【李宏毅《机器学习》2022】作业1:COVID 19 Cases Prediction (Regression)
文章目录
- 【李宏毅《机器学习》2022】作业1:COVID 19 Cases Prediction (Regression)
-
- 作业内容
-
- 1.目标
- 2.任务描述
- 3.数据
- 4.评价指标
- 代码
-
- 1.下载数据
- 2.导入软件包
- 3.定义公用函数(这一部分不需要修改)
- 4.数据集
- 5.神经网络模型
- 6.特征选择
- 7.训练器
- 8.超参数设置
- 9.加载数据
- 10.开始训练
- 11.可视化训练过程
- 12.保存测试集结果
- 13.改进方案
-
- 13.1.选择更有效的特征
- 13.2.修改模型
- 13.3.修改优化器
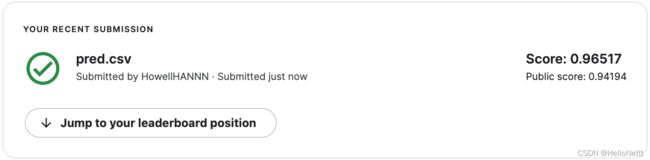
- 14. 测试结果
【李宏毅《机器学习》2022】作业1:COVID 19 Cases Prediction (Regression)
【作业1】来源
作业内容
1.目标
- Solve a regression problem with deep neural networks (DNN).
- Understand basic DNN training tips.
- Familiarize yourself with PyTorch.
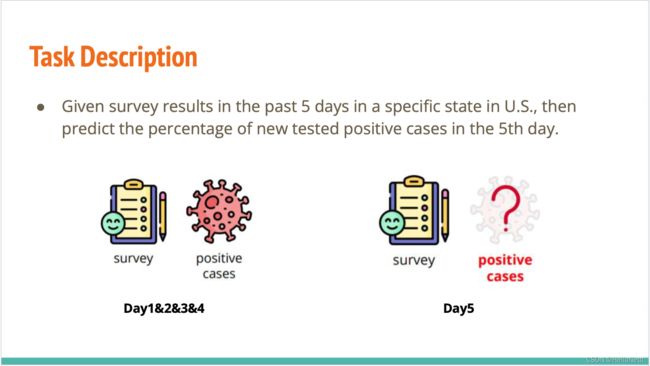
2.任务描述
Given survey results in the past 5 days in a specific state in U.S., then predict the percentage of new tested positive cases in the 5 th day.
3.数据
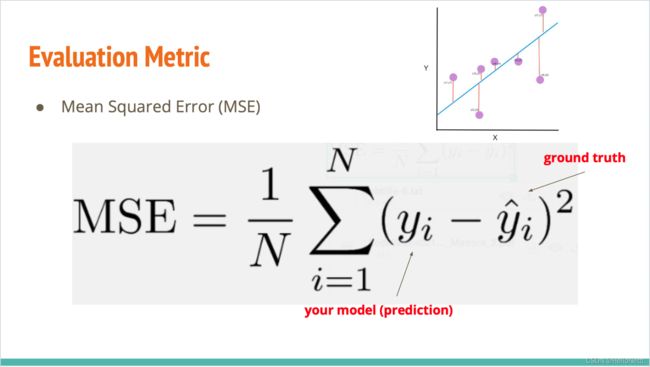
4.评价指标
代码
1.下载数据
!gdown --id '1kLSW_-cW2Huj7bh84YTdimGBOJaODiOS' --output covid.train.csv
!gdown --id '1iiI5qROrAhZn-o4FPqsE97bMzDEFvIdg' --output covid.test.csv
如果没有安装gdown(比如作者),可以采用按如下方法安装:
git clone https://github.com/wkentaro/gdown.git
cd gdown
pip install gdown
2.导入软件包
# Numerical Operations
import math
import numpy as np
# Reading/Writing Data
import pandas as pd#我一般喜欢用这个读入数据
import os
import csv
# For Progress Bar
from tqdm import tqdm
# Pytorch
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader, random_split
# For plotting learning curve
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
3.定义公用函数(这一部分不需要修改)
def same_seed(seed):
'''Fixes random number generator seeds for reproducibility.'''
