《SpringBoot启动流程六》:源码分析SpringBoot如何内嵌并启动Tomcat服务器的?
文章目录
- 一、前言
- 二、整体执行流程图
- 三、内嵌Tomcat入口 --> onRefresh()
-
-
- 1、推断Web应用类型
- 2、创建应用上下文
- 3、AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext的类图
- 4、AbstractApplicationContext#onRefresh()
-
- 1> createWebServer() --> 创建WebServer
- 2> getTomcatWebServer(tomcat) --> 构建Tomcat服务
- 3> TomcatServletWebServerFactory#initialize()
- 4> 执行完createWebServer()方法之后的日志输出
-
- 四、真正启动Tomcat --> finishRefresh()
-
- 1、启动Tomcat
-
- 1)addPreviouslyRemovedConnectors()
- 2)performDeferredLoadOnStartup()
- 3)checkThatConnectorsHaveStarted()
- 2、关闭Tomcat
- 五、总结
一、前言
在前面的文章我们聊了Spring Boot的整体启动流程、自动装配、条件装配等内容:
1> 《SpringBoot启动流程一》:万字debug梳理SpringBoot如何加载并处理META-INF/spring.factories文件中的信息;
2> 《SpringBoot启动流程二》:七千字源码分析SpringApplication构造阶段;
3> 《SpringBoot启动流程三》:两万+字图文带你debug源码分析SpringApplication准备阶段(含配置文件加载时机、日志系统初始化时机);
4> 《SpringBoot启动流程四》:图文带你debug源码分析SpringApplication运行阶段和运行后阶段。
5> 《SpringBoot启动流程五》:你真的知道SpringBoot自动装配原理吗(两万字图文源码分析)
在使用springboot搭建一个web应用程序的时候,我们发现不需要自己搭建一个tomcat服务器,只需要引入spring-boot-starter-web,在应用启动时会自动启动嵌入式的tomcat作为服务器。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
注意:SpringBoot版本:2.3.7.RELEASE(博主写博客时最新Spring-boot版本 – 2.6.X代码逻辑几乎一样)
本文我们接着讨论Spring Boot 如何内嵌 并 启动 Tomcat的?
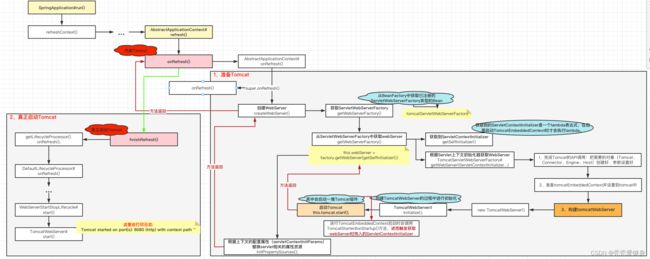
二、整体执行流程图
三、内嵌Tomcat入口 --> onRefresh()
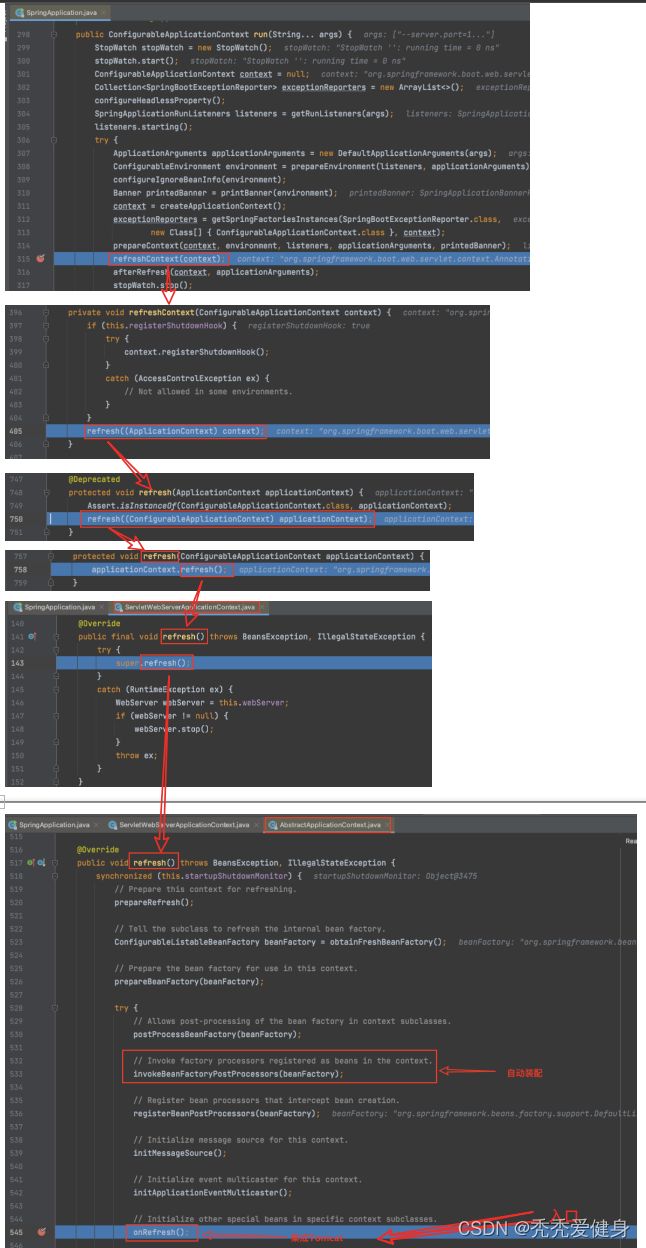
从SpringApplication#run()开始往下追,追到AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()方法中,其内部会调用onRefresh()方法,这里负责开始内嵌Tomcat服务器。
