MybatisPlus笔记
文章目录
- MybatisPlus笔记
-
- 1、简介
- 2、快速开始
- 3、主键策略
- 4、自动填充
-
- 4.1、数据库的自动填充
- 4.2、Mybatis-Plus的自动填充
- 5、乐观锁插件
- 6、分页插件
- 7、逻辑删除插件
- 8、条件构造器Wrapper
- 9、代码生成器(新)
MybatisPlus笔记
1、简介
Mybatis-Plus官网:https://baomidou.com/
MyBatis-Plus (opens new window)(简称 MP)是一个 MyBatis (opens new window)的增强工具,在 MyBatis 的基础上只做增强不做改变,为简化开发、提高效率而生。
特点:
- 无侵入:只做增强不做改变,引入它不会对现有工程产生影响,如丝般顺滑
- 损耗小:启动即会自动注入基本 CURD,性能基本无损耗,直接面向对象操作
- 强大的 CRUD 操作:内置通用 Mapper、通用 Service,仅仅通过少量配置即可实现单表大部分 CRUD 操作,更有强大的条件构造器,满足各类使用需求
- 支持 Lambda 形式调用:通过 Lambda 表达式,方便的编写各类查询条件,无需再担心字段写错
- 支持主键自动生成:支持多达 4 种主键策略(内含分布式唯一 ID 生成器 - Sequence),可自由配置,完美解决主键问题
- 支持 ActiveRecord 模式:支持 ActiveRecord 形式调用,实体类只需继承 Model 类即可进行强大的 CRUD 操作
- 支持自定义全局通用操作:支持全局通用方法注入( Write once, use anywhere )
- 内置代码生成器:采用代码或者 Maven 插件可快速生成 Mapper 、 Model 、 Service 、 Controller 层代码,支持模板引擎,更有超多自定义配置等您来使用
- 内置分页插件:基于 MyBatis 物理分页,开发者无需关心具体操作,配置好插件之后,写分页等同于普通 List 查询
- 分页插件支持多种数据库:支持 MySQL、MariaDB、Oracle、DB2、H2、HSQL、SQLite、Postgre、SQLServer 等多种数据库
- 内置性能分析插件:可输出 SQL 语句以及其执行时间,建议开发测试时启用该功能,能快速揪出慢查询
- 内置全局拦截插件:提供全表 delete 、 update 操作智能分析阻断,也可自定义拦截规则,预防误操作
2、快速开始
初始化一个SpringBoot项目,并创建数据库和对应的表。
步骤:
- 创建数据库
mybatis_plus和user表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS user;
CREATE TABLE user
(
id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键ID',
name VARCHAR(30) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名',
age INT(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄',
email VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '邮箱',
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
DELETE FROM user;
INSERT INTO user (id, name, age, email) VALUES
(1, 'Jone', 18, '[email protected]'),
(2, 'Jack', 20, '[email protected]'),
(3, 'Tom', 28, '[email protected]'),
(4, 'Sandy', 21, '[email protected]'),
(5, 'Billie', 24, '[email protected]');
- 创建SpringBoot初始化项目,导入对应的依赖(mysql、jdbc、lombok),并配置好数据库的连接
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mybatis_plus?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serveTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: 1234567
- 导入Mybatis-Plus的依赖
注意Mybatis-Plus的依赖和Mybatis的依赖不要同时导入
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidougroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>3.5.0version>
dependency>
- 创建实体类
User
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
- 编写接口,并配置主启动类的接口扫描
@MapperScan({“com.xiaotanke.mapper”}) 主启动类的扫描
// 只需要继承BaseMapper这个接口,这个接口的实现类就是CRUD代码,注意需要传入一个实体的泛型
@Repository
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
}
- 测试
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(null);
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
3、主键策略
// 插入的测试
@Test
public void testInsert(){
User user = new User();
user.setName("xiaotanke");
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
user.setAge(18);
int result = userMapper.insert(user);
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println(user);
}
我们并没有给插入的user设置一个主键,但是插入的时候它会自动给插入的user生成一个long类型的主键,这个主键是全局唯一的,并回写到插入的user类上,这个就是主键策略。常见的主键策略:uuid、主键自增、redis生成id、雪花算法(默认)
雪花算法:
SnowFlake 算法,是 Twitter 开源的分布式 id 生成算法。其核心思想就是:使用一个 64 bit 的 long 型的数字作为全局唯一 id。在分布式系统中的应用十分广泛,且ID 引入了时间戳,基本上保持自增的,后面的代码中有详细的注解。这 64 个 bit 中,其中 1 个 bit 是不用,然后用其中的 41 bit 作为毫秒数,用 10 bit 作为工作机器 id,12 bit 作为序列号。
配置主键策略:
mybatis-plus默认的主键策略就是雪花算法,会自动生成一个全局唯一的id。我们可以再实体类的主键字段上进行主键策略的配置,通过@TableId注解设置。
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
// 参数是一个枚举类型
@TableId(type = IdType.ASSIGN_ID)
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
