Java数据结构与算法(树)——平衡二叉树(AVL树)
文章目录
- 一、定义
- 二、不平衡情况及处理方法
-
-
- 1、左左(右旋)
- 2、右右(左旋)
- 3、双旋
-
- 三、代码实现
-
-
- 1、节点类抽象数据类型
- 2、节点类
- 3、平衡二叉树测试类
-
一、定义
平衡二叉查找树(Balanced Binary Sort Tree,BBST)简称平衡二叉树,是一种高度平衡的二叉树,由苏联数学家 Adele - Veliki 和 Landis 在 1962 年提出,故又命名为 AVL 树。
平衡二叉树的性质:首先是一种二叉查找树,并且其中每个节点的左子树和右子树的高度相差至多等于 1。
平衡因子BF(Balance Factor)——将二叉树上节点的左子树高度减去右子树高度的值称为平衡因子。平衡二叉树上,所有节点的平衡因子只可能是 -1,0,1。
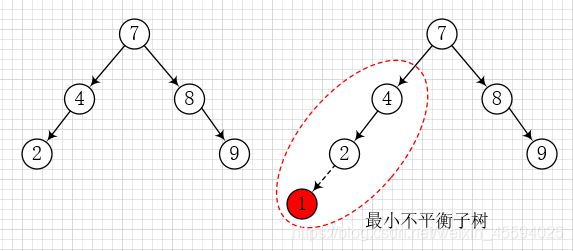
最小不平衡子树——距离插入节点最近的,且平衡因子的绝对值大于 1 的节点为根的子树。以下图为例,左图是一棵平衡二叉树,当插入节点 1 时,节点 4 的 BF = 2(左子树高度 - 右子树高度 = 2 - 0 = 2),则以节点 4 为根节点的子树即为最小不平衡子树。
二、不平衡情况及处理方法
构建平衡二叉树的基本思想就是在构建二叉搜索树的过程中,每当插入一个新节点时,先检查是否因插入而破坏了树的平衡性,若是,则在保持二叉搜索树特性的前提下,调整最小不平衡子树中各节点之间的链接关系,进行相应的旋转调整,使之成为新的平衡二叉树。
注意:
不平衡的情况其实千变万化,比如左边深度为一万,右边深度为 0。但是我们考虑的是,在平衡二叉树中修改一个节点以后引起的不平衡,所以,左右子树的差的绝对值只能为 2。
旋转的情况:
(1)单旋:
最小不平衡子树的根节点的 BF 与它的子树的 BF 符号相同时,需要一次旋转。最小不平衡子树的根节点的 BF 大于 1 时,右旋;小于 -1 时,左旋。
(2)双旋:
最小不平衡子树的根节点的 BF 与它的子树的 BF 符号相反时,需要两次旋转,即先对子树进行一次旋转后使得 BF 符号相同之后,再反向旋转一次完成平衡。
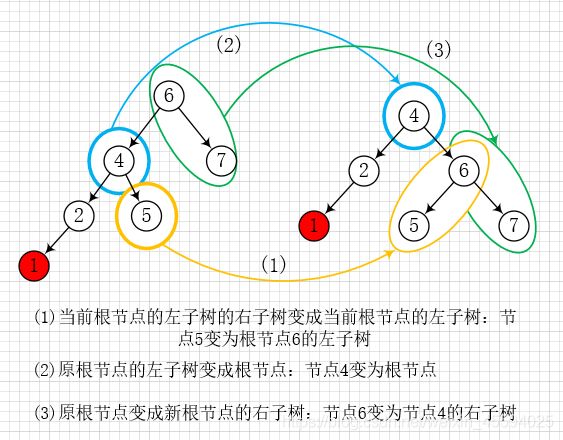
1、左左(右旋)
最小不平衡子树的根节点 6 的 BF = 2,左子树根节点 4 的 BF = 1,同号且大于 1,右旋。具体操作:
- 当前根节点的左子树的右子树变成当前根节点的左子树(因为它满足大于左子树且小于根节点的要求);
- 原根节点的左子树变成新的根节点;
- 原根节点变成新根节点的右子树。
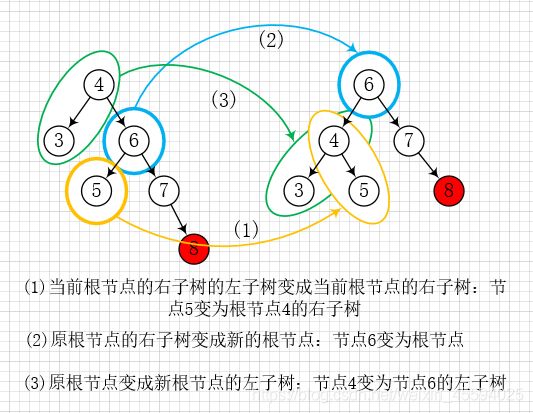
2、右右(左旋)
最小不平衡子树的根节点 4 的 BF = -2,右子树根节点 6 的 BF = -1,同号且小于 -1,左旋。具体操作:
- 当前根节点的右子树的左子树变成当前根节点的右子树;
- 原根节点的右子树变成新的根节点;
- 原根节点变成新根节点的左子树。
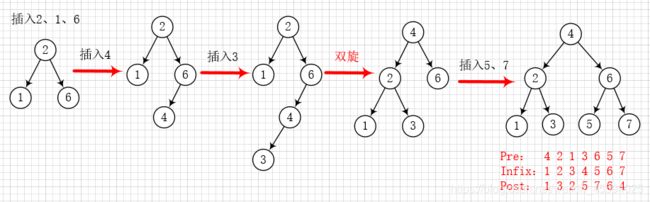
3、双旋
如下图,插入节点 8 时,最小不平衡子树的根节点 9 的 BF = 2,左子树根节点 6 的 BF = -1,反号,仅一次单旋不能解决问题。
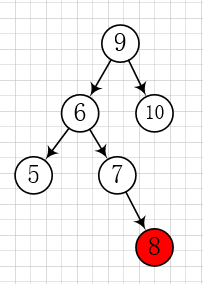
解决方法:
双旋:最小不平衡子树的左子树根节点 6 的 BF = -1,先左旋最小不平衡子树的左子树,再右旋最小不平衡子树。如下图所示:
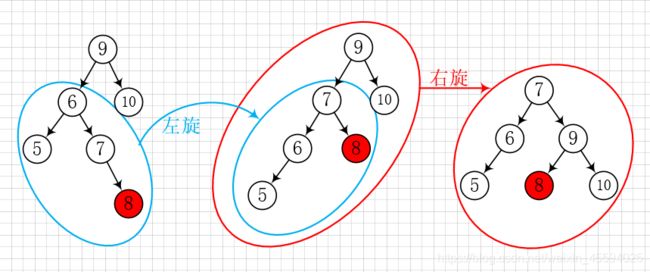
先右旋再左旋的情况类似。
三、代码实现
1、节点类抽象数据类型
public interface AVLNodeADT {
void insert(AVLNode node);// 向平衡二叉树插入节点
void preOrder();// 前序遍历
void infixOrder();// 中序遍历
void postOrder();// 后序遍历
AVLNode find(int value);// 查找
int getHeight();// 当前节点的高度
int getLeftHeight();// 左子树的高度
int getRightHeight();// 右子树的高度
void leftRotate();// 左旋
void rightRotate();// 右旋
}2、节点类
public class AVLNode implements AVLNodeADT{
private int value;
private AVLNode left;
private AVLNode right;
public AVLNode(){}
public AVLNode(int value){ this.value = value; }
public int getValue() { return value; }
public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; }
public AVLNode getLeft() { return left; }
public void setLeft(AVLNode left) { this.left = left; }
public AVLNode getRight() { return right; }
