Authors: Gita Das & Catherine Lopes
作者:Gita Das和Catherine Lopes
In the past eight months since January 2020, COVID-19 has made the entire world upside down; and different types of measures are used by countries and governments to flatten the curve.
自2020年1月以来的过去8个月中,COVID-19使整个世界颠倒了。 各国和政府采用了不同类型的措施来使曲线变平。
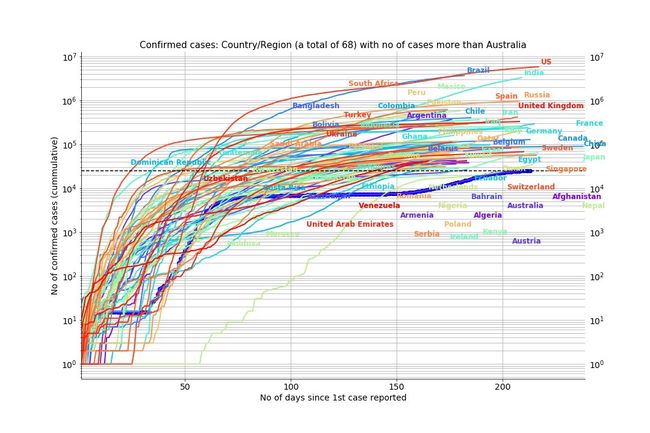
In our previous article we studied the countries which had more confirmed cases (cumulative) than Australia, and it was very clear that the earlier the measures were introduced, the more impact they had in controlling the spread of the disease. As of 28th Aug, 2020, there are 68 countries having more confirmed cumulative cases than Australia as illustrated in Fig 1 below.
在我们之前的文章中,我们研究了确诊病例(累计)比澳大利亚多的国家,很清楚地发现,尽早采取这些措施,对控制疾病传播的影响更大。 如下图1所示,截至2020年8月28日,已有68个国家的确诊病例超过澳大利亚。
Fig 1: 68 countries with more confirmed (cumulative) cases than in Australia 图1:68个确诊(累积)病例多于澳大利亚的国家本研究中的数据和国家(Data & countries in this study)
We used the following two datasets from the Humanitarian Data Exchange (HDE) in this study. One dataset contains the number of people affected by COVID-19 world wide, another dataset tracks the imposed measures obtained by HDE. Among the 69 countries including Australia, two were excluded due to absence of measures data, so a total 67 countries with 33 measures were used in this study and the list of measures is:
在本研究中,我们使用了来自人道主义数据交换(HDE)的以下两个数据集。 一个数据集包含全球受COVID-19影响的人数,另一个数据集跟踪HDE获得的强制措施。 在包括澳大利亚在内的69个国家中,由于缺少措施数据而被排除在两个国家之外,因此本研究使用了总共33个措施的67个国家,措施清单为:
'Additional health/documents requirements upon arrival', 'Amendments to funeral and burial regulations', 'Awareness campaigns', 'Border checks', 'Border closure', 'Changes in prison-related policies', 'Checkpoints within the country', 'Closure of businesses and public services', 'Curfews', 'Domestic travel restrictions', 'Economic measures', 'Emergency administrative structures activated or established', 'Full lockdown', 'General recommendations', 'Health screenings in airports and border crossings', 'Humanitarian exemptions', 'International flights suspension', 'Isolation and quarantine policies', 'Limit product imports/exports', 'Limit public gatherings', 'Lockdown of refugee/idp camps or other minorities', 'Mass population testing', 'Military deployment', 'Other public health measures enforced', 'Partial lockdown', 'Psychological assistance and medical social work', 'Requirement to wear protective gear in public', 'Schools closure', 'State of emergency declared', 'Strengthening the public health system', 'Surveillance and monitoring', 'Testing policy', 'Visa restrictions'The 33 measures are scaled to [0,1] based on the timing of each specific measure used by a country. From the day of the 1st case reported in a country, if a measure was not used, then the measure is recorded as 0. The earlier a measure was introduced by a country, the higher is the value (closer to 1) for that specific measure.
根据一个国家使用每种特定措施的时间,将33种措施缩放为[0,1]。 从某个国家/地区报告的第一个案例的日期开始,如果未使用度量,则该度量记录为0。一个国家/地区采用的度量值越早,该特定值的值就越高(接近1)。测量。
In order to measure the effectiveness with the timing of each measure that was used by different countries, these countries are broadly categorised into three types:
为了按照不同国家/地区采用的每项措施的时间来衡量有效性,这些国家大致分为三类:
- Type A countries have their number of cases still growing and have not reached their peak yet. For example, Argentina as shown in Fig 2 (left). A类国家的案件数量仍在增长,尚未达到顶峰。 例如,阿根廷如图2所示(左)。
- Type B countries have reached their peak and the curve is going down. For example, Afghanistan as shown in Fig 2 (middle). B类国家已达到顶峰,曲线呈下降趋势。 例如,阿富汗如图2所示(中)。
- Type C countries have gone past the first wave and peaked their second wave, the second wave could be lower or higher than the first one such as Australia as in Fig 2 (right). C型国家已经超越了第一波,并达到了第二波的顶峰,第二波可能低于或高于第一波,例如图2中的澳大利亚(右图)。
To estimate the effectiveness of the measures in relation to the reduction of the daily cases, we used a derived variable “reduction percentage” that is computed by finding the difference from the peak and the valley based on a 30-day rolling average of daily curves. The 30-day rolling range was chosen to avoid too many local max and local min. For type A countries, the reduction percentage is 0 because they have not reached their peak yet in the first curve. For type B, the reduction percentage is calculated based on the reduction from the peak value to the latest day because they have not started their second curve yet. For example, it is calculated as 90% for Afghanistan. With type C countries that are experiencing their second wave, the reduction percentage is the reduction from the first peak to the first lowest valley before the second wave. Given that measures can be stopped and re-imposed, it is difficult to incorporate the exact dates of withdrawing and re-imposing measures. Hence we only used the reduction value related to the first wave. Australia has a 95% reduction percentage even though it is in the process of flattening second wave.
为了评估与减少每日病例有关的措施的有效性,我们使用了派生变量“减少百分比”,该变量是通过根据30天的每日曲线滚动平均值找到与峰谷之间的差异来计算的。 选择30天滚动范围是为了避免过多的局部最大值和局部最小值。 对于A类国家,减排百分比为0,因为它们在第一条曲线中尚未达到峰值。 对于类型B,由于他们尚未开始第二条曲线,所以根据从峰值到最近一天的减少量来计算减少量百分比。 例如,对于阿富汗,计算得出为90%。 对于正在经历第二次浪潮的C型国家,减少百分比是从第二次浪潮之前的第一个高峰到第一个最低谷的减少。 鉴于可以停止采取措施并重新采取措施,很难纳入撤回和采取措施的确切日期。 因此,我们仅使用与第一波有关的减少值。 即使澳大利亚正在减缓第二波浪潮,澳大利亚的减排率仍达到95%。
衡量所采取措施的有效性的功能重要性 (Feature importance to measure the effectiveness of imposed measures)
We used three regression algorithms to measure the features importance with Linear regression as the baseline. The matrix is composed with all countries listed in this study and 33 measures with 1 target variable that is the reduction percentage as described above. The 3 algorithms used are:
我们使用三种回归算法以线性回归为基准来衡量特征重要性。 该矩阵由本研究中列出的所有国家和33个带有1个目标变量(即减排百分比)的指标组成。 使用的3种算法是:
- Lasso: 套索:
Linear Regression is the simplest and most widely used statistical technique for predictive modelling where we have a number of input variables and one target variable. In Lasso both
variable selection and regularisation (L1-type) are used to achieve better prediction accuracy.- XGBoost (with and without hyperparameters tuning): XGBoost(带有和不带有超参数调整):
XGBoost is a decision-tree-based ensemble machine learning algorithm that is known for its speed and performance. By tuning the hyper-parameters of the model, we can achieve better prediction accuracy.- LightGBM (with default parameters): LightGBM(具有默认参数):
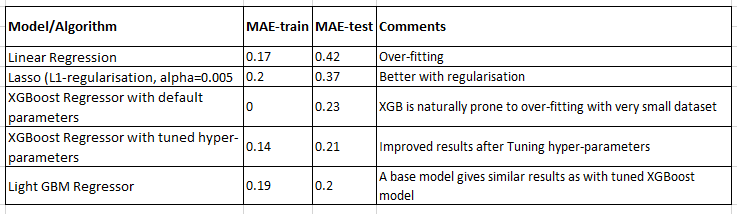
LightGBM is relatively new in the market that uses similar implementation to XGBoost but with a little different tree structure. It is faster in training time.Both XGBoost with hyperparameters tuning and LightGBM with default parameters) produced very similar results. The data set is split into train (80%) and test data (20%) and test error greater than train error indicates an over-fitting. Minimum Absolute Error (MAE) is used to evaluate the model performance in both training and testing sets. The results are shown in Table 1 below.
具有超参数调整功能的XGBoost和具有默认参数的LightGBM两者都产生了非常相似的结果。 数据集分为火车(80%)和测试数据(20%),并且测试误差大于火车误差表示拟合过度。 最小绝对误差(MAE)用于评估训练和测试集中的模型性能。 结果示于下表1。
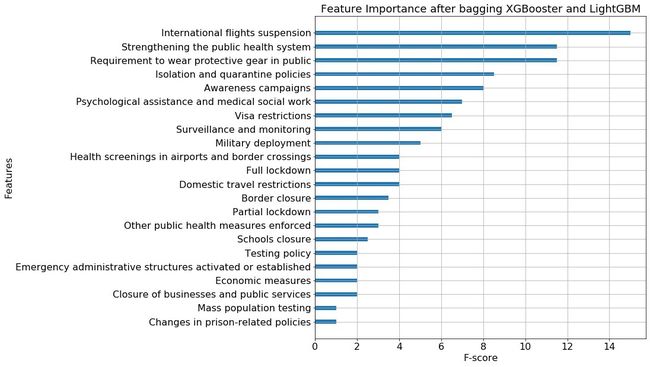
Table 1: 3 Comparison of 3 models of their MAE with Linear regression baseline 表1:3种MAE模型与线性回归基线的比较Out of 33 measures, we bagged the features importance with a positive F-score based on the average from XGBoost and LightGBM. The features importance ranked from high to low are shown in Fig 3 below.
在33个度量中,我们根据XGBoost和LightGBM的平均值将正F分数归为特征重要性。 重要性特征从高到低排列如下图3所示。
Fig 3: Top ranked features with high feature importance 图3:具有较高功能重要性的排名最高的功能哪些措施比其他措施更有效?(What measures are more effective than others?)
Based on the results from our bagged model, it is clear that:
根据我们袋装模型的结果,很明显:
1号。国际航班暂停 (No 1. International flights suspension)
image credit: freepik 图片来源:freepikis ranked first indicating as the most effective measure in controlling the spread of infection. This is in line with many epidemiologists’ view that stopping international flights especially from the epicentre early on is crucial in controlling the COVID-19. This measure has been effectively used by many countries with success.
排名第一,表明它是控制感染扩散的最有效措施。 这与许多流行病学家的观点是一致的,即特别是从震中尽早停止国际航班对于控制COVID-19至关重要。 许多国家都成功地有效使用了该措施。
No. 2在公共场所穿戴防护装备和加强公共卫生系统的R设备 (No 2. Requirement to wear protective gear in public & Strengthening the public health system)
image credit: freepik 图片来源:freepikare ranked as second. A good public healthcare system can help to detect and support recovery of the infected patients; and masks wearing in public is effective against spreading the disease. This is evident in most of the Asian countries which have controlled the COVID-19 spread.
排名第二。 良好的公共医疗体系可以帮助发现并支持感染患者的康复; 在公共场合戴口罩可有效防止疾病传播。 在大多数控制COVID-19传播的亚洲国家中,这是显而易见的。
否3.隔离和检疫政策与宣传运动 (No 3. Isolation and quarantine policies & awareness campaigns)
image credit: freepik 图片来源:freepikcome third on the list in terms of effectiveness. This verifies that isolation and contact tracing are extremely important to contain the disease in the community, and many countries have seen the evidence in the result of suppression of the curve.
在有效性方面排名第三。 这证明隔离和接触者追踪对于控制社区内的疾病极为重要,许多国家已经看到了抑制曲线结果的证据。
Interestingly measures such as full lock down, border closure, school closure & testing policy are not ranked as highly effective as the measures discussed above. To summarise our study with the data from 67 countries with 33 different types of measures, we find that:
有趣的是,诸如全面封锁,边境关闭,学校关闭和考试政策之类的措施没有像上述措施那样有效。 用来自33个不同类型的衡量指标的67个国家的数据总结我们的研究,我们发现:
“international flights, wearing masks and quarantine are the most effective measures”
“国际航班,戴口罩和隔离是最有效的措施”
Feel free to access the GitHub repo, and we welcome your feedback and comments.
随时访问GitHub存储库,我们欢迎您的反馈和评论。
翻译自: https://towardsdatascience.com/which-measures-are-more-effective-in-controlling-covid-19-f85cf0951b2b