public enum IdType {
AUTO(0), // 数据库字段自增
NONE(1), // 未设置主键
INPUT(2), // 手动输入主键
ASSIGN_ID(3), // 雪花算法(默认)
ASSIGN_UUID(4); // uuid
private final int key;
private IdType(int key) {
this.key = key;
}
public int getKey() {
return this.key;
}
}
如果使用自增的主键策略,需要将数据库的字段也要改成自增字段。使用手动输入id策略,就必须给实体类设置一个id。
4、自动填充
在一些操作中某一些操作不需要手动去完成,直接可以通过自动去完成操作。例如创建的时间和更新的时间,直接通过系统的时间自动去完成操作。
4.1、数据库的自动填充
添加create_time和update_time两个字段,这两个字段的是timestamp类型,在数据库中添加配置就能完成自动操作。
对于Navicat的自动填充才是这样,其他sql工具可能不一样。
这样向表中添加数据时,create_time字段就会有一个当前系统的默认值;更新的时候,update_time字段的日期也会更新,即使sql语句中没有更新时间。但是在实际工作中不会接触到数据库,只会进行sql的操作。
4.2、Mybatis-Plus的自动填充
Mybatis-Plus使用的是代码来进行的自动填充,进行下面操作完成。
- 在实体类上添加注解
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
// 当插入的时候进行填充
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private Date createTime;
// 当插入和更新的时候自动填充
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Date updateTime;
}
- 编写处理器来进行自动填充
这个处理类需要放入到spring容器中,处理类实现MetaObjectHandler接口,重写方法。
// 需要将这个处理类放入spring容器中
@Component
public class MyMetaObjectHandler implements MetaObjectHandler{
// 需要实现MetaObjectHandler接口,并实现这两个方法
// 插入时的自动填充
@Override
public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
// 三个参数,(填充的实体属性名、填充的值、metaObject)
this.setFieldValByName("createTime",new Date(),metaObject);
this.setFieldValByName("updateTime",new Date(),metaObject);
}
// 更新时的自动填充
@Override
public void updateFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
// 三个参数,(填充的实体属性名、填充的值、metaObject)
this.setFieldValByName("updateTime",new Date(),metaObject);
}
}
5、乐观锁插件
乐观锁:总是认为不会出现问题,所以无论干什么就不会去上锁,如果出现问题就加锁测试。
悲观锁:无论干什么都会觉得出现问题,所有所有操作都会加上锁然后操作。
在Mybatis-Plus中已经实现了乐观锁的插件,只需要简单的配置就可以使用乐观锁。当要更新一条记录的时候,希望这条记录没有被别人更新,乐观锁实现方式:
- 取出记录时,获取当前 version(需要有一个version字段)
- 更新时,带上这个 version
- 执行更新时, set version = newVersion where version = oldVersion(newVersion 就是原来的version+1)
- 如果 version 不对,就更新失败
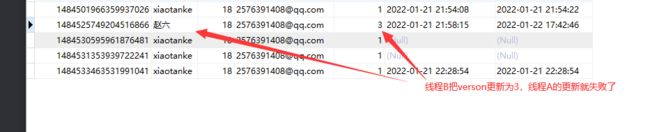
现在有A线程在执行更新数据的操作(获取到的version为1),但是还没有确定。突然B线程也来修改这一条记录,获取到version为1,执行完更新后的版本version就为2,这时A线程继续执行操作,发现原先取出来的version(1)和表中新的version(2)不一样,这就会跟新失败。实际就是在sql语句中添加了一个and条件判断。
Mybatis-Plus实现乐观锁:
- 表中添加一个version字段,默认值为1。实体类也加上对应的version属性。
- 实体类的version字段是添加
@Version注解,表示是一个乐观锁。
@Version
private Integer version;
- 编写配置类
MybatisPlusConfig
// 开启mybatis的事务管理
@EnableTransactionManagement
// 这个注解可以写到mybatis的配置类上
@MapperScan({"com.xiaotanke.mapper"})
@Configuration
public class MybatisPlusConfig {
// 添加Mybatis-Plus的插件,注意要注入到spring中
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() {
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
// 添加乐观锁的插件,也可以添加其他的插件
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new OptimisticLockerInnerInterceptor());
return interceptor;
}
}
- 测试成功的乐观锁
使用乐观锁之前需要将这个实体的version查询出来携带到查询实体中
@Test
public void updateTest(){
// 使用乐观锁之前需要将这个实体的version查询出来携带到查询实体中
User user = userMapper.selectById(1484525749204516866L);
user.setName("赵六");
int nums = userMapper.updateById(user);
System.out.println(nums);
}
- 测试失败的乐观锁
@Test
public void updateTest1(){
// 线程A
User user = userMapper.selectById(1484525749204516866L);
user.setName("田七");
// 线程B
User user2 = userMapper.selectById(1484525749204516866L);
user.setName("张三");
// 线程B比线程A先执行操作,并更新了version为3
userMapper.updateById(user2);
// 线程A后执行更新操作,发现version不合法,更新就不会成功
userMapper.updateById(user);
}
- 支持的数据类型只有:int,Integer,long,Long,Date,Timestamp,LocalDateTime
- 整数类型下
newVersion = oldVersion + 1newVersion会回写到entity中- 仅支持
updateById(id)与update(entity, wrapper)方法- 在
update(entity, wrapper)方法下,wrapper不能复用!!!