在开始讨论onRefresh()方法之前,我们先找到当前Web应用的ApplicationContext具体是哪个(即AbstractApplicationContext的子类)?
下面结合整个Spring Boot的启动流程,有两点是有迹可循的:
1、推断Web应用类型
在博文 <《SpringBoot启动流程二》:七千字源码分析SpringApplication构造阶段> 中我们讨论过SpringApplication的构建过程中会推断Web应用的类型;
WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
因为Web应用类型可能在SpringApplication构造后及run方法之前,再通过setWebApplicatioinType(WebApplicationType)方法调整;又在推断Web应用类型的过程中,由于当前Spring应用上下文尚未准备,所以采用检查当前ClassLoader下基准Class的存在性来推断Web应用类型。
public enum WebApplicationType {
NONE,
SERVLET,
REACTIVE;
private static final String[] SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES = { "javax.servlet.Servlet",
"org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" };
private static final String WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet";
private static final String WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler";
private static final String JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer";
....
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
// 1. 如果`DispatcherHandler`存在,并且`DispatcherServlet`和`ServletContainer`不存在时,Web应用类型为REACTIVE;
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
// 2. 如果`Servlet`和`ConfigurableWebApplicationContext`不存在,则当前应用为非Web引应用,即NONE。
for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
// 3.当Spring WebFlux和Spring Web MVC同时存在时,Web应用依旧是SERVLET。
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
}
....
