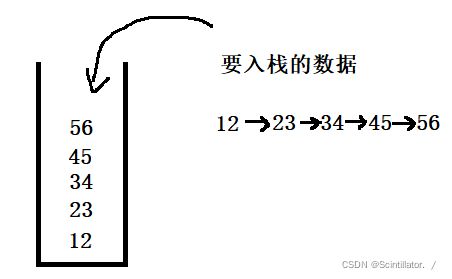
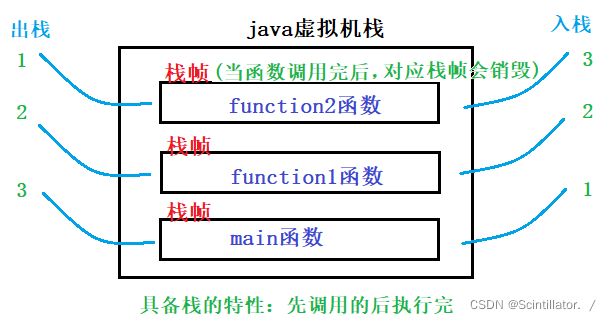
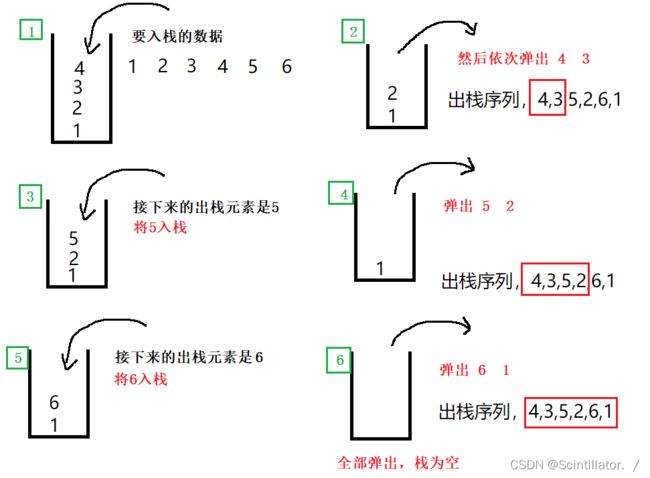
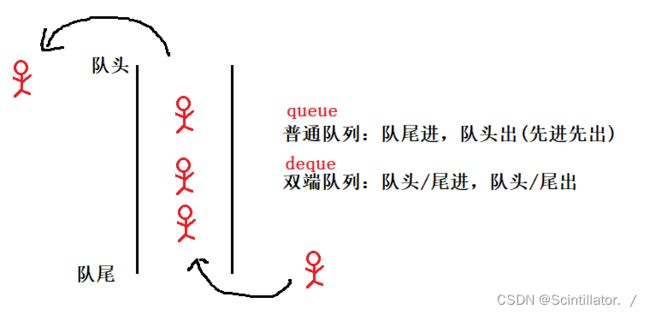
- electron-vue 安装环境、构建+打包(mac和windows)这一篇就够了
阿毛sky
electronvue前端
由于公司需要,下一个项目需要做CS开发,技术选型分析后,选择了electron(Electron是一个使用JavaScript,HTML和CSS等Web技术创建原生程序的框架)研究发现,electron与vue-cli3.0脚手架做了很好的融合,对于我们这种用惯了vue,以及elementUI这些UI框架的Web前端开发工程师来说,实在太友好了,不过,这是一门国外框架技术,不仅是环境搭建、安装、文
- Node.js使用教程
m0_74824112
面试学习路线阿里巴巴node.jsvim编辑器
Node.js使用教程Node.js是一个基于ChromeV8引擎的JavaScript运行环境,它让JavaScript运行在服务器端。以下是一个简单的Node.js使用教程:一、Node.js开发环境和编译1.1安装Node.js访问Node.js官网下载并安装适合您操作系统的Node.js版本。1.2创建一个Node.js项目在您的工作目录中,创建一个新的文件夹作为项目目录,例如命名为my_
- 【Spring:Caused by java.lang.ClassNotFoundException 】
m0_74823490
面试学习路线阿里巴巴javaspringtomcat
Spring:Causedby:java.lang.ClassNotFoundException:org.springframework.dao.support.DaoSupportSpring中使用Mybatis连接数据库时可能会出现以上错误,但是当出现以上错误时说明你在applicationContext.xml文件中所做的相关操作:spring整合myBATis后控制的创建连接用的对象加载M
- three.js性能优化
火辣辣-
学习总结学习笔记three.js性能优化
本文持续更新~~~参考文章three.js是JavaScript编写的WebGL第三方库。提供了非常多的3D显示功能。在使用的时候,虽然three.js做了优化,但是在使用不恰当的代码,也会产生性能损耗。帧率越低,给人感觉就越卡。这是我在开发中自己百度总结的,有不对的可以联系我啊2019-08-22更新———————1、disppose()方法得重要性每当你创建一个three.js中的实例时,都会
- Java 环境安装和第一个程序:使用 VSCode 轻松上手
极梦网络无忧
JAVAjavavscode开发语言
引言Java作为一门广泛应用于软件开发各个领域的编程语言,对于初学者而言,快速搭建开发环境并运行第一个程序是迈向Java编程世界的重要起点。本文将介绍一种简单的方式,借助VisualStudioCode(简称VSCode)来完成Java环境的安装、配置,以及编写并运行第一个Java程序。一、Java环境安装1.下载并安装JDKJDK(JavaDevelopmentKit)是Java开发的核心工具包
- pandas(02 pandas基本功能和描述性统计)
twilight ember
pandaspython开发语言
前面内容:pandas(01入门)目录一、PythonPandas基本功能1.1Series基本功能1.2DataFrame基本功能二、PythonPandas描述性统计2.1常用函数*2.2汇总数据(describe)*一、PythonPandas基本功能到目前为止,我们已经学习了三种Pandas数据结构以及如何创建它们。我们将主要关注DataFrame对象,因为它在实时数据处理中非常重要,并讨
