
6 Overcast Cool Normal Strong Yes
11 Overcast Mild High Strong Yes
12 Overcast Hot Normal Weak Yes
Rain Outlook Temperature Humidity Wind PlayTennis
3 Rain Mild High Weak Yes
4 Rain Cool Normal Weak Yes
5 Rain Cool Normal Strong No
9 Rain Mild Normal Weak Yes
13 Rain Mild High Strong No
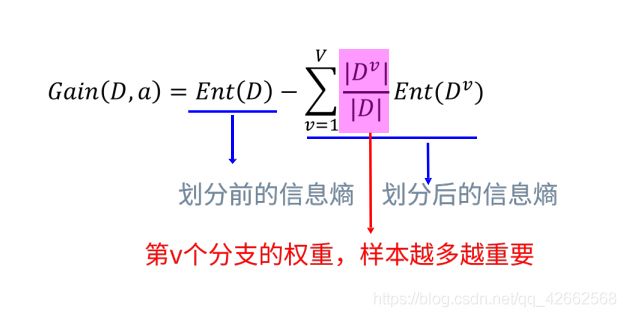
# 选取信息增益最大的特征
def choose_best_col(data, label):
entropy_D = calc_ent(data[label].tolist()) # 划分前的信息熵
cols = [col for col in data.columns if col not in [label]]
# 初始化
max_value, best_col = -999, None
max_splited = None
# 根据不同的特征拆分数据
for col in cols:
splited_set = split_dataframe(data, col)
entropy_DA = 0
for subset_col, subset in splited_set.items():
entropy_Di = calc_ent(subset[label].tolist()) # 划分后的信息熵
entropy_DA += len(subset)/len(data) * entropy_Di # 求经验条件熵
info_gain = entropy_D - entropy_DA # 求信息增益
if info_gain > max_value:
max_value, best_col = info_gain, col
max_splited = splited_set
return max_value, best_col, max_splited
choose_best_col(dataset, 'PlayTennis')
(0.2467498197744391,
'Outlook',
{'Sunny': Outlook Temperature Humidity Wind PlayTennis
0 Sunny Hot High Weak No
1 Sunny Hot High Strong No
7 Sunny Mild High Weak No
8 Sunny Cool Normal Weak Yes
10 Sunny Mild Normal Strong Yes,
'Overcast': Outlook Temperature Humidity Wind PlayTennis
2 Overcast Hot High Weak Yes
6 Overcast Cool Normal Strong Yes
11 Overcast Mild High Strong Yes
12 Overcast Hot Normal Weak Yes,
'Rain': Outlook Temperature Humidity Wind PlayTennis
3 Rain Mild High Weak Yes
4 Rain Cool Normal Weak Yes
5 Rain Cool Normal Strong No
9 Rain Mild Normal Weak Yes
13 Rain Mild High Strong No})
# ID3算法实现
class ID3Tree:
# 定义一个节点类
class Node:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
self.connections = {}
def connect(self, label, node):
self.connections[label] = node
def __init__(self, data, label):
self.columns = data.columns
self.data = data
self.label = label
self.root = self.Node("Root")
# 打印树的方法
def print_tree(self, node, tabs):
print(tabs + node.name)
for connection, child_node in node.connections.items():
print(tabs + "\t" + "(" + connection + ")")
self.print_tree(child_node, tabs + "\t\t")
def construct_tree(self):
self.construct(self.root, "", self.data, self.columns)
# 构建树
def construct(self, parent_node, parent_connection_label, input_data, columns):
max_value, best_col, max_splited = choose_best_col(input_data[columns], self.label)
if not best_col:
node = self.Node(input_data[self.label].iloc[0])
parent_node.connect(parent_connection_label, node)
return
node = self.Node(best_col)
parent_node.connect(parent_connection_label, node)
new_columns = [col for col in columns if col != best_col]
# 递归构建决策树
for splited_value, splited_data in max_splited.items():
self.construct(node, splited_value, splited_data, new_columns)
treeId3 = ID3Tree(dataset, 'PlayTennis')
treeId3.construct_tree()
treeId3.print_tree(treeId3.root, "")
Root
()
Outlook
(Sunny)
Humidity
(High)
