Java学习(Day 35)
学习来源:日撸 Java 三百行(71-80天,BP 神经网络)_闵帆的博客-CSDN博客
文章目录
- BP 神经网络
-
- 一、前言
- 二、神经元模型
- 三、BP 神经网络机制
-
- 1. 前向 forward 预测
- 2. 后向 backpropagation 调整权重
- 3. 固定网络结构
- 四、具体实现
-
- 1. 代码
- 2. 运行截图
- 总结
BP 神经网络
一、前言
神经网络顾名思义是利用类似生物神经元的结构来完成数据处理的任务, 进而实现分类或者识别的功能.
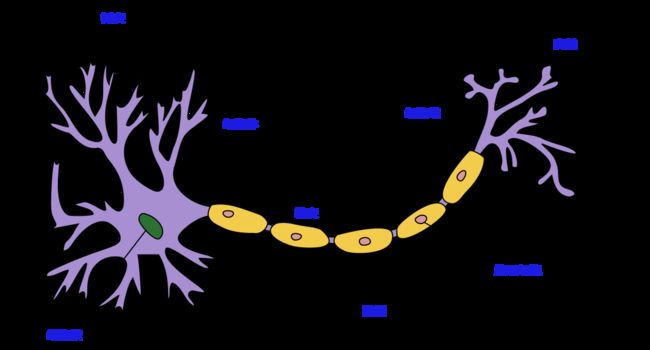
生物神经网络处理的是电信号, 处理的基本单元就叫做神经元, 如下 图1 所示.
一个神经元的突触与其他一个或者多个神经元的树突相连接, 以此来传递电信号. 数以亿计的神经元相互连接就构成了神经网络, 也被叫做生物神经网络.
按照这样的思想, 通过代码构建出类似的结构, 这就叫做人工神经网络. BP 神经网络不过是人工神经网络的一种, 是因为其中采用了 BP 算法.
更加详细的解释和内容可以观看视频 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1bx411M7Zx
二、神经元模型
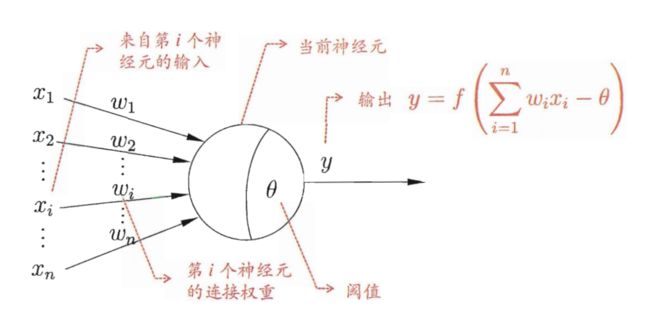
在周志华的机器学习一书中提到了一种简单但是非常经典的模型, 就是 “M-P 神经元模型”, 如下 图2 所示.
在这个模型中, 神经元接收到来自 n n n 个其他神经元传递过来的输入信号, 这些输入信号通过带权重的连接进行传递, 神经元接收到的总输入将与神经元的阈值进行比较, 然后通过激活函数处理以产生神经元的输出.
激活函数和其他的函数并无差别. 作为函数, 我们通过上面的图就已经了解到了函数的输入. 此时函数的输出就只有一个值, 这个值根据不同的激活函数有不同的表示.
最简单的激活函数跃迁函数 S g n Sgn Sgn, 其表达式如下:
s g n ( x ) = { 1 , x ≥ 0 ; 0 , x < 0 ; (1) sgn(x) = \left\{ \begin{array}{c} 1,\ x \ge 0; \\ 0,\ x < 0; \end{array} \right. \tag{1} sgn(x)={1, x≥0;0, x<0;(1)
这就好像一种非黑即白的思想, 当然对于函数图像来说自然也就是不平滑和不连续. 所以在神经网络中常用的是另一个激活函数 S i g m o i d Sigmoid Sigmoid, 其表达式如下.
s i g m o i d ( x ) = 1 1 + e − x (2) sigmoid(x) = \frac{1}{1+e^{-x}} \tag{2} sigmoid(x)=1+e−x1(2)
该函数输出值的范围在 ( 0 , 1 ) (0,1) (0,1) 之间, 函数图像平滑且连续. 并且这个函数的导数为:
s i g m o i d ( x ) ′ = 1 1 + e − x ( 1 − 1 1 + e − x ) = s i g m o i d ( x ) ( 1 − s i g m o i d ( x ) ) (3) sigmoid(x)' = \frac{1}{1+e^{-x}}(1-\frac{1}{1+e^{-x}})=sigmoid(x)(1-sigmoid(x)) \tag{3} sigmoid(x)′=1+e−x1(1−1+e−x1)=sigmoid(x)(1−sigmoid(x))(3)
三、BP 神经网络机制
BP神经网络是一种多层前馈神经网络, 主要特点是信号前向传递, 误差反向传播.
