Python刷题系列(6)_列表List
文章目录
- List列表
-
- 1、对某一个列表进行计数
- 2、从列表中获取最大数字
- 3、将列表中的所有项目相乘
- 4、计算字符串的数量
- 5、对列表中元组最后一个元素递增排序
- 6、从列表中删除重复项
- 6、将字符列表转换为字符串
- 7、访问列表的索引
-
-
- 【1】enumerate
-
- 8、两个列表之间的区别
- 9、删除指定元素后打印列表
- 10、若两列表至少有一个公共成员,返回 True
- 11、从列表中找长度超过 n 的单词列表
- 12、克隆或复制列表
- 13、检查列表是否为空
- 14、将多个整数的列表转换为单个整数
- 15、获取列表中元素的频率
-
-
- 【2】counter
-
- 16、从列表中获取唯一值
- 17、查找列表中第二小的数字
- 18、将列表拆分成元组
- 19、连接列表的元素
- 20、将字符串转换为列表
-
-
- 【3】eval
-
- 21、从给定列表中删除特定单词
- 22、将字符串和字符列表转换为单个字符列表
- 23、计算给定列表列表中子列表的最大和最小和
- 24、查找给定列表中出现次数最多的项目
- 25、列表中提取给定数量的随机选择的元素
List列表
列表是一个有序的,可修改的(增删查改),元素以逗号分隔,以中括号包围的序列。
【1】支持动态的元素的增加。
【2】支持不同类型的元素在一个列表中。
【3】List is an Object。
参考:》》List
1、对某一个列表进行计数
方法一:在不用count这个函数的情况下,如何对某一个列表进行计数
首先创建一个列表,主要思想是建立了一个字典,然后遍历整个列表,判断字符串是不是字典的key,如果是则value加1,如果不是则value赋值为1,最终打印出统计结果。
list = ['qwe','xsa','jiu','qwe','xsa','jiu','www','oouy']
s={}
for i in list:
if i not in s:
s[i]=1
else:
s[i]+=1
for k in s:
print(k,s[k])
list = ['qwe','xsa','jiu','qwe','xsa','jiu','www','oouy']
list = ['qwe','xsa','jiu','qwe','xsa','jiu','www','oouy']
a=set(list)
for i in a:
num=list.count(i)
print(i,num)
上面的代码当中有使用set函数:
这里使用set是为了给列表进行去重,因为set当中的元素不能有重复值
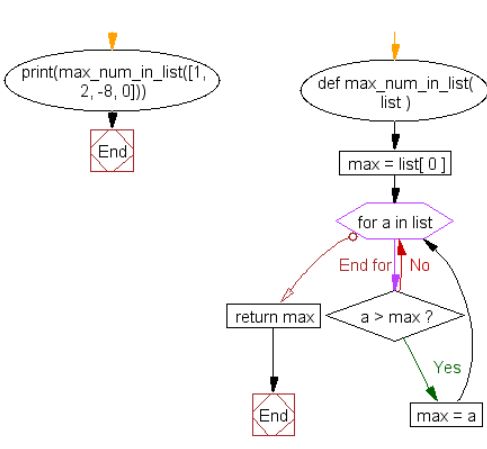
2、从列表中获取最大数字
def max_num_in_list( List ):
max = List[ 0 ] # 初始最大的是列表的第一个值
for a in List:
if a > max:
max = a
return max
print(max_num_in_list([1, 2, -8, 0])) # 2
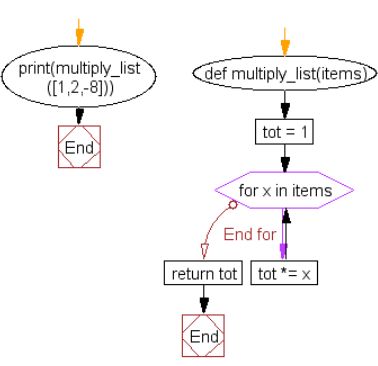
