【数据结构初阶】(2)C语言实现线性表之单链表、双向链表
文章目录
- 一、不带头单链表
- 二、带头双向循环链表
- 三、链表常见OJ题
-
- 1. LeetCode:反转链表
- 2. LeetCode:链表的中间结点
- 3. LeetCode:合并两个有序链表
- 4. LeetCode:环形链表
- 总结
一、不带头单链表
- SingleList.h
#pragma once
#include - SingleList.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "SingleList.h"
//打印
void SListPrint(SLTNode* phead)
{
SLTNode* cur = phead;
while (cur != NULL)
{
printf("%d->", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
//创建新结点
SLTNode* BuySListNode(SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* newNode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
//注意这里要用传址才能把newNode的值传给实参
//pphead是pList的地址
//尾插
void SListPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode *newNode = BuySListNode(x);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newNode;
}
else
{
//找尾结点的指针
SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
//尾结点链接新结点
tail->next = newNode;
}
}
//传址
//头插
void SListPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* newNode = BuySListNode(x);
//头插不需要区分刚开始有没有结点
newNode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newNode;
}
//头删
void SListPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{
//*和->优先级相同
SLTNode* next = (*pphead)->next;//用next记住下一个结点
free(*pphead);
*pphead = next;
}
//尾删
void SListPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{
// 1. 空链表
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
return;
}
// 2. 一个结点
else if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
}
// 3. 节点数 > 1
else
{
SLTNode* prev = NULL;
SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
prev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail);
prev->next = NULL;
}
}
//查找
SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* cur = phead;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
//在pos前面插入x
void SListInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* newNode = BuySListNode(x);
SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
//pos为第一个结点位置就是头插
if (pos == *pphead)
{
SListPushFront(pphead, x);
}
else
{
while (prev->next != pos)
{
prev = prev->next;
}
newNode->next = prev->next;
prev->next = newNode;
}
}
//删除pos位置的值
void SListErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
{
SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
//只有一个结点是头删
if (pos == *pphead)
{
SListPopFront(pphead);
}
else
{
while (prev->next != pos)
{
prev = prev->next;
}
prev->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
}
}
- test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "SingleList.h"
//单向不带头不循环
void TestSList()
{
/*SLTNode *pList = NULL;
SListPushBack(&pList, 1);
SListPushBack(&pList, 2);
SListPushBack(&pList, 3);
SListPushBack(&pList, 4);
SListPrint(pList);
SListPushFront(&pList, 0);
SListPrint(pList);
SListPopFront(&pList);
SListPrint(pList);
SListPopBack(&pList);
SListPrint(pList);*/
/*SLTNode* pList = NULL;
SListPushBack(&pList, 1);
SListPushBack(&pList, 2);
SListPushBack(&pList, 3);
SListPushBack(&pList, 4);
SListPrint(pList);
//在1前面插入10
SLTNode* pos = SListFind(pList,1);
if (pos)
{
SListInsert(&pList,pos,10);
}
SListPrint(pList);
pos = SListFind(pList, 4);
if (pos)
{
SListInsert(&pList, pos, 30);
}
SListPrint(pList);*/
SLTNode* pList = NULL;
SListPushBack(&pList, 1);
SListPushBack(&pList, 2);
SListPushBack(&pList, 3);
SListPushBack(&pList, 4);
SListPrint(pList);
SLTNode* pos = SListFind(pList, 1);
if (pos)
{
SListErase(&pList, pos);
}
SListPrint(pList);
}
int main()
{
TestSList();
return 0;
}
二、带头双向循环链表
- List.h
#pragma once
#include - List.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "List.h"
//创建新结点
ListNode* BuyListNode(LTDataType x)
{
ListNode* newNode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
newNode->prev = NULL;
return newNode;
}
//初始化
ListNode* ListInit()
{
ListNode* phead = BuyListNode(0);
phead->next = phead;
phead->prev = phead;
return phead;
}
void ListPrint(ListNode* phead)
{
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void ListDestory(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
ListNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
cur = next;
}
free(phead);
phead = NULL;
}
void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(phead);
ListInsert(phead, x);
//ListNode* tail = phead->prev;
//ListNode* newNode = BuyListNode(x);
//tail->next = newNode;
//newNode->prev = tail;
//newNode->next = phead;
//phead->prev = newNode;
}
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(phead);
ListInsert(phead->next,x);
//ListNode* first = phead->next;
//ListNode* newNode = BuyListNode(x);
// phead newNode first
//phead->next = newNode;
//newNode->prev = phead;
//newNode->next = first;
//first->prev = newNode;
// 前插另外版本
// 注意顺序
/*newNode->next = phead->next;
phead->next->prev = newNode;
newNode->prev = phead;
phead->next = newNode;*/
}
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);//不能是空链表
assert(phead->next != phead);//删完就不能再删头结点
ListErase(phead->next);
//ListNode* first = phead->next;
//ListNode* second = first->next;
//phead->next = second;
//second->prev = phead;
//free(first);
//first = NULL;
}
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead);