public void setRight(AVLNode right) { this.right = right; }
public String toString(){ return value + " "; }// 方便打印
@Override
// 插入:(1)插入节点(2)检查是否需要调整平衡
public void insert(AVLNode node) {
// (1)插入节点
if(node == null)// 插入节点为空,直接返回
return;
if(node.value < this.value){// 插入节点值小于根节点的值,递归插入左子树
if(this.left == null)
this.setLeft(node);
else
this.left.insert(node);
}else if(node.value > this.value){// 插入节点值大于根节点的值,递归插入右子树
if(this.right == null)
this.setRight(node);
else
this.right.insert(node);
}else{// 相等说明节点已存在,不用再插入
return;
}
// (2)检查是否需要调整平衡
int BF = this.getLeftHeight() - this.getRightHeight();// 平衡因子
if(BF < -1){// 左旋
// 若其右子树的BF > 1,需要双旋;否则只需单旋
int rightBF = this.right.getLeftHeight() - this.right.getRightHeight();
if(this.right != null && rightBF > 1){
this.right.rightRotate();// 先对该节点的右子树进行右旋
}
this.leftRotate();// 再对当前节点进行左旋
}else if(BF > 1){// 右旋
// 若其左子树的BF < -1,需要双旋;否则只需单旋
int leftBF = this.left.getLeftHeight() - this.left.getRightHeight();
if(this.left != null && leftBF < -1){
this.left.leftRotate();// 先对该节点的左子树进行左旋
}
this.rightRotate();// 再对当前节点进行右旋
}else{// 平衡,不用调整
return;
}
}
@Override
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
System.out.print(this);
if(this.getLeft() != null)
this.left.preOrder();
if(this.getRight() != null)
this.right.preOrder();
}
@Override
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if(this.getLeft() != null)
this.left.infixOrder();
System.out.print(this);
if(this.getRight() != null)
this.right.infixOrder();
}
@Override
// 后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
if(this.getLeft() != null)
this.left.postOrder();
if(this.getRight() != null)
this.right.postOrder();
System.out.print(this);
}
@Override
// 查找
public AVLNode find(int value) {
if(value < this.value){// 搜索左子树
if(this.left == null)
return null;
else
return this.left.find(value);
}else if(value > this.value){
if(this.right == null)
return null;
else
return this.right.find(value);
}else{
return this;
}
}
@Override
// 获取当前节点的高度(左子树高度和右子树高度较大值 + 1)
public int getHeight() {
// 666
return Math.max(this.left == null ? 0 : this.left.getHeight(),
this.right== null ? 0 : this.right.getHeight()) + 1;
}
@Override
// 获取左子树的高度
public int getLeftHeight() {
return this.left == null ? 0 : this.left.getHeight();
}
@Override
// 获取右子树的高度
public int getRightHeight() {