3、将列表中的所有项目相乘
def multiply_list(items):
tot = 1
for x in items:
tot *= x
return tot
print(multiply_list([1,2,-8])) # -16
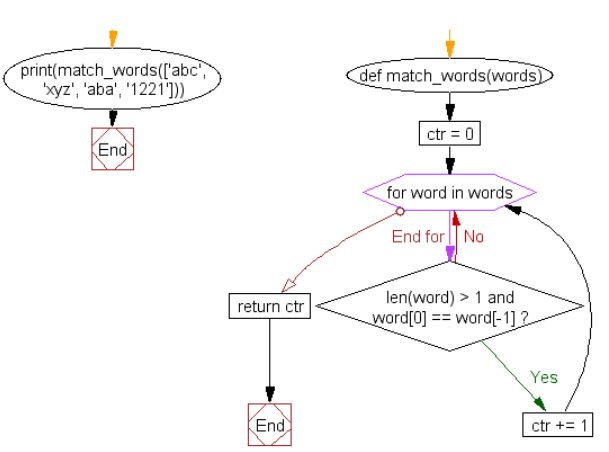
4、计算字符串的数量
编写一个Python程序来计算字符串的数量,其中字符串长度为2或更多,并且给定字符串列表中的第一个和最后一个字符相同。
def match_words(words):
ctr = 0
for word in words:
if len(word) > 1 and word[0] == word[-1]:
ctr += 1
return ctr
print(match_words(['abc', 'xyz', 'aba', '1221']))
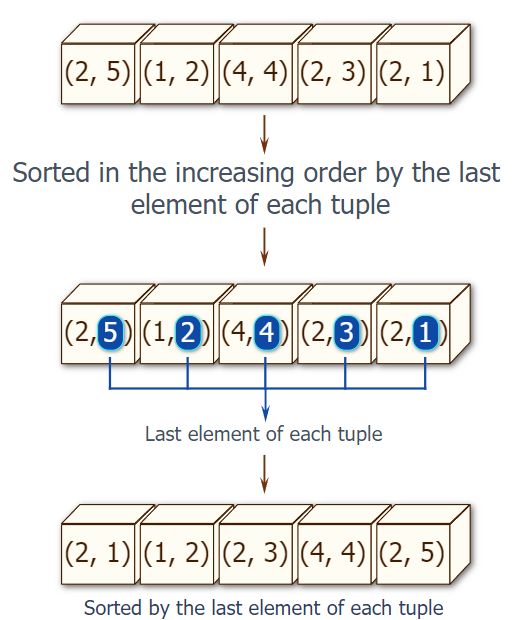
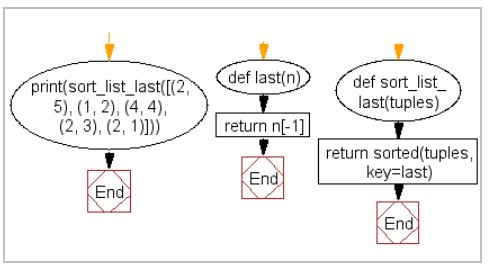
5、对列表中元组最后一个元素递增排序
编写一个 Python 程序来获取一个列表,该列表按给定的非空元组列表中每个元组中的最后一个元素按递增顺序排序。
def last(n): return n[-1]
def sort_list_last(tuples):
return sorted(tuples, key=last) # key是一个函数
print(sort_list_last([(2, 5), (1, 2), (4, 4), (2, 3), (2, 1)]))
# [(2, 1), (1, 2), (2, 3), (4, 4), (2, 5)]
注:这里如果把 return n[-1]改成 return n[0]则就是用元组的第一个元素来排序。
6、从列表中删除重复项
a = [10,20,30,20,10,50,60,40,80,50,40]
dup_items = set() #set当中的元素不重复
uniq_items = []
for x in a:
if x not in dup_items:
uniq_items.append(x)
dup_items.add(x)
print(list(dup_items)) #[40, 10, 80, 50, 20, 60, 30]
print(dup_items)#{40, 10, 80, 50, 20, 60, 30}
print(uniq_items)#[40, 10, 80, 50, 20, 60, 30]
6、将字符列表转换为字符串

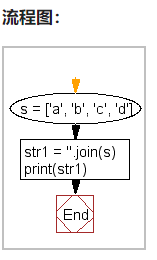
Python join() 方法用于将序列中的元素以指定的字符连接生成一个新的字符串。
s = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
str1 = ''.join(s)
print(str1)
print(type(str1))
'''
abcd
'''
7、访问列表的索引