}
WEB 应用类型,一共有三种:NONE,SERVLET,REACTIVE。
deduceFromClasspath()方法利用ClassUtils.isPresent(String, ClassLoader)方法依次判断reactive.DispatcherHandler、ConfigurableWebApplicationContext、Servlet、servlet.DispatcherServlet的存在性组合情况,从而判断Web 引用类型,具体逻辑如下:
- 如果
DispatcherHandler存在,并且DispatcherServlet和ServletContainer不存在时,即:Spring Boot仅依赖WebFlux时,Web应用类型为REACTIVE;- 如果
Servlet和ConfigurableWebApplicationContext不存在,则当前应用为非Web应用,即NONE。因为这两个API是Spring Web MVC必须的依赖。- 当Spring WebFlux和Spring Web MVC同时存在时,Web应用类型依旧是SERVLET。
2、创建应用上下文
在博文 <《SpringBoot启动流程三》:两万+字图文带你debug源码分析SpringApplication准备阶段 > 中 我们讨论过的SpringAppliation准备阶段的第八步会根据上面推断出的Web应用来创建相应的 ApplicationContext应用上下文对象。

根据应用类型利用反射创建Spring应用上下文,可以理解为创建一个容器;就SERVLET而言:实例化AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext。
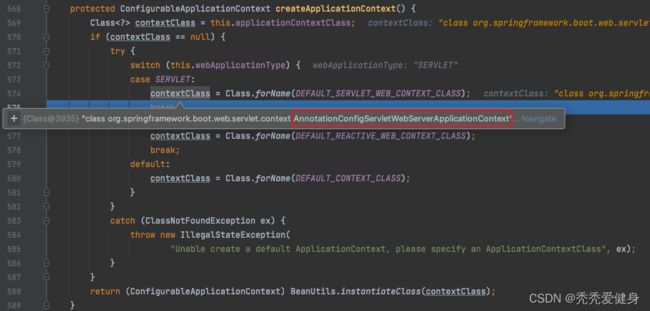
3、AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext的类图
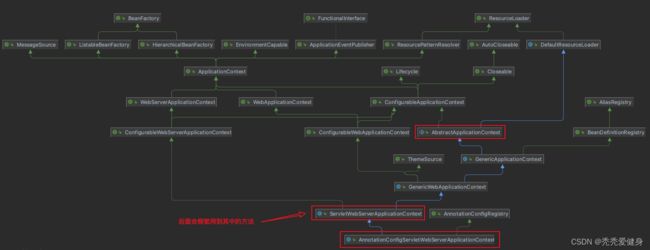
AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext 继承自 ServletWebServerApplicationContext,ServletWebServerApplicationContext 又间接继承自AbstractApplicationContext,这样再回到AbstractApplicationContext#onRefresh(),我们便知道这里的应用上下文是哪个实例了。
4、AbstractApplicationContext#onRefresh()
由于AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext类中没有重写onRefresh方法,所以从类图的最下方往上找到ServletWebServerApplicationContext#onRefresh()方法。
// ServletWebServerApplicationContext#onRefresh()
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
//创建主题对象,不用在意
super.onRefresh();
try {
//开始创建web服务
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
方法逻辑:
- 首先调用父类AbstractApplicationContext的onRefresh()方法,创建一个主题对象(无需特意关注)。
- 接着调用自己的createWebServer()方法创建WebServer。
下面接着看createWebServer()方法做了什么?
1> createWebServer() --> 创建WebServer
private void createWebServer() {
// 第一次进来,默认webServer 是 null
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
// 第一次进行,默认servletContext 是 null
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
// 从BeanFactory中获取ServletWebServerFactory的实现类
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
// 获取servletContextInitializer(getSelfInitializer()方法会初始化Tomcat对象),获取webServer(完成内嵌Tomcat的API调用)
// todo 注意getSelfInitializer()返回一个lambdab表达式,其中的内容不会执行,而是在启动TomcatEmbeddedContext时才会执行lambda
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerGracefulShutdown",
new WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle(this.webServer));
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerStartStop",
new WebServerStartStopLifecycle(this, this.webServer));
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex);
}
}
// 根据上下文的配置属性 替换servlet相关的属性资源
