pytorch之warm-up预热学习策略
文章目录
- 一、warm-up
-
- 1、什么是Warmup
- 2、为什么使用Warmup
- 3、Warmup的实现方法
-
- 3.1 constant warmup
- 3.1 gradual warmup
- 3.3 WarmupMultiStepLR
-
- 3.3.1 build_lr_scheduler
- 3.3.2 WarmupMultiSetpLR
- 3.3.3 仿真
- 4、总结
- 二、PyTorch学习之六个学习率调整策略
-
- 1、等间隔调整学习率 StepLR
-
- 1.1 参数
- 1.2 示例·
- 2、按需调整学习率 MultiStepLR
-
- 2.1 参数
- 2.2 示例
- 3、指数衰减调整学习率 ExponentialLR
-
- 3.1 参数
- 3.2 示例
- 4、余弦退火调整学习率 CosineAnnealingLR
-
- 4.1 参数
- 4.2 示例
- 5、自适应调整学习率 ReduceLROnPlateau
-
- 5.1 参数
- 6、自定义调整学习率 LambdaLR
-
- 6.1 参数:
一、warm-up
学习率是神经网络训练中最重要的超参数之一,针对学习率的优化方式很多,Warmup是其中的一种
1、什么是Warmup
Warmup是在ResNet论文中提到的一种学习率预热的方法,它在训练开始的时候先选择使用一个较小的学习率,训练了一些epoches或者steps(比如4个epoches,10000steps),再修改为预先设置的学习来进行训练。
2、为什么使用Warmup
由于刚开始训练时,模型的权重(weights)是随机初始化的,此时若选择一个较大的学习率,可能带来模型的不稳定(振荡),选择Warmup预热学习率的方式,可以使得开始训练的几个epoches或者一些steps内学习率较小,在预热的小学习率下,模型可以慢慢趋于稳定,等模型相对稳定后再选择预先设置的学习率进行训练,使得模型收敛速度变得更快,模型效果更佳。
Example:
3、Warmup的实现方法
3.1 constant warmup
Resnet论文中使用一个110层的ResNet在cifar10上训练时,先用0.01的学习率训练直到训练误差低于80%(大概训练了400个steps),然后使用0.1的学习率进行训练。
3.1 gradual warmup
constant warmup的不足之处在于从一个很小的学习率一下变为比较大的学习率可能会导致训练误差突然增大。于是18年Facebook提出了gradual warmup来解决这个问题,即从最初的小学习率开始,每个step增大一点点,直到达到最初设置的比较大的学习率时,采用最初设置的学习率进行训练。gradual warmup的实现模拟代码如下:
"""
Implements gradual warmup, if train_steps < warmup_steps, the
learning rate will be `train_steps/warmup_steps * init_lr`.
Args:
warmup_steps:warmup步长阈值,即train_steps
import numpy as np
warmup_steps = 2500
init_lr = 0.1
# 模拟训练15000步
max_steps = 15000
for train_steps in range(max_steps):
if warmup_steps and train_steps < warmup_steps:
warmup_percent_done = train_steps / warmup_steps
warmup_learning_rate = init_lr * warmup_percent_done #gradual warmup_lr
learning_rate = warmup_learning_rate
else:
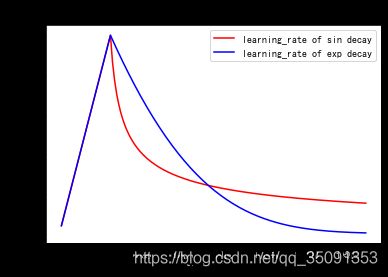
#learning_rate = np.sin(learning_rate) #预热学习率结束后,学习率呈sin衰减
learning_rate = learning_rate**1.0001 #预热学习率结束后,学习率呈指数衰减(近似模拟指数衰减)
if (train_steps+1) % 100 == 0:
print("train_steps:%.3f--warmup_steps:%.3f--learning_rate:%.3f" % (
train_steps+1,warmup_steps,learning_rate))
上述代码实现的Warmup预热学习率以及学习率预热完成后衰减(sin or exp decay)的曲线图如下:
3.3 WarmupMultiStepLR
3.3.1 build_lr_scheduler
# ->箭头表示函数输出返回值类型
# LR_SCHEDULER_NAME有两种WarmupMultiSetpLR, WarmupCosineLR
def build_lr_scheduler(cfg: CfgNode, optimizer: torch.optim.Optimizer) -> torch.optim.lr_scheduler._LRScheduler:
"""
Build a LR scheduler from config.
