1 SQL语句的执行过程介绍
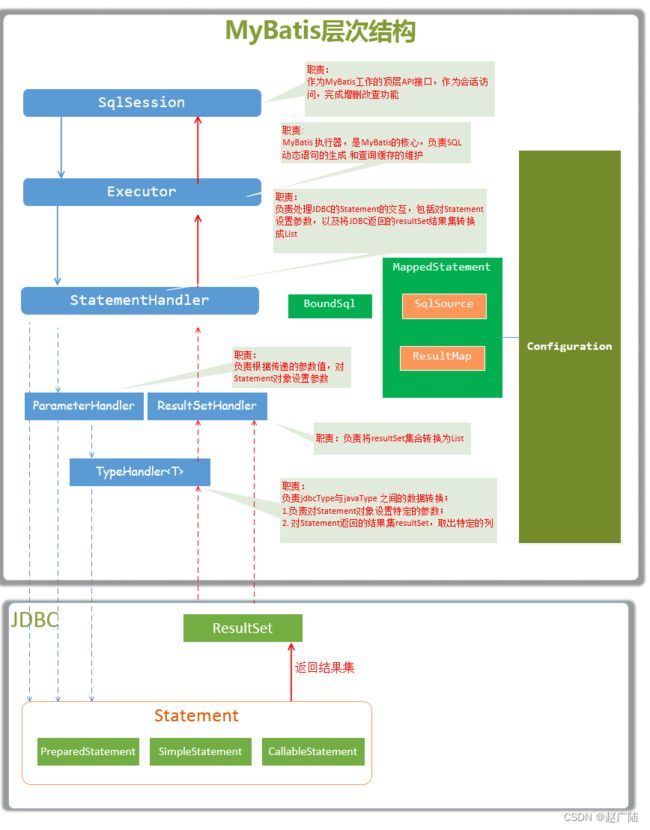
MyBatis核心执行组件:
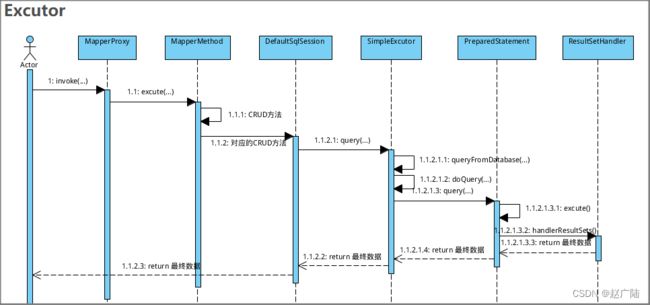
2 SQL执行的入口分析
2.1 为Mapper接口创建代理对象
// 方式1:
User user = session.selectOne("com.oldlu.dao.UserMapper.findUserById", 101);
// 方式2:
UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List userList = mapper.findAll();
2.2 执行代理逻辑
方式1入口分析:
session是DefaultSqlSession类型的,因为sqlSessionFactory默认生成的SqlSession是
DefaultSqlSession类型。
selectOne()会调用selectList()。
// DefaultSqlSession类 publicList selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) { try { MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement); // CURD操作是交给Excetor去处理的 return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
方式2入口分析:
获取代理对象:
//DefaultSqlSession类 ====================> @Override publicT getMapper(Class type) { return configuration.getMapper(type, this); } // Configuration类 ====================> public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) { return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession); } //MapperRegistry ----> apperProxyFactory.newInstance ====================> public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) { //从缓存中获取该Mapper接口的代理工厂对象 final MapperProxyFactory mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory ) knownMappers.get(type); //如果该Mapper接口没有注册过,则抛异常 if (mapperProxyFactory == null) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry."); } try { //【使用代理工厂创建Mapper接口的代理对象】 return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e); } } //MapperProxyFactory --->此时生成代理对象 ====================> protected T newInstance(MapperProxy mapperProxy) { //Mybatis底层是调用JDK的Proxy类来创建代理实例 return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy); } public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) { final MapperProxy mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache); return newInstance(mapperProxy); }
代理对象执行逻辑:
//MapperProxy ====================>
/**代理对象执行的方法,代理以后,所有Mapper的方法调用时,都会调用这个invoke方法*/
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws
Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
//如果是Object方法,则调用方法本身
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
//调用接口方法:根据被调用接口的Method对象,从缓存中获取MapperMethodInvoker对象
//apper接口中的每一个方法都对应一个MapperMethodInvoker对象,而MapperMethodInvoker
对象里面的MapperMethod保存着对应的SQL信息和返回类型以完成SQL调用 ...