- linux常用基础命令_最新版
脚大江山稳
linux运维服务器
常用命令查看当前目录下个各个文件大小查看当前系统储存使用情况查看当前路径删除当前目录下所有包含".log"的文件linux开机启动jar更改自动配置文件后操作关闭自启动linux静默启动java服务查询端口被占用查看软件版本重启关机开机启动取别名清空当前行创建文件touch创建文件夹查找文件/文件名/大小查找查看文件内容cat/more删除文件或文件夹管道符|过滤grep命令echo命令输出内容重
- vue字符串的常用方法,截取字符串,获取字符串长度,检索字符串
luckyext
vue.jsjavascript前端
1.使用substr方法截取字符串letstr="12345";letpart=str.substr(0,3);//截取从索引0开始到索引3的子字符串console.log(part);//"123"2.获取字符串长度JavaScript中的字符串有一个length属性,该属性可以用在VUE获取字符串的长度conststr='hello';str.length输出结果:53.检索字符串是否包含特定
- Java程序性能优化读书笔记(一):Java性能调优概述
anxunnian1498
java数据库操作系统
程序性能的主要表现点:执行速度:程序的反映是否迅速,响应时间是否足够短内存分配:内存分配是否合理,是否过多地消耗内存或者存在内存泄漏启动时间:程序从运行到可以正常处理业务需要花费多少时间负载承受能力:当系统压力上升时,系统的执行速度、响应时间的上升曲线是否平缓衡量程序性能的主要指标:执行时间:程序从运行到结束所使用的时间CPU时间:函数或者线程占用CPU的时间内存分配:程序在运行时占用内容的空间磁
- 代码随想录算法训练营第一天:二分查找,移除元素,有序数组的平方
坚持不懈的猫喵
算法
一.数组1.要点:数组下标都是从0开始的。数组内存空间的地址是连续的数组的元素是不能删的,只能覆盖。C++中二维数组在地址空间上是连续的。(java就不是了)二.二分查找二分查找有两种方法1.target在左闭右闭[left,right]while(lefttarget)target偏小,在left与middle的左侧,right要赋值为middle-1,left不用改变,因为当前这个nums[m
- 1.如何配置开发环境(JDK、Maven、IDEA)搭建SpringBoot项目
yjx012
javamavenintellij-ideaspringboot
搭建SpringBoot项目的开发环境主要包括安装和配置JDK、Maven和IDEA(IntelliJIDEA)。以下是详细的步骤和注意事项。1.安装JDK1.1下载JDKDownloadIntelliJIDEA–TheLeadingJavaandKotlinIDE1.2安装JDK下载后,按照安装向导完成安装。安装过程中请记住安装路径,通常为C:\ProgramFiles\Java\jdk-11或
- JProfiler_windows:Java 性能分析与优化
心灵宝贝
java开发语言
JProfiler是一款功能强大的Java性能分析工具,专门用于监控和分析Java应用程序的性能瓶颈、内存泄漏、线程问题等。以下是关于JProfiler_windows-x64_8_0_2的详细介绍:一、JProfiler简介JProfiler是由ej-technologies公司开发的一款Java性能分析工具,支持对本地和远程JVM的监控。它能够帮助开发者深入分析Java应用程序的CPU使用、内
- Python的垃圾回收机制,详解Python的GC体系