return this.right== null ? 0 : this.right.getHeight();
}
@Override
/*
* 左旋:
* (1)当前根节点的右子树的左子树变成当前根节点的右子树;
* (2)原根节点的右子树变成根节点;
* (3)原根节点变成新左子树。
*/
public void leftRotate() {
// (1)当前根节点的右子树的左子树变成当前根节点的右子树;
AVLNode node = new AVLNode(this.value);// 以当前根节点的值创建一个新节点,作为旋转之后根节点的左子树
node.left = this.left;// 新节点的左子树还是其原来的左子树
node.right = this.right.left;// 当前根节点的右子树的左子树变成当前根节点的右子树
// (2)原根节点的右子树变成新根节点;
this.value = this.right.value;
this.right = this.right.right;// 新根节点的右子树还是其原来的右子树
// (3)原根节点变成新根节点的左子树。
this.left = node;
}
@Override
/*
* 右旋:
* (1)当前根节点的左子树的右子树变成当前根节点的左子树;
* (2)原根节点的左子树变成新根节点,
* (3)原根节点变成新根节点的右子树。
*/
public void rightRotate() {
// (1)当前根节点的左子树的右子树变成当前根节点的左子树;
AVLNode node = new AVLNode(this.value);// 以当前根节点的值创建新节点,作为旋转之后根节点的右子树
node.right = this.right;// 新节点的右子树还是其原来的右子树
node.left = this.left.right;// 当前根节点的左子树的右子树变成当前根节点的左子树
// (2)原根节点的左子树变成新根节点;
this.value = this.left.value;
this.left = this.left.left;// 新根节点的左子树还是其原来的左子树
// (3)原根节点变成新根节点的右子树。
this.right = node;
}
}3、平衡二叉树测试类
public class AVL {
private AVLNode root;
public AVL(){}
public AVL(AVLNode root){ this.root = root; }
// 插入
public void insert(AVLNode node){
if(root == null)
root = node;
else
root.insert(node);
}
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder(){
if(root == null){
System.out.println("The tree is empty!");
return;
}else{
root.preOrder();
}
System.out.println();
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder(){
if(root == null){
System.out.println("The tree is empty!");
return;
}else{
root.infixOrder();
}
System.out.println();
}
// 后序遍历
public void postOrder(){
if(root == null){
System.out.println("The tree is empty!");
return;
}else{
root.postOrder();
}
System.out.println();
}
// 查找节点
public AVLNode find(int value){
if(root == null){
System.out.println("The tree is empty!");
return null;
}
return root.find(value);
}
// 树的高度
public int getHeight(){
if(root == null)
return 0;
return root.getHeight();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AVL tree = new AVL();
tree.insert(new AVLNode(2));
tree.insert(new AVLNode(1));
tree.insert(new AVLNode(6));
tree.insert(new AVLNode(4));
tree.insert(new AVLNode(3));
tree.insert(new AVLNode(5));
tree.insert(new AVLNode(7));
tree.infixOrder();
tree.preOrder();
tree.postOrder();
}
}关于单旋(左旋,右旋)与双旋的处理都在添加节点后完成。添加一个节点,就对新的树进行判断是否需要"平衡",所以添加节点的过程就是平衡二叉树的构建过程。上面的测试程序中,添加了 7 个数据,其构建平衡二叉树的过程图示如下: