coggle30天机器学习打卡之Pytorch篇
文章目录
- 任务1 PyTorch张量计算与Numpy的转换
- 任务2 PyTorch梯度计算和梯度下降过程
- 任务3 PyTorch全连接层原理和使用
- 任务4 PyTorchPyTorch激活函数原理和使用
- 任务5 PyTorch卷积层原理和使用
- 任务6 PyTorch常见的损失函数和优化器使用
- 任务7 PyTorch池化层和归一化层
- 任务8 使用PyTorch搭建VGG网络
- 任务9 使用PyTorch搭建ResNet网络
- 任务10 使用PyTorch完成Fashion-MNIST分类
- 任务11:使用PyTorch完成人脸关键点检测
- 任务12 使用PyTorch搭建对抗生成网络
任务1 PyTorch张量计算与Numpy的转换
- 步骤1:配置本地Notebook环境,或使用天池DSW:https://dsw-dev.data.aliyun.com/#/
- 步骤2:学习Pytorch的基础语法,并成功执行以下代码
- 基础pytorch教程:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/25572330
- 官方教程:https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/basics/intro.html
代码:
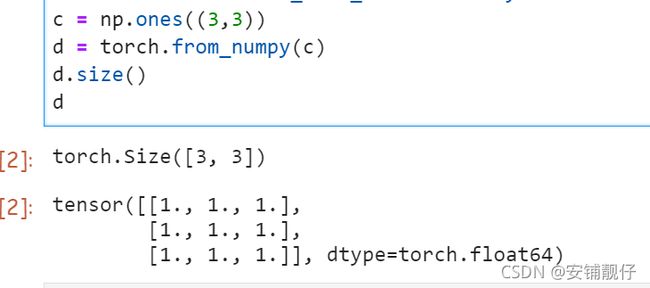
c = np.ones((3,3))
d = torch.from_numpy(c)
d.size()
d
任务2 PyTorch梯度计算和梯度下降过程
- 步骤1:学习自动求梯度原理,https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/basics/autogradqs_tutorial.html
- 步骤2:学习随机梯度下降原理,https://www.cnblogs.com/BYRans/p/4700202.html
- 步骤3:
- 使用numpy创建一个y=10*x+4+noise(0,1)的数据,其中x是0到100的范围,以0.01进行等差数列
- 使用pytroch定义w和b,并使用随机梯度下降,完成回归拟合。
源码:
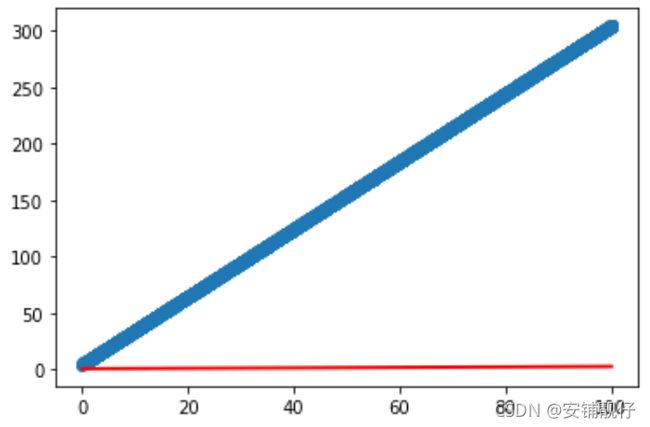
X = np.linspace(start=0, stop=100, num=10000)
y = 3*X + 4 + np.random.uniform(0, 1, size=(10000,))
X = torch.from_numpy(X)
X = X.to(torch.float32)
y = torch.from_numpy(y)
y = y.to(torch.float32)
w = Variable(torch.randn(1), requires_grad=True)
b = Variable(torch.randn(1), requires_grad=True)
prediction = w*X + b
plt.scatter(X.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(X.data.numpy(), prediction.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=2)
plt.show()
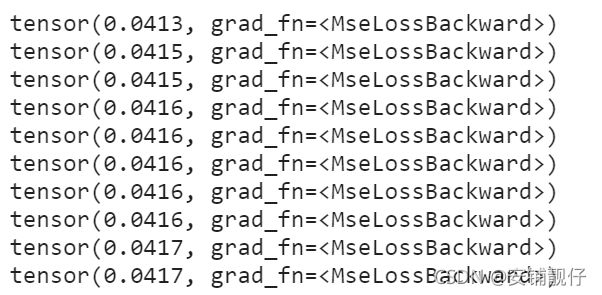
for epoch in range(500):
for i, (trn_x, trn_y) in enumerate(zip(X, y)):
z = w * trn_x + b
loss = torch.nn.functional.mse_loss(z, trn_y)
loss.backward()
w.data -= 1e-5*w.grad.data
b.data -= 1e-5*b.grad.data
l1 = w.grad.data.zero_()
l2 = b.grad.data.zero_()
if (epoch+1)%50 == 0:
print(loss)
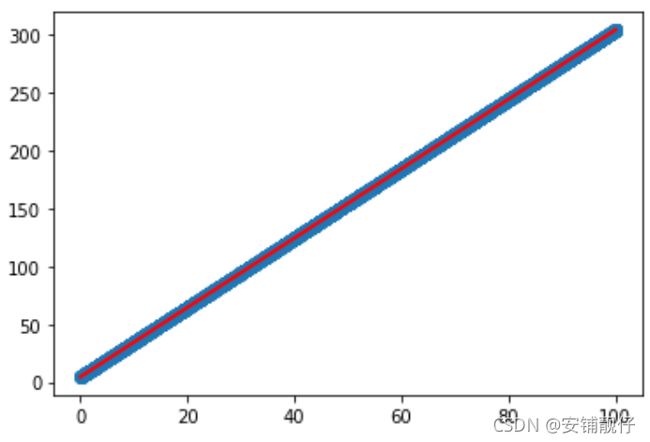
prediction = w*X + b
plt.scatter(X.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(X.data.numpy(), prediction.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=2)
plt.show()
任务3 PyTorch全连接层原理和使用
- 步骤1:学习全连接网络原理,https://blog.csdn.net/xiaodong_11/article/details/82015456
- 步骤2:在pytorch中使用矩阵乘法实现全连接层
- 步骤3:在pytorch中使用nn.Linear层
手动实现全连接层:
class MyLinear(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_features, output):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.w = Parameter(torch.randn(output, input_features, requires_grad=True))
self.b = Parameter(torch.randn(output, input_features, requires_grad=True))
# 给模型添加parameter
self.register_parameter('weight', self.w)
self.register_parameter('bias', self.b)
def forward(self, x):
return self.w*x + self.b
ps.注意self.register_parameter,这个函数是给model.parameters()添加元素(model.parameters()是从一个字典逐步返回参数值),如果不添加,那么使用不了Pytorch自带的优化器。
