COVID-19 Cases Prediction (Regression)
目录
- Objectives:
- Task Description
- Data
- Data -- One-hot Vector
- Evaluation Metric
- Download data
- Import packages
- Some Utility Functions
- Dataset
- Neural Network Model
- Feature Selection
- Training Loop
- Configurations
- Dataloader
- Start training!
- Plot learning curves with `tensorboard` (optional)
- Testing
- Some optimization
- Reference
Objectives:
- Solve a regression problem with deep neural networks (DNN).
- Understand basic DNN training tips.
- Familiarize yourself with PyTorch.
Task Description
-
COVID-19 Cases Prediction
-
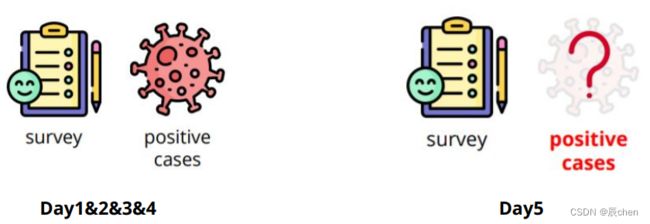
Source: Delphi group @ CMU
- A daily survey since April 2020 via facebook.
Try to find out the data and use it to your training is forbidden
- Given survey results in the past 5 days in a specific state in U.S., then predict the percentage of new tested positive cases in the 5th day.
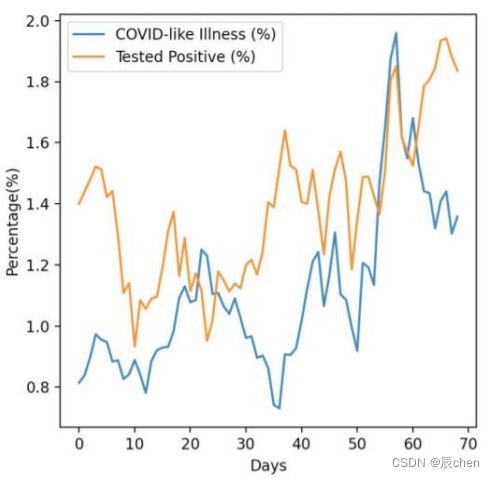
Data
Conducted surveys via facebook (every day & every state) Survey: symptoms, COVID-19 testing, social distancing, mental health, demographics, economic effects, …
- States (37, encoded to one-hot vectors)
- COVID-like illness (4)
- cli、ili …
- Behavior Indicators (8)
- wearing_mask、travel_outside_state …
- Mental Health Indicators (3)
- anxious、depressed …
- Tested Positive Cases (1)
- tested_positive (this is what we want to predict)
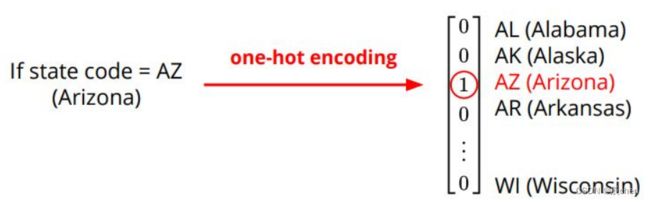
Data – One-hot Vector
- One-hot vectors:
Vectors with only one element equals to one while others are zero. Usually used to encode discrete values.
the details about One-hot Vector please read the blog:One-Hot
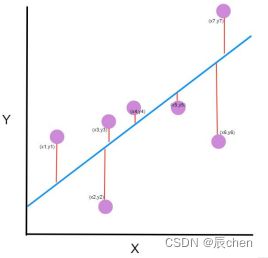
Evaluation Metric
- Mean Squared Error (MSE)
Download data
If the Google Drive links below do not work, you can download data from Kaggle, and upload data manually to the workspace.
!gdown --id '1kLSW_-cW2Huj7bh84YTdimGBOJaODiOS' --output covid.train.csv
!gdown --id '1iiI5qROrAhZn-o4FPqsE97bMzDEFvIdg' --output covid.test.csv
/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/gdown/cli.py:131: FutureWarning: Option `--id` was deprecated in version 4.3.1 and will be removed in 5.0. You don't need to pass it anymore to use a file ID.
category=FutureWarning,
Downloading...
From: https://drive.google.com/uc?id=1kLSW_-cW2Huj7bh84YTdimGBOJaODiOS
To: /content/covid.train.csv
100% 2.49M/2.49M [00:00<00:00, 238MB/s]
/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/gdown/cli.py:131: FutureWarning: Option `--id` was deprecated in version 4.3.1 and will be removed in 5.0. You don't need to pass it anymore to use a file ID.
category=FutureWarning,
Downloading...
From: https://drive.google.com/uc?id=1iiI5qROrAhZn-o4FPqsE97bMzDEFvIdg
To: /content/covid.test.csv
100% 993k/993k [00:00<00:00, 137MB/s]
Import packages
# Numerical Operations
import math
import numpy as np
# Reading/Writing Data
import pandas as pd
import os
import csv
# For Progress Bar
from tqdm import tqdm
# Pytorch
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader, random_split
# For plotting learning curve
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
Some Utility Functions
You do not need to modify this part.
def same_seed(seed):
'''Fixes random number generator seeds for reproducibility.'''
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
np.random.seed(seed)
torch.manual_seed(seed)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)
def train_valid_split(data_set, valid_ratio, seed):
'''Split provided training data into training set and validation set'''
valid_set_size = int(valid_ratio * len(data_set))
train_set_size = len(data_set) - valid_set_size
train_set, valid_set = random_split(data_set, [train_set_size, valid_set_size], generator=torch.Generator().manual_seed(seed))
return np.array(train_set), np.array(valid_set)
def predict(test_loader, model, device):
model.eval() # Set your model to evaluation mode.
preds = []
for x in tqdm(test_loader):
x = x.to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
pred = model(x)
preds.append(pred.detach().cpu())
preds = torch.cat(preds, dim=0).numpy()
return preds
Dataset
class COVID19Dataset(Dataset):
'''
x: Features.
y: Targets, if none, do prediction.
'''
def __init__(self, x, y=None):
if y is None:
self.y = y
else:
self.y = torch.FloatTensor(y)
self.x = torch.FloatTensor(x)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
if self.y is None:
return self.x[idx]
else:
return self.x[idx], self.y[idx]
def __len__(self):
return len(self.x)
Neural Network Model
Try out different model architectures by modifying the class below.
class My_Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim):
super(My_Model, self).__init__()
# TODO: modify model's structure, be aware of dimensions.
self.layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(input_dim, 16),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(16, 8),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(8, 1)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.layers(x)
x = x.squeeze(1) # (B, 1) -> (B)
return x
Feature Selection
Choose features you deem useful by modifying the function below.
def select_feat(train_data, valid_data, test_data, select_all=True):
'''Selects useful features to perform regression'''
y_train, y_valid = train_data[:,-1], valid_data[:,-1]
raw_x_train, raw_x_valid, raw_x_test = train_data[:,:-1], valid_data[:,:-1], test_data
if select_all:
feat_idx = list(range(raw_x_train.shape[1]))
else:
feat_idx = [0,1,2,3,4] # TODO: Select suitable feature columns.
return raw_x_train[:,feat_idx], raw_x_valid[:,feat_idx], raw_x_test[:,feat_idx], y_train, y_valid
Training Loop
def trainer(train_loader, valid_loader, model, config, device):
criterion = nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean') # Define your loss function, do not modify this.
# Define your optimization algorithm.
# TODO: Please check https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/optim.html to get more available algorithms.
# TODO: L2 regularization (optimizer(weight decay...) or implement by your self).
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=config['learning_rate'], momentum=0.9)
writer = SummaryWriter() # Writer of tensoboard.
if not os.path.isdir('./models'):
os.mkdir('./models') # Create directory of saving models.
n_epochs, best_loss, step, early_stop_count = config['n_epochs'], math.inf, 0, 0
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
model.train() # Set your model to train mode.
loss_record = []
# tqdm is a package to visualize your training progress.
train_pbar = tqdm(train_loader, position=0, leave=True)
for x, y in train_pbar:
optimizer.zero_grad() # Set gradient to zero.
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device) # Move your data to device.
pred = model(x)
loss = criterion(pred, y)
loss.backward() # Compute gradient(backpropagation).
optimizer.step() # Update parameters.
step += 1
loss_record.append(loss.detach().item())
# Display current epoch number and loss on tqdm progress bar.
train_pbar.set_description(f'Epoch [{epoch+1}/{n_epochs}]')
train_pbar.set_postfix({'loss': loss.detach().item()})
mean_train_loss = sum(loss_record)/len(loss_record)
writer.add_scalar('Loss/train', mean_train_loss, step)
model.eval() # Set your model to evaluation mode.
loss_record = []
for x, y in valid_loader:
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
pred = model(x)
loss = criterion(pred, y)
loss_record.append(loss.item())
mean_valid_loss = sum(loss_record)/len(loss_record)
print(f'Epoch [{epoch+1}/{n_epochs}]: Train loss: {mean_train_loss:.4f}, Valid loss: {mean_valid_loss:.4f}')
writer.add_scalar('Loss/valid', mean_valid_loss, step)
if mean_valid_loss < best_loss:
best_loss = mean_valid_loss
torch.save(model.state_dict(), config['save_path']) # Save your best model
print('Saving model with loss {:.3f}...'.format(best_loss))
early_stop_count = 0
else:
early_stop_count += 1
if early_stop_count >= config['early_stop']:
print('\nModel is not improving, so we halt the training session.')
return
Configurations
config contains hyper-parameters for training and the path to save your model.
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
config = {
'seed': 5201314, # Your seed number, you can pick your lucky number. :)
'select_all': True, # Whether to use all features.
'valid_ratio': 0.2, # validation_size = train_size * valid_ratio
'n_epochs': 3000, # Number of epochs.
'batch_size': 256,
'learning_rate': 1e-5,
'early_stop': 400, # If model has not improved for this many consecutive epochs, stop training.
'save_path': './models/model.ckpt' # Your model will be saved here.
}
Dataloader
Read data from files and set up training, validation, and testing sets. You do not need to modify this part.
# Set seed for reproducibility
same_seed(config['seed'])
# train_data size: 2699 x 118 (id + 37 states + 16 features x 5 days)
# test_data size: 1078 x 117 (without last day's positive rate)
train_data, test_data = pd.read_csv('./covid.train.csv').values, pd.read_csv('./covid.test.csv').values
train_data, valid_data = train_valid_split(train_data, config['valid_ratio'], config['seed'])
# Print out the data size.
print(f"""train_data size: {train_data.shape}
valid_data size: {valid_data.shape}
test_data size: {test_data.shape}""")
# Select features
x_train, x_valid, x_test, y_train, y_valid = select_feat(train_data, valid_data, test_data, config['select_all'])
# Print out the number of features.
print(f'number of features: {x_train.shape[1]}')
train_dataset, valid_dataset, test_dataset = COVID19Dataset(x_train, y_train), \
COVID19Dataset(x_valid, y_valid), \
COVID19Dataset(x_test)
# Pytorch data loader loads pytorch dataset into batches.
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=config['batch_size'], shuffle=True, pin_memory=True)
valid_loader = DataLoader(valid_dataset, batch_size=config['batch_size'], shuffle=True, pin_memory=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=config['batch_size'], shuffle=False, pin_memory=True)
Start training!
it may take lots of time(depends on GPU you drew),be sure stay front your computer or get some scripts or devices to make your screen stay light.
model = My_Model(input_dim=x_train.shape[1]).to(device) # put your model and data on the same computation device.
trainer(train_loader, valid_loader, model, config, device)
and if you never modify any above code,it may train 1883 times
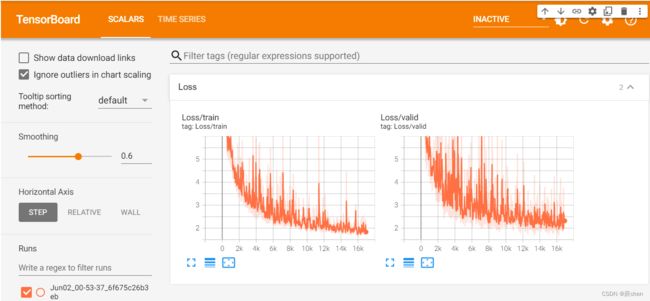
Plot learning curves with tensorboard (optional)
tensorboard is a tool that allows you to visualize your training progress.
If this block does not display your learning curve, please wait for few minutes, and re-run this block. It might take some time to load your logging information.
%reload_ext tensorboard
%tensorboard --logdir=./runs/
you will get a picture like this.
Testing
The predictions of your model on testing set will be stored at pred.csv.
def save_pred(preds, file):
''' Save predictions to specified file '''
with open(file, 'w') as fp:
writer = csv.writer(fp)
writer.writerow(['id', 'tested_positive'])
for i, p in enumerate(preds):
writer.writerow([i, p])
model = My_Model(input_dim=x_train.shape[1]).to(device)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(config['save_path']))
preds = predict(test_loader, model, device)
save_pred(preds, 'pred.csv')
100%|██████████| 5/5 [00:00<00:00, 554.88it/s]
after these cells,you will get a pred.csv in the files

you can download this doc and submit it in kaggle
and the kaggle will give you a score,if you never modify,you may have a low score like this:
Some optimization
if you work above code,you will pass the Simple Baseline. About how can pass Medium Baseline & Strong Baseline, i will try to give the answer in the future(maybe in 09/2022), teaching assistant gave some hints:
- 特征选择(Feature selection-what other features are useful?)
- DNN结构:层数,维度,激活函数(DNN construction-layers, dimension, activation function)
- 训练(training-mini batch, optimizer, leaning rate)
- L2 regularization
Reference
all the code was from HUNG-Yi LEE(李宏毅),you can study the 《MACHINE LEARNING 2022 SPRING》 in https://speech.ee.ntu.edu.tw/~hylee/ml/2022-spring.php
above all was my study note, if you have any suggestions, welcome to comment.