initPropertySources();
}
方法逻辑:
进入到方法的时候,webServer和servletContext均为null。
- 首先从BeanFactory中获取ServletWebServerFactory的实现类;
- 然后根据获取到的ServletWebServerFactory,进而获取Servlet上下文初始化器servletContextInitializer、获取WebServer。
在获取servletContextInitializer时,返回的是一个lambda表达式,lambda表达式中的内容(即:初始化Tomcat对象)在启动TomcatEmbeddedContext时才会执行。
- 根据上下文的配置属性 替换servlet相关的属性资源;
(1 从BeanFactory中获取ServletWebServerFactory:
protected ServletWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory() {
// Use bean names so that we don't consider the hierarchy
String[] beanNames = getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(ServletWebServerFactory.class);
if (beanNames.length == 0) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to missing "
+ "ServletWebServerFactory bean.");
}
if (beanNames.length > 1) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to multiple "
+ "ServletWebServerFactory beans : " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(beanNames));
}
return getBeanFactory().getBean(beanNames[0], ServletWebServerFactory.class);
}
getWebServerFactory()方法会从BeanFactory中获取所有ServletWebServerFactory接口的实现类,如果存在多个,则抛异常。
ServletWebServerFactory接口有四个主要的实现类:
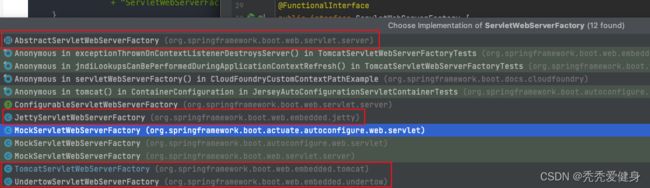
其中默认的 Web 环境就是 TomcatServletWebServerFactory,而UndertowServletWebServerFactory用于响应式编程。

本文debug应用时用的正是默认的Web环境 --> TomcatServletWebServerFactory。
(2 获取Servlet上下文初始化器servletContextInitializer:
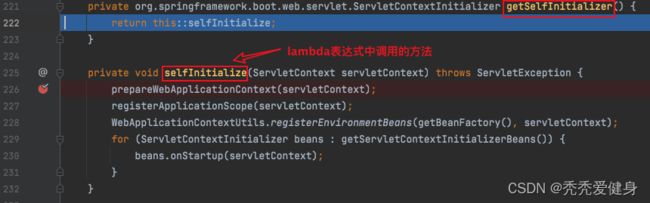
返回一个lambda表达式,在后面启动TomcatEmbeddedContext时才会执行lambda。
(3 获取WebServer:
接着进入到TomcatServletWebServerFactory # getWebServer() 方法:
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
// 走进这里时,initializers还没有执行
if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) {
Registry.disableRegistry();
}
// 完成Tomcat的API调用,把需要的对象创建好、参数设置好
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
// 准备tomcatEmbeddedContext并将其设置到tomcat中,其中会把上面获取到的servletContextInitializer绑定到tomcatEmbeddedContext。
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
// 构建tomcatWebServer
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
方法逻辑:
- 首先完成Tomcat的API调用,把需要的对象创建好、参数设置好;
而Tomcat有两个核心功能:<处理 Socket 连接,负责网络字节流与 Request 和 Response 对象的转化>、<加载和管理 Servlet,以及具体处理 Request 请求>。而针对这两个功能,Tomcat 设计了两个核心组件来分别完成这两件事,即:连接器Connector和容器Container(包括:Engine、Host、Context、Wrapper)。
所以,其中最重要的两件事是:1> 把连接器 Connector 对象添加到 Tomcat 中;
2> 配置容器引擎,configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());- 准备tomcatEmbeddedContext并将其设置到tomcat中,其中会把上面获取到的servletContextInitializer绑定到tomcatEmbeddedContext。
- 构建tomcatWebServer。
下面我们着重讨论如何构建Tomcat服务的?
2> getTomcatWebServer(tomcat) --> 构建Tomcat服务
整个构建Tomcat服务的代码执行流程如下:
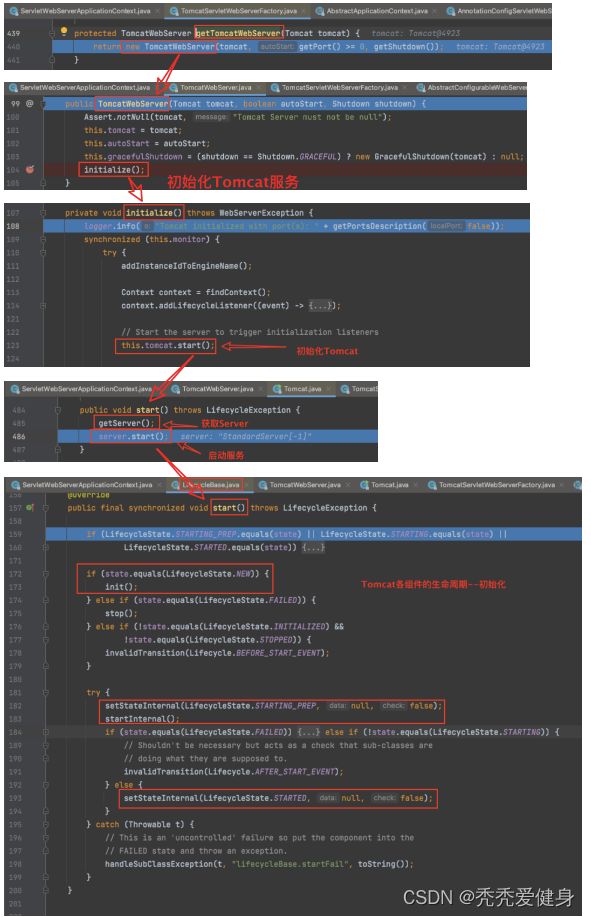
其中牵扯到Tomcat其他组件(StandardServer、StandardService、StandardEngine、MapperListener、Connector)的初始化,整个生命周期流转如下:
3> TomcatServletWebServerFactory#initialize()
初始化Tomcat服务详细代码如下:
private void initialize() throws WebServerException {
logger.info("Tomcat initialized with port(s): " + getPortsDescription(false));
synchronized (this.monitor) {
try {
// 将engineName和instanceId用-拼接到一起
addInstanceIdToEngineName();
Context context = findContext();
context.addLifecycleListener((event) -> {
if (context.equals(event.getSource()) && Lifecycle.START_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
// Remove service connectors so that protocol binding doesn't
// happen when the service is started.
// 删除Connectors,以便再启动服务时不发生协议绑定,点进去看一下
removeServiceConnectors();
}
});
// 启动服务触发初始化监听器
this.tomcat.start();
// 在主线程中重新抛出失败异常
rethrowDeferredStartupExceptions();
try {
ContextBindings.bindClassLoader(context, context.getNamingToken(), getClass().getClassLoader());
}
catch (NamingException ex) {
// Naming is not enabled. Continue
}
// Unlike Jetty, all Tomcat threads are daemon threads. We create a
// blocking non-daemon to stop immediate shutdown
// 所有的tomcat线程都是守护线程,所以创建一个阻塞非守护线程来避免立即关闭
startDaemonAwaitThread();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// 出现异常时,停止Tomcat
stopSilently();
destroySilently();
throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat", ex);
}
}
}
4> 执行完createWebServer()方法之后的日志输出

从日志输出来看,createWebServer() 方法看似是用来启动web服务的,并没有真正启动 Tomcat,只是通过ServletWebServerFactory 创建了一个 WebServer,初始化了一堆设置(包括:Port、Service、Engine、embeddedWebApplicationContext)。真正的启动发生在AbstractApplicationContext#finishRefresh()中。
四、真正启动Tomcat --> finishRefresh()
代码整理执行流程如下:

WebServerStartStopLifecycle类负责处理WebServer(Tomcat)的启动和关闭;