在前向传递中, 输入信号从输入层经隐含层逐层处理, 直至输出层. 每一层的神经元状态只影响下一层神经元状态.
如果输出层得不到期望输出, 则转入反向传播, 根据预测误差调整网络权值和阈值, 从而使 BP 神经网络预测输出不断逼近期望输出.
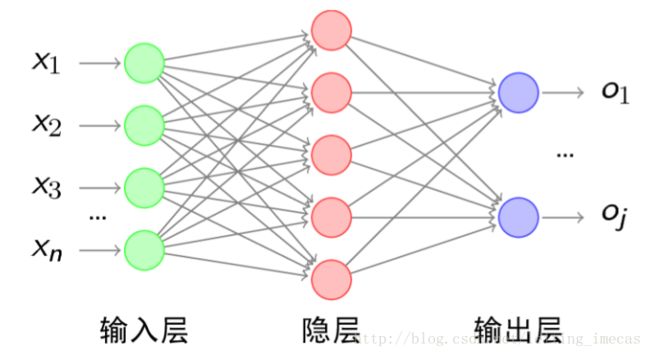
单隐藏层 BP 神经网络的拓扑结构如下 图3 所示:
1. 前向 forward 预测
以上图为例, 输入层有 n n n 个节点, 隐藏层有 q q q 各节点, 输出层有 j j j 个节点. 输入层和隐藏层间的权重为 V V V, 隐藏层与输出层的权重为 W W W, 输入变量为 X X X
则隐藏层的输出为:
Z k = f 1 ( ∑ i = 1 n V k i X i ) , k = 1 , … , q (4) Z_k = f_1(\sum_{i=1}^{n}V_{ki}X_i), \ k = 1,\dots,q \tag{4} Zk=f1(i=1∑nVkiXi), k=1,…,q(4)
输出层的输出为:
O l = f 2 ( ∑ k = 1 q W l k Z k ) , l = 1 , … , j (5) O_l = f_2(\sum_{k=1}^{q}W_{lk}Z_k), \ l = 1,\dots,j \tag{5} Ol=f2(k=1∑qWlkZk), l=1,…,j(5)
输出层有几个节点就代表有几个类别, 哪个节点的输出值大就判断为哪类.
2. 后向 backpropagation 调整权重
虽然在输出层说过谁的输出值大就归到哪一类, 但是输出结果往往不尽人意.
例如有三个类别 A B C, 有个物品是 A 类, 用三元组表示输出就应该是 [1,0,0]. 可实际结果却是 [0.3,0.5,0.6], 错误就是 [0.7,-0.5,-0.6].
为了缓解这种问题的出现, 所以就需要对与输出层相连的隐藏层进行一个问责机制, 因为是隐藏层的输入导致了最后的输出. 由此问题转换为了调节权重进而降低错误偏差. 这是一个函数, 很自然的就联想到之前矩阵分解中的梯度下降方法.
整体来看, 这是一个迭代的过程, 反向地对节点间权重都进行了修改.
误差函数: 假设有 p p p 个输入样本, 则每个输入样本的误差函数为:
E p = 1 2 ∑ l = 1 j ( y l p − y l p ′ ) 2 (6) E_p=\frac{1}{2}\sum_{l=1}^{j}(y_{lp} - y'_{lp})^2 \tag{6} Ep=21l=1∑j(ylp−ylp′)2(6)
3. 固定网络结构
隐藏层的节点个数是人为设置的, 各个节点之间的权值也是随机生成的.
对于不同的问题, 存在着不同的节点和权值.
四、具体实现
1. 代码
将读取数据和一些工具类函数例如 a r g m a x argmax argmax 用以获取数组中最大值的下标封装为一个抽象类.
package ann;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
import weka.core.Instances;
/**
* General ANN. Two methods are abstract: forward and backPropagation.
*
* @author Shi-Huai Wen Email: [email protected].
*/
public abstract class GeneralAnn {
/**
* The whole dataset.
*/
Instances dataset;
/**
* Number of layers. It is counted according to nodes instead of edges.
*/
int numLayers;
/**
* The number of nodes for each layer, e.g., [3, 4, 6, 2] means that there
* are 3 input nodes (conditional attributes), 2 hidden layers with 4 and 6
* nodes, respectively, and 2 class values (binary classification).
*/
int[] layerNumNodes;
/**
* Momentum coefficient.
*/
public double mobp;
/**
* Learning rate.
*/
public double learningRate;
/**
* For random number generation.
*/
Random random = new Random();
/**
* *******************
* The first constructor.
*
* @param paraFilename The arff filename.
* @param paraLayerNumNodes The number of nodes for each layer (maybe different).
* @param paraLearningRate Learning rate.
* @param paraMobp Momentum coefficient.
