机器学习——决策树(ID3)的实现
相关定义的补充:
熵
在信息论与概率统计中,熵(entropy)是表示随机变量不确定性的度量。设 X X X是一个取有限个值的离散随机变量,其概率分布为: P ( X = x i ) = p i , i = 1 , 2 , ⋯ , n P(X=x_i)=p_i,i=1,2,\cdots ,n P(X=xi)=pi,i=1,2,⋯,n,则随机变量 X X X的熵定义为:
H ( X ) = − ∑ i = 1 n p i l o g p i , ( 其 中 , 对 数 以 2 为 底 或 e 为 底 ) H(X)=-\sum\limits_{i=1}^np_i\ log\ p_i,(其中,对数以2为底或e为底) H(X)=−i=1∑npi log pi,(其中,对数以2为底或e为底)
熵的单位分别称做比特(bit)或纳特(nat)。熵越大,随机变量的不确定性就越大。
条件熵
条件熵(conditional entropy) H ( Y ∣ X ) H(Y|X) H(Y∣X)表示在已知随机变量 X X X的条件下随机变量 Y Y Y的不确定性,定义为 X X X给定条件下 Y Y Y的条件概率分布的熵对 X X X的数学期望:
H ( Y ∣ X ) = ∑ i = 1 n p i H ( Y ∣ X = x i ) , ( 其 中 , p i = P ( X = x i ) , i = 1 , 2 , ⋯ , n . ) H(Y|X)=\sum\limits_{i=1}^np_iH(Y|X=x_i),(其中,p_i=P(X=x_i),i=1,2,\cdots,n.) H(Y∣X)=i=1∑npiH(Y∣X=xi),(其中,pi=P(X=xi),i=1,2,⋯,n.)
信息增益
信息增益(information gain)表示得知特征 X X X的信息而使得类 Y Y Y的信息的不确定性减少的程度。特征 A A A对训练数据集 D D D的信息增益 g ( D , A ) g(D,A) g(D,A),定义为集合 D D D的信息熵 H ( D ) H(D) H(D)与特征 A A A给定条件下 D D D的经验条件熵 H ( D ∣ A ) H(D|A) H(D∣A)之差,即:
g ( D , A ) = H ( D ) − H ( D ∣ A ) g(D,A)=H(D)-H(D|A) g(D,A)=H(D)−H(D∣A)
对于数据集 D D D而言,信息增益依赖于特征,不同的特征往往具有不同的信息增益。信息增益大的特征具有更强的分类能力。
信息增益准则选择特征的方法:对训练数据集 D D D,计算其每个特征的信息增益,并比较他们的大小,选择信息增益最大的特征。
ID3算法的核心是在决策树各个结点上应用信息增益准则选择特征,递归的构建决策树。
构建过程:从根结点出发,对结点计算所有特征的信息增益,选择信息增益最大的特征作为结点的特征,由该特征的不同取值建立子结点;再对子结点递归调用以上方法,直到所有特征信息增益均很小或没有特征可以选择为止。
相关数据的定义:
public class ID3 {
/**
* The data set.
*/
Instances dataset;
/**
* Is this data set pure (only one label)?
*/
boolean pure;
/**
* The number of classes. For binary classification it is 2.
*/
int numClasses;
/**
* Available instances. Other instances do not belong this branch.
*/
int[] availableInstances;
/**
* Available attributes. Other attributes have been selected in the path from
* root.
*/
int[] availableAttributes;
/**
* The selected attribute.
*/
int splitAttribute;
/**
* The children nodes.
*/
ID3[] children;
/**
* The label. Inner nodes also have a label. For example, never appear in the training data, but is
* valid in other cases.
*/
int label;
/**
* The prediction,including queried and predicted labels.
*/
int[] predicts;
/**
* Small block cannot be split further.
*/
static int smallBlockThreshold = 3;
第一个构造函数,当读文件初始化数据的时候调用:
/**
*********************
* The constructor.
*
* @param paraFilename The given file.
*********************
*/
public ID3(String paraFilename) {
dataset = null;
try {
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(paraFilename);
dataset = new Instances(fileReader);
fileReader.close();
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println("Cannot read the file: " + paraFilename + "\r\n" + ee);
System.exit(0);
} // Of try
dataset.setClassIndex(dataset.numAttributes() - 1);
numClasses = dataset.numClasses();
availableInstances = new int[dataset.numInstances()];
for (int i = 0; i < availableInstances.length; i++) {
availableInstances[i] = i;
} // Of for i
availableAttributes = new int[dataset.numAttributes()];
for (int i = 0; i < availableAttributes.length; i++) {
availableAttributes[i] = i;
} // Of for i
// Initialize.
children = null;
// Determine the label by simple voting.
label = getMajorityClass(availableAttributes);
// Determine whether or not it is pure.
pure = pureJudge(availableInstances);
}// Of the constructor
第二个构造函数,当递归构建决策树时使用:
/**
*********************
* The constructor.
