LeetCode_4_树----恢复二叉搜索树
大家好!我是你们的好朋友,大数据老虾。相遇是缘,既然来了就拎着小板凳坐下来一起唠会儿,如果在文中有所收获,请别忘了一键三连,你的鼓励,是我创作的动力,废话不多说,直接**开干 吧。
先别急着走,文末干货,记得拎着小板凳离开的时候也给它顺走
树-恢复二叉搜索树
- 恢复二叉搜索树
-
- 题目
- 方式1:显式中序遍历
- Java解题代码
-
- 复杂度分析
- 文末彩蛋
恢复二叉搜索树
题目
解析:
给出一个二叉搜索树的根节点root,该树中恰好两个节点的值被错误的交换。
示例1:
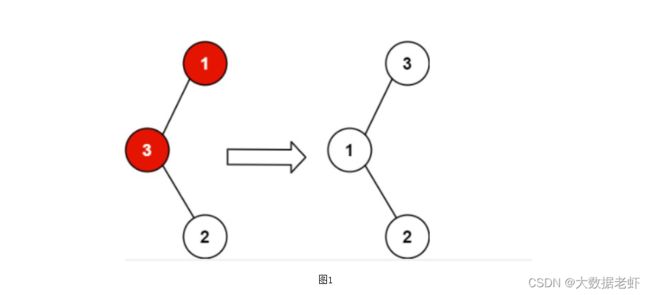
input:root = [1, 3, null, null, 2]
output:[3, 1, null, null, 2]
// 3 不能为1的左孩子,因为 3 > 1。交换 1 和 3 使二叉搜索树恢复有效
示例2:
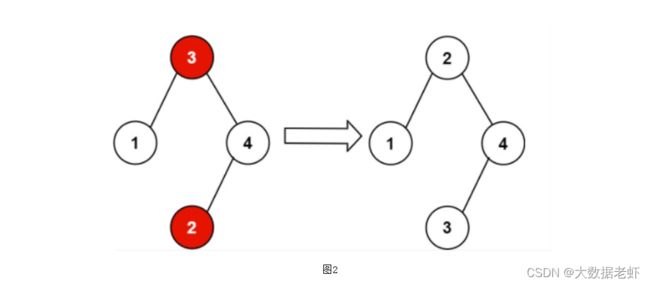
input:root = [3, 1, 4, null, null, 2]
output:[2, 1, 4, null, null, 3]
// 2 不能在 3 的右子树中,因为 2 < 3。交换 2 和 3 使二叉搜索树恢复有效。
方式1:显式中序遍历
思考:
如果两个节点被错误地交换后,会对原有的二叉树造成什么样地影响?
回答:
对于二叉搜索树而言,如果对其进行中序遍历,得到的值序列是递增有序的,而如果错误地交换了两个节点,等价于在这个值序列中交换了两个值,破坏了值序列的递增性。
假设有一个递增序列 a=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7]:
如果交换两个不相邻的数字,例如 22 和 66,原序列变成了a=[1,6,3,4,5,2,7],那么显然序列中有两个位置不满足 ai < ai+1,在这个序列中体现为 6>3,5>2,因此只要找到这两个位置,即可找到被错误交换的两个节点。如果交换两个相邻的数字,例如 22 和 33,此时交换后的序列只有一个位置不满足ai 题解: 开辟一个新数组nums 来记录中序遍历得到的值序列,然后线性遍历找到两个位置 i 和 j,并重新遍历原二叉搜索树修改对应节点的值完成修复。 找资料很累吧,别急客官,俺统统安排上。程序员不可缺少的书籍,程序员经典名言:"收藏了就等于学会啦"Java解题代码
class Solution {
public void recoverTree(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<Integer>();
inorder(root, nums);
int[] swapped = findTwoSwapped(nums);
recover(root, 2, swapped[0], swapped[1]);
}
public void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> nums) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
inorder(root.left, nums);
nums.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right, nums);
}
public int[] findTwoSwapped(List<Integer> nums) {
int n = nums.size();
int index1 = -1, index2 = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
if (nums.get(i + 1) < nums.get(i)) {
index2 = i + 1;
if (index1 == -1) {
index1 = i;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
int x = nums.get(index1), y = nums.get(index2);
return new int[]{x, y};
}
public void recover(TreeNode root, int count, int x, int y) {
if (root != null) {
if (root.val == x || root.val == y) {
root.val = root.val == x ? y : x;
if (--count == 0) {
return;
}
}
recover(root.right, count, x, y);
recover(root.left, count, x, y);
}
}
}
复杂度分析
文末彩蛋
图灵程序丛书300+
Linux实战100讲
Linux书籍
计算机基础硬核总结
计算机基础相关书籍
操作系统硬核总结
Java自学宝典
Java学习资料
Java硬核资料
Java面试必备
Java面试深度剖析
阿里巴巴Java开发手册
MySQL入门资料
MySQL进阶资料
深入浅出的SQL
Go语言书籍
我的个人仓库:私人仓库