springboot动态多数据源配置和使用(二)
很久之前写一篇静态的springboot多数据源配置,一直没写下篇,这里补充一下自己用动态多数据源的场景和开发逻辑。
之前说的静态多数据源是每个数据源配置一套mapper,现在说说如何动态多数据源共用一套mapper,以及数据源不从application.yml中配置,实现从数据库中读取数据源配置并动态切换数据源。
springboot+mybatisplus多数据源配置和使用(一)
一、先讲讲原理,了解AbstractRoutingDataSource类
1.AbstractRoutingDataSource类的定义
Spring提供了AbstractRoutingDataSource用于动态路由数据源,继承AbstractRoutingDataSource类并覆写其protected abstract Object determineCurrentLookupKey()即可。
AbstractRoutingDataSource继承了AbstractDataSource,AbstractDataSource继承了DataSource,
所以该类充当了DataSource的路由中介, 能有在运行时, 根据某种key值来动态切换到真正的DataSource上,即AbstractRoutingDataSource封装了(多个)DataSource,可以根据key找到对应的数据源。
2. AbstractRoutingDataSource实现动态多数据源的原理
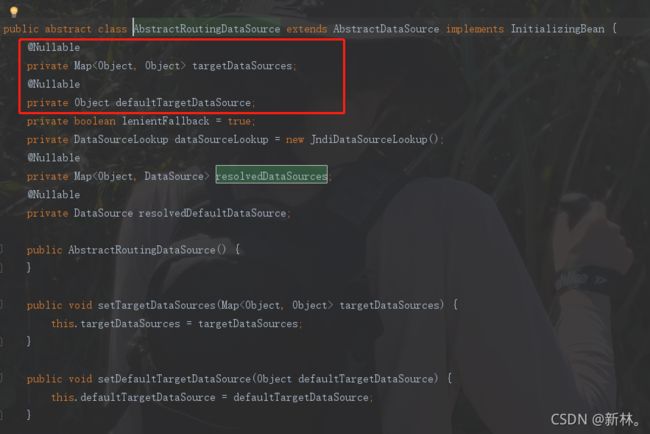
我们先看看AbstractRoutingDataSource类的源码,可以看到有几个入参。
重要的入参是targetDataSources,和defaultTargetDataSource
targetDataSources:保存多个数据源的map
defaultTargetDataSource:指默认的数据源
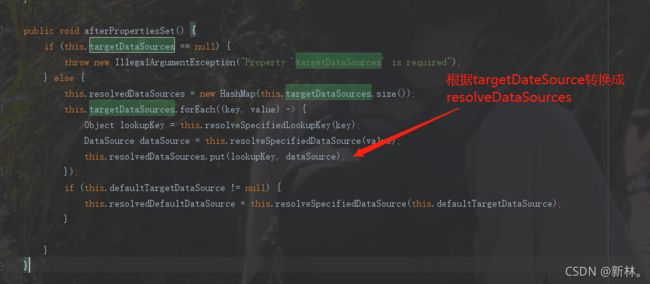
首先targetDataSources是一个map,根据key保存不同的数据源,源码里面看到targetDataSources会转换成另一个map的变量resolvedDataSources,而defaultTargetDataSource转换成resolvedDefaultDataSource
其实没什么变化,只是由Object类型转成了DataSource类型
protected DataSource determineTargetDataSource() {
Assert.notNull(this.resolvedDataSources, "DataSource router not initialized");
Object lookupKey = this.determineCurrentLookupKey();
DataSource dataSource = (DataSource)this.resolvedDataSources.get(lookupKey);
if (dataSource == null && (this.lenientFallback || lookupKey == null)) {
dataSource = this.resolvedDefaultDataSource;
}
if (dataSource == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot determine target DataSource for lookup key [" + lookupKey + "]");
} else {
return dataSource;
}
}
@Nullable
protected abstract Object determineCurrentLookupKey();
从这段代码可以看出,根据determineCurrentLookupKey()方法获取当前的数据源的key,然后根据这个lookupKey 去从存放有多个数据源的map的变量resolvedDataSources中取对应的dataSource,如果dataSource为null,则取默认的的resolvedDefaultDataSource作为数据源
determineCurrentLookupKey是抽象方法,是由子类继承实现的。所以我们要实现动态多数据源,就继承AbstractRoutingDataSource,实现里面的determineCurrentLookupKey方法就相当于实现了动态多数据源的路由了
我们改成这个determineCurrentLookupKey方法返回的key就相当于改变了数据源
二、springboot使用动态多数据源
从上面的原理解析,我们就知道实现动态多数据源,就需要写一个类继承AbstractRoutingDataSource类,重写里面的抽象方法determineCurrentLookupKey()即可,那么如何做呢?