*
* @param paraDataset The given data set.
* @param paraAvailableInstances The available instances.
* @param paraAvailableAttributes The available attributes.
*********************
*/
public ID3(Instances paraDataset, int[] paraAvailableInstances, int[] paraAvailableAttributes) {
// Copy its reference instead of clone the available instances.
dataset = paraDataset;
availableInstances = paraAvailableInstances;
availableAttributes = paraAvailableAttributes;
// Initialize
children = null;
// Determine the label by simple voting.
label = getMajorityClass(availableInstances);
// Determine whether or not it is pure.
pure = pureJudge(availableInstances);
}// Of the second constructor
判断当前结点划分的数据集是否为同一类,如果是,那么就不用继续分支了。
/**
********************
* Is the given block pure?
*
* @param paraBlock The block.
* @return True if pure.
*********************
*/
public boolean pureJudge(int[] paraBlock) {
pure = true;
for (int i = 0; i < paraBlock.length; i++) {
if (dataset.instance(paraBlock[i]).classValue() != dataset.instance(paraBlock[0]).classValue()) {
pure = false;
break;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
return pure;
}// Of pureJudge
投票选取当前结点中个数最多的类来代表当前结点的类。
/**
********************
* Compute the majority class of the given block for voting.
*
* @param paraBlock The block.
* @return The majority class.
*********************
*/
public int getMajorityClass(int[] paraBlock) {
int[] tempClassCounts = new int[dataset.numClasses()];
for (int i = 0; i < paraBlock.length; i++) {
tempClassCounts[(int) dataset.instance(paraBlock[i]).classValue()]++;
} // Of for i;
int resultMajorityClass = -1;
int tempMaxCount = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < tempClassCounts.length; i++) {
if (tempClassCounts[i] > tempMaxCount) {
resultMajorityClass = i;
tempMaxCount = tempClassCounts[i];
} // Of if
} // Of for i
return resultMajorityClass;
}// Of getMajorityClass
选择信息增益最大(条件熵最小)的特征作为当前结点的特征:
/**
********************
* Select the best attribute.
*
* @return The best attribute index.
*********************
*/
public int selectBestAttribute() {
splitAttribute = -1;
double tempMinimalEntropy = 10000;
double tempEntropy;
for (int i = 0; i < availableAttributes.length; i++) {
tempEntropy = conditionalEntropy(availableAttributes[i]);
if (tempMinimalEntropy > tempEntropy) {
tempMinimalEntropy = tempEntropy;
splitAttribute = availableAttributes[i];
} // Of if
} // Of for i
return splitAttribute;
}// Of selectBestAttribute
计算特征下的条件熵:
/**
********************
* Compute the conditional entropy of an attribute.
*
* @param paraAttribute The given attribute.
* @return The entropy.
*********************
*/
public double conditionalEntropy(int paraAttribute) {
// Step 1. Statistics.
int tempNumClasses = dataset.numClasses();
int tempNumValues = dataset.attribute(paraAttribute).numValues();
int tempNumInstances = availableAttributes.length;
double[] tempValueCounts = new double[tempNumValues];
double[][] tempCountMatrix = new double[tempNumValues][tempNumClasses];
int tempClass, tempValue;
for (int i = 0; i < tempNumClasses; i++) {
tempClass = (int) dataset.instance(availableInstances[i]).classValue();
tempValue = (int) dataset.instance(availableInstances[i]).value(paraAttribute);
tempValueCounts[tempValue]++;
tempCountMatrix[tempValue][tempClass]++;
} // Of for i
// Step 2.
double reslutEntropy = 0;
double tempEntropy, tempFraction;
for (int i = 0; i < tempNumValues; i++) {
if (tempValueCounts[i] == 0) {
continue;
} // Of if
tempEntropy = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < tempNumClasses; j++) {
tempFraction = tempCountMatrix[i][j] / tempValueCounts[i];
if (tempFraction == 0) {
continue;
} // Of if
tempEntropy += -tempFraction * Math.log(tempFraction);
} // Of for j
reslutEntropy += tempValueCounts[i] / tempNumInstances * tempEntropy;
} // Of for i
return reslutEntropy;
}// Of conditionalEntropy
选择特征后,需要将数据集根据特征值划分成多个子数据集,用于根据各个子数据集递归构建子结点:
/**
********************
* Split the data according to the given attribute.
*
* @return The blocks.