6、分页插件
Mybatis-Plus中内置了分页插件,通过简单的分页插件的配置就可以使用了。
- 编写配置类
// 开启mybatis的事务管理
@EnableTransactionManagement
// 这个注解可以写到mybatis的配置类上
@MapperScan({"com.xiaotanke.mapper"})
@Configuration
public class MybatisPlusConfig {
// 添加Mybatis-Plus的插件,注意要注入到spring中
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() {
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
// 添加乐观锁的插件,也可以添加其他的插件
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new OptimisticLockerInnerInterceptor());
// 添加分页插件,DbType是一个泛型,指定使用的数据库类型
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor(DbType.MYSQL));
return interceptor;
}
}
- 编写好配置文件后就可以使用分页插件了,内置Page对象,可以直接使用这个对象进行分页查询
// 分页的测试
@Test
public void pageTest(){
// 参数1:查询的页码(为负数默认为第一页); 参数2:一页的数量(为负数就查询所有的数据); 泛型的查询的实体类
Page<User> page = new Page<>(1, -1);
// 进行查询,参数1:Page对象,第二个参数是Wrapper条件对象
// 查询完成后,将查询的数据都封装到了传入的page对象中
userMapper.selectPage(page,null);
// 获取查询的数据
List<User> users = page.getRecords();
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println(user);
}
System.out.println("================");
// 数据的总页数
long pages = page.getPages();
System.out.println(pages);
System.out.println("================");
// 当前的页码
long current = page.getCurrent();
System.out.println(current);
System.out.println("================");
// 一页的数量
long size = page.getSize();
System.out.println(size);
System.out.println("================");
// 总的数据数
long total = page.getTotal();
System.out.println(total);
}
7、逻辑删除插件
物理删除:直接从数据库中删除。
逻辑删除:在数据库中没有被移除,而是通过一个字段表示是否被删除的状态,例如0表示未删除,1表示已删除,但是并不是从数据库中删除了。实际上删除sql变成了更新sql,把deleted字段设置为1了,查询的使用也添加了
and deleted=0的条件
-
在数据库中添加
deleted字段,默认值为0表示未删除 -
实体类上添加deleted属性,并使用注解表示是一个逻辑删除属性
// 逻辑删除的注解
@TableLogic
private Integer deleted;
- 编写配置文件
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
global-config:
db-config:
logic-delete-field: deleted # 全局逻辑删除的实体字段名(since 3.3.0,配置后可以忽略不配置步骤2)
logic-delete-value: 1 # 逻辑已删除值
logic-not-delete-value: 0 # 逻辑未删除值
- 测试
@Test
public void deleteTest(){
// 删除id为1484525749204516866L的用户
userMapper.deleteById(1484525749204516866L);
}
再次查询id为1484525749204516866L的用户就不会查询出来。
8、条件构造器Wrapper
一些复杂的sql语句可以使用条件构造器来进行数据的查询,在sql能执行的一般Wrapper都可以实现。
AbstractWrapper是条件构造器的父类(抽象类,不能new,所以只能使用子类),主要使用的条件构造器有两个,
QueryWrapper和UpdateWrapper通过这两个类构造条件。
例子:
@Test
public void selectTest(){
// 创建一个Wrapper对象
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
// 通过链式编程将条件封装进去(name字段不为空同时name为xiaotanke的数据)
wrapper.isNotNull("name").eq("name","xiaotanke");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
AbstractWrapper能构造的条件:
它的子类
QueryWrapper和UpdateWrapper都可以使用下面的构造条件。
| 条件名 | 解释 | 例子 |
|---|---|---|
| allEq(map,boolean) | 参数为一个map,key为字段的名称,value是对应字段的值,第二个参数为true时值为null的条件会被解析为is Null,为false时会忽略值为null的数据。(默认为true) | allEq({id:1,name:"老王",age:null})--->id = 1 and name = '老王' and age is null |
| eq(v1,v2) | v1为数据库字段名,v2是字段对应的值,选择出v1字段等于v2的数据 | eq("name", "老王")--->name = '老王' |
| nq(v1,v2) | 不等于 | ne("name", "老王")--->name <> '老王' |
| gt(v1,v2) | 大于 | gt("age", 18)--->age > 18 |
