Java学习(Day 34)
学习来源:日撸 Java 三百行(61-70天,决策树与集成学习)_闵帆的博客-CSDN博客
文章目录
- 矩阵分解
-
- 一、推荐系统中的矩阵
- 二、SVD 算法
- 三、Funk-SVD 算法
- 四、随机梯度下降
- 五、具体实现
-
- 1. 描述
- 2. 代码
- 3. 运行截图
- 总结
矩阵分解
一、推荐系统中的矩阵
对于一个推荐系统, 用户和物品之间的关系可以整理为如下这样的一个矩阵.
| User-Item | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | … |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 4 | 4.5 | ? | 3.9 | … |
| 2 | ? | 4.5 | ? | 4.5 | ? | … |
| 3 | 4.5 | ? | 4.4 | 4 | 4 | … |
| 4 | ? | 4.8 | ? | ? | 4.5 | … |
| 5 | 4 | ? | 4.5 | 5 | ? | … |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
矩阵中每一行代表一个用户, 而每一列则代表一个物品. 若用户对物品有过评分, 则矩阵中处在用户对应的行与物品对应的列交叉的位置表示用户对物品的评分值. 矩阵中的问号代表用户对物品未评分. 这个矩阵就叫做User-Item 评分矩阵, 这个矩阵中的数在实际统计后大多数现显示为问号.
推荐系统需要做的事情就是对于任意一个用户, 预测出所有未评分物品的分值, 并按分值大小从高到低的顺序推荐将对应的物品推荐给用户.
二、SVD 算法
传统的推荐方法通过对 User-Item 评分矩阵采用基于近邻的协同过滤来发现与用户具有相似偏好的其他用户, 进而产生推荐, 也就是之前所写过的 MBR. 但这种方法存在着数据稀疏和信息冗余大的缺陷, 当矩阵中评分元素稀疏, 以及信息量并非随着向量维度增加而线性增加.
那么就有人利用线性代数中的奇异值分解, 把原来大的评分矩阵分解称小矩阵的乘积.
对于奇异值分解的描述: 假设矩阵 M M M 是一个 m × n m \times n m×n 的矩阵, 则一定存在一个分解 M = U Σ V T M = U \Sigma V^{\mathrm{T}} M=UΣVT, 其中 U U U 是 m × m m \times m m×m 的正交矩阵, V V V 是 n × n n \times n n×n 的正交矩阵, Σ \Sigma Σ 是 m × m m \times m m×m 的对角阵.
M m × n = U m × m Σ m × m V n × n M_{m \times n} = U_{m \times m} \ \Sigma_{m \times m} \ V_{n \times n} Mm×n=Um×m Σm×m Vn×n
但是传统奇异值分解不允许矩阵中有空白元素存在, 也就是说评分矩阵中不能存在问号. 这对推荐系统来说是不可能做到的. 基于这个问题, 所以 Simon Funk 就提出了 Funk-SVD 算法.
三、Funk-SVD 算法
例如评分矩阵从 M M M 是一个 m × n m \times n m×n 的矩阵, 一共有 m m m 个用户, n n n 个物品. 通过一系列运算将矩阵 M M M 转化为两个矩阵 P P P 和 Q Q Q, 矩阵 U U U 的大小是 m × k m \times k m×k, 矩阵 Q Q Q 的大小是 k × n k \times n k×n. 式子如下所示:
M m × n ≈ P m × k Q k × n M_{m \times n} \approx P_{m \times k} Q_{k \times n} Mm×n≈Pm×kQk×n
因为矩阵 M M M 中存在未知, 我们只是在对这个矩阵进行拟合, 所以是约等于.
该方法基于这样一个假设: 用户对一个物品的喜爱程度主要由 k k k 个因素决定, P n i P_{ni} Pni 表示第 n n n 个用户对第 i i i 个因素的偏好程度, 而 Q i x Q_{ix} Qix 表示第 x x x 个物品满足第 i i i 个因素的程度, M n x M_{nx} Mnx 表示用户 n n n 对物品 x x x 最终的喜好程度.
那么对于原始矩阵中有评分的位置 M U I M_{UI} MUI 来说, 其在分解后矩阵中对应的值为:
M U I ′ = ∑ k = 1 K P U , k Q k , I M'_{UI} = {\textstyle \sum_{k=1}^{K}}P_{U,k} \ Q_{k,I} MUI′=∑k=1KPU,k Qk,I
其中 U U U 表示用户, I I I 表示物品.
那么对于整个评分矩阵而言, 总的损失就是:
S S E = E 2 = ∑ U , I ( M U , I − M U , I ′ ) 2 SSE = E^2 = {\textstyle \sum_{U,I}}(M_{U,I} \ - \ M'_{U,I})^2 SSE=E2=∑U,I(MU,I − MU,I′)2
现在的问题就转化为了求在损失 S S E SSE SSE 最小时的矩阵 P P P 和 Q Q Q.