1. 继承AbstractRoutingDataSource,重写抽象方法
/**
* 多数据源
*
*/
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DynamicContextHolder.peek();
}
}
2. DynamicContextHolder操作数据源的key的上下文
里面用了DynamicContextHolder.peek()返回数据源的key,而DynamicContextHolder是我们自己写的类,用于切换数据源的上下文的key,代码如下
/**
* 多数据源上下文
*
*/
public class DynamicContextHolder {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private static final ThreadLocal<Deque<String>> CONTEXT_HOLDER = new ThreadLocal() {
@Override
protected Object initialValue() {
return new ArrayDeque();
}
};
/**
* 获得当前线程数据源
*
* @return 数据源名称
*/
public static String peek() {
return CONTEXT_HOLDER.get().peek();
}
/**
* 设置当前线程数据源
*
* @param dataSource 数据源名称
*/
public static void push(String dataSource) {
CONTEXT_HOLDER.get().push(dataSource);
}
/**
* 清空当前线程数据源
*/
public static void poll() {
Deque<String> deque = CONTEXT_HOLDER.get();
deque.poll();
if (deque.isEmpty()) {
CONTEXT_HOLDER.remove();
}
}
}
这个DynamicContextHolder类的peek()是返回数据源的key名称,push是设置数据源的名称,然后我们只要操作这个类的push方法改变数据源的名称key,就相当于切换了数据源。
- 为什么里面使用了ThreadLocal?
ThreadLocal是指当前线程的本地变量,每个线程里面都有一个自己的变量,其他线程无法操作当前线程的这个变量。确保当前访问请求的线程不会被其他线程改变这个当前线程的数据。- 我们在哪个位置使用DynamicContextHolder.push来改变数据源的key呢?
我们利用aop,再写一个注解,把注解加在相应的service方法上,通过这个注解的切面类来调用DynamicContextHolder.push,从而改变determineCurrentLookupKey,从而切换数据源
3.application.yml的配置
spring:
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
druid:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.33.76:3306/database?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
username: master
password: 123456
initial-size: 10
max-active: 100
min-idle: 10
max-wait: 60000
pool-prepared-statements: true
max-pool-prepared-statement-per-connection-size: 20
time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 60000
min-evictable-idle-time-millis: 300000
#Oracle需要打开注释
#validation-query: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
test-while-idle: true
test-on-borrow: false
test-on-return: false
stat-view-servlet:
enabled: true
url-pattern: /druid/*
#login-username: admin
#login-password: admin
filter:
stat:
log-slow-sql: true
slow-sql-millis: 1000
merge-sql: false
wall:
config:
multi-statement-allow: true
##多数据源的配置
dynamic:
datasource:
slave1:
driver-class-name: com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.33.76:3306/database1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
username: test1
password: 123456
slave2:
driver-class-name: org.postgresql.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.33.76:3306/database2?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
username: test2
password: 123456
4. 配置我们自定义的DynamicDataSource类,注入spring容器
主要的方法是
DynamicDataSource dynamicDataSource(DataSourceProperties dataSourceProperties)
相当于在spring容器中配置这个bean的实例
@Bean
public DynamicDataSource dynamicDataSource(DataSourceProperties dataSourceProperties) {
DynamicDataSource dynamicDataSource = new DynamicDataSource();
//设置多个数据源的map
dynamicDataSource.setTargetDataSources(getDynamicDataSource());
//默认数据源
DruidDataSource defaultDataSource = DynamicDataSourceFactory.buildDruidDataSource(dataSourceProperties);
dynamicDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(defaultDataSource);
return dynamicDataSource;
}
整个类的全部代码如下,核心代码为:dynamicDataSource.setTargetDataSources(getDynamicDataSource())
下面代码看出,先把多个数据源配置从appliaiton.yml读出出来,然后转成targetDataSources
/**
* 配置多数据源
*
*/
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(DynamicDataSourceProperties.class)
public class DynamicDataSourceConfig {
@Autowired
private DynamicDataSourceProperties properties;
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.druid")
public DataSourceProperties dataSourceProperties() {
return new DataSourceProperties();
}
@Bean
public DynamicDataSource dynamicDataSource(DataSourceProperties dataSourceProperties) {
DynamicDataSource dynamicDataSource = new DynamicDataSource();
//设置多个数据源的map
dynamicDataSource.setTargetDataSources(getDynamicDataSource())
//默认数据源
DruidDataSource defaultDataSource = DynamicDataSourceFactory.buildDruidDataSource(dataSourceProperties);
dynamicDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(defaultDataSource);
return dynamicDataSource;
}
private Map<Object, Object> getDynamicDataSource(){
Map<String, DataSourceProperties> dataSourcePropertiesMap = properties.getDatasource();
Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources = new HashMap<>(dataSourcePropertiesMap.size());
dataSourcePropertiesMap.forEach((k, v) -> {
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = DynamicDataSourceFactory.buildDruidDataSource(v);
targetDataSources.put(k, druidDataSource);
});
return targetDataSources;
}
}
其他涉及的类
/**