* *******************
*/
public GeneralAnn(String paraFilename, int[] paraLayerNumNodes, double paraLearningRate, double paraMobp) {
// Step 1. Read data.
try {
FileReader tempReader = new FileReader(paraFilename);
dataset = new Instances(tempReader);
// The last attribute is the decision class.
dataset.setClassIndex(dataset.numAttributes() - 1);
tempReader.close();
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println("Error occurred while trying to read '" + paraFilename + "' in GeneralAnn constructor.\r\n" + ee);
System.exit(0);
} // Of try
// Step 2. Accept parameters.
layerNumNodes = paraLayerNumNodes;
numLayers = layerNumNodes.length;
// Adjust if necessary.
layerNumNodes[0] = dataset.numAttributes() - 1;
layerNumNodes[numLayers - 1] = dataset.numClasses();
learningRate = paraLearningRate;
mobp = paraMobp;
}//Of the first constructor
/**
* *******************
* Forward prediction.
*
* @param paraInput The input data of one instance.
* @return The data at the output end.
* *******************
*/
public abstract double[] forward(double[] paraInput);
/**
* *******************
* Back propagation.
*
* @param paraTarget For 3-class data, it is [0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0] or [1, 0, 0].
* *******************
*/
public abstract void backPropagation(double[] paraTarget);
/**
* *******************
* Train using the dataset.
* *******************
*/
public void train() {
double[] tempInput = new double[dataset.numAttributes() - 1];
double[] tempTarget = new double[dataset.numClasses()];
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numInstances(); i++) {
// Fill the data.
for (int j = 0; j < tempInput.length; j++) {
tempInput[j] = dataset.instance(i).value(j);
} // Of for j
// Fill the class label.
Arrays.fill(tempTarget, 0);
tempTarget[(int) dataset.instance(i).classValue()] = 1;
// Train with this instance.
forward(tempInput);
backPropagation(tempTarget);
} // Of for i
}// Of train
/**
* *******************
* Get the index corresponding to the max value of the array.
*
* @return the index.
* *******************
*/
public static int argmax(double[] paraArray) {
int resultIndex = -1;
double tempMax = -1e10;
for (int i = 0; i < paraArray.length; i++) {
if (tempMax < paraArray[i]) {
tempMax = paraArray[i];
resultIndex = i;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
return resultIndex;
}// Of argmax
/**
* *******************
* Test using the dataset.
*
* @return The precision.
* *******************
*/
public double test() {
double[] tempInput = new double[dataset.numAttributes() - 1];
double tempNumCorrect = 0;
double[] tempPrediction;
int tempPredictedClass = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numInstances(); i++) {
// Fill the data.
for (int j = 0; j < tempInput.length; j++) {
tempInput[j] = dataset.instance(i).value(j);
} // Of for j
// Train with this instance.
tempPrediction = forward(tempInput);
tempPredictedClass = argmax(tempPrediction);
if (tempPredictedClass == (int) dataset.instance(i).classValue()) {
tempNumCorrect++;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
System.out.println("Correct: " + tempNumCorrect + " out of " + dataset.numInstances());
return tempNumCorrect / dataset.numInstances();
}// Of test
} //Of class GeneralAnn
在进行 forward 时, 对输入层和隐藏层之间的加权计算添加了一个偏移值.
在进行 backPropagation 时, 一个样本只进行一次权重修改.
package ann;
/**
* Back-propagation neural networks.
*
* @author Shi-Huai Wen Email: [email protected].
*/
public class SimpleAnn extends GeneralAnn {
/**
* The value of each node that changes during the forward process. The first
* dimension stands for the layer, and the second stands for the node.
*/
public double[][] layerNodeValues;
/**
* The error on each node that changes during the back-propagation process.
* The first dimension stands for the layer, and the second stands for the
* node.
*/
public double[][] layerNodeErrors;
/**
* The weights of edges. The first dimension stands for the layer, the
* second stands for the node index of the layer, and the third dimension
* stands for the node index of the next layer.
*/
public double[][][] edgeWeights;
/**
* The change of edge weights. It has the same size as edgeWeights.
*/
public double[][][] edgeWeightsDelta;
/**
* *******************
* The first constructor.
*
* @param paraFilename The arff filename.
* @param paraLayerNumNodes The number of nodes for each layer (maybe different).
* @param paraLearningRate Learning rate.
* @param paraMobp Momentum coefficient.