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
np.random.seed(seed)
torch.manual_seed(seed)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)
#sklearn有一个包也可以实现train_valid_split和predict功能。
def train_valid_split(data_set, valid_ratio, seed):
'''Split provided training data into training set and validation set'''
valid_set_size = int(valid_ratio * len(data_set))
train_set_size = len(data_set) - valid_set_size
train_set, valid_set = random_split(data_set, [train_set_size, valid_set_size], generator=torch.Generator().manual_seed(seed))
return np.array(train_set), np.array(valid_set)
def predict(test_loader, model, device):
model.eval() # Set your model to evaluation mode.
preds = []
for x in tqdm(test_loader):
x = x.to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
pred = model(x)
preds.append(pred.detach().cpu())
preds = torch.cat(preds, dim=0).numpy()
return preds
scikit-learn是一个强大的机器学习软件包,其使用方法可以参考sklearn中文文档。
4.数据集
class COVID19Dataset(Dataset):
'''
x: Features.
y: Targets, if none, do prediction.
'''
def __init__(self, x, y=None):
if y is None:
self.y = y
else:
self.y = torch.FloatTensor(y)
self.x = torch.FloatTensor(x)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
if self.y is None:
return self.x[idx]
else:
return self.x[idx], self.y[idx]
def __len__(self):
return len(self.x)
5.神经网络模型
通过修改下面的类来尝试不同的模型。
class My_Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim):
super(My_Model, self).__init__()
# TODO: modify model's structure, be aware of dimensions.
#一个简单的三层全链接层的神经网络模型
self.layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(input_dim, 16),#全连接层
nn.ReLU(),#激活函数
nn.Linear(16, 8),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(8, 1)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.layers(x)
x = x.squeeze(1) # (B, 1) -> (B)
return x
可以参考torch.nn
PyTorch的torch.nn.Linear()是用于设置网络中的全连接层的,需要注意在二维图像处理的任务中,全连接层的输入与输出一般都设置为二维张量,形状通常为[batch_size, size],不同于卷积层要求输入输出是四维张量。

6.特征选择
通过修改下面的函数,选择更有用的特征。
def select_feat(train_data, valid_data, test_data, select_all=True):
'''Selects useful features to perform regression'''
y_train, y_valid = train_data[:,-1], valid_data[:,-1]
raw_x_train, raw_x_valid, raw_x_test = train_data[:,:-1], valid_data[:,:-1], test_data
if select_all:
feat_idx = list(range(raw_x_train.shape[1]))
else:
feat_idx = [0,1,2,3,4] # TODO: Select suitable feature columns.
return raw_x_train[:,feat_idx], raw_x_valid[:,feat_idx], raw_x_test[:,feat_idx], y_train, y_valid
7.训练器
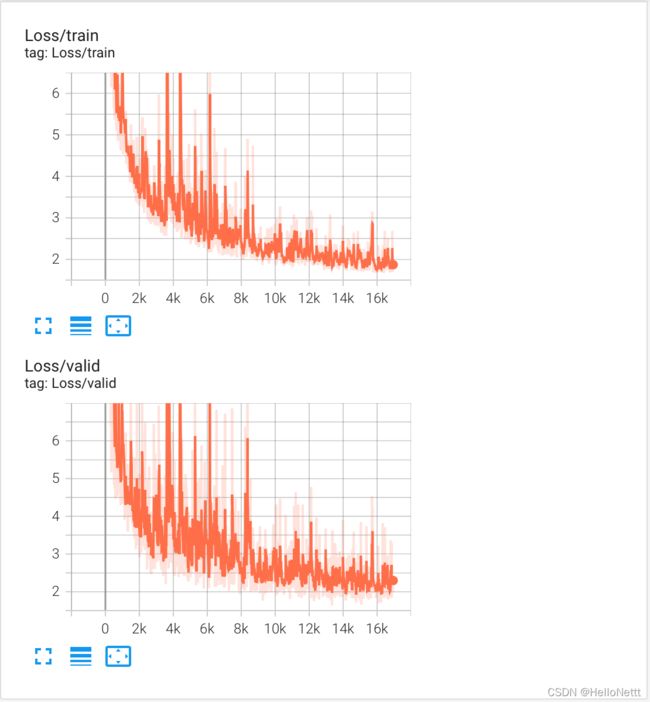
训练阶段创建模型的实例并进行迭代时训练。注意每次迭代都需要保存模型。训练结束后,对模型Loss随迭代次数的变化进行可视化,用于选取更合适的迭代次数。
def trainer(train_loader, valid_loader, model, config, device):
criterion = nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean') # Define your loss function, do not modify this.