四、随机梯度下降
梯度是一个向量, 表示的是一个函数在该点处沿梯度的方向变化最快, 变化率最大, 而梯度下降的方向就是指的负梯度方向. 想象下山的过程, 越是陡峭那么下山的速度就会越快 (这个过程不保证生命安全). 我们要找的就是类似最快下山这一过程.
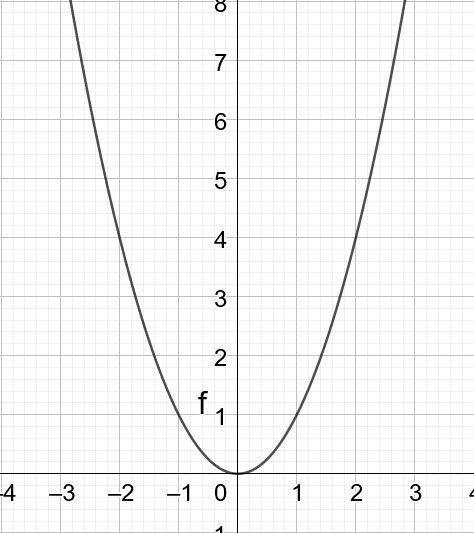
梯度下降需要考虑所有的样本, 在求函数的最小值最后会在驻点或者极值点停下来, 所以这样的方法只适合凸函数. 例如函数 f ( x ) = x 2 f(x)=x^2 f(x)=x2 就是一个凸函数, 满足 f ( x 1 + x 2 2 ) ≤ f ( x 1 ) + f ( x 2 ) 2 f(\frac{x_1+x_2}{2}) \le \frac{f(x_1)+f(x_2)}{2} f(2x1+x2)≤2f(x1)+f(x2). 其图像如下所示:
在这个函数上做梯度下降总会到达 ( 0 , 0 ) (0,0) (0,0) 这个点, 当然这也是这个函数的最小值的点.
随机梯度下降法主要是用来解决求和形式的优化问题, 与上面需要优化的目标函数一致. 其思想也很简单, 既然对于求和式中每一项求梯度很麻烦, 那么干脆就随机选其中一项计算梯度当作总的梯度来使用. 也就是说梯度下降是整体样本, 随机梯度下降是单个样本.
上面的目标函数为:
S S E = E 2 = ∑ U , I ( M U , I − ∑ k = 1 K P U , k Q k , I ) 2 SSE = E^2 = {\textstyle \sum_{U,I}}(M_{U,I} \ - \ {\textstyle \sum_{k=1}^{K}}P_{U,k} \ Q_{k,I} )^2 SSE=E2=∑U,I(MU,I − ∑k=1KPU,k Qk,I)2
S S E SSE SSE 是关于 P P P 和 Q Q Q 的多元函数, 当随机选定 U U U 和 I I I 后, 需要枚举所有的 k k k, 并且对 P U , k P_{U,k} PU,k 以及 Q k , I Q_{k,I} Qk,I 求偏导数.
∂ ∂ P u , k E U , I 2 = 2 E U , I ∂ E U , I ∂ P u , k = − 2 E U , I Q k , I \frac{\partial}{\partial P_{u,k}}{E_{U,I}}^2 = 2 E_{U,I}\frac{\partial E_{U,I}}{\partial P_{u,k}} = -2E_{U,I}Q_{k,I} ∂Pu,k∂EU,I2=2EU,I∂Pu,k∂EU,I=−2EU,IQk,I
∂ ∂ Q k , I E U , I 2 = 2 E U , I ∂ E U , I ∂ Q k , I = − 2 E U , I P U , k \frac{\partial}{\partial Q_{k,I}}{E_{U,I}}^2 = 2 E_{U,I}\frac{\partial E_{U,I}}{\partial Q_{k,I}} = -2E_{U,I}P_{U,k} ∂Qk,I∂EU,I2=2EU,I∂Qk,I∂EU,I=−2EU,IPU,k
五、具体实现
1. 描述
生成两个随机矩阵, 这两个随机矩阵就是之前式子中提到的 P P P 和 Q Q Q. 利用随机梯度下降的公式求出变化的趋势, 再乘以一个非常小的变化量. 使用这样的方式对这两个矩阵不断更新.