* 多数据源属性(从applition.yml读取数据源配置)
*
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "dynamic")
public class DynamicDataSourceProperties {
private Map<String, DataSourceProperties> datasource = new LinkedHashMap<>();
public Map<String, DataSourceProperties> getDatasource() {
return datasource;
}
public void setDatasource(Map<String, DataSourceProperties> datasource) {
this.datasource = datasource;
}
}
/**
* 将数据源配置构建实际的数据源
*
*/
public class DynamicDataSourceFactory {
public static DruidDataSource buildDruidDataSource(DataSourceProperties properties) {
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource();
druidDataSource.setDriverClassName(properties.getDriverClassName());
druidDataSource.setUrl(properties.getUrl());
druidDataSource.setUsername(properties.getUsername());
druidDataSource.setPassword(properties.getPassword());
druidDataSource.setInitialSize(properties.getInitialSize());
druidDataSource.setMaxActive(properties.getMaxActive());
druidDataSource.setMinIdle(properties.getMinIdle());
druidDataSource.setMaxWait(properties.getMaxWait());
druidDataSource.setTimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis(properties.getTimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis());
druidDataSource.setMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis(properties.getMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis());
druidDataSource.setMaxEvictableIdleTimeMillis(properties.getMaxEvictableIdleTimeMillis());
druidDataSource.setValidationQuery(properties.getValidationQuery());
druidDataSource.setValidationQueryTimeout(properties.getValidationQueryTimeout());
druidDataSource.setTestOnBorrow(properties.isTestOnBorrow());
druidDataSource.setTestOnReturn(properties.isTestOnReturn());
druidDataSource.setPoolPreparedStatements(properties.isPoolPreparedStatements());
druidDataSource.setMaxOpenPreparedStatements(properties.getMaxOpenPreparedStatements());
druidDataSource.setSharePreparedStatements(properties.isSharePreparedStatements());
try {
druidDataSource.setFilters(properties.getFilters());
druidDataSource.init();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return druidDataSource;
}
}
5. 通过注解切换数据源
上面已经完成了大部分逻辑了,还有最重要的一步,如何通过aop切换数据源
1)先写一个注解
/**
* 多数据源注解
*
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
public @interface DataSource {
String value() default "";
}
2)再写这个注解的切面类
下面的代码很简单,可以看出,所有使用了这个注解的都会经过这个切面类,这个切面类先判断注解是在方法上还是类上,如果方法上有注解优先使用方法上的,获取注解的value属性的值,把这个值作为数据源的key。
通过 DynamicContextHolder.push(value)来设置数据源的key(这里改变后, determineCurrentLookupKey()重写的方法返回的key也就改变了,从而切换了数据源)
/**
* 多数据源,切面处理类
*
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
public class DataSourceAspect {
protected Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Pointcut("@annotation(io.renren.datasource.annotation.DataSource) " +
"|| @within(io.renren.datasource.annotation.DataSource)")
public void dataSourcePointCut() {
}
@Around("dataSourcePointCut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) point.getSignature();
Class targetClass = point.getTarget().getClass();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
DataSource targetDataSource = (DataSource)targetClass.getAnnotation(DataSource.class);
DataSource methodDataSource = method.getAnnotation(DataSource.class);
if(targetDataSource != null || methodDataSource != null){
String value;
if(methodDataSource != null){
value = methodDataSource.value();
}else {
value = targetDataSource.value();
}
DynamicContextHolder.push(value);
logger.debug("set datasource is {}", value);
}
try {
return point.proceed();
} finally {
DynamicContextHolder.poll();
logger.debug("clean datasource");
}
}
}
3)把这个注解加在需要使用多数据源的service方法或类上
注解加在controller上的类或方法也可以的
注解不是很懂的话,可以看这篇文章:springboot项目中自定义注解的使用总结
@Service
//@DataSource("slave1")
public class DynamicDataSourceTestService {
@Autowired
private SysUserDao sysUserDao;
@Transactional
public void updateUser(Long id){
SysUserEntity user = new SysUserEntity();
user.setUserId(id);
user.setMobile("13500000000");
sysUserDao.updateById(user);
}
@Transactional
@DataSource("slave1")
public void updateUserBySlave1(Long id){
SysUserEntity user = new SysUserEntity();
user.setUserId(id);
user.setMobile("13500000001");
sysUserDao.updateById(user);
}
@DataSource("slave2")
@Transactional
public void updateUserBySlave2(Long id){
SysUserEntity user = new SysUserEntity();
user.setUserId(id);
user.setMobile("13500000002");
sysUserDao.updateById(user);
}
}
从上面的三个方法逐个调用测试,可以看到操作了三个不同的数据源的数据
三、从数据库中读取动态多数据源的配置
这里还有挺多东西的,有点长,在下篇博客总结
springboot动态多数据源配置和使用(从数据库读取数据源配置)(三)
参考:
这里的代码参考了人人开源项目的renren-fast项目,要想看全部源码,可以通过git把项目下载回来看看
项目:https://gitee.com/renrenio/renren-fast.git