C++学习记录1
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、基础知识
-
- 1. C++书写HelloWorld
- 2.注释
- 3.变量的使用-变量的意义
- 4.常量
- 5.关键字
- 6.标识符明明规则
- 二、数据类型
-
- 1.整型
- 2. sizeof关键字
- 3. 实型(浮点型)
- 4.字符型
- 5.转义字符
- 6.字符串型
- 7.布尔类型bool
- 8.数据的输入
- 总结
前言
Visual Studio 2022详细安装使用调试教程C语言编译器,C++编译器
一、基础知识
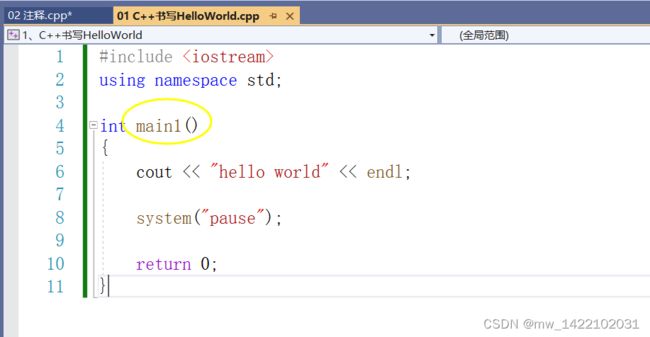
1. C++书写HelloWorld
#include 2.注释
注释分为单行注释和多行注释
#include .写多个main程序出现问题
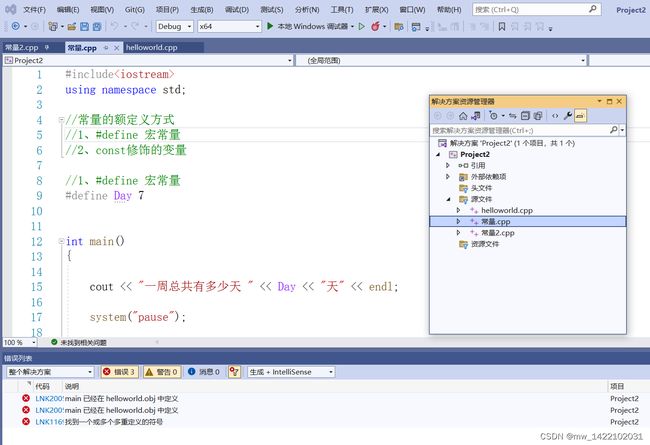
将第一个程序的“main”改成“main1”
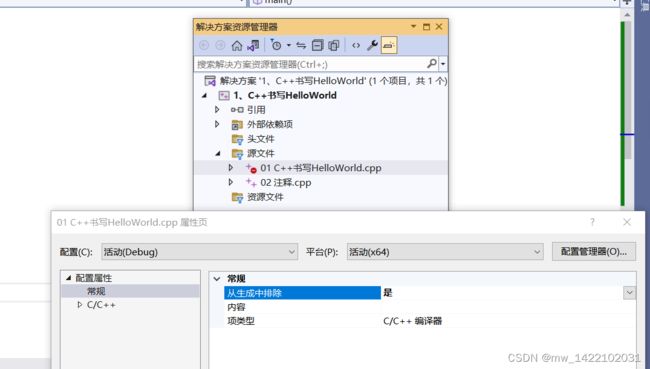
或者参照博客C++ Visual Studio中同一个项目包含多个有main函数的源文件怎么分别运行
具体流程:
- 右键点击该项目名称,点击“属性”;
- 在属性页中,点击“常规”选项卡,将“从生成中排除”的属性值设置为“是”,点击“确定”,进行保存;
- 其他需要排除运行的文件,依次进行上述操作,只保留要运行的文件(被排除的文件的小图标会发生改变)
3.变量的使用-变量的意义
变量存在的意义:方便我们管理内存空间
变量创建的语法:
数据类型 变量名 = 变量初始值
int a = 10;
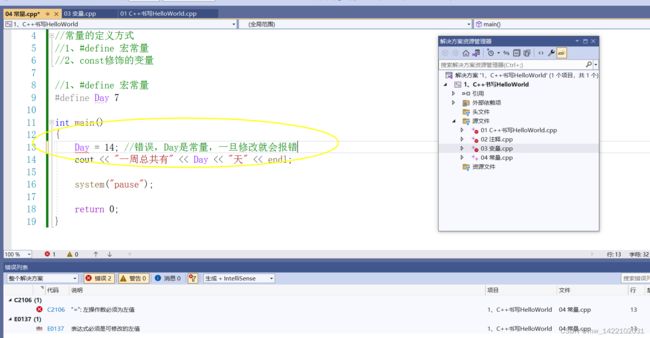
#include 4.常量
#include 5.关键字
作用:关键字是C++中预先保留的单次(标识符)
- 在定义变量过着常量的时候,不要用关键字,否则会产生歧义
#include 6.标识符明明规则
作用:C++规定给标识符(变量、常量)命名时,有一套自己的规则
- 标识符不可以是关键字;
- 标识符是由字母、数字、下划线构成;
- 标识符第一个字符只能是字母或下划线;
- 标识符是区分大小写的。
#include 二、数据类型
-
C++规定在创建一个变量或者常量时,必须要制顶出相应的数据类型,否则无法给变量分配内存
-
数据类型的存在意义:给变量分配合适的内存空间
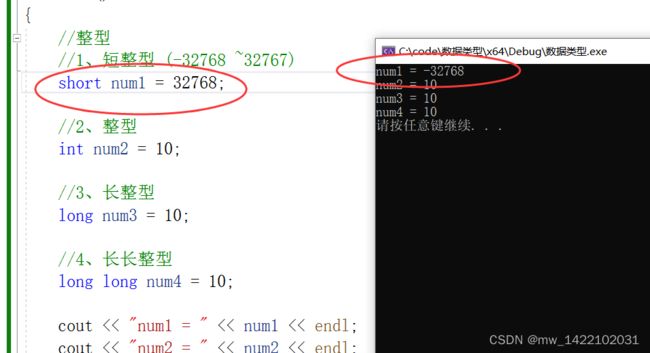
1.整型
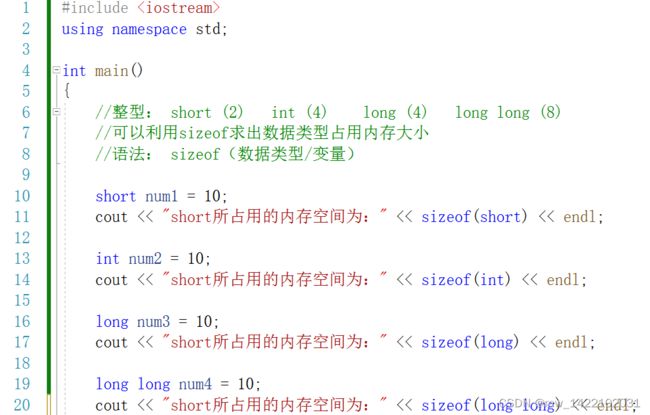
#include 2. sizeof关键字
- 作用:利用sizeof关键字可以统计数据类型所占内存大小
- 语法:sizeof(数据类型/变量)
示例:
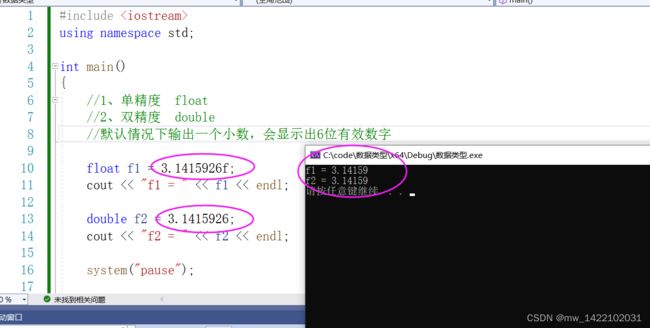
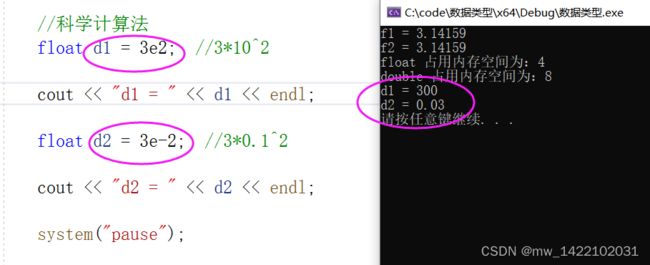
#include 3. 实型(浮点型)
- 作用:用于表示小数
浮点型变量分为两种:
- 单精度float
- 双精度double
两者的区别在于表示的有效数字范围不同。
| 数据类型 | 占用空间 | 有效数字范围 |
|---|---|---|
| float | 4字节 | 7位有效数字 |
| double | 8字节 | 15~16位有效数字 |
#include 4.字符型
- 作用:字符型变量用于显示单个字符
- 语法:char ch = ‘a’;
- 注意1:创建字符型变量的时候,要用单引号,不能用双引号
- 注意2:创建字符型变量时候,单引号内只能有一个字符,不可以是字符串
- C和C++中字符型变量所占内存大小为1个字节
- 字符型变量并不是把字符本身放到内存中存储,而是对应的ASSCII编码放入到存储单元
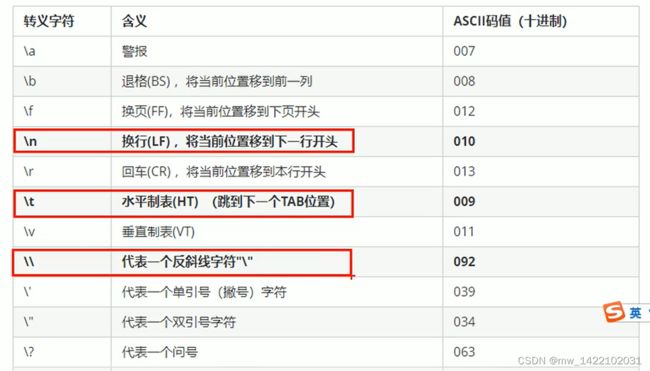
#include 5.转义字符
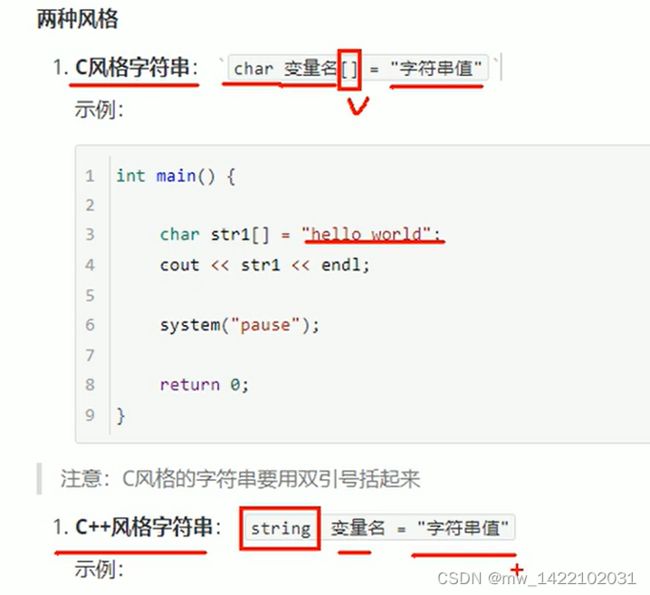
#include 6.字符串型
#include 注:vs2022版本不用写头文件
string str2 = "hello world2";
cout << str2 << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
7.布尔类型bool
- 作用:布尔数据类型代表真或假的值
- bool类型只有两个值
| true | 真 | 本质是1 |
|---|---|---|
| false | 假 | 本质是0 |
- bool类型占一个字节大小
#include 8.数据的输入
- 作用:用于从键盘获取数据
- 关键字: cin
- 语法: cin >> 变量
#include
总结
提示:这里对文章进行总结:
例如:以上就是今天要讲的内容,本文仅仅简单介绍了pandas的使用,而pandas提供了大量能使我们快速便捷地处理数据的函数和方法。