1、启动Tomcat
WebServerStartStopLifecycle#start()代码执行流程如下:

TomcatWebServer#start()详细代码如下:
@Override
public void start() throws WebServerException {
synchronized (this.monitor) {
if (this.started) {
return;
}
try {
// 添加之前移除的connector,绑定service和Connector
addPreviouslyRemovedConnectors();
// 获取当前Tomcat绑定的Connector
Connector connector = this.tomcat.getConnector();
// 默认会走进去
if (connector != null && this.autoStart) {
// 启动时执行延迟加载
performDeferredLoadOnStartup();
}
// 检查connector启动状态是否为失败,失败抛出异常
checkThatConnectorsHaveStarted();
this.started = true;
// Tomcat启动成功之后打印日志
logger.info("Tomcat started on port(s): " + getPortsDescription(true) + " with context path '"
+ getContextPath() + "'");
}
catch (ConnectorStartFailedException ex) {
stopSilently();
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
PortInUseException.throwIfPortBindingException(ex, () -> this.tomcat.getConnector().getPort());
throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat server", ex);
}
finally {
Context context = findContext();
ContextBindings.unbindClassLoader(context, context.getNamingToken(), getClass().getClassLoader());
}
}
}
方法逻辑:
- 首先添加之前移除的connector,绑定service和Connector;
- 获取到当前Tomcat绑定的Connector,接着进行执行延迟加载启动;
- 然后 检查connector启动状态是否为失败,失败抛出异常,否则打印Tomcat启动成功日志。
1)addPreviouslyRemovedConnectors()
private void addPreviouslyRemovedConnectors() {
Service[] services = this.tomcat.getServer().findServices();
for (Service service : services) {
// 从上面移除connector添加的缓存中取出connector
Connector[] connectors = this.serviceConnectors.get(service);
if (connectors != null) {
for (Connector connector : connectors) {
// connector添加到tomcat service中
service.addConnector(connector);
if (!this.autoStart) {
// 如果不是自动启动,则暂停connector
stopProtocolHandler(connector);
}
}
// 添加完成后移除connector
this.serviceConnectors.remove(service);
}
}
}