* *******************
*/
public SimpleAnn(String paraFilename, int[] paraLayerNumNodes, double paraLearningRate, double paraMobp) {
// Father constructor
super(paraFilename, paraLayerNumNodes, paraLearningRate, paraMobp);
// Step 1. Across layer initialization.
layerNodeValues = new double[numLayers][];
layerNodeErrors = new double[numLayers][];
edgeWeights = new double[numLayers - 1][][];
edgeWeightsDelta = new double[numLayers - 1][][];
// Step 2. Inner layer initialization.
for (int l = 0; l < numLayers; l++) {
layerNodeValues[l] = new double[layerNumNodes[l]];
layerNodeErrors[l] = new double[layerNumNodes[l]];
// One less layer because each edge crosses two layers.
if (l + 1 == numLayers) {
break;
} // of if
// In layerNumNodes[l] + 1, the last one is reserved for the offset.
edgeWeights[l] = new double[layerNumNodes[l] + 1][layerNumNodes[l + 1]];
edgeWeightsDelta[l] = new double[layerNumNodes[l] + 1][layerNumNodes[l + 1]];
for (int j = 0; j < layerNumNodes[l] + 1; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < layerNumNodes[l + 1]; i++) {
// Initialize weights.
edgeWeights[l][j][i] = random.nextDouble();
} // Of for i
} // Of for j
} // Of for l
}// Of the constructor
/**
* *******************
* Forward prediction.
*
* @param paraInput The input data of one instance.
* @return The data at the output end.
* *******************
*/
public double[] forward(double[] paraInput) {
// Initialize the input layer.
System.arraycopy(paraInput, 0, layerNodeValues[0], 0, layerNodeValues[0].length);
// Calculate the node values of each layer.
double z;
for (int l = 1; l < numLayers; l++) {
for (int j = 0; j < layerNodeValues[l].length; j++) {
// Initialize according to the offset, which is always +1
z = edgeWeights[l - 1][layerNodeValues[l - 1].length][j];
// Weighted sum on all edges for this node.
for (int i = 0; i < layerNodeValues[l - 1].length; i++) {
z += edgeWeights[l - 1][i][j] * layerNodeValues[l - 1][i];
} // Of for i
// Sigmoid activation.
// This line should be changed for other activation functions.
layerNodeValues[l][j] = 1 / (1 + Math.exp(-z));
} // Of for j
} // Of for l
return layerNodeValues[numLayers - 1];
}// Of forward
/**
* *******************
* Back propagation and change the edge weights.
*
* @param paraTarget For 3-class data, it is [0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0] or [1, 0, 0].
* *******************
*/
public void backPropagation(double[] paraTarget) {
// Step 1. Initialize the output layer error.
int l = numLayers - 1;
for (int j = 0; j < layerNodeErrors[l].length; j++) {
layerNodeErrors[l][j] = layerNodeValues[l][j] * (1 - layerNodeValues[l][j]) * (paraTarget[j] - layerNodeValues[l][j]);
} // Of for j
// Step 2. Back-propagation even for l == 0
while (l > 0) {
l--;
// Layer l, for each node.
for (int j = 0; j < layerNumNodes[l]; j++) {
double z = 0.0;
// For each node of the next layer.
for (int i = 0; i < layerNumNodes[l + 1]; i++) {
if (l > 0) {
z += layerNodeErrors[l + 1][i] * edgeWeights[l][j][i];
} // Of if
// Weight adjusting.
edgeWeightsDelta[l][j][i] = mobp * edgeWeightsDelta[l][j][i] + learningRate * layerNodeErrors[l + 1][i] * layerNodeValues[l][j];
edgeWeights[l][j][i] += edgeWeightsDelta[l][j][i];
if (j == layerNumNodes[l] - 1) {
// Weight adjusting for the offset part.
edgeWeightsDelta[l][j + 1][i] = mobp * edgeWeightsDelta[l][j + 1][i] + learningRate * layerNodeErrors[l + 1][i];
edgeWeights[l][j + 1][i] += edgeWeightsDelta[l][j + 1][i];
} // Of if
} // Of for i
// Record the error according to the differential of Sigmoid.
// This line should be changed for other activation functions.
layerNodeErrors[l][j] = layerNodeValues[l][j] * (1 - layerNodeValues[l][j]) * z;
} // Of for j
} // Of while
}// Of backPropagation
/**
* *******************
* Test the algorithm.
* *******************
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] tempLayerNodes = {4, 8, 8, 3};
SimpleAnn tempNetwork = new SimpleAnn("D:/Work/sampledata/iris.arff", tempLayerNodes, 0.01, 0.6);
for (int round = 0; round < 5000; round++) {
tempNetwork.train();
} // Of for n
double tempAccuracy = tempNetwork.test();
System.out.println("The accuracy is: " + tempAccuracy);
}// Of main
}// Of class SimpleAnn
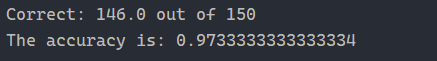
2. 运行截图
总结
和矩阵分解的思想类似, 通过随机然后再来靠近真实值. 实际代码和公式推导还存在存在着一些问题, 尤其是进行后向 backPropagation 的权值调整公式. 还是需要多动手推导一下.