# Define your optimization algorithm.
# TODO: Please check https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/optim.html to get more available algorithms.
# TODO: L2 regularization (optimizer(weight decay...) or implement by your self).
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=config['learning_rate'], momentum=0.9)
#训练过程可视化器
writer = SummaryWriter() # Writer of tensoboard.
#创建保存model的路径,每次迭代都需要保存model
if not os.path.isdir('./models'):
os.mkdir('./models') # Create directory of saving models.
n_epochs, best_loss, step, early_stop_count = config['n_epochs'], math.inf, 0, 0
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
model.train() # Set your model to train mode.
loss_record = []
# tqdm is a package to visualize your training progress.
train_pbar = tqdm(train_loader, position=0, leave=True)
for x, y in train_pbar:
optimizer.zero_grad() # Set gradient to zero.
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device) # Move your data to device.
pred = model(x)
loss = criterion(pred, y)
loss.backward() # Compute gradient(backpropagation).
optimizer.step() # Update parameters.
step += 1
loss_record.append(loss.detach().item())
# Display current epoch number and loss on tqdm progress bar.
train_pbar.set_description(f'Epoch [{epoch+1}/{n_epochs}]')
train_pbar.set_postfix({'loss': loss.detach().item()})
mean_train_loss = sum(loss_record)/len(loss_record)
writer.add_scalar('Loss/train', mean_train_loss, step)
# 在验证集上进行模型准确率的分析验证。
model.eval() # Set your model to evaluation mode.
loss_record = []
for x, y in valid_loader:
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
pred = model(x)
loss = criterion(pred, y)
loss_record.append(loss.item())
mean_valid_loss = sum(loss_record)/len(loss_record)
print(f'Epoch [{epoch+1}/{n_epochs}]: Train loss: {mean_train_loss:.4f}, Valid loss: {mean_valid_loss:.4f}')
writer.add_scalar('Loss/valid', mean_valid_loss, step)
if mean_valid_loss < best_loss:#如果当前loss低于过去最低的loss,则记录loss,并保存当前最好的模型。
best_loss = mean_valid_loss
torch.save(model.state_dict(), config['save_path']) # Save your best model
print('Saving model with loss {:.3f}...'.format(best_loss))
early_stop_count = 0
else:
early_stop_count += 1
if early_stop_count >= config['early_stop']:
print('\nModel is not improving, so we halt the training session.')
return
8.超参数设置
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
config = {
'seed': 5201314, # 制定模型的随即种子以保证模型的可恢复性。Your seed number, you can pick your lucky number. :)
'select_all': True, # Whether to use all features.
'valid_ratio': 0.2, # validation_size = train_size * valid_ratio
'n_epochs': 3000, # Number of epochs.
'batch_size': 256,
'learning_rate': 1e-5,
'early_stop': 400, # If model has not improved for this many consecutive epochs, stop training. 任一时刻连续400次没有模型训练降低loss,就会提前停止。
'save_path': './models/model.ckpt' # Your model will be saved here.