2)performDeferredLoadOnStartup()
private void performDeferredLoadOnStartup() {
try {
for (Container child : this.tomcat.getHost().findChildren()) {
if (child instanceof TomcatEmbeddedContext) {
// 延迟加载启动
((TomcatEmbeddedContext) child).deferredLoadOnStartup();
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (ex instanceof WebServerException) {
throw (WebServerException) ex;
}
throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat connectors", ex);
}
}
3)checkThatConnectorsHaveStarted()
private void checkThatConnectorsHaveStarted() {
checkConnectorHasStarted(this.tomcat.getConnector());
for (Connector connector : this.tomcat.getService().findConnectors()) {
checkConnectorHasStarted(connector);
}
}
TomcatWebServer#start()方法执行完之后的日志输出:

2、关闭Tomcat
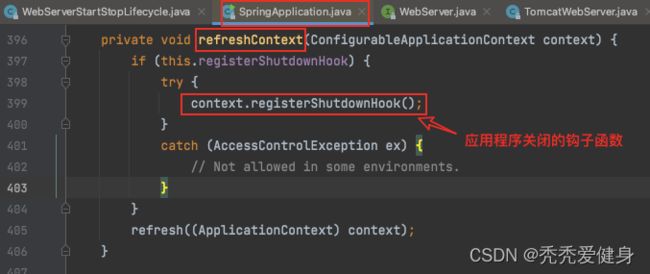
在refreshContext()方法中会通过AbstractApplicationContext#registerShutdownHook()方法注册一个shutdownhook线程,当JVM退出时,确保后续Spring应用上下文所管理的Bean能够在标准的Spring生命周期中回调,从而合理的销毁Bean所依赖的资源(即:注册一个关闭webServer的钩子函数,而钩子函数可以完成关闭的功能)。
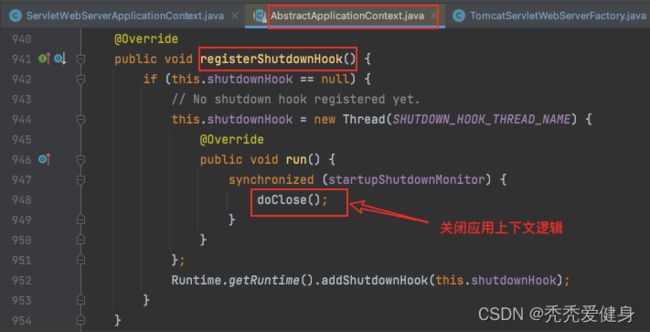
我们知道应用的上下文实例是ServletWebServerApplicationContext,而它重写了其父类AbstractApplicationContext中的doClose()方法,所以进入到ServletWebServerApplicationContext#doClose()方法;

发布一个事件之后,调用其父类AbstractApplicationContext#doClose()方法;
整体代码执行流程如下:
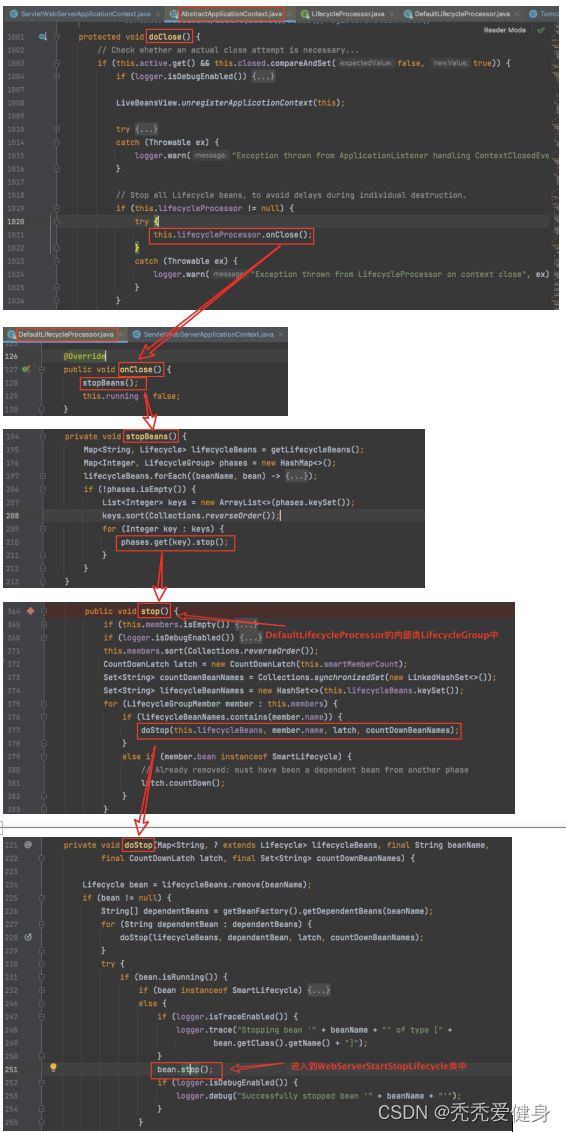
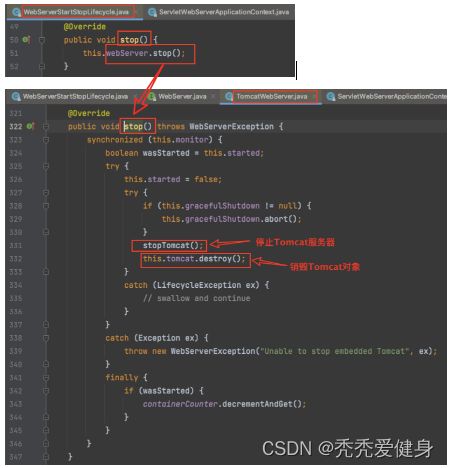
最后进入到WebServerStartStopLifecycle#stop():
五、总结
在SpringApplication的运行阶段会通过refreshContext()方法进行上下文的刷新操作,其会进入到AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()方法中,进而调用onRefresh()方法内嵌Tomcat,进行Tomcat的初始化,在finishRefresh()方法中进行Tomcat的启动。
1> 创建WebServer:
- 从BeanFactory中获取ServletWebServerFactory的实现类
TomcatServletWebServerFactory,然后通过其获取到WebServer;- 在获取WebServer的同时,初始化相关的Tomcat对象,包括:Connector、Container。
2> 启动WebServer:
- 通过生命周期回调的方式将Tomcat和Connector绑定、延时加载启动Connector、启动成功后打印Tomcat启动成功日志。