"""
name = cfg.SOLVER.LR_SCHEDULER_NAME
if name == "WarmupMultiStepLR":
return WarmupMultiStepLR(
optimizer,
cfg.SOLVER.STEPS, # tuple (300, 400)
cfg.SOLVER.GAMMA, #[0.1]
warmup_factor=cfg.SOLVER.WARMUP_FACTOR, # 0.001
warmup_iters=cfg.SOLVER.WARMUP_ITERS, # 1000
warmup_method=cfg.SOLVER.WARMUP_METHOD, # 'linear'
)
elif name == "WarmupCosineLR":
return WarmupCosineLR(
optimizer,
cfg.SOLVER.MAX_ITER,
warmup_factor=cfg.SOLVER.WARMUP_FACTOR,
warmup_iters=cfg.SOLVER.WARMUP_ITERS,
warmup_method=cfg.SOLVER.WARMUP_METHOD,
)
else:
raise ValueError("Unknown LR scheduler: {}".format(name))
3.3.2 WarmupMultiSetpLR
class WarmupMultiStepLR(torch.optim.lr_scheduler._LRScheduler):
def __init__(
self,
optimizer: torch.optim.Optimizer,
milestones: List[int],
gamma: float = 0.1,
warmup_factor: float = 0.001,
warmup_iters: int = 1000,
warmup_method: str = "linear",
last_epoch: int = -1,
):
if not list(milestones) == sorted(milestones):
raise ValueError(
"Milestones should be a list of" " increasing integers. Got {}", milestones
)
self.milestones = milestones
self.gamma = gamma
self.warmup_factor = warmup_factor
self.warmup_iters = warmup_iters
self.warmup_method = warmup_method
super().__init__(optimizer, last_epoch)
def get_lr(self) -> List[float]:
warmup_factor = _get_warmup_factor_at_iter(
self.warmup_method, self.last_epoch, self.warmup_iters, self.warmup_factor
)
return [
base_lr * warmup_factor * self.gamma ** bisect_right(self.milestones, self.last_epoch)
for base_lr in self.base_lrs
##################################################
## self.base_lrs 【0.001,.... 0.001】 len = 84
#################################################
]
def _compute_values(self) -> List[float]:
# The new interface
return self.get_lr()
def _get_warmup_factor_at_iter(method: str, iter: int, warmup_iters: int, warmup_factor: float) -> float:
"""
Return the learning rate warmup factor at a specific iteration.
See https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.02677 for more details.
Args:
method (str): warmup method; either "constant" or "linear".
iter (int): iteration at which to calculate the warmup factor.
warmup_iters (int): the number of warmup iterations.
warmup_factor (float): the base warmup factor (the meaning changes according
to the method used).
Returns:
float: the effective warmup factor at the given iteration.
"""
if iter >= warmup_iters:
return 1.0
if method == "constant":
return warmup_factor
elif method == "linear":
alpha = iter / warmup_iters
return warmup_factor * (1 - alpha) + alpha
else:
raise ValueError("Unknown warmup method: {}".format(method))
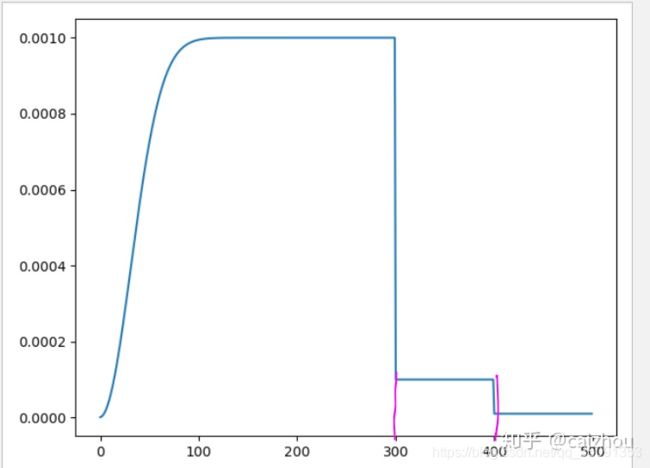
3.3.3 仿真
import bisect
from bisect import bisect_right
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
warmup_factor = 0.001
Steps = (300,400)
gamma = 0.1
warmup_iters = 1000
base_lr = 0.001
import numpy as np
lr = []
iters=[]
for iter in range(500):
alpha = iter/warmup_iters
warmup_factor = warmup_factor*(1-alpha)+alpha
lr.append( base_lr * warmup_factor * gamma ** bisect_right(Steps, iter))
iters.append(iter)
plt.plot(iters,lr)
plt.show()
4、总结
使用Warmup预热学习率的方式,即先用最初的小学习率训练,然后每个step增大一点点,直到达到最初设置的比较大的学习率时(注:此时预热学习率完成),之后采用最初设置的学习率进行训练(注:预热学习率完成后的训练过程,学习率是衰减的),有助于使模型收敛速度变快,效果更佳。
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_36618660/article/details/99650804
参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/99568607
二、PyTorch学习之六个学习率调整策略
PyTorch学习率调整策略通过torch.optim.lr_scheduler接口实现。PyTorch提供的学习率调整策略分为三大类,分别是
- 有序调整:等间隔调整(Step),按需调整学习率(MultiStep),指数衰减调整(Exponential)和余弦退火CosineAnnealing。
- 自适应调整:自适应调整学习率 ReduceLROnPlateau。
- 自定义调整:自定义调整学习率 LambdaLR。
1、等间隔调整学习率 StepLR
torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size, gamma=0.1, last_epoch=-1)
等间隔调整学习率,调整倍数为 gamma 倍,调整间隔为 step_size。间隔单位是step。需要注意的是, step 通常是指 epoch,不要弄成 iteration 了
1.1 参数
- optimizer:优化器
- step_size(int): 学习率下降间隔数,若为 30,则会在 30、 60、 90…个 step 时,将学习率调整为 lr*gamma。
- gamma(float):学习率调整倍数,默认为 0.1 倍,即下降 10 倍。
- last_epoch(int):上一个 epoch 数,这个变量用来指示学习率是否需要调整。当last_epoch 符合设定的间隔时,就会对学习率进行调整。当为-1 时,学习率设置为初始值。
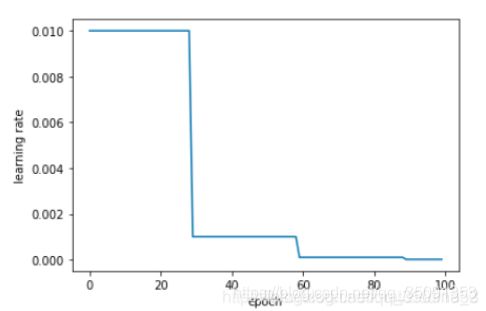
1.2 示例·
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
from torchvision.models import AlexNet
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
model = AlexNet(num_classes=2)
optimizer = optim.SGD(params=model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 官方用法
# lr_scheduler.StepLR()
# Assuming optimizer uses lr = 0.05 for all groups
# lr = 0.05 if epoch < 30
# lr = 0.005 if 30 <= epoch < 60
# lr = 0.0005 if 60 <= epoch < 90
#
# scheduler = StepLR(optimizer, step_size=30, gamma=0.1)
# for epoch in range(100):
# train(...)
# validate(...)
# scheduler.step()
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
scheduler = lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=30, gamma=0.1)
plt.figure()
x = list(range(100))
y = []
for epoch in range(100):
scheduler.step()
lr = scheduler.get_lr()
print(epoch, scheduler.get_lr()[0])
y.append(scheduler.get_lr()[0])
plt.xlabel("epoch")
plt.ylabel("learning rate")
plt.plot(x, y)
2、按需调整学习率 MultiStepLR
torch.optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optimizer, milestones, gamma=0.1, last_epoch=-1)
- 按设定的间隔调整学习率。这个方法适合后期调试使用,观察 loss 曲线,为每个实验定制学习率调整时机。
与StepLR的区别是,调节的epoch是自己定义,无须一定是【30, 60, 90】 这种等差数列;请注意,这种衰减是由外部的设置来更改的
2.1 参数
- milestones(list):一个 list,每一个元素代表何时调整学习率, list 元素必须是递增的。如milestones=[30,80,120]
- gamma(float)- 学习率调整倍数,默认为 0.1 倍,即下降 10 倍
- last_epoch(int):上一个epoch数,这个变量用来指示学习率是否需要调整。当last_epoch符合设定的间隔时,就会对学习率进行调整;当为-1时,学习率设置为初始值。
2.2 示例
model = AlexNet(num_classes=2)
optimizer = optim.SGD(params = model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Assuming optimizer uses lr = 0.05 for all groups