李云龙炮击平安线程
python系统架构面试跳槽后端架构
什么是垃圾回收?为什么需要垃圾回收?垃圾回收即Garbagecollection简称为GC,是Python,Java等高级语言所使用的内存回收机制,由虚拟机帮助我们管理内存,让它自动把我们去追踪和回收内存中的对象。没有作用的对象就是垃圾,虚拟机就是扫地机器人,在某个时机自动帮我们清除垃圾。区别于C和C++这种让用户自己进行内存管理的方式,由虚拟机代用户管理内存。让用户自己进行内存管理的方式固然自由
- 使用JvaScript做一个猜数字游戏And条件语句和循环语句整合
偷只猫来养
javascript游戏js
**使用JvaScript做一个简单的猜数字游戏(这里设置的数字范围是0-100)**JavaScript是一门目前流行的面向对象的脚本语言,可以使用它来做很多事情,这里为大家分享一下如何使用js语言来写出一个猜数字游戏。1、需求用户可以控制游戏的开始和结束。在用户点击开始后,系统自动为用户生成一个0-100的随机数,用户在输入框中输入内容后点击确认后可以根据输入内容提示相关信息。2、逻辑分析使用
- 【Jvascript 算法】-- JavaScript实现对树结构数据的增删以及树型数据与数组的相互转换
野生松
在日常开发中我们经常会碰到树结构数据,以下是我的笔记:constarr=[{id:2,name:'部门B',parentId:0},{id:3,name:'部门C',parentId:1},{id:1,name:'部门A',parentId:2},{id:4,name:'部门D',parentId:1},{id:5,name:'部门E',parentId:2},{id:6,name:'部门F',p
- 使用JavaScript设计一款简单的数字时钟
布啦啦李
javascript时钟
本文目录使用JavaScript设计一款带日期显示的数字时钟效果预览1.项目概述2.HTML结构代码说明3.CSS样式代码说明4.JavaScript逻辑代码说明5.运行效果使用JavaScript设计一款带日期显示的数字时钟本文将详细介绍如何使用HTML、CSS和JavaScript设计一款带日期显示的数字时钟。我们将逐步讲解每一行代码的作用,帮助你理解如何实现一个实时更新的时钟,并扩展功能以显
- 转:javascript获取上一访问页面
dianai7709
javascript移动开发ViewUI
原文链接:移动端返回上一页,刚需!document.referrer详解全文如下:返回上一页,在PC端我们可以使用:history.go(-1)或者history.back(),可以正常返回第一层。这样,我们不需要上一页的url具体是什么,只要使用history一般都没啥问题。但是在移动端,如果想要返回上一页。比如从A页面跳到B页面,如果B页面想返回A页面,为了防止不会跳错,必须要有一个返回那如果
- Spring Security(六)RBAC 结构实现
是晓周哦
Spring-Securityspringjava后端springboot安全架构springcloud
博主前言:本以为这个就是代替传统jwt的插件,没想到复杂程度如此之高。SpringSecurity本身是个高度自定义化的组件,必须花时间重点学习一下。以下为个人配置学习的流程,从零到权限管理、redis嵌入等步骤。本文基于尚硅谷的SpringSecurity教程学习,文章与原教程有不小出入,仅供参考。B站视频链接:尚硅谷Java项目SpringSecurity+OAuth2权限管理实战教程RBAC
- Java API文档使用指南与详解
Kay Lam