【1】enumerate
【1】enumerate()是python的内置函数
【2】enumerate在字典上是枚举、列举的意思
【3】对于一个可迭代的(iterable)可遍历的对象(如列表、字符串),enumerate将其组成一个索引序列,利用它可以同时获得索引和值
【4】enumerate多用于在for循环中得到计数
【5】例如对于一个seq,得到:
(0, seq[0]), (1, seq[1]), (2, seq[2])
【6】enumerate()返回的是一个enumerate对象,例如:
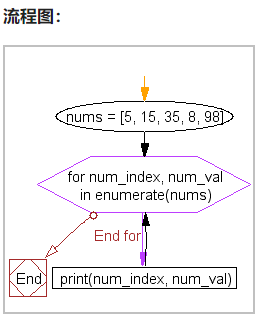
nums = [5, 15, 35, 8, 98]
for num_index, num_val in enumerate(nums):
print(num_index, num_val)
'''
0 5
1 15
2 35
3 8
4 98
'''
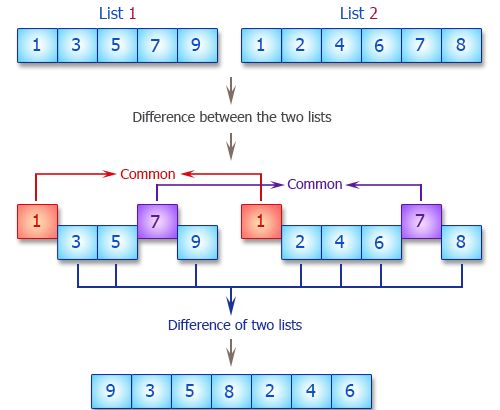
8、两个列表之间的区别
list1 = [1, "3", 5, 7, "你好"]
list2=[1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 7, 8]
diff_list1_list2 = list(set(list1) - set(list2))
diff_list2_list1 = list(set(list2) - set(list1))
total_diff = diff_list1_list2 + diff_list2_list1
print(total_diff)#['你好', 5, '3', 8, 2, 4, 6]
9、删除指定元素后打印列表
编写一个 Python 程序,以便在删除第 0、第 4 和第 5 个元素后打印指定的列表。
color = ['Red', 'Green', 'White', 'Black', 'Pink', 'Yellow']
color = [x for (i,x) in enumerate(color) if i not in (0,4,5)]
print(color) #['Green', 'White', 'Black']
10、若两列表至少有一个公共成员,返回 True
编写一个 Python 函数,该函数采用两个列表,如果它们至少有一个公共成员,则返回 True。
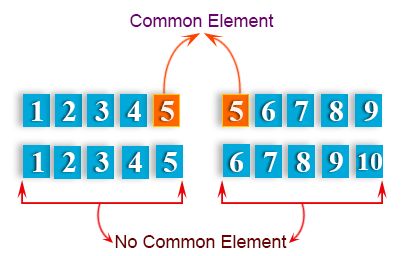
def common_data(list1, list2):
result = False
for x in list1:
for y in list2:
if x == y:
result = True
return result
print(common_data([1,2,3,4,5], [5,6,7,8,9]))
print(common_data([1,2,3,4,5], [6,7,8,9]))
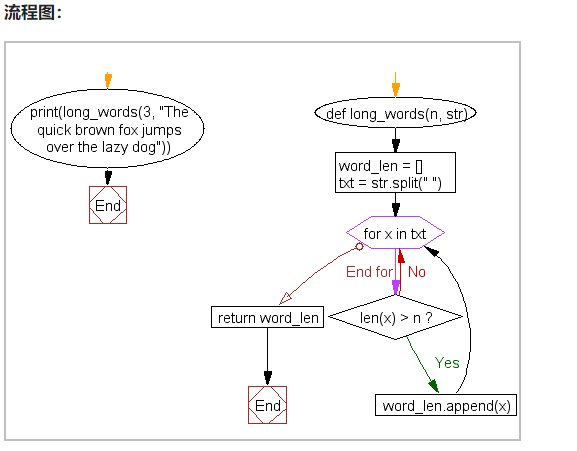
11、从列表中找长度超过 n 的单词列表
编写一个 Python 程序,从给定的单词列表中查找长度超过 n 的单词列表。

def long_words(n, str):
word_len = []
txt = str.split(" ")
for x in txt:
if len(x) > n:
word_len.append(x)
return word_len
print(long_words(3, "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"))
# ['quick', 'brown', 'jumps', 'over', 'lazy']
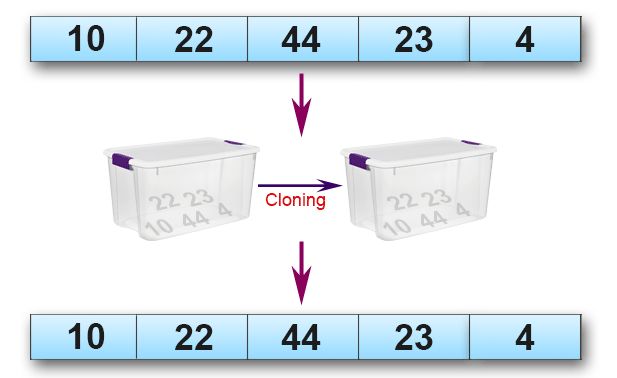
12、克隆或复制列表
original_list = [10, 22, 44, 23, 4]
new_list = list(original_list)
print(original_list)
print(new_list)
13、检查列表是否为空
l = []
if not l:
print("List is empty")
14、将多个整数的列表转换为单个整数
编写一个 Python 程序,将多个整数的列表转换为单个整数。
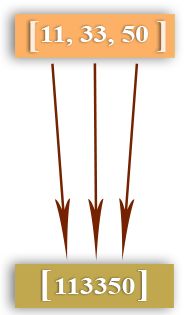
L = [11, 33, 50]
print("Original List: ",L)
x = int("".join(map(str, L)))
#map函数可以作用于列表的每一个元素上面
print("Single Integer: ",x)
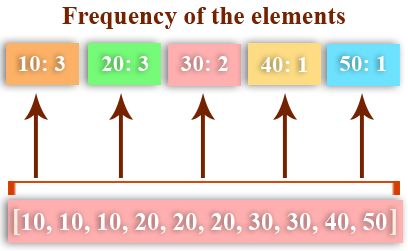
15、获取列表中元素的频率
import collections
my_list = [10,10,10,10,20,20,20,20,40,40,50,50,30]
print("Original List :\n",my_list)
ctr = collections.Counter(my_list)
print("Frequency of the elements in the List :\n",ctr)
print(type(ctr))
'''
Original List :
[10, 10, 10, 10, 20, 20, 20, 20, 40, 40, 50, 50, 30]
Frequency of the elements in the List :
Counter({10: 4, 20: 4, 40: 2, 50: 2, 30: 1})
'''
【2】counter
》》counter详细
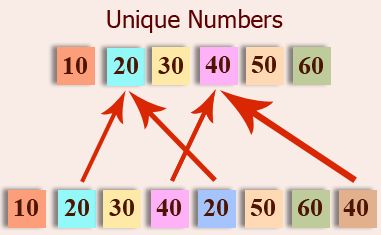
16、从列表中获取唯一值
my_list = [10, 20, 30, 40, 20, 50, 60, 40]
print("Original List : ",my_list)
my_set = set(my_list)
my_new_list = list(my_set)
print("List of unique numbers : ",my_new_list)
'''
Original List : [10, 20, 30, 40, 20, 50, 60, 40]
List of unique numbers : [40, 10, 50, 20, 60, 30]
'''
17、查找列表中第二小的数字
情况一:

情况二:
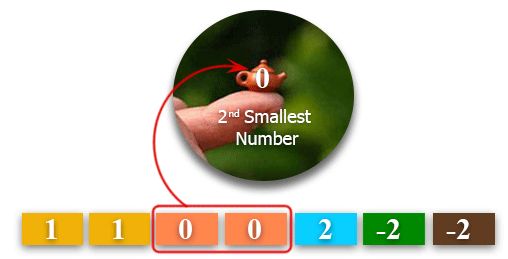
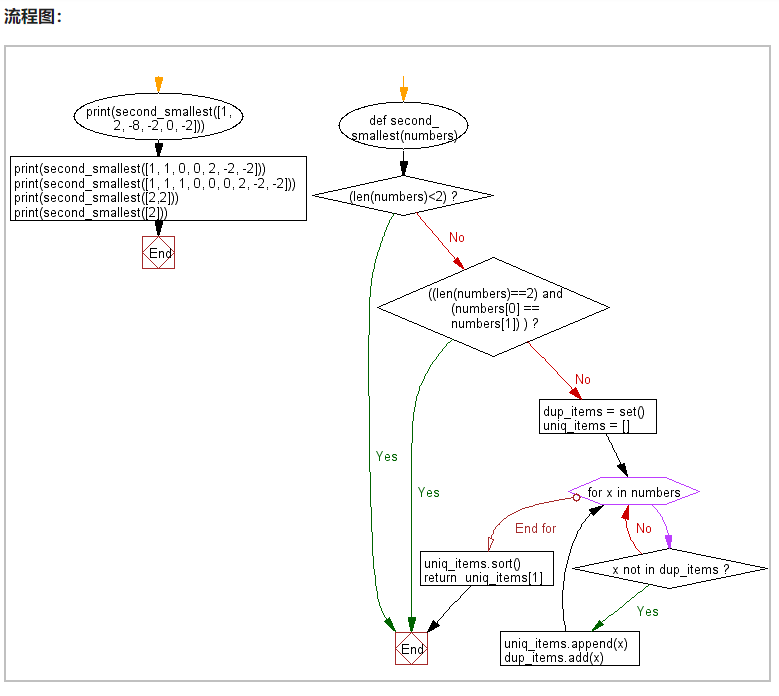
分析:需要使用列表和集合,并进行排序,最后找到第二小的数字,如果题目问的是第二大的也是如此
def second_smallest(numbers):
if (len(numbers)<2):
return
if ((len(numbers)==2) and (numbers[0] == numbers[1]) ):
return
dup_items = set()# 空集合
uniq_items = []# 空列表
for x in numbers:
if x not in dup_items:
uniq_items.append(x)
dup_items.add(x)
uniq_items.sort() #将列表中的元素从小到大进行排序
return uniq_items[1]
print(second_smallest([1, 2, -8, -2, 0, -2]))
print(second_smallest([1, 1, 0, 0, 2, -2, -2]))
print(second_smallest([1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 2, -2, -2]))
print(second_smallest([2,2]))
print(second_smallest([2]))
'''
-2
0
0
None
None
'''
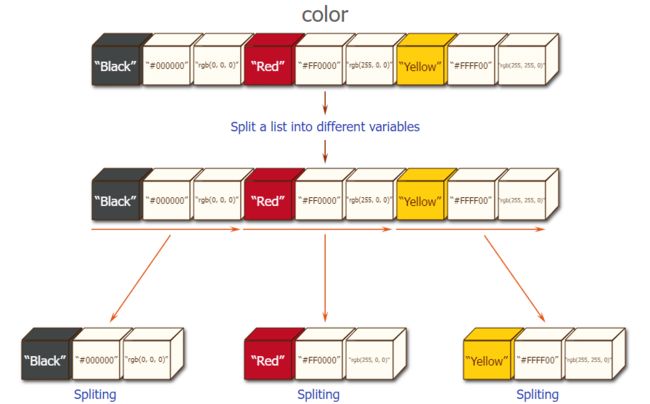
18、将列表拆分成元组
color = [("Black", "#000000", "rgb(0, 0, 0)"), ("Red", "#FF0000", "rgb(255, 0, 0)"),
("Yellow", "#FFFF00", "rgb(255, 255, 0)")]
var1, var2, var3 = color
print(var1)
print(var2)
print(var3)
print(type(var1))
'''
('Black', '#000000', 'rgb(0, 0, 0)')
('Red', '#FF0000', 'rgb(255, 0, 0)')
('Yellow', '#FFFF00', 'rgb(255, 255, 0)')
'''
19、连接列表的元素
color = ['red', 'green', 'orange']
print('-'.join(color))
print(''.join(color))
'''
red-green-orange
redgreenorange
'''
但是color本身是没有变的
20、将字符串转换为列表
import ast
color ="['Red', 'Green', 'White']"
print(ast.literal_eval(color)) #['Red', 'Green', 'White']
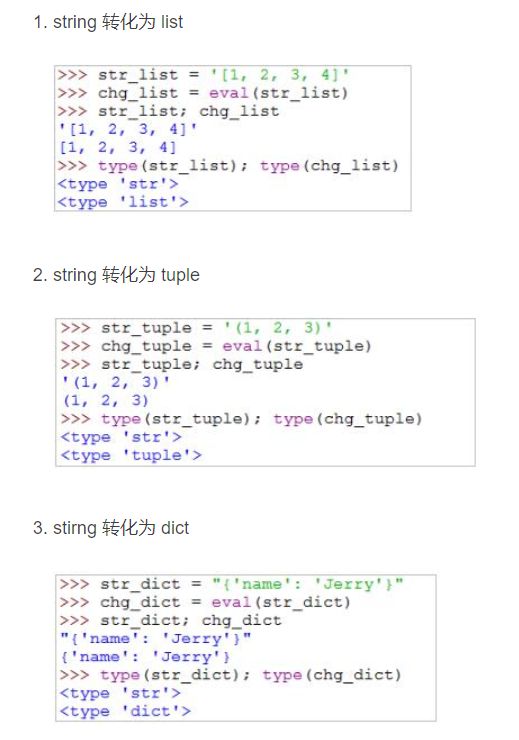
【3】eval
eval 函数在Python中做数据类型的转换还是很有用的。
由于eval存在安全隐患,因此可以使用literal_eval()函数:
则会判断需要计算的内容计算后是不是合法的python类型,如果是则进行运算,否则就不进行运算。
Python中函数 eval 和 ast.literal_eval 的区别详解
21、从给定列表中删除特定单词
def remove_words(list1, remove_words):
for word in list(list1):
if word in remove_words:
list1.remove(word)
return list1
colors = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'white', 'black', 'orange']
remove_colors = ['white', 'orange']
print("Original list:")
print(colors)
print("\nRemove words:")
print(remove_colors)
print("\nAfter removing the specified words from the said list:")
print(remove_words(colors, remove_colors))
'''
Original list:
['red', 'green', 'blue', 'white', 'black', 'orange']
Remove words:
['white', 'orange']
After removing the specified words from the said list:
['red', 'green', 'blue', 'black']
'''
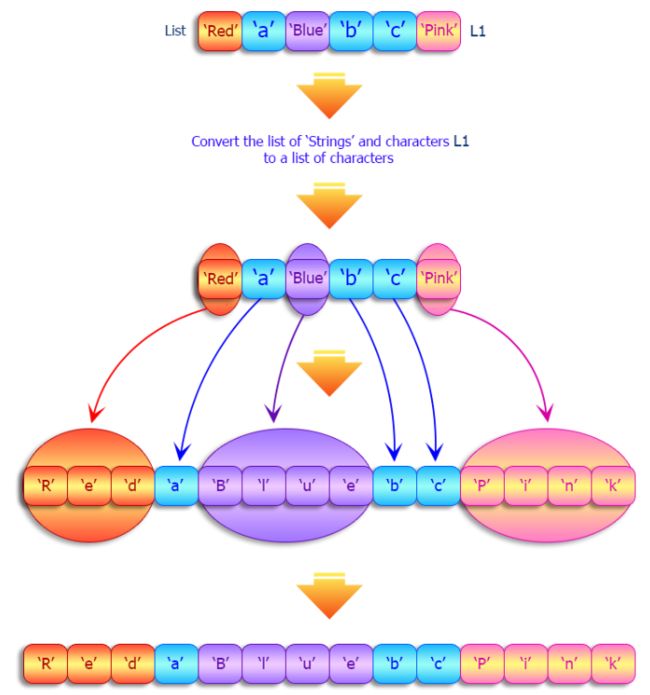
22、将字符串和字符列表转换为单个字符列表
def l_strs_to_l_chars(lst):
result = [i for element in lst for i in element]
return result
colors = ["red", "white", "a", "b", "black", "f"]
print("Original list:")
print(colors)
print("\nConvert the said list of strings and characters to a single list of characters:")
print(l_strs_to_l_chars(colors))
'''
Original list:
['red', 'white', 'a', 'b', 'black', 'f']