Pytorch的nn.Linear的使用(这里简单搭建一个只含全连接层的网络):
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_features, output):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(input_features, 4)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(4, output)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.fc1(x)
out = self.fc2(out)
return out
model = Net(5, 3)
print(model)
任务4 PyTorchPyTorch激活函数原理和使用
- 步骤1:学习激活函数的原理,https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/8842993488429934
- 步骤2:在pytorch中手动实现上述激活函数
实现源码:
def elu(x, alpha=1.0, inplace=False):
# ELU(x)=max(0,x) + min(0,α∗(exp(x)−1))
zeros = torch.zeros_like(x)
left = torch.cat([x, zeros], dim=0)
right = alpha * (torch.exp(x) - 1)
right = torch.cat([zeros, right])
result = torch.max(left, dim=0)[0] + torch.min(right, dim=0)[0]
return result
def leaky_relu(x, negative_slope=0.01,inplace=False):
# LeakyReLU(x) = max(0,x) + negative_slope∗min(0,x)
zeros = torch.zeros_like(x)
cat_mat = torch.cat([x, zeros], dim=0)
result = torch.max(cat_mat, dim=0)[0] + negative_slope*torch.min(cat_mat, dim=0)[0]
return result
def p_relu(x, num_parameters=1, init=0.25):
# PReLU(x)=max(0,x)+a∗min(0,x)
zeros = torch.zeros_like(x)
cat_mat = torch.cat([x, zeros], dim=0)
result = torch.max(cat_mat, dim=0)[0] + init*torch.min(cat_mat, dim=0)[0]
return result
def relu(x, inplace=False):
# ReLU(x)=max(0,x)
zeros = torch.zeros_like(x)
cat_mat = torch.cat([x, zeros], dim=0)
result = torch.max(cat_mat, dim=0)[0]
return result
def relu6(x, inplace=False):
# ReLU6(x)=min(max(0,x),6)
mat_zero = torch.zeros_like(x)
x = torch.cat([x, mat_zero], dim=0)
result = torch.max(x, dim=0)[0]
result = torch.cat([torch.unsqueeze(result, dim=0), mat_zero+6], dim=0)
result = torch.min(result, dim=0)[0]
return result
def selu(x, inplace=True):
# SELU(x) = scale∗(max(0, x) + min(0, α∗(exp(x)−1)))
alpha = 1.6732632423543772848170429916717
scale = 1.0507009873554804934193349852946
zeros = torch.zeros_like(x)
left = torch.cat([x, zeros], dim=0)
right = alpha * (torch.exp(x) - 1)
right = torch.cat([zeros, right])
result = torch.max(left, dim=0)[0] + torch.min(right, dim=0)[0]
result *= scale
return result
def celu(x, alpha=1.0,inplace=False):
if not alpha:
raise Exception(f"{alpha}不能为0")
# CELU(x)=max(0,x)+min(0,α∗(exp(x/α)−1))
zeros = torch.zeros_like(x)
left = torch.cat([x, zeros], dim=0)
right = alpha * (torch.exp(x / alpha) - 1)
right = torch.cat([zeros, right])
result = torch.max(left, dim=0)[0] + torch.min(right, dim=0)[0]
return result
def sigmoid(x):
# Sigmoid(x) = 1 / (1 + exp(-x))
return 1 / (1 + torch.exp(-1 * x))
def log_sigmoid(x):
# LogSigmoid(x) = log(1 / (1 + exp(-x)))
return torch.log(sigmoid(x))
def tanh(x):
# Tanh(x) = (exp(x) - exp(-x)) / (exp(x) + exp(-x))
# solution 1:
# return torch.tanh(x)
# solution 2:
return (torch.exp(x) - torch.exp(-x)) / (torch.exp(x) + torch.exp(-x))