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:JavaAPI文档是Java开发者的权威参考资料,详细描述了Java标准库中的所有公开组件,涵盖了I/O、网络编程、多线程、集合框架、数据库连接(JDBC)、XML处理、图形用户界面(GUI)等多个领域。文档提供清晰的指南帮助理解并使用Java的功能,包含每个类或接口的详细注释、使用示例和常见用途。此外,还介绍了JDK6版本的中文离线文档CHM文件及其下载方式
- java word在线编辑_[原创]Java开发在线打开编辑保存Word文件(支持多浏览器)
嘻嘻哈哈哦哦吧
javaword在线编辑
Java调用PageOffice实现在线编辑保存Word文件(以jsp调用为例,支持SSM、SSH、SpringMVC等流行框架)1.下载PageOffice开发包:http://www.zhuozhengsoft.com/dowm/下载PageOfficeforJAVA2.以Myeclipse为例,新建一个WebProject,比如:wordonline3.解压PageOffice开发包,拷贝“
- 6.1 理解API的概念
programmer120986
apijava平台class虚拟机网络应用
JavaAPI通过支持平台无关性和安全性,使得Java适应于网络应用。JavaAPI是运行库的集合,它提供了一套访问主机系统资源的标准方法。运行Java程序时,虚拟机装载程序的class文件所使用的JavaAPIclass文件。所有被装载的class文件(包括从应用程序中和从JavaAPI中提取的)和所有已经装载的动态库(包含本地方法)共同组成了再Java虚拟机上运行的整个程序。在一个平台能够支持
- java jdk & java api 帮助文档(中文、英文版)
黑色白色
技术--javajavaapi文档jdkchmsun
javaapi帮助文档chm1.51.6中文版英文版.收藏Sun公司提供的JavaAPIDocs是学习和使用Java语言中最经常使用的参考资料之一。但是长期以来此文档只有英文版,对于中国地区的Java开发者来说相当的不便。目前Sun公司正在组织多方力量将此文档翻译成中文,并于2005年10月31日在Sun中国技术社区(http://gceclub.sun.com.cn/)正式发布第一批中文版Jav
- 扫描线/矩形面积并
一条大祥脚
android算法
扫描线的思想很早就会了,所以一直以为这个板子自己会了,但实际上并没有,这题还是不简单。首先,扫描线的思想很简单,就是当我们要处理多维的问题时,我们可以对其中一个维度进行排序,然后用数据结构维护剩下的维度,这样可以问题降低一个来考虑。当然实际上我们没有凭空吃掉一个维度,降低的维度实际上是被我们放到时间维上了。比如我们如果要求一个不规则形状的二维图像的面积,我们可以对x轴维度排序,然后y轴在任意时刻都
- 2025年如何选择合适的微服务工具
zxzy_org
微服务架构云原生算法
选择合适的工具是成功实施微服务架构的关键,而2025年市场上可供选择的工具种类更加丰富,这也让开发者需要更为谨慎地做出决策。首先,需要根据团队的技术栈选择合适的开发框架。例如,Java开发者可以选择SpringBoot,而Node.js开发者可能更倾向于使用Express或NestJS。其次,在服务通信方面,工具的选择应基于业务需求。如果追求低延迟和高效数据传输,gRPC是一个值得考虑的方案;而对
- shrio反序列化分析
红队蓝军
java开发语言安全
shiro550环境搭建https://codeload.github.com/apache/shiro/zip/shiro-root-1.2.4配置pom.xmljavax.servletjstlruntimejavax.servletservlet-apiprovidedorg.slf4jslf4j-log4j12runtimelog4jlog4jruntimenet.sourceforge.