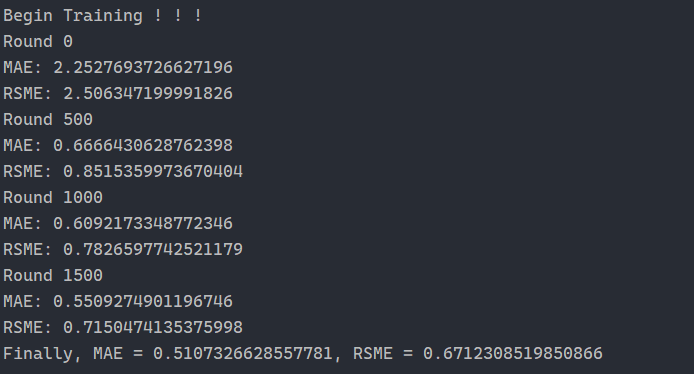
代码中并没有达到完全收敛, 而是设定了一个矩阵更新次数的阈值. 并在每 500 轮次时输出平均绝对误差和均方根误差, 用于观察收敛的效果.
2. 代码
package recommendersystem;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* Matrix factorization for recommender systems.
*
* @author Shi-Huai Wen Email: [email protected].
*/
public class MatrixFactorization {
/**
* Used to generate random numbers.
*/
Random rand = new Random();
/**
* Number of users.
*/
int numUsers;
/**
* Number of items.
*/
int numItems;
/**
* Number of ratings.
*/
int numRatings;
/**
* Training data.
*/
Triple[] dataset;
/**
* A parameter for controlling learning regular.
*/
double alpha;
/**
* A parameter for controlling the learning speed.
*/
double lambda;
/**
* The low rank of the small matrices.
*/
int rank;
/**
* The user matrix U.
*/
double[][] userSubspace;
/**
* The item matrix V.
*/
double[][] itemSubspace;
/**
* The lower bound of the rating value.
*/
double ratingLowerBound;
/**
* The upper bound of the rating value.
*/
double ratingUpperBound;
/**
* ***********************
* The first constructor.
*
* @param paraFilename The data filename.
* @param paraNumUsers The number of users.
* @param paraNumItems The number of items.
* @param paraNumRatings The number of ratings.
* ***********************
*/
public MatrixFactorization(String paraFilename, int paraNumUsers, int paraNumItems,
int paraNumRatings, double paraRatingLowerBound, double paraRatingUpperBound) {
numUsers = paraNumUsers;
numItems = paraNumItems;
numRatings = paraNumRatings;
ratingLowerBound = paraRatingLowerBound;
ratingUpperBound = paraRatingUpperBound;
try {
readData(paraFilename, paraNumUsers, paraNumItems, paraNumRatings);
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println("File " + paraFilename + " cannot be read! " + ee);
System.exit(0);
} // Of try
}// Of the first constructor
/**
* ***********************
* Set parameters.
*
* @param paraRank The given rank.
* ***********************
*/
public void setParameters(int paraRank, double paraAlpha, double paraLambda) {
rank = paraRank;
alpha = paraAlpha;
lambda = paraLambda;
}// Of setParameters
/**
* ***********************
* Read the data from the file.
*
* @param paraFilename The given file.
* @throws IOException
* ***********************
*/
public void readData(String paraFilename, int paraNumUsers, int paraNumItems,
int paraNumRatings) throws IOException {
File tempFile = new File(paraFilename);
if (!tempFile.exists()) {
System.out.println("File " + paraFilename + " does not exists.");
System.exit(0);
} // Of if
BufferedReader tempBufferReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(tempFile));
// Allocate space.
dataset = new Triple[paraNumRatings];
String tempString;
String[] tempStringArray;
for (int i = 0; i < paraNumRatings; i++) {
tempString = tempBufferReader.readLine();
tempStringArray = tempString.split(",");
dataset[i] = new Triple(Integer.parseInt(tempStringArray[0]),
Integer.parseInt(tempStringArray[1]), Double.parseDouble(tempStringArray[2]));
} // Of for i
tempBufferReader.close();
}// Of readData
/**
* ***********************
* Initialize subspaces. Each value is in [0, 1].
* ***********************
*/
void initializeSubspaces() {
userSubspace = new double[numUsers][rank];
for (int i = 0; i < numUsers; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < rank; j++) {
userSubspace[i][j] = rand.nextDouble();
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
itemSubspace = new double[numItems][rank];
for (int i = 0; i < numItems; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < rank; j++) {
itemSubspace[i][j] = rand.nextDouble();
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
}// Of initializeSubspaces
/**
* ***********************
* Predict the rating of the user to the item
*
* @param paraUser The user index.
* ***********************
*/
public double predict(int paraUser, int paraItem) {
double resultValue = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < rank; i++) {
// The row vector of a user and the column vector of an item
resultValue += userSubspace[paraUser][i] * itemSubspace[paraItem][i];
} // Of for i
return resultValue;
}// Of predict
/**
* ***********************
* Train.
*
* @param paraRounds The number of rounds.