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
/**
获取缓存中MapperMethodInvoker,如果没有则创建一个,而MapperMethodInvoker内部封装这一
个MethodHandler
*/
private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {
try {
return methodCache.computeIfAbsent(method, m -> {
if (m.isDefault()) {
//如果调用接口的是默认方法(default方法)
try {
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
return new
DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));
} else {
return new
DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException |
InvocationTargetException
| NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else {
//如果调用的普通方法(非default方法),则创建一个PlainMethodInvoker并放
入缓存,其中MapperMethod保存对应接口方法的SQL以及入参和出参的数据类型等信息
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface,
method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
});
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
Throwable cause = re.getCause();
throw cause == null ? re : cause;
}
}
// MapperProxy内部类: PainMethodInvoker ====================>
// 当cacheInvoker返回了PalinMethodInvoker实例之后,紧接着调用了这个实例的
PlainMethodInvoker:invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession
sqlSession) throws Throwable {
//Mybatis实现接口方法的核心: MapperMethod::execute方法:
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
// MapperMethod ====================>
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
// 将args进行解析,如果是多个参数则,则根据@Param注解指定名称将参数转换为Map,
如果是封装实体则不转换
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(),
param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(),
param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(),
param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
//查询操作
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
//解析参数,因为SqlSession::selectOne方法参数只能传入一个,但是我们
Mapper中可能传入多个参数,
//有可能是通过@Param注解指定参数名,所以这里需要将Mapper接口方法中的多个参
数转化为一个ParamMap,
//也就是说如果是传入的单个封装实体,那么直接返回出来;如果传入的是多个参数,
实际上都转换成了Map
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
//可以看到动态代理最后还是使用SqlSession操作数据库的
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null ||
!method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " +
command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() &&
!method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method
with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
// 此时我们发现: 回到了sqlsession中
private Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
List result;
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
} else {
result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param);
}
// ...
return result;
}
3 查询语句的执行过程分析
3.1 selectOne方法分析
// DefaultSqlSession类 ===============> // selectOne @Override publicT selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) { // //selectOne()会调用selectList()。 List list = this.selectList(statement, parameter); if (list.size() == 1) { return list.get(0); } else if (list.size() > 1) { throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size()); } else { return null; } } // selectList public List selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) { try { MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement); // CURD操作是交给Excetor去处理的 return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
3.2 sql获取
// CachingExecutor ===============> publicList query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { // 获取绑定的sql命令,比如"SELECT * FROM xxx" BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject); CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql); return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } @Override public List query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Cache cache = ms.getCache(); if (cache != null) { flushCacheIfRequired(ms); if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) { ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") List list = (List ) tcm.getObject(cache, key); if (list == null) { list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116 } return list; } } return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } //真正执行query操作的是SimplyExecutor代理来完成的,SimplyExecutor的父类BaseExecutor的 query方法中: // BaseExecutor类:SimplyExecutor的父类 =================> @Override public List query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId()); if (closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); } if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) { clearLocalCache(); } List list; try { queryStack++; //localCache是一级缓存,如果找不到就调用queryFromDatabase从数据库中查找 list = resultHandler == null ? (List ) localCache.getObject(key) : null; if (list != null) { handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql); } else { list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } } finally { queryStack--; } if (queryStack == 0) { for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) { deferredLoad.load(); } deferredLoads.clear(); if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) { clearLocalCache(); } } return list; } //第一次,没有缓存,所以会调用queryFromDatabase方法来执行查询。 private List queryFromDatabase(...) throws SQLException { List list; localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER); try { // 查询 list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); } finally { localCache.removeObject(key); } localCache.putObject(key, list); if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) { localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter); } return list; } // SimpleExecutor类 ============================> public List doQuery(...) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(....); // 1:SQL查询参数的设置 stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); // StatementHandler封装了Statement // 2:SQL查询操作和结果集的封装 return handler. query(stmt); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } }
3.3 参数设置
// SimplyExecutor类 ============================>
// 【1】 参数设置: prepareStatement
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog)
throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
// 通过getConnection方法来获取一个Connection,
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// 调用prepare方法来获取一个Statement
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// 设置SQL查询中的参数值 ***
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
// RoutingStatementHandler ============================>
// PreparedStatementHandler ============================>
@Override
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement);
}
// DefaultParameterHandler ============================> 此时参数设置成功
@Override
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting
parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
List parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if
(typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject =
configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException | SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for
mapping.....");
}
}
}
}
}
3.4 SQL执行和结果集的封装
// RoutingStatementHandler ============================> @Override publicList query(Statement statement) throws SQLException { return delegate. query(statement); } // PreparedStatementHandler ============================> @Override public List query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { // 这里就到了熟悉的PreparedStatement了 PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement; // 执行SQL查询操作 ps.execute(); // 结果交给ResultHandler来处理 return resultSetHandler. handleResultSets(ps); } // DefaultResultSetHandler类(封装返回值,将查询结果封装成Object对象) @Override public List
4 更新语句的执行过程分析
- xecutor 的 update 方法分析
- insert、update 和 delete 操作都会清空一二级缓存
- doUpdate 方法
- PreparedStatementHandler 的 update 方法
- 默认是创建PreparedStatementHandler,然后执行prepareStatement方法。
- 执行结果为受影响行数
- 执行更新语句的SQL
4.1 sqlsession增删改方法分析
// DefaultSqlSession ===============>
@Override
public int insert(...) {
return update(statement, parameter);
}
@Override
public int update(String statement) {
return update(statement, null);
}
@Override
public int delete(...) {
return update(....);
}
// insert 、delete操作是通过调用update语句进行的相关逻辑
@Override
public int update(String statement, Object parameter) {
try {
dirty = true;
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// 增删改 最终底层都是 update
return executor.update(ms, wrapCollection(parameter));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error updating database. Cause: " +
e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
4.2 sql获取
// CachingExecutor ===============>
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws
SQLException {
// 执行增删改,清除缓存
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
// 跳转BaseExecutor
return delegate.update(ms, parameterObject);
}
// BaseExecutor ===============>
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing an
update").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
// 清除 LocalCache 一级缓存
clearLocalCache();
//执行 doUpdate
return doUpdate(ms, parameter);
}
// SimpleExecutor ===============>
// doUpdate
@Override
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(...);
// 【1】.获取statement,并进行参数映射
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 【2】.handler.update()方法执行具体sql指令
return handler.update(stmt);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
4.3 参数设置
// SimplyExecutor类 ============================>
//【1】 prepareStatement
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog)
throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// 使用connection对象信息创建statement,并将超时时间绑定
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// parameterize方法设置sql执行时候需要的参数
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
// RoutingStatementHandler ============================>
// PreparedStatementHandler ============================>
@Override
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement);
}
// DefaultParameterHandler ============================> 此时参数设置成功
@Override
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting
parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
List parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if
(typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject =
configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException | SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for
mapping.....");
}
}
}
}
}
4.4 SQL执行
// RoutingStatementHandler ============================>
@Override
public int update(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
return delegate.update(statement);
}
// PreparedStatementHandler ============================>
@Override
public int update(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
// 这里就是底层JDBC的PreparedStatement 操作了
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
// 执行SQL增删改操作
ps.execute();
// 获取影响的行数
int rows = ps.getUpdateCount();
Object parameterObject = boundSql.getParameterObject();
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator();
keyGenerator.processAfter(executor, mappedStatement, ps, parameterObject);
// 返回影响的行数
return rows;
}
5 小结
mybatis执行SQL的流程都是:
1.根据statement字符串从configuration中获取对应的mappedStatement;
2.根据获取的mappedStatement创建相应的Statement实例;
3.根据传入的参数对statement实例进行参数设置;
4.执行statement并执行后置操作;
到此这篇关于MyBatis核心源码深度剖析SQL执行过程的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关MyBatis核心源码剖析SQL执行过程内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!