- controller入参异常 No primary or default constructor found for class
Lin_Miao_09
java优秀例子java
一、记一次的常见报错java.lang.IllegalStateException:Noprimaryordefaultconstructorfoundforclassjava.time.LocalDateTime错误写法:@GetMappingpublicStringquery(LocalDatestart,LocalDateend){return"开始时间:"+start+"结束时间:"+en
- Redis
Lin_Miao_09
技术架构Redisredis数据库缓存
目录一、Redis基础知识数据持久化高可用性和扩展性性能优化应用场景二、Redis的Java常用客户端JedislettuceRedisson三、Redis实战Jedis1.添加依赖2.基本使用例子3.使用连接池优化性能spring-boot-starter-data-redis1.添加依赖2.配置文件设置3.使用RedisTemplate或Repository使用RedisTemplate使用R
- DeepSeek R1 与 OpenAI O1:机器学习模型的巅峰对决
学无止尽5
机器学习人工智能
我的个人主页我的专栏:人工智能领域、java-数据结构、Javase、C语言,希望能帮助到大家!!!点赞收藏❤一、引言在机器学习的广袤天地中,大型语言模型(LLM)无疑是最为璀璨的明珠。它们凭借卓越的语言理解与生成能力,正以前所未有的方式重塑着我们与信息交互的模式。DeepSeekR1和OpenAIO1作为其中的佼佼者,代表了当前技术的前沿水准,在架构设计、训练方法、性能表现以及应用场景等诸多层面
- List对象进行排序
Lin_Miao_09
java优秀例子listjava
目录一、List对象中某个值进行排序代码示例注意事项二、List.sort和Collections.sort异同1.方法所属2.使用方式3.是否修改原列表4.泛型支持5.性能6.适用场景7.示例代码对比使用testList.sort使用Collections.sort8.总结三、为对象多个属性进行排序示例代码一、List对象中某个值进行排序用空间换时间,Java在内存中进行对象集合排序。在Java
- 前端为什么要使用new Promise包裹一个函数
没资格抱怨
JS核心前端javascript
在前端开发中,使用newPromise包裹一个函数主要是为了将原本不支持Promise规范的操作转化为支持Promise规范的操作,从而可以更好地处理异步操作,提升代码的可读性和可维护性。下面详细介绍这么做的常见原因和应用场景:1.封装回调风格的异步操作在JavaScript中,早期的异步操作(如setTimeout、XMLHttpRequest等)通常使用回调函数来处理结果。这种方式容易导致回调
- Java实现的简单双向Map,支持重复Value
superlxw1234
java双向map
关键字:Java双向Map、DualHashBidiMap
有个需求,需要根据即时修改Map结构中的Value值,比如,将Map中所有value=V1的记录改成value=V2,key保持不变。
数据量比较大,遍历Map性能太差,这就需要根据Value先找到Key,然后去修改。
即:既要根据Key找Value,又要根据Value
- PL/SQL触发器基础及例子
百合不是茶
oracle数据库触发器PL/SQL编程
触发器的简介;
触发器的定义就是说某个条件成立的时候,触发器里面所定义的语句就会被自动的执行。因此触发器不需要人为的去调用,也不能调用。触发器和过程函数类似 过程函数必须要调用,
一个表中最多只能有12个触发器类型的,触发器和过程函数相似 触发器不需要调用直接执行,
触发时间:指明触发器何时执行,该值可取:
before:表示在数据库动作之前触发
- [时空与探索]穿越时空的一些问题
comsci
问题
我们还没有进行过任何数学形式上的证明,仅仅是一个猜想.....
这个猜想就是; 任何有质量的物体(哪怕只有一微克)都不可能穿越时空,该物体强行穿越时空的时候,物体的质量会与时空粒子产生反应,物体会变成暗物质,也就是说,任何物体穿越时空会变成暗物质..(暗物质就我的理
- easy ui datagrid上移下移一行
商人shang
js上移下移easyuidatagrid
/**
* 向上移动一行
*
* @param dg
* @param row
*/
function moveupRow(dg, row) {
var datagrid = $(dg);
var index = datagrid.datagrid("getRowIndex", row);
if (isFirstRow(dg, row)) {
- Java反射
oloz
反射
本人菜鸟,今天恰好有时间,写写博客,总结复习一下java反射方面的知识,欢迎大家探讨交流学习指教
首先看看java中的Class
package demo;
public class ClassTest {
/*先了解java中的Class*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
//任何一个类都
- springMVC 使用JSR-303 Validation验证
杨白白
springmvc
JSR-303是一个数据验证的规范,但是spring并没有对其进行实现,Hibernate Validator是实现了这一规范的,通过此这个实现来讲SpringMVC对JSR-303的支持。
JSR-303的校验是基于注解的,首先要把这些注解标记在需要验证的实体类的属性上或是其对应的get方法上。
登录需要验证类
public class Login {
@NotEmpty
- log4j
香水浓
log4j
log4j.rootCategory=DEBUG, STDOUT, DAILYFILE, HTML, DATABASE
#log4j.rootCategory=DEBUG, STDOUT, DAILYFILE, ROLLINGFILE, HTML
#console
log4j.appender.STDOUT=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4
- 使用ajax和history.pushState无刷新改变页面URL
agevs
jquery框架Ajaxhtml5chrome
表现
如果你使用chrome或者firefox等浏览器访问本博客、github.com、plus.google.com等网站时,细心的你会发现页面之间的点击是通过ajax异步请求的,同时页面的URL发生了了改变。并且能够很好的支持浏览器前进和后退。
是什么有这么强大的功能呢?