*********************
*/
public int[][] splitData(int paraAttribute) {
int tempNumValues = dataset.attribute(paraAttribute).numValues();
int[][] resultBlocks = new int[tempNumValues][];
int[] tempSizes = new int[tempNumValues];
// First scan to count the size of each block.
int tempValue;
for (int i = 0; i < availableInstances.length; i++) {
tempValue = (int) dataset.instance(availableInstances[i]).value(paraAttribute);
tempSizes[tempValue]++;
} // Of for i
// Allocate space.
for (int i = 0; i < tempNumValues; i++) {
resultBlocks[i] = new int[tempSizes[i]];
} // Of for i
// Second scan to fill;
Arrays.fill(tempSizes, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < availableInstances.length; i++) {
tempValue = (int) dataset.instance(availableInstances[i]).value(paraAttribute);
// Copy data.
resultBlocks[tempValue][tempSizes[tempValue]] = availableInstances[i];
tempSizes[tempValue]++;
} // Of for i
return resultBlocks;
}// Of splitData
构建决策树:
/**
********************
* Build the tree recursively.
*********************
*/
public void buildTree() {
if (pureJudge(availableInstances)) {
return;
} // Of if
if (availableInstances.length <= smallBlockThreshold) {
return;
} // Of if
selectBestAttribute();
int[][] tempSubBlocks = splitData(splitAttribute);
children = new ID3[tempSubBlocks.length];
// Construct the remaining attribute set.
int[] tempRemainingAttributes = new int[availableAttributes.length - 1];
for (int i = 0; i < availableAttributes.length; i++) {
if (availableAttributes[i] < splitAttribute) {
tempRemainingAttributes[i] = availableAttributes[i];
} else if (availableAttributes[i] > splitAttribute) {
tempRemainingAttributes[i - 1] = availableAttributes[i];
} // Of if
} // Of for i
// Construct children.
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
if ((tempSubBlocks[i] == null) || (tempSubBlocks[i].length == 0)) {
children[i] = null;
continue;
} else {
children[i] = new ID3(dataset, tempSubBlocks[i], tempRemainingAttributes);
// Important code: do this recursively.
children[i].buildTree();
} // Of if
} // Of for i
}// Of buildTree
以实验数据weather.arff为例:

计算Outlook属性的条件熵为例:
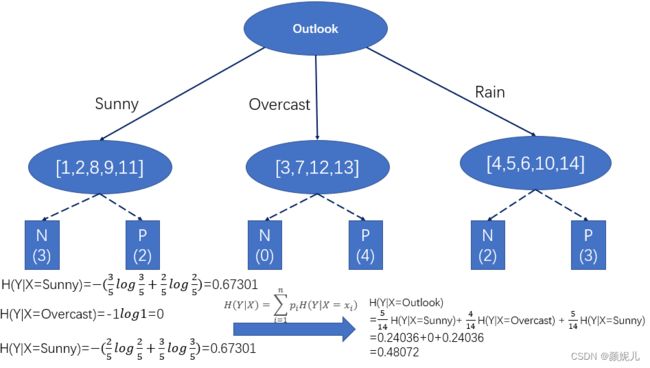
用同样的方式计算其它属性下的条件熵,选择条件熵最小的特征:

然后递归建立子树结点:

再继续向下建立子树:
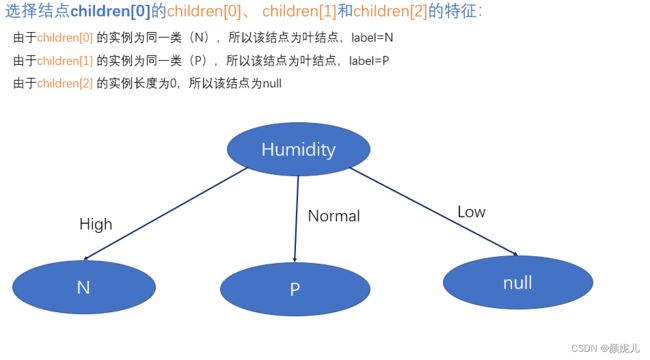
完成children[0]的子树建立后,回到函数调用的地方,开始建立children[1]:
