李沐动手学深度学习V2-风格迁移学习(style transfer learning)和代码实现
一. 风格迁移学习(style transfer learning)
1. 介绍
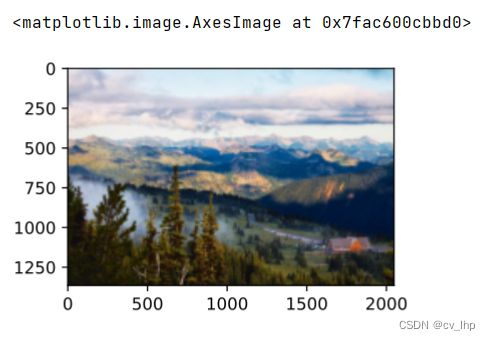
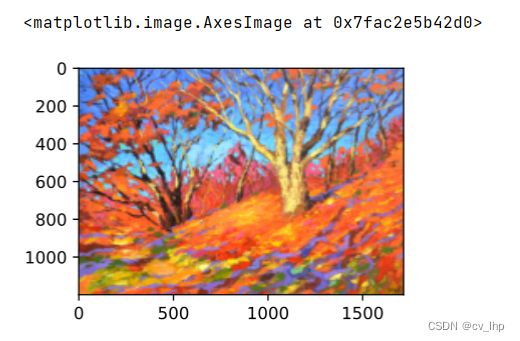
本节介绍如何使用卷积神经网络,自动将一个图像中的风格应用在另一图像之上,即风格迁移学习(style transfer learning)。 这里需要两张输入图像:一张是内容图像,另一张是风格图像,使用卷积神经网络修改内容图像,使其在风格上接近风格图像。 例如下图中内容图像为李沐老师在西雅图郊区的雷尼尔山国家公园拍摄的风景照,而风格图像则是一幅主题为秋天橡树的油画,最终输出的合成图像应用了风格图像的油画笔触让整体颜色更加鲜艳,同时保留了内容图像中物体主体的形状。

2. 方法
首先初始化合成图像,例如将其初始化为内容图像,该合成图像是风格迁移过程中唯一需要更新的变量,将该合成图像像素值作为模型训练权重参数,也即风格迁移学习所需迭代的模型参数;然后选择一个预训练的卷积神经网络来抽取图像的特征,其中预训练模型的参数在训练中无须更新,只更新合成图像的像素值权重参数。 由于深度卷积神经网络凭借多个层逐级抽取图像的特征,因此可以选择其中某些层的输出作为内容特征或风格特征。 如下图风格迁移学习为例选取的预训练的神经网络含有3个卷积层,其中第二层输出特征图作为内容特征,第一层和第三层输出特征图内容作为风格特征。
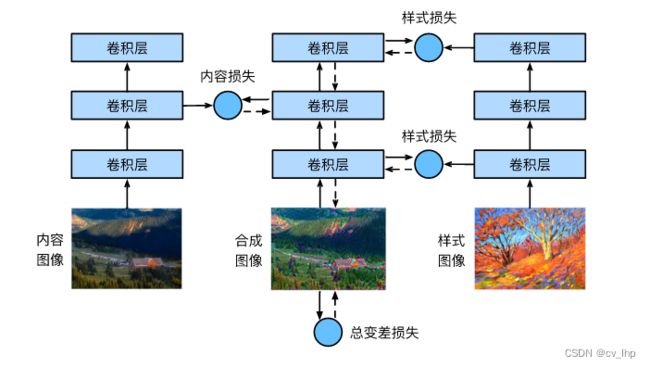
接下来通过前向传播(实线箭头方向)计算风格迁移的损失函数,并通过反向传播(虚线箭头方向)迭代模型参数,即不断更新合成图像像素权重参数。 风格迁移常用的损失函数由3部分组成: (i)内容损失使合成图像与内容图像在内容特征上接近; (ii)风格损失使合成图像与风格图像在风格特征上接近; (iii)全变分损失则有助于减少合成图像中的噪点。 最后,当模型训练结束时,我们输出风格迁移模型参数,也即是最终的合成图像像素值。
3.读取内容和风格图像
import torch
import torchvision
import d2l.torch
from torch import nn
d2l.torch.set_figsize()
content_img = d2l.torch.Image.open('../images/rainier.jpg')
d2l.torch.plt.imshow(content_img)
style_img = d2l.torch.Image.open('../images/autumn-oak.jpg')
d2l.torch.plt.imshow(style_img)
4.图像预处理和后处理
预处理函数preprocess()对输入图像在RGB三个通道分别做标准化,并将结果变换成卷积神经网络接受的输入格式。 后处理函数postprocess则将输出图像中的像素值还原回标准化之前的值,由于图像打印函数要求每个像素的浮点数值在0到1之间,因此需要对小于0和大于1的值分别取0和1。
#rgb_mean,rgb_std标准化的值是从ImageNet数据集中得到的
rgb_mean = torch.tensor([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
rgb_std = torch.tensor([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
def preprocess(img,img_shape):
transforms = torchvision.transforms.Compose([
torchvision.transforms.Resize(size=img_shape),
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
torchvision.transforms.Normalize(mean=rgb_mean,std=rgb_std)])
return transforms(img).unsqueeze(0)
def postprocess(img):
img = img[0].to(rgb_std.device)
img = img.permute(1,2,0)*rgb_std+rgb_mean
img = torch.clamp(img,min=0,max=1)
return torchvision.transforms.ToPILImage()(img.permute(2,0,1))
5. 抽取图像特征
使用基于ImageNet数据集预训练的VGG-19模型来抽取图像特征。
pretrained_net = torchvision.models.vgg19(pretrained=True)
pretrained_net
打印结果如下:
VGG(
(features): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(3): ReLU(inplace=True)
(4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(5): Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(6): ReLU(inplace=True)
(7): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(8): ReLU(inplace=True)
(9): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(10): Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(11): ReLU(inplace=True)
(12): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(13): ReLU(inplace=True)
(14): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(15): ReLU(inplace=True)
(16): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(17): ReLU(inplace=True)
(18): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(19): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(20): ReLU(inplace=True)
(21): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(22): ReLU(inplace=True)
(23): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(24): ReLU(inplace=True)
(25): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(26): ReLU(inplace=True)