HTML5里引用了新的API,history.pushState和history.replaceState,就是通过
- centos中文乱码
AILIKES
centosOSssh
一、CentOS系统访问 g.cn ,发现中文乱码。
于是用以前的方式:yum -y install fonts-chinese
CentOS系统安装后,还是不能显示中文字体。我使用 gedit 编辑源码,其中文注释也为乱码。
后来,终于找到以下方法可以解决,需要两个中文支持的包:
fonts-chinese-3.02-12.
- 触发器
baalwolf
触发器
触发器(trigger):监视某种情况,并触发某种操作。
触发器创建语法四要素:1.监视地点(table) 2.监视事件(insert/update/delete) 3.触发时间(after/before) 4.触发事件(insert/update/delete)
语法:
create trigger triggerName
after/before
- JS正则表达式的i m g
bijian1013
JavaScript正则表达式
g:表示全局(global)模式,即模式将被应用于所有字符串,而非在发现第一个匹配项时立即停止。 i:表示不区分大小写(case-insensitive)模式,即在确定匹配项时忽略模式与字符串的大小写。 m:表示
- HTML5模式和Hashbang模式
bijian1013
JavaScriptAngularJSHashbang模式HTML5模式
我们可以用$locationProvider来配置$location服务(可以采用注入的方式,就像AngularJS中其他所有东西一样)。这里provider的两个参数很有意思,介绍如下。
html5Mode
一个布尔值,标识$location服务是否运行在HTML5模式下。
ha
- [Maven学习笔记六]Maven生命周期
bit1129
maven
从mvn test的输出开始说起
当我们在user-core中执行mvn test时,执行的输出如下:
/software/devsoftware/jdk1.7.0_55/bin/java -Dmaven.home=/software/devsoftware/apache-maven-3.2.1 -Dclassworlds.conf=/software/devs
- 【Hadoop七】基于Yarn的Hadoop Map Reduce容错
bit1129
hadoop
运行于Yarn的Map Reduce作业,可能发生失败的点包括
Task Failure
Application Master Failure
Node Manager Failure
Resource Manager Failure
1. Task Failure
任务执行过程中产生的异常和JVM的意外终止会汇报给Application Master。僵死的任务也会被A
- 记一次数据推送的异常解决端口解决
ronin47
记一次数据推送的异常解决
需求:从db获取数据然后推送到B
程序开发完成,上jboss,刚开始报了很多错,逐一解决,可最后显示连接不到数据库。机房的同事说可以ping 通。
自已画了个图,逐一排除,把linux 防火墙 和 setenforce 设置最低。
service iptables stop
- 巧用视错觉-UI更有趣
brotherlamp
UIui视频ui教程ui自学ui资料
我们每个人在生活中都曾感受过视错觉(optical illusion)的魅力。
视错觉现象是双眼跟我们开的一个玩笑,而我们往往还心甘情愿地接受我们看到的假象。其实不止如此,视觉错现象的背后还有一个重要的科学原理——格式塔原理。
格式塔原理解释了人们如何以视觉方式感觉物体,以及图像的结构,视角,大小等要素是如何影响我们的视觉的。
在下面这篇文章中,我们首先会简单介绍一下格式塔原理中的基本概念,
- 线段树-poj1177-N个矩形求边长(离散化+扫描线)
bylijinnan
数据结构算法线段树
package com.ljn.base;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
/**
* POJ 1177 (线段树+离散化+扫描线),题目链接为http://poj.org/problem?id=1177
- HTTP协议详解
chicony
http协议
引言
- Scala设计模式
chenchao051
设计模式scala
Scala设计模式
我的话: 在国外网站上看到一篇文章,里面详细描述了很多设计模式,并且用Java及Scala两种语言描述,清晰的让我们看到各种常规的设计模式,在Scala中是如何在语言特性层面直接支持的。基于文章很nice,我利用今天的空闲时间将其翻译,希望大家能一起学习,讨论。翻译
- 安装mysql
daizj
mysql安装
安装mysql
(1)删除linux上已经安装的mysql相关库信息。rpm -e xxxxxxx --nodeps (强制删除)
执行命令rpm -qa |grep mysql 检查是否删除干净
(2)执行命令 rpm -i MySQL-server-5.5.31-2.el