Convert the said list of strings and characters to a single list of characters:
['r', 'e', 'd', 'w', 'h', 'i', 't', 'e', 'a', 'b', 'b', 'l', 'a', 'c', 'k', 'f']
'''
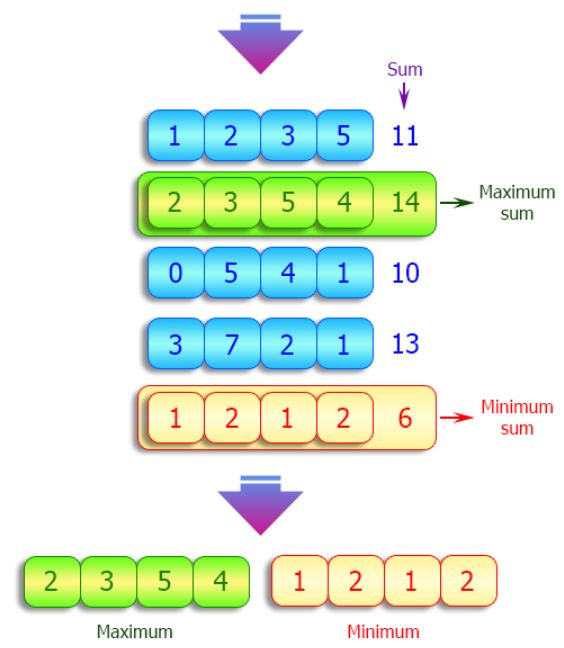
23、计算给定列表列表中子列表的最大和最小和
def max_min_sublist(lst):
max_result = (max(lst, key=sum))
min_result = (min(lst, key=sum))
return max_result,min_result
nums = [[1,2,3,5], [2,3,5,4], [0,5,4,1], [3,7,2,1], [1,2,1,2]]
print("Original list:")
print(nums)
result = max_min_sublist(nums)
print("\nMaximum sum of sub list of the said list of lists:")
print(result[0])
print("\nMinimum sum of sub list of the said list of lists:")
print(result[1])
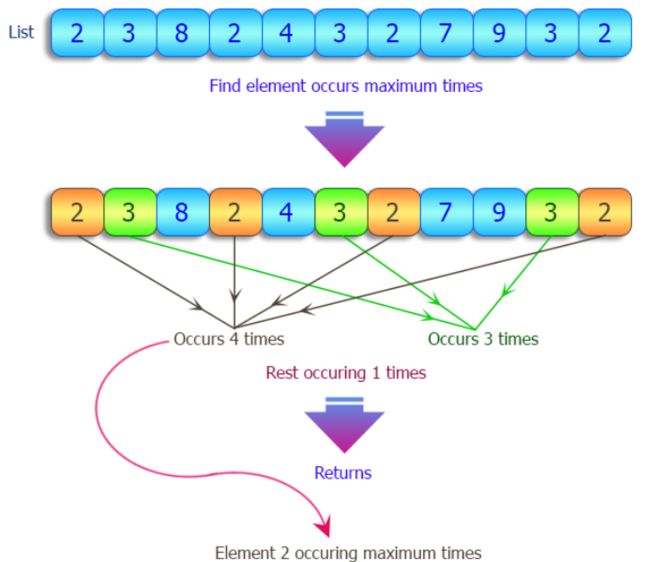
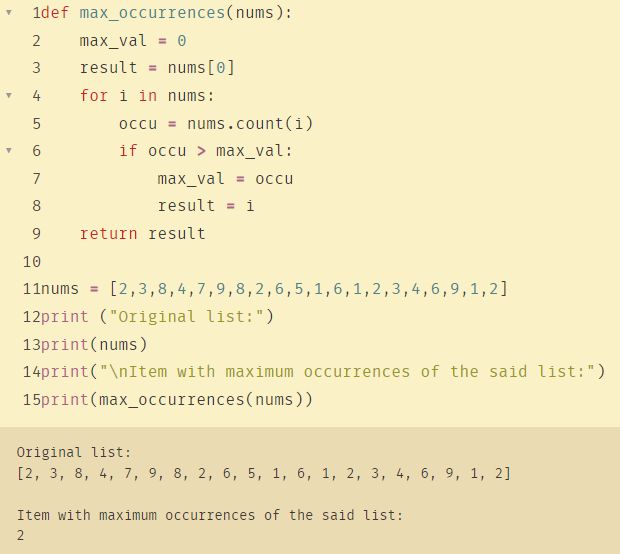
24、查找给定列表中出现次数最多的项目
def max_occurrences(nums):
max_val = 0
result = nums[0]
for i in nums:
occu = nums.count(i)
if occu > max_val:
max_val = occu
result = i
return result
nums = [2,3,8,4,7,9,8,2,6,5,1,6,1,2,3,4,6,9,1,2]
print ("Original list:")
print(nums)
print("\nItem with maximum occurrences of the said list:")
print(max_occurrences(nums))
25、列表中提取给定数量的随机选择的元素
import random
def random_select_nums(n_list, n):
return random.sample(n_list, n)
n_list = [1,1,2,3,4,4,5,1]
print("Original list:")
print(n_list)
selec_nums = 3
result = random_select_nums(n_list, selec_nums)
print("\nSelected 3 random numbers of the above list:")
print(result)