}
9.加载数据
# Set seed for reproducibility
same_seed(config['seed'])
# train_data size: 2699 x 118 (id + 37 states + 16 features x 5 days)
# test_data size: 1078 x 117 (without last day's positive rate)
train_data, test_data = pd.read_csv('./covid.train.csv').values, pd.read_csv('./covid.test.csv').values
train_data, valid_data = train_valid_split(train_data, config['valid_ratio'], config['seed'])# 按照k折交叉验证法分成训练集和验证集
# Print out the data size.
print(f"""train_data size: {train_data.shape}
valid_data size: {valid_data.shape}
test_data size: {test_data.shape}""")
# Select features
x_train, x_valid, x_test, y_train, y_valid = select_feat(train_data, valid_data, test_data, config['select_all'])
# Print out the number of features.
print(f'number of features: {x_train.shape[1]}')
train_dataset, valid_dataset, test_dataset = COVID19Dataset(x_train, y_train), \
COVID19Dataset(x_valid, y_valid), \
COVID19Dataset(x_test)
# 用统一的Pytorch加载器包装待处理数据 Pytorch data loader loads pytorch dataset into batches.
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=config['batch_size'], shuffle=True, pin_memory=True)
valid_loader = DataLoader(valid_dataset, batch_size=config['batch_size'], shuffle=True, pin_memory=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=config['batch_size'], shuffle=False, pin_memory=True)
10.开始训练
model = My_Model(input_dim=x_train.shape[1]).to(device) # put your model and data on the same computation device.
trainer(train_loader, valid_loader, model, config, device)
11.可视化训练过程
tensorboard 是一个可视化训练过程的工具。
%reload_ext tensorboard
%tensorboard --logdir=./runs/
12.保存测试集结果
输出保存测试集的结果,并在Kaggle上查看模型得分。
def save_pred(preds, file):
''' Save predictions to specified file '''
with open(file, 'w') as fp:
writer = csv.writer(fp)
writer.writerow(['id', 'tested_positive'])
for i, p in enumerate(preds):
writer.writerow([i, p])
model = My_Model(input_dim=x_train.shape[1]).to(device)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(config['save_path']))#加载你保存好的best model
preds = predict(test_loader, model, device)
save_pred(preds, 'pred.csv')
可以看考state_dict和load_state_dict
13.改进方案
运行上述程序,即可通过simple_baseline。
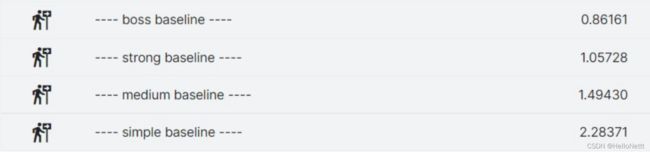
但还不能通过medium_baseline,而我们的目标是boss_baseline,因此需要修改方案。
13.1.选择更有效的特征
首先,我们观察一下数据内部。
df = pd.read_csv('./covid.train.csv')
#df.head()
df.describe()
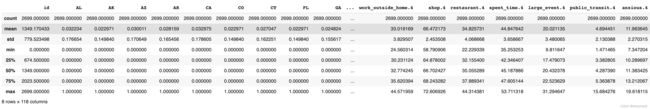
共有2699个data,117个feature,1个label。
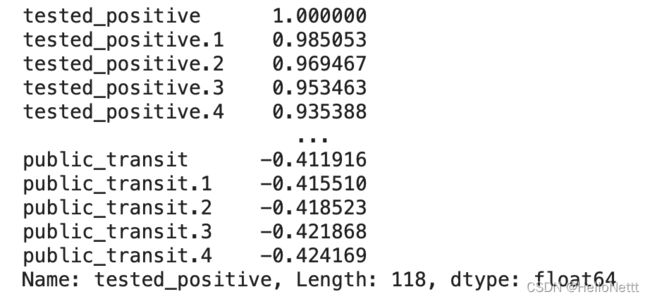
我们利用Pearson相关系数分析不同feature与label的相关性强弱。
df.corr()['tested_positive'].sort_values(ascending=False)
def select_feat(train_data, valid_data, test_data, select_all=True):
'''Selects useful features to perform regression'''
y_train, y_valid = train_data[:,-1], valid_data[:,-1]
raw_x_train, raw_x_valid, raw_x_test = train_data[:,:-1], valid_data[:,:-1], test_data
if select_all:
feat_idx = list(range(raw_x_train.shape[1]))
else:
feat_idx = list(range(38))+[53, 69, 85, 101] # TODO: Select suitable feature columns.