def tanh_shrink(x):
return x - tanh(x)
def soft_plus(x, beta=1,threshold=20):
#
if not beta:
raise
return 1/beta*torch.log(1+torch.exp(beta*x))
def soft_shrink(x: Tensor, lambd=0.5):
x.apply_(lambda x_: x_-lambd if x_ > lambd else x_+lambd if x_ < -lambd else 0)
return x
任务5 PyTorch卷积层原理和使用
-
步骤1:理解卷积层的原理和具体使用
- https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37385726/article/details/81739179
- https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangxiann/p/13584415.html
-
步骤2:计算下如下卷积层的参数量:
nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=1,
out_channels=32,
kernel_size=5,
stride=1,
padding=2
)
卷积层参数量计算方法:
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/77471991
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/395354063
总结一点就是:参数量=(filter size * 前一层特征图的通道数 )* 当前层filter数量+偏置数量
所以答案为: 5 × 5 × 1 × 32 + 32 = 832 5\times5\times1\times32+32=832 5×5×1×32+32=832
也可以使用相关库来查看:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41979513/article/details/102369396
任务6 PyTorch常见的损失函数和优化器使用
- 步骤1:学习损失函数的细节,https://www.cnblogs.com/wanghui-garcia/p/10862733.html
- 步骤2:学习优化器的使用,https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/optim.html
- 步骤3:设置不同的优化器和学习率,重复任务2的回归过程
- 损失函数MSE、优化器SGD、学习率0.1
- 损失函数MSE、优化器SGD、学习率0.5
- 损失函数MSE、优化器SGD、学习率0.01
任务7 PyTorch池化层和归一化层
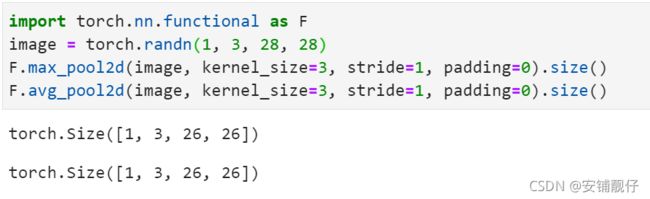
- 步骤1:使用pytroch代码实现2d pool中的mean-pooling、max-pooling
- https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#pooling-layers
- https://blog.csdn.net/shanglianlm/article/details/85313924
- 步骤2:学习归一化的原理,https://blog.csdn.net/qq_23981335/article/details/106572171
实现两种2d pool,有两种方法:
max_pool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=0)
mean_pool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=0)
image = torch.randn(1, 3, 28, 28)
image.size()
max_pool(image).size()
mean_pool(image).size()
import torch.nn.functional as F
image = torch.randn(1, 3, 28, 28)
F.max_pool2d(image, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=0).size()
F.avg_pool2d(image, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=0).size()
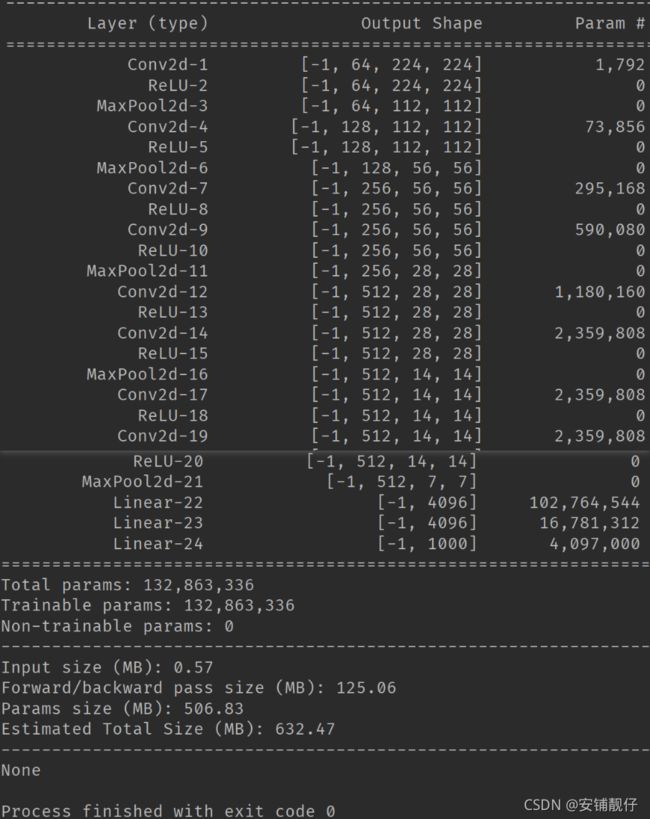
任务8 使用PyTorch搭建VGG网络
学习链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/263527295
- 步骤1:理解VGG网络的原理。
- 步骤2:使用pytorch搭建VGG网络模型。
- 步骤3:打印出VGG 11层模型 每层特征图的尺寸,以及参数量
论文地址(推荐第一个地址):
- https://readpaper.com/paper/1686810756
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.1556.pdf
论文中各种VGG结构如下图:
Table 1: ConvNet configurations (shown in columns). The depth of the configurations increases from the left (A) to the right (E), as more layers are added (the added layers are shown in bold). The convolutional layer parameters are denoted as “conv〈receptive field size〉-〈number of channels〉”. The ReLU activation function is not shown for brevity.