# lr = 0.05 if epoch < 30
# lr = 0.005 if 30 <= epoch < 80
# lr = 0.0005 if epoch >= 80
# scheduler = MultiStepLR(optimizer, milestones=[30,80], gamma=0.1)
# for epoch in range(100):
# train(...)
# validate(...)
# scheduler.step()
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#在指定的epoch值,如[5,20,25,80]处对学习率进行衰减,lr = lr * gamma
scheduler = lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optimizer, milestones=[5,20,25,80], gamma=0.1)
plt.figure()
x = list(range(100))
y = []
for epoch in range(100):
scheduler.step()
lr = scheduler.get_lr()
print(epoch, scheduler.get_lr()[0])
y.append(scheduler.get_lr()[0])
plt.xlabel("epoch")
plt.ylabel("learning rate")
plt.plot(x,y)
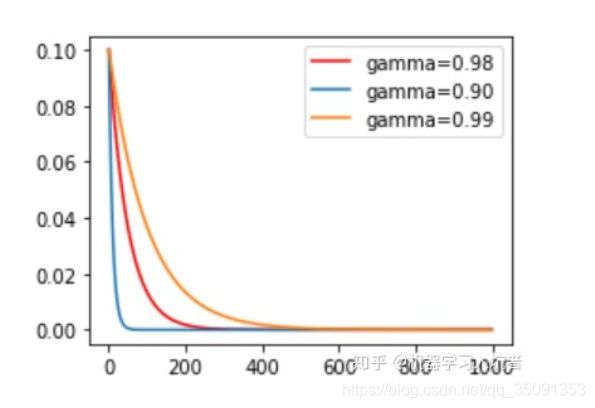
3、指数衰减调整学习率 ExponentialLR
torch.optim.lr_scheduler.ExponentialLR(optimizer, gamma, last_epoch=-1)
- 指数衰减调整学习率的调整公式: l r = l r ∗ g a m m a e p o c h lr=lr∗gamma^{epoch} lr=lr∗gammaepoch
3.1 参数
- gamma:学习率调衰减的底数,选择不同的gamma值可以获得幅度不同的衰减曲线,指数为 epoch,即 gamma**epoch(或 g a m m a e p o c h gamma^{epoch} gammaepoch)
3.2 示例
4、余弦退火调整学习率 CosineAnnealingLR
- 以初始学习率为最大学习率,以 2 ∗ T _ m a x 2 ∗ T\_max 2∗T_max 为周期,在一个周期内先下降,后上升。
torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer, T_max, eta_min=0, last_epoch=-1)
4.1 参数
- T_max(int):学习率下降到最小值时的epoch数,即当epoch=T_max时,学习率下降到余弦函数最小值,当epoch>T_max时,学习率将增大
- eta_min(float):学习率的最小值,即在一个周期中,学习率最小会下降到 eta_min,默认值为 0
- 上一个epoch数,这个变量用来指示学习率是否需要调整。当last_epoch符合设定的间隔时,就会对学习率进行调整;当为-1时,学习率设置为初始值。
4.2 示例
5、自适应调整学习率 ReduceLROnPlateau
当某指标不再变化(下降或升高),调整学习率,这是非常实用的学习率调整策略。例如,当验证集的 loss 不再下降时,进行学习率调整;或者监测验证集的 accuracy,当accuracy 不再上升时,则调整学习率。
torch.optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, mode='min', factor=0.1, patience=10, verbose=False, threshold=0.0001, threshold_mode='rel', cooldown=0, min_lr=0, eps=1e-08)
5.1 参数
- mode(str)- 模式选择,有 min 和 max 两种模式, min 表示当指标不再降低(如监测loss), max 表示当指标不再升高(如监测 accuracy)。
- factor(float)- 学习率调整倍数(等同于其它方法的 gamma),即学习率更新为 lr = lr * factor
- patience(int)- 忍受该指标多少个 step 不变化,当忍无可忍时,调整学习率。
- verbose(bool)- 是否打印学习率信息, print(‘Epoch {:5d}: reducing learning rate of group {} to {:.4e}.’.format(epoch, i, new_lr))
- threshold_mode(str)- 选择判断指标是否达最优的模式,有两种模式, rel 和 abs。
- 当 threshold_mode == rel,并且 mode == max 时, dynamic_threshold = best * (1 +threshold );
- 当 threshold_mode == rel,并且 mode == min 时,dynamic_threshold = best * ( 1 -threshold );
- 当 threshold_mode abs,并且 mode max 时, dynamic_threshold = best + threshold ; > - 当threshold_mode == rel,并且 mode == max 时, dynamic_threshold = best - threshold; threshold(float)- 配合 threshold_mode 使用。
- cooldown(int)- “冷却时间“,当调整学习率之后,让学习率调整策略冷静一下,让模型再训练一段时间,再重启监测模式。
- min_lr(float or list)- 学习率下限,可为 float,或者 list,当有多个参数组时,可用 list 进行设置。
- eps(float)- 学习率衰减的最小值,当学习率变化小于 eps 时,则不调整学习率。
6、自定义调整学习率 LambdaLR
为不同参数组设定不同学习率调整策略。调整规则为, l r = b a s e l r ∗ l m b d a ( s e l f . l a s t e p o c h ) lr=base_lr∗lmbda(self.last_epoch) lr=baselr∗lmbda(self.lastepoch),这在fine-tune 中十分有用,我们不仅可为不同的层设定不同的学习率,还可以为其设定不同的学习率调整策略。
torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda, last_epoch=-1)
6.1 参数:
- lr_lambda(function or list)- 一个计算学习率调整倍数的函数,输入通常为 step,当有多个参数组时,设为 list。
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/shanglianlm/article/details/85143614
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/26a7dbc15246