return raw_x_train[:,feat_idx], raw_x_valid[:,feat_idx], raw_x_test[:,feat_idx], y_train, y_valid
这时,我们要把参数设置中的select_all设置为False。此外,我们还要减小batch_size,这样可以避免训练中梯度在极小值点附近被捕捉。同时,小batch_size好处还有减少一次训练的数据量,降低网络负载,也加快网络的收敛速度。
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
config = {
'seed': 5201314, # Your seed number, you can pick your lucky number. :)
'select_all': False, # Whether to use all features.
'valid_ratio': 0.2, # validation_size = train_size * valid_ratio
'n_epochs': 3000, # Number of epochs.
'batch_size': 100,
'learning_rate': 1e-5,
'early_stop': 400, # If model has not improved for this many consecutive epochs, stop training.
'save_path': './models/model.ckpt' # Your model will be saved here.
}
13.2.修改模型
首先,我们很容易想到的方法是:加深神经网络的层数。但是这个问题本身足够简单,数据量也不大,所以不能带来明显提升。
为了防止过拟合,引入L2正则化项可以通过给loss增加模型惩罚项使模型的结构化风险最小。
class NN_Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim):
super(NN_Model, self).__init__()
# TODO: modify model's structure, be aware of dimensions.
self.layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(input_dim, 16),
nn.BatchNorm1d(16),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.1),
nn.Linear(16, 1)
nn.BatchNorm1d(8),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.1),
nn.Linear(8,1)
)
self.criterion = nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean')
#self.criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.layers(x)
x = x.squeeze(1) # (B, 1) -> (B)
return x
#添加L2正则项
def regularization(self, coef):
item = 0
for param in self.net.parameters():
item += torch.norm(param,2)
res = coef*item
return res
def cal_loss(self,pred,target):
#RMSE+L2 regularization
loss = torch.sqrt(self.criterion(pred, target)) + self.regularization(0)
return loss
return loss
其中,torch.nn.Dropout(num)是一种为了防止训练模型过拟合的方法。通过丢弃num比例的隐藏层神经元,不参与训练,可以有效的防止过拟合。
torch.nn.BatchNorm1d()是为了保持深度神经网络训练过程中每一层神经网络的输入同分布的方法。训练深度网络的时候经常发生训练困难的问题:因为,每一次参数迭代更新后,上一层网络的输出数据经过这一层网络计算后,数据的分布会发生变化,为下一层网络的学习带来困难,这被称为Internal Covariate Shift。为了解决Internal Covariate Shift,我们使用Batch Normalization。
torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(num_features, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
num_features– 特征维度eps– 为数值稳定性而加到分母上的值。momentum– 移动平均的动量值。affine– 一个布尔值,当设置为真时,此模块具有可学习的仿射参数。
13.3.修改优化器
经过测试,使用AdamW优化器效果最佳,其数学原理:
grad = decay-rate ∗ grad + ( 1 − decay-rate ) ∗ d x 2 \text { grad = decay-{rate} } * \text { grad }+(1-\text { decay-{rate} }) * d x^{2} grad = decay-rate ∗ grad +(1− decay-rate )∗dx2
优化器的参数设置。
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=config['learning_rate'], weight_decay=0.08)