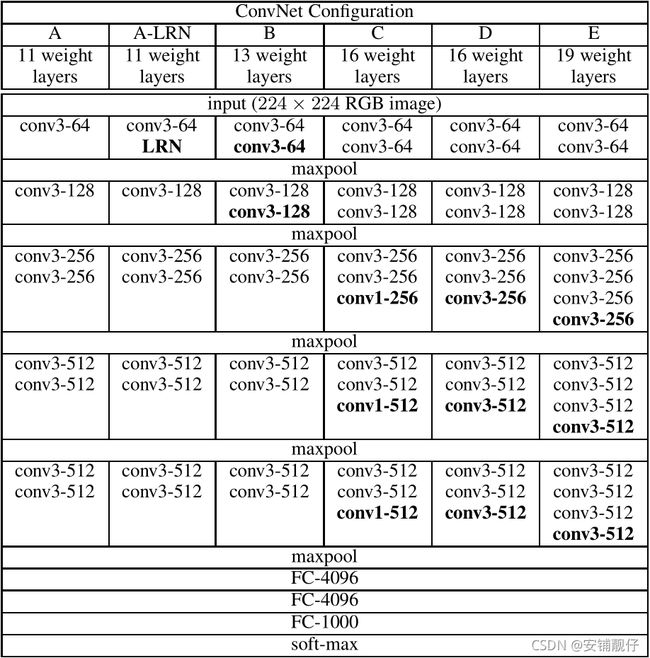
从上图可以看出,除A-LRN、C两列外,其余列的每行的卷积层都是一样的,所以我会分开两部分来复现,接下来看看一些细节,例如stride和padding。

开始复现:
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from typing import List
# 第一部分
class VGG(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, arch: List[int], num_classes=1000):
super(VGG, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = 3
self.conv_pool1 = self.make_layer(64, arch[0])
self.conv_pool2 = self.make_layer(128, arch[1])
self.conv_pool3 = self.make_layer(256, arch[2])
self.conv_pool4 = self.make_layer(512, arch[3])
self.conv_pool5 = self.make_layer(512, arch[4])
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(7*7*512, 4096)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(4096, 4096)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(4096, num_classes)
def make_layer(self, output_channels, num):
layers = []
for _ in range(num):
layers.append(nn.Conv2d(self.in_channels, output_channels,
kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1))
layers.append(nn.ReLU())
self.in_channels = output_channels
layers.append(nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.conv_pool1(x)
out = self.conv_pool2(out)
out = self.conv_pool3(out)
out = self.conv_pool4(out)
out = self.conv_pool5(out)
out = out.view(out.size(0), -1)
out = self.fc1(out)
out = F.relu(out)
out = self.fc2(out)
out = F.relu(out)
out = self.fc3(out)
return F.softmax(out)
def VGG_11():
return VGG([1, 1, 2, 2, 2], num_classes=1000)
def VGG_13():
return VGG([1, 1, 2, 2, 2], num_classes=1000)
def VGG_16():
return VGG([2, 2, 3, 3, 3], num_classes=1000)
def VGG_19():
return VGG([2, 2, 4, 4, 4], num_classes=1000)
任务9 使用PyTorch搭建ResNet网络
学习链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/263526658
- 步骤1:理解ResNet网络的原理。
- 步骤2:使用pytorch搭建ResNet网络模型。
- 步骤3:打印出ResNet 18模型 每层特征图的尺寸,以及参数量
任务10 使用PyTorch完成Fashion-MNIST分类
学习链接:https://github.com/masoudrostami/Fashion-MNIST-using-PyTorch/blob/main/MNIST%20Fashion%20Project.ipynb
- 步骤1:搭建4层卷积 + 2层全连接的分类模型。
- 步骤2:在训练过程中记录下每个epoch的训练集精度和测试集精度
任务11:使用PyTorch完成人脸关键点检测
数据集下载
示例
- 步骤1:搭建4层卷积 + 2层的模型完成关键点回归。
- 步骤2:使用resnet18预训练模型完成关键点回归
# 导入相关库
import os, sys, codecs, glob
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import cv2
import torch
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
import torchvision.models as models
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torchvision.datasets as datasets
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.autograd import Variable
from torch.utils.data.dataset import Dataset
from IPython.core.interactiveshell import InteractiveShell
InteractiveShell.ast_node_interactivity = 'all'
import time
import random
接下来定义和创建Dataset类数据集
# 定义
class MyDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, img, keypoint, transform=None):
self.img = img