* ***********************
*/
public void train(int paraRounds) {
initializeSubspaces();
for (int i = 0; i < paraRounds; i++) {
updateNoRegular();
if (i % 500 == 0) {
// Show the process
System.out.println("Round " + i);
System.out.println("MAE: " + mae());
System.out.println("RSME: " + rsme());
} // Of if
} // Of for i
}// Of train
/**
* ***********************
* Update sub-spaces using the training data.
* ***********************
*/
public void updateNoRegular() {
for (int i = 0; i < numRatings; i++) {
int tempUserId = dataset[i].user;
int tempItemId = dataset[i].item;
double tempRate = dataset[i].rating;
// Residual
double tempResidual = tempRate - predict(tempUserId, tempItemId);
// Update user subspace
double tempValue;
for (int j = 0; j < rank; j++) {
tempValue = 2 * tempResidual * itemSubspace[tempItemId][j];
userSubspace[tempUserId][j] += alpha * tempValue;
} // Of for j
// Update item subspace
for (int j = 0; j < rank; j++) {
tempValue = 2 * tempResidual * userSubspace[tempUserId][j];
itemSubspace[tempItemId][j] += alpha * tempValue;
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
}// Of updateNoRegular
/**
* ***********************
* Compute the RSME.
*
* @return RSME of the current factorization.
* ***********************
*/
public double rsme() {
double resultRsme = 0;
int tempTestCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numRatings; i++) {
int tempUserIndex = dataset[i].user;
int tempItemIndex = dataset[i].item;
double tempRate = dataset[i].rating;
double tempPrediction = predict(tempUserIndex, tempItemIndex);
// DataInfo.mean_rating;
if (tempPrediction < ratingLowerBound) {
tempPrediction = ratingLowerBound;
} else if (tempPrediction > ratingUpperBound) {
tempPrediction = ratingUpperBound;
} // Of if
double tempError = tempRate - tempPrediction;
resultRsme += tempError * tempError;
tempTestCount++;
} // Of for i
return Math.sqrt(resultRsme / tempTestCount);
}// Of rsme
/**
* ***********************
* Compute the MAE.
*
* @return MAE of the current factorization.
* ***********************
*/
public double mae() {
double resultMae = 0;
int tempTestCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numRatings; i++) {
int tempUserIndex = dataset[i].user;
int tempItemIndex = dataset[i].item;
double tempRate = dataset[i].rating;
double tempPrediction = predict(tempUserIndex, tempItemIndex);
if (tempPrediction < ratingLowerBound) {
tempPrediction = ratingLowerBound;
} // Of if
if (tempPrediction > ratingUpperBound) {
tempPrediction = ratingUpperBound;
} // Of if
double tempError = tempRate - tempPrediction;
resultMae += Math.abs(tempError);
tempTestCount++;
} // Of for i
return (resultMae / tempTestCount);
}// Of mae
/**
* ***********************
* Test accuracy
*
* Out MAE and RSME
* ***********************
*/
public static void testTrainingTesting(String paraFilename, int paraNumUsers, int paraNumItems,
int paraNumRatings, double paraRatingLowerBound, double paraRatingUpperBound,
int paraRounds) {
try {
// Step 1. read the training and testing data
MatrixFactorization tempMF = new MatrixFactorization(paraFilename, paraNumUsers,
paraNumItems, paraNumRatings, paraRatingLowerBound, paraRatingUpperBound);
// Step 2. read the training and testing data
tempMF.setParameters(5, 0.0001, 0.005);
// Step 3. update and predict
System.out.println("Begin Training ! ! !");
tempMF.train(paraRounds);
double tempMAE = tempMF.mae();
double tempRSME = tempMF.rsme();
System.out.println("Finally, MAE = " + tempMAE + ", RSME = " + tempRSME);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} // Of try
}// Of testTrainingTesting
/**
* ************************
* Test this class.
*
* @param args Not used now.
* ************************
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
testTrainingTesting("D:/Work/sampledata/movielens-943u1682m.txt", 943, 1682, 10000, 1, 5, 2000);
}// Of main
public static class Triple {
public int user;
public int item;
public double rating;
/**
* ********************
* The constructor.
* ********************
*/
public Triple(int paraUser, int paraItem, double paraRating) {
user = paraUser;
item = paraItem;
rating = paraRating;
}// Of the first constructor
/**
* ********************
* Show me.
* ********************
*/
public String toString() {
return "" + user + ", " + item + ", " + rating;
}// Of toString
}// Of class Triple
} // Of class MatrixFactorization
3. 运行截图
总结
随机梯度下降的方法有点像牛顿迭代法求平方根的感觉. 然后最神奇的地方还是考虑到隐藏属性这个点, 然后依靠随机后再收敛的方法处理, 就不需要考虑用作计算的中间矩阵的各个值. 纵使这些值能够得到, 但也免不了中间矩阵有空白出现.