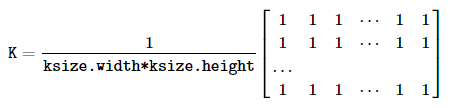常见的图像滤波方法
0 前言
图像滤波,即在尽量保留图像细节特征的条件下对目标图像的噪声进行抑制,是图像预处理中不可缺少的操作,其处理效果的好坏将直接影响到后续图像处理和分析的有效性和可靠性。
参考文章:
cv2.blur图像滤波(Filter)处理学习笔记_AI算法联盟-CSDN博客
常见的图像滤波算法_weixin_30413739的博客-CSDN博客
图像处理(12)--图像各种噪声及消除方法_ShaneHolmes-CSDN博客_图像噪声
1.常见的图像滤波方式
2.线性滤波
线性滤波原理:每个像素的输出值是输入像素的加权和。
(1)均值滤波
图片中一个方块区域(一般为3*3)内,中心点的像素为全部点像素值的平均值。均值滤波就是对于整张图片进行以上操作。
缺陷:均值滤波本身存在着固有的缺陷,即它不能很好地保护图像细节,在图像去噪的同时也破坏了图像的细节部分,从而使图像变得模糊,不能很好地去除噪声点。特别是椒盐噪声
函数接口:
cv.blur(
src,
ksize[,dst[,anchor[,borderType]]]
)
->dst参考官方手册:OpenCV: Image Filtering
参数说明:
src input image; it can have any number of channels, which are processed independently, but the depth should be CV_8U, CV_16U, CV_16S, CV_32F or CV_64F. dst output image of the same size and type as src. ksize blurring kernel size. anchor anchor point; default value Point(-1,-1) means that the anchor is at the kernel center. borderType border mode used to extrapolate pixels outside of the image, see BorderTypes. BORDER_WRAP is not supported.
取卷积核(Kernel)区域下所有像素的平均值并替换中心元素,如下公式:
3*3的卷积核参考:
![]()
均值滤波在图像去噪的同时也破坏了图像的细节部分,从而使图像变得模糊。
(2)方框滤波
函数接口:
cv.boxFilter(
src,
ddepth,
ksize[, dst[, anchor[, normalize[, borderType]]]]
)
->dst
参考官方手册:OpenCV: Image Filtering
参数说明:
src input image. dst output image of the same size and type as src. ddepth the output image depth (-1 to use src.depth()). ksize blurring kernel size. anchor anchor point; default value Point(-1,-1) means that the anchor is at the kernel center. normalize flag, specifying whether the kernel is normalized by its area or not. borderType border mode used to extrapolate pixels outside of the image, see BorderTypes. BORDER_WRAP is not supported.
当normalize=True时,与均值滤波结果相同;
normalize=False,表示对加和后的结果不进行平均操作,大于255的使用255表示。
(3)高斯滤波
函数接口:
cv.GaussianBlur(
src,
ksize,
sigmaX[, dst[, sigmaY[, borderType]]]
)
->dst
参考官方手册:OpenCV: Image Filtering
参数说明:
src
input image; the image can have any number of channels, which are processed independently, but the depth should be CV_8U, CV_16U, CV_16S, CV_32F or CV_64F. dst output image of the same size and type as src. ksize Gaussian kernel size. ksize.width and ksize.height can differ but they both must be positive and odd. Or, they can be zero's and then they are computed from sigma. sigmaX Gaussian kernel standard deviation in X direction. sigmaY Gaussian kernel standard deviation in Y direction; if sigmaY is zero, it is set to be equal to sigmaX, if both sigmas are zeros, they are computed from ksize.width and ksize.height, respectively (see getGaussianKernel for details); to fully control the result regardless of possible future modifications of all this semantics, it is recommended to specify all of ksize, sigmaX, and sigmaY. borderType pixel extrapolation method, see BorderTypes. BORDER_WRAP is not supported.
3.非线性滤波
(1)中值滤波
用像素点邻域灰度值的中值来代替该像素点的灰度值。
函数接口:
cv.medianBlur(
src,
ksize[, dst]
)
->dst
参考官方手册:OpenCV: Image Filtering
参数说明:
src input 1-, 3-, or 4-channel image; when ksize is 3 or 5, the image depth should be CV_8U, CV_16U, or CV_32F, for larger aperture sizes, it can only be CV_8U. dst destination array of the same size and type as src. ksize aperture linear size; it must be odd and greater than 1, for example: 3, 5, 7 ...
(2)双边滤波
结合图像的空间邻近度和像素值相似度的一种折衷处理,同时考虑空间与信息和灰度相似性,达到保边去噪的目的。
函数接口:
cv.bilateralFilter(
src,
d,
sigmaColor,
sigmaSpace[, dst[, borderType]]
)
->dst
参考官方手册:OpenCV: Image Filtering
参数说明:
src Source 8-bit or floating-point, 1-channel or 3-channel image. dst Destination image of the same size and type as src . d Diameter of each pixel neighborhood that is used during filtering. If it is non-positive, it is computed from sigmaSpace. sigmaColor Filter sigma in the color space. A larger value of the parameter means that farther colors within the pixel neighborhood (see sigmaSpace) will be mixed together, resulting in larger areas of semi-equal color. sigmaSpace Filter sigma in the coordinate space. A larger value of the parameter means that farther pixels will influence each other as long as their colors are close enough (see sigmaColor ). When d>0, it specifies the neighborhood size regardless of sigmaSpace. Otherwise, d is proportional to sigmaSpace. borderType border mode used to extrapolate pixels outside of the image, see BorderTypes
测试代码:
import cv2
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 彩色照片
img_bgr = cv2.imread(r'C:\Users\Nobody\Desktop\filter.png', 1)
cv2.imshow('img_bgr',img_bgr)
# 均值滤波
img_blur=cv2.blur(img_bgr,(3,3))
cv2.imshow('blur', img_blur)
# 方框滤波
img_boxFilter1 = cv2.boxFilter(img_bgr, -1, (3, 3), normalize=True)
cv2.imshow('oxFilter1', img_boxFilter1)
img_boxFilter2 = cv2.boxFilter(img_bgr, -1, (3, 3), normalize=False)
cv2.imshow('boxFilter2', img_boxFilter2)
# 高斯滤波
img_GaussianBlur= cv2.GaussianBlur(img_bgr, (3, 3), 0, 0)
cv2.imshow('GaussianBlur', img_GaussianBlur)
# 中值滤波
img_medianBlur = cv2.medianBlur(img_bgr, 3)
cv2.imshow('medianBlur', img_medianBlur)
# 双边滤波
img_bilateralFilter=cv2.bilateralFilter(img_bgr,50,100,100)
cv2.imshow('bilateralFilter', img_bilateralFilter)结果输出:
以上5种方法中,滤波效果较好的是中值滤波,这有点像平均工资和中位数工资比较时,中位数工资更复合现实情况。