self.transform = transform
self.keypoint = keypoint
def __getitem__(self, index):
img = Image.fromarray(self.img[:, :, index]).convert('RGB')
if self.transform is not None:
img = self.transform(img)
return img, self.keypoint[index] / 96.0 # 除以96是为了归一化
def __len__(self):
return self.img.shape[-1]
接着导入相关数据:

其中test.npy暂时用不到,要有fillna,因为标签有空值。
imgs_trans = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(),])
train_dataset = MyDataset(train_img[:, :, :-500], train_df.values[:-500], imgs_trans)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
train_dataset, batch_size=10, shuffle=True, num_workers=5
)
val_dataset = MyDataset(train_img[:, :, -500:], train_df.values[-500:], imgs_trans)
val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
val_dataset, batch_size=10, shuffle=False, num_workers=5
)
定义自己的模型,四层卷积核两层全连接:
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=32, kernel_size=3) #94
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3) #92
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3) #90
self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3) # 88
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(64*88*88, 128)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(128, 8)
super(Model, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.conv4(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = F.relu(x)
return feat
from tqdm import tqdm
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error
def train(train_dat, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch):
model.train()
for i, (input, target) in enumerate(tqdm(train_dat)):
input = Variable(input).float().cuda()
target = Variable(target).float().cuda()
output = model(input, target)
loss = criterion(output, target)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print(f"train dataset's loss: {loss.data}")
def evaluate(val_dat, net):
net.eval()
val_preds = []
with torch.no_grad():
end = time.time()
for i, (input, target) in enumerate(tqdm(val_dat)):
input = input.float().cuda()
target = target.float().cuda()
output = net(input)
val_preds.append(output.data)
val_loss = mean_absolute_error(torch.cat(val_preds)*96, train_df.values[-500:])
print(f"valid dataset's loss: {val_loss}")
model = XunFeiNet().cuda()
criterion = nn.MSELoss().cuda()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), 0.001)
scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=10, gamma=0.85)
for epoch in range(1):
print('Epoch: ', epoch)
train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch)
evaluate(val_loader, model)
scheduler.step()
任务12 使用PyTorch搭建对抗生成网络
- 步骤1:学习对抗生成网络的原理,https://blog.csdn.net/DFCED/article/details/105175097
- 步骤2:学习DCGAN的代码实现,https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/dcgan_faces_tutorial.html
- 步骤3:使用任务11中的人脸数据(缩放至64*64),并使用DCGAN完成训练,生成人脸
未完待续。。。