- HTTP状态码大全
dcj3sjt126com
http状态码
完整的 HTTP 1.1规范说明书来自于RFC 2616,你可以在http://www.talentdigger.cn/home/link.php?url=d3d3LnJmYy1lZGl0b3Iub3JnLw%3D%3D在线查阅。HTTP 1.1的状态码被标记为新特性,因为许多浏览器只支持 HTTP 1.0。你应只把状态码发送给支持 HTTP 1.1的客户端,支持协议版本可以通过调用request
- asihttprequest上传图片
dcj3sjt126com
ASIHTTPRequest
NSURL *url =@"yourURL";
ASIFormDataRequest*currentRequest =[ASIFormDataRequest requestWithURL:url];
[currentRequest setPostFormat:ASIMultipartFormDataPostFormat];[currentRequest se
- C语言中,关键字static的作用
e200702084
C++cC#
在C语言中,关键字static有三个明显的作用:
1)在函数体,局部的static变量。生存期为程序的整个生命周期,(它存活多长时间);作用域却在函数体内(它在什么地方能被访问(空间))。
一个被声明为静态的变量在这一函数被调用过程中维持其值不变。因为它分配在静态存储区,函数调用结束后并不释放单元,但是在其它的作用域的无法访问。当再次调用这个函数时,这个局部的静态变量还存活,而且用在它的访
- win7/8使用curl
geeksun
win7
1. WIN7/8下要使用curl,需要下载curl-7.20.0-win64-ssl-sspi.zip和Win64OpenSSL_Light-1_0_2d.exe。 下载地址:
http://curl.haxx.se/download.html 请选择不带SSL的版本,否则还需要安装SSL的支持包 2. 可以给Windows增加c
- Creating a Shared Repository; Users Sharing The Repository
hongtoushizi
git
转载自:
http://www.gitguys.com/topics/creating-a-shared-repository-users-sharing-the-repository/ Commands discussed in this section:
git init –bare
git clone
git remote
git pull
git p
- Java实现字符串反转的8种或9种方法
Josh_Persistence
异或反转递归反转二分交换反转java字符串反转栈反转
注:对于第7种使用异或的方式来实现字符串的反转,如果不太看得明白的,可以参照另一篇博客:
http://josh-persistence.iteye.com/blog/2205768
/**
*
*/
package com.wsheng.aggregator.algorithm.string;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
- 代码实现任意容量倒水问题
home198979
PHP算法倒水
形象化设计模式实战 HELLO!架构 redis命令源码解析
倒水问题:有两个杯子,一个A升,一个B升,水有无限多,现要求利用这两杯子装C
- Druid datasource
zhb8015
druid
推荐大家使用数据库连接池 DruidDataSource. http://code.alibabatech.com/wiki/display/Druid/DruidDataSource DruidDataSource经过阿里巴巴数百个应用一年多生产环境运行验证,稳定可靠。 它最重要的特点是:监控、扩展和性能。 下载和Maven配置看这里: http
- 两种启动监听器ApplicationListener和ServletContextListener
spjich
javaspring框架
引言:有时候需要在项目初始化的时候进行一系列工作,比如初始化一个线程池,初始化配置文件,初始化缓存等等,这时候就需要用到启动监听器,下面分别介绍一下两种常用的项目启动监听器
ServletContextListener
特点: 依赖于sevlet容器,需要配置web.xml
使用方法:
public class StartListener implements
- JavaScript Rounding Methods of the Math object
何不笑
JavaScriptMath
The next group of methods has to do with rounding decimal values into integers. Three methods — Math.ceil(), Math.floor(), and Math.round() — handle rounding in differen