| ge(v1,v2) | 大于等于 | ge("age", 18)--->age >= 18 |
| lt(v1,v2) | 小于 | lt("age", 18)--->age < 18 |
| le(v1,v2) | 小于等于 | le("age", 18)--->age <= 18 |
| between(v1,v2,v3) | v1为数据库的字段名,v1字段的值在v2和v3之间的数据 | between("age", 18, 30)--->age between 18 and 30 |
| notBetween(v1,v2,v3) | v1的值不在v2和v3之间 | notBetween("age", 18, 30)--->age not between 18 and 30 |
| like(v1,v2) | v1是字段名,v2是值,相当于是一个模糊查询%v2% |
like("name", "王")--->name like '%王%' |
| notLike(v1,v2) | 排除包括模糊查询的其他内容 | notLike("name", "王")--->name not like '%王%' |
| likeLeft(v1,v2) | 相当于%v2,值得左边进行模糊查询 |
likeLeft("name", "王")--->name like '%王' |
| likeRight(v1,v2) | 相当于v2%,值得右边进行模糊查询 |
likeRight("name", "王")--->name like '王%' |
| isNull(v1,v2) | v1字段名,v2字段值,查询v1字段值为null的数据 | isNull("name")--->name is null |
| isNotNull(v1,v2) | 查询v1的值不为null的数据 | isNotNull("name")--->name is not null |
| in(v1,v2) | v1字段名,v2是一个集合,查询v1字段中值是v2集合中的值 | in("age",{1,2,3})--->age in (1,2,3) |
| notIn(v1,v2) | 查询v1字段的值不是v2集合中的值 | notIn("age",{1,2,3})--->age not in (1,2,3) |
| inSql(v1,v2) | v1字段名,v2是一个子查询的sql语句,将查询的结果作为v1字段的in来使用(查询的字段和v1的字段名需要保持一致) | inSql("id", "select id from table where id < 3")--->id in (select id from table where id < 3) |
| notInSql(v1,v2) | 不包含v2sql语句中查询到的结果 | notInSql("id", "select id from table where id < 3")--->id not in (select id from table where id < 3) |
| groupBy(v…) | 按照字段进行分组查询,可以传入多个字段 | groupBy("id", "name")--->group by id,name |
| orderByAsc(v…) | 按照字段将查询的结果进行升序排序 |
orderByAsc("id", "name")--->order by id ASC,name ASC |
| orderByDesc(v…) | 按照字段将查询的结果进行降序排序 |
orderByDesc("id", "name")--->order by id DESC,name DESC |
| having(v1,v2) | v1是sql语句,v2是可变参数 | having("sum(age) > {0}", 11)--->having sum(age) > 11 |
| or() | 主动调用or表示紧接着下一个方法不是用and连接!(不调用or则默认为使用and连接) |
eq("id",1).or().eq("name","老王")--->id = 1 or name = '老王' |
| and() | `and(i -> i.eq(“name”, “李白”).ne(“status”, “活着”))—>and (name = ‘李白’ and status <> ‘活着’) |
9、代码生成器(新)
- 导入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidougroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-generatorartifactId>
<version>3.5.1version>
dependency>
- 编写代码生成的代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取项目的根目录
String projectPath = System.getProperty("user.dir");
System.out.println(projectPath);
// 代码生成
FastAutoGenerator.create("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mybatis_plus?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serveTimezone=UTC",
"root", "1234567")
.globalConfig(builder -> {
builder.author("xiaotanke") // 设置作者
.enableSwagger() // 开启 swagger 模式
// .fileOverride() // 覆盖已生成文件
.disableOpenDir() // 不打开资源管理器
.outputDir(projectPath); // 指定输出目录
})
.packageConfig(builder -> {
builder.parent("com.xiaotanke") // 设置父包名
.moduleName("system") // 设置父包模块名
.pathInfo(Collections.singletonMap(OutputFile.mapperXml, projectPath)); // 设置mapperXml生成路径
})
.strategyConfig(builder -> {
builder.addInclude("user") // 设置需要生成的表名
.addTablePrefix("t_", "c_"); // 设置过滤表前缀
})
.templateEngine(new FreemarkerTemplateEngine()) // 使用Freemarker引擎模板,默认的是Velocity引擎模板
.execute();
}