Temperature
(Hot)
Wind
(Weak)
No
(Strong)
No
(Mild)
Wind
(Weak)
No
(Normal)
Temperature
(Cool)
Wind
(Weak)
Yes
(Mild)
Wind
(Strong)
Yes
(Overcast)
Temperature
(Hot)
Humidity
(High)
Wind
(Weak)
Yes
(Normal)
Wind
(Weak)
Yes
(Cool)
Humidity
(Normal)
Wind
(Strong)
Yes
(Mild)
Humidity
(High)
Wind
(Strong)
Yes
(Rain)
Wind
(Weak)
Temperature
(Mild)
Humidity
(High)
Yes
(Normal)
Yes
(Cool)
Humidity
(Normal)
Yes
(Strong)
Temperature
(Cool)
Humidity
(Normal)
No
(Mild)
Humidity
(High)
No
Cart
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from math import log
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
dataset = pd.read_csv('data.csv')
dataset = dataset.iloc[:, 1:]
dataset
| Outlook | Temperature | Humidity | Wind | PlayTennis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Sunny | Hot | High | Weak | No |
| 1 | Sunny | Hot | High | Strong | No |
| 2 | Overcast | Hot | High | Weak | Yes |
| 3 | Rain | Mild | High | Weak | Yes |
| 4 | Rain | Cool | Normal | Weak | Yes |
| 5 | Rain | Cool | Normal | Strong | No |
| 6 | Overcast | Cool | Normal | Strong | Yes |
| 7 | Sunny | Mild | High | Weak | No |
| 8 | Sunny | Cool | Normal | Weak | Yes |
| 9 | Rain | Mild | Normal | Weak | Yes |
| 10 | Sunny | Mild | Normal | Strong | Yes |
| 11 | Overcast | Mild | High | Strong | Yes |
| 12 | Overcast | Hot | Normal | Weak | Yes |
| 13 | Rain | Mild | High | Strong | No |
# 计算Gini指数
def gini(data):
probs = [data.count(i) / len(data) for i in set(data)]
gini = sum([p * (1 - p) for p in probs])
return gini
gini(dataset['PlayTennis'].tolist())
0.4591836734693877
# 根据某一特征划分数据
def split_dataframe(data, col):
unique_values = data[col].unique()
result_dict = {elem: pd.DataFrame for elem in unique_values}
for key in result_dict.keys():
result_dict[key] = data[:][data[col] == key]
return result_dict
split_dataframe(dataset, 'Temperature')
{'Hot': Outlook Temperature Humidity Wind PlayTennis
0 Sunny Hot High Weak No
1 Sunny Hot High Strong No
2 Overcast Hot High Weak Yes
12 Overcast Hot Normal Weak Yes,
'Mild': Outlook Temperature Humidity Wind PlayTennis
3 Rain Mild High Weak Yes
7 Sunny Mild High Weak No
9 Rain Mild Normal Weak Yes
10 Sunny Mild Normal Strong Yes
11 Overcast Mild High Strong Yes
13 Rain Mild High Strong No,
'Cool': Outlook Temperature Humidity Wind PlayTennis
4 Rain Cool Normal Weak Yes
5 Rain Cool Normal Strong No
6 Overcast Cool Normal Strong Yes
8 Sunny Cool Normal Weak Yes}
# 选取Gini指数最小的特征
def choose_best_col(data, label):
gini_D = gini(df[label].tolist()) # 划分前的Gini指数
cols = [col for col in data.columns if col not in [label]]
# 初始化
min_value, best_col = 999, None
min_splited = None
# 根据不同的特征拆分数据
for col in cols:
splited_set = split_dataframe(data, col)
gini_DA = 0
for subset_col, subset in splited_set.items():
gini_Di = gini(subset[label].tolist()) # 划分后的Gini指数
gini_DA += len(subset) / len(data) * gini_Di # 计算当前特征的Gini指数
if gini_DA < min_value:
min_value, best_col = gini_DA, col
min_splited = splited_set
return min_value, best_col, min_splited
choose_best_col(dataset, 'PlayTennis')
(0.34285714285714286,
'Outlook',
{'Sunny': Outlook Temperature Humidity Wind PlayTennis
0 Sunny Hot High Weak No
1 Sunny Hot High Strong No
7 Sunny Mild High Weak No
8 Sunny Cool Normal Weak Yes
10 Sunny Mild Normal Strong Yes,
'Overcast': Outlook Temperature Humidity Wind PlayTennis
2 Overcast Hot High Weak Yes
6 Overcast Cool Normal Strong Yes
11 Overcast Mild High Strong Yes
12 Overcast Hot Normal Weak Yes,
'Rain': Outlook Temperature Humidity Wind PlayTennis
3 Rain Mild High Weak Yes
4 Rain Cool Normal Weak Yes
5 Rain Cool Normal Strong No
9 Rain Mild Normal Weak Yes
13 Rain Mild High Strong No})
# Cart算法实现
class CartTree:
# 定义一个节点类
class Node:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
self.connections = {}
def connect(self, label, node):
self.connections[label] = node
def __init__(self, data, label):
self.columns = data.columns
self.data = data
self.label = label
self.root = self.Node("Root")
# 打印树的方法
def print_tree(self, node, tabs):
print(tabs + node.name)
for connection, child_node in node.connections.items():
print(tabs + "\t" + "(" + connection + ")")
self.print_tree(child_node, tabs + "\t\t")
def construct_tree(self):
self.construct(self.root, "", self.data, self.columns)
# 构建树
def construct(self, parent_node, parent_connection_label, input_data,
columns):
min_value, best_col, min_splited = choose_best_col(
input_data[columns], self.label)
if not best_col:
node = self.Node(input_data[self.label].iloc[0])
parent_node.connect(parent_connection_label, node)
return
node = self.Node(best_col)
parent_node.connect(parent_connection_label, node)
new_columns = [col for col in columns if col != best_col]
# 递归构建树
for splited_value, splited_data in min_splited.items():
self.construct(node, splited_value, splited_data, new_columns)
treeCart = CartTree(dataset, 'PlayTennis')
treeCart.construct_tree()
treeCart.print_tree(treeCart.root, "")
Root
()
Outlook
(Sunny)
Humidity
(High)
Temperature
(Hot)
Wind
(Weak)
No
(Strong)
No
(Mild)
Wind
(Weak)
No
(Normal)
Temperature
(Cool)
Wind
(Weak)
Yes
(Mild)
Wind
(Strong)
Yes
(Overcast)
Temperature
(Hot)
Humidity
(High)
Wind
(Weak)
Yes
(Normal)
Wind
(Weak)
Yes
(Cool)
Humidity
(Normal)
Wind
(Strong)
Yes
(Mild)
Humidity
(High)
Wind
(Strong)
Yes
(Rain)
Wind
(Weak)
Temperature
(Mild)
Humidity
(High)
Yes
(Normal)
Yes
(Cool)
Humidity
(Normal)
Yes
(Strong)
Temperature
(Cool)
Humidity
(Normal)
No
(Mild)
Humidity
(High)
No
Reference:
- https://github.com/NLP-LOVE/ML-NLP/blob/master/Machine Learning/3.Desition Tree/Desition Tree.md
- https://cuijiahua.com/blog/2017/11/ml_2_decision_tree_1.html
- https://cuijiahua.com/blog/2017/11/ml_3_decision_tree_2.html
- https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/6ixsCP8dvNYfqhQYUbnNHw
- https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/jdUQIPM2AhAh7rzl1DPgIQ