ListErase(phead->prev);
//ListNode* tail = phead->prev;
//ListNode* prev = tail->prev;
//phead->prev = prev;
//prev->next = phead;
//free(tail);
//tail = NULL;
}
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
// 在pos位置前插入x
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* prev = pos->prev;
ListNode* newNode = BuyListNode(x);
// prev newNode pos
prev->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = prev;
newNode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newNode;
}
// 删除pos位置的值
void ListErase(ListNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* prev = pos->prev;
ListNode* next = pos->next;
prev->next = next;
next->prev = prev;
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
}
bool ListEmpty(ListNode* phead)//判空
{
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
if (cur != phead)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
int ListSize(ListNode* phead)//链表长度
{
int count = 0;
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
count++;
}
return count;
}
- test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "List.h"
void test()
{
ListNode* pList = ListInit();
ListPushBack(pList, 1);
ListPushBack(pList, 2);
ListPushBack(pList, 3);
ListPushFront(pList, 0);
ListPushFront(pList, -1);
ListPrint(pList);
ListPopFront(pList);
ListPopBack(pList);
ListPrint(pList);
ListNode*pos = ListFind(pList, 1);
if (pos)
{
// 既可以查找,又可以修改
pos->data *= 10;
printf("找到了,并将节点值*10\n");
}
else
{
printf("没找到\n");
}
ListPrint(pList);
ListInsert(pos, 30);
ListPrint(pList);
ListErase(pos);
ListPrint(pList);
//ListDestory(pList);
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
三、链表常见OJ题
1. LeetCode:反转链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
//如果为空链表,n2为空不能解引用
if (NULL == head)
{
return NULL;
}
//初始条件
struct ListNode* n1 = NULL,*n2 = head,*n3 = n2->next;//注意语法细节*n2
// 翻转指针指向
//n2不为空翻转
while (n2)
{
//迭代
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if (n3)//n3为空是不能解引用
{
n3 = n3->next;
}
}
return n1;
}
- 思路二:头插法
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
//取原链表结点,头插到新链表
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* newHead = NULL;
while (cur)
{
struct ListNode*next = cur->next;
cur->next = newHead;
newHead = cur;
cur = next;
}
return newHead;
}
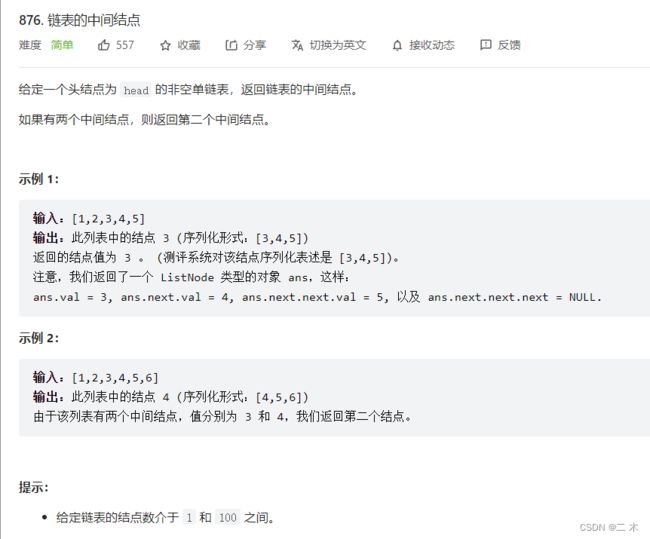
2. LeetCode:链表的中间结点
- LeetCode:链表的中间结点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){
struct ListNode* slow = head,*fast = head;
//快慢指针
//快指针走两步,慢指针走一步
//结束条件
//奇数:fast-next为空
//偶数:fast为空
while (fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
3. LeetCode:合并两个有序链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
if (NULL == list1)
{
return list2;
}
if (NULL == list2)
{
return list1;
}
//取小尾插到新链表
struct ListNode* head = NULL,*tail = NULL;
//list1 和 list2都不为空
while (list1 != NULL && list2 != NULL)
{
if (list1->val < list2->val)
{
//尾插
if (NULL == tail)//没有结点,第一个值的尾插
{
head = tail = list1;
}
else
{
tail->next = list1;
tail = tail->next;
}
list1 = list1->next;
}
else
{
if (NULL == tail)
{
head = tail = list2;
}
else
{
tail->next = list2;
tail = tail->next;
}
list2 = list2->next;
}
}
//没走完的直接链接到尾
if (list1)
{
tail->next = list1;
}
if (list2)
{
tail->next = list2;
}
return head;
}
优化一:先取一个小的作为头结点,while循环只进行尾插
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
if (NULL == list1)
{
return list2;
}
if (NULL == list2)
{
return list1;
}
//取小尾插到新链表
struct ListNode* head = NULL,*tail = NULL;
//取一个小的作为头结点
if (list1->val < list2->val)
{
head = tail = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
}
else
{
head = tail = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
while (list1 != NULL && list2 != NULL)
{
//尾插
if (list1->val < list2->val)
{
tail->next = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
}
else
{
tail->next = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
//没走完的直接链接到尾
if (list1)
{
tail->next = list1;
}
if (list2)
{
tail->next = list2;
}
return head;
}
优化二:增加哨兵位,注意返回值和释放哨兵位
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
if (NULL == list1)
{
return list2;
}
if (NULL == list2)
{
return list1;
}
//取小尾插到新链表
struct ListNode* head = NULL,*tail = NULL;
//哨兵位
head = tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
//这里不需要把next置为空
//tail->next = NULL;
while (list1 != NULL && list2 != NULL)
{
//尾插
if (list1->val < list2->val)
{
tail->next = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
}
else
{
tail->next = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
//没走完的直接链接到尾
if (list1)
{
tail->next = list1;
}
if (list2)
{
tail->next = list2;
}
//不能返回head
struct ListNode*first = head->next;
free(head);
head = NULL;
return first;
//return head;
}
4. LeetCode:环形链表
- LeetCode:环形链表
/**
1. Definition for singly-linked list.
2. struct ListNode {
3. int val;
4. struct ListNode *next;
5. };
*/
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
//快慢指针
struct ListNode* slow = head,*fast = head;
while (fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (fast == slow)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
问:
- 请证明slow和fast一定会在环里相遇?
- slow一次走1步,fast一次走n步(n=3、4、5……)行不行?
总结
本文到此就结束了,如果有错误,请指正。