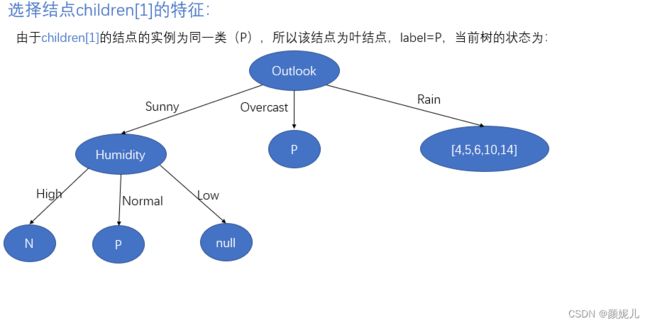
创建根结点的最后一个子树:
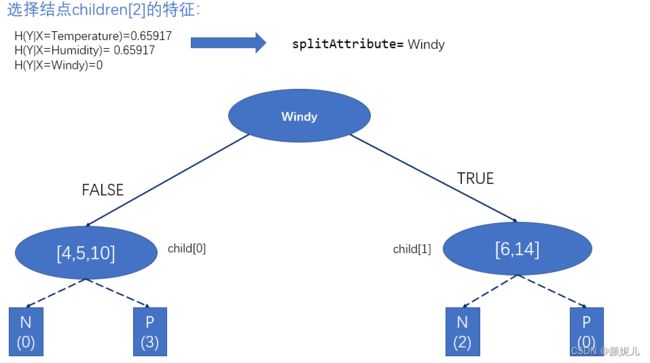
和children[0]同样,需要建立子树的子树:
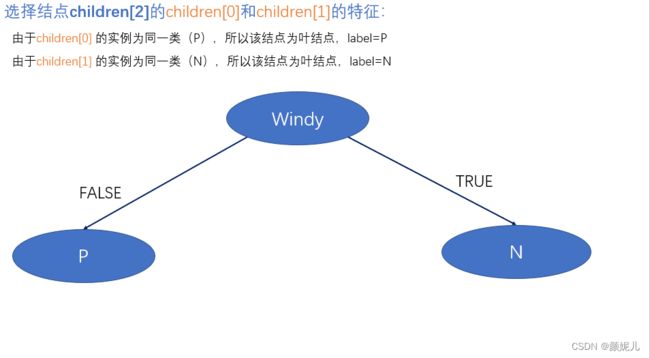
建树完成:

分类和测试:
分类的过程就是根据当前结点的特征向下层遍历,直到叶节点或结点为null。
1:children == null:说明当前结点为叶子结点,直接返回当前结点的标签;
2:当前特征的某个属性值指向的结点为null:返回当前结点的标签;
/**
********************
* Classify an instance.
*
* @param paraInstance The given instance.
* @return The prediction.
*********************
*/
public int classify(Instance paraInstance) {
if (children == null) {
return label;
} // Of if
ID3 tempChild = children[(int) paraInstance.value(splitAttribute)];
if (tempChild == null) {
return label;
} // Of if
return tempChild.classify(paraInstance);
}// Of classify
/**
********************
* Test on a testing set.
*
* @param paraDataset The given testing data.
* @return The accuracy.
*********************
*/
public double test(Instances paraDataset) {
double tempCorrect = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < paraDataset.numInstances(); i++) {
if (classify(paraDataset.instance(i)) == (int) paraDataset.instance(i).classValue()) {
tempCorrect++;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
return tempCorrect / paraDataset.numInstances();
}// Of test
/**
********************
* Test on the training set.
*
* @return The accuracy.
*********************
*/
public double selfTest() {
return test(dataset);
}// Of selfTest
以第一个实例的分类测试过程为例:
首先进入根结点,由于Outlook==Suny(代码中的体现:children[(int) paraInstance.value(0)]),会进入特征为Humidity的结点(children[0]),然后Humidity==High(代码中的体现:children[(int) paraInstance.value(2)]),最后到达叶子结点,返回叶子结点的label。
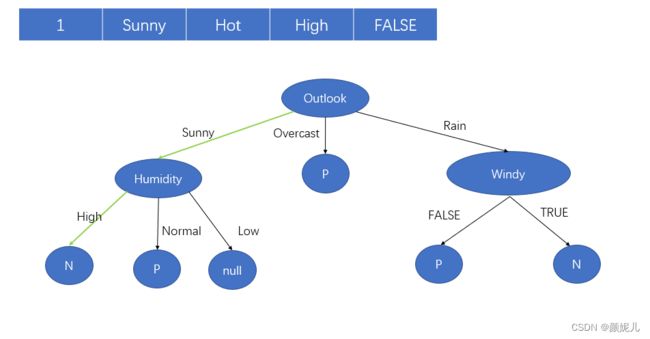
为了能更美观的打印决策树,我重新写了一个方法:
/**
********************
* Print the tree.
*
* @param paraString The given string.
*********************
*/
public void printDecisionTree(String paraString) {
if (children == null) {
System.out.println(paraString + "class: " + label + "\r\n");
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
String tempAttributeName = dataset.attribute(splitAttribute).name();
String tempString = tempAttributeName + ": " + dataset.attribute(splitAttribute).value(i) + "----> ";
if (children[i] == null) {
System.out.println(paraString + tempString + "class: " + label + "\r\n");
} else {
children[i].printDecisionTree(paraString + tempString);
} // Of if
} // Of for i
}// Of printDecisionTree