(27): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(28): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(29): ReLU(inplace=True)
(30): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(31): ReLU(inplace=True)
(32): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(33): ReLU(inplace=True)
(34): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(35): ReLU(inplace=True)
(36): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(avgpool): AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=(7, 7))
(classifier): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=25088, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(2): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(3): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(4): ReLU(inplace=True)
(5): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(6): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1000, bias=True)
)
)
为了抽取图像的内容特征和风格特征,可以选择VGG网络中某些层的输出。 一般来说,越靠近输入层,越容易抽取图像的细节信息(如颜色,纹理等特征);反之,越靠近输出层则越容易抽取图像的全局信息。 为了避免合成图像过多保留内容图像的细节,选择VGG较靠近输出的层即内容层,来输出图像的内容特征(全局内容),同时从VGG中选择不同层的输出来匹配局部和全局的风格,这些图层也称为风格层。 正如上面打印结果看出VGG网络使用了5个卷积块,实验中选择第四卷积块的最后一个卷积层作为内容层,选择每个卷积块的第一个卷积层作为风格层,这些层的索引可以通过打印pretrained_net实例获取。
content_layers = [25]
style_layers = [0,5,10,19,28]
使用VGG层抽取特征时,只需要用到从输入层到最靠近输出层的内容层或风格层之间的所有层,下面构建一个新的网络net,它只保留需要用到的VGG的所有层。
net = nn.Sequential(*[pretrained_net.features[i] for i in range(max(content_layers+style_layers)+1)])
给定输入X,如果简单地调用前向传播net(X),只能获得最后一层的输出,由于还需要中间层的输出,因此需要逐层计算,并保留内容层和风格层的输出。
def extract_features(X,content_layers,style_layers):
contents = []
styles = []
for i in range(len(net)):
X = net[i](X)
if i in content_layers:
contents.append(X)
if i in style_layers:
styles.append(X)
return contents,styles
接下来定义两个函数:get_contents()函数对内容图像抽取内容特征; get_styles()函数对风格图像抽取风格特征。 因为在训练时无须改变预训练的VGG的模型参数,所以可以在训练开始之前就提取出内容特征和风格特征。 由于合成图像是风格迁移所需迭代的模型参数,因此只能在训练过程中通过调用extract_features()函数来抽取合成图像的内容特征和风格特征。
def get_contents(img_shape,device):
#content_X为原始内容图片的tensor值,contents_Y为从网络中抽取内容特征的特征图聚合
content_X = preprocess(content_img,img_shape).to(device)
contents_Y,_ = extract_features(content_X,content_layers,style_layers)
return content_X,contents_Y
def get_styles(img_shape,device):
#style_X为原始风格图片的tensor值,styles_Y为从网络中抽取内容特征的特征图聚合
style_X = preprocess(style_img,img_shape).to(device)
_,styles_Y = extract_features(style_X,content_layers,style_layers)
return style_X,styles_Y
6. 损失函数
风格迁移的损失函数由内容损失、风格损失和全变分损失3部分组成,下面依次介绍它们。
6.1 内容损失
与线性回归中的损失函数类似,内容损失通过平方误差函数衡量合成图像与内容图像在内容特征上的差异,平方误差函数的两个输入均为extract_features()函数计算所得到的内容层的输出。
def content_loss(Y_hat,Y):
return torch.square(Y_hat-Y.detach()).mean()
6.2 风格损失
风格损失与内容损失类似,也通过平方误差函数衡量合成图像与风格图像在风格上的差异。为了表达风格层输出的风格,先通过extract_feature()函数得到卷积网络风格层的输出。假设该输出的样本数为1,通道数为 c c c,高和宽分别为 h h h和 w w w,可以将此输出转换为矩阵 X \mathbf{X} X,其有 c c c行和 h w hw hw列。这个矩阵可以被看作是由 c c c个长度为 h w hw hw的向量 x 1 , … , x c \mathbf{x}_1, \ldots, \mathbf{x}_c x1,…,xc组合而成的,其中向量 x i \mathbf{x}_i xi代表了通道 i i i上的风格特征。
在这些向量的格拉姆矩阵 X X ⊤ ∈ R c × c \mathbf{X}\mathbf{X}^\top \in \mathbb{R}^{c \times c} XX⊤∈Rc×c中, i i i行 j j j列的元素 x i j x_{ij} xij即向量 x i \mathbf{x}_i xi和 x j \mathbf{x}_j xj的内积。它表达了通道 i i i和通道 j j j上风格特征的相关性,用格拉姆矩阵来表达风格层输出的特征图风格。注意当 h w hw hw的值较大时,格拉姆矩阵中的元素容易出现较大的值,为了风格损失不受这些值的大小影响,下面定义的gram函数将格拉姆矩阵除以了矩阵中元素的个数,即 c h w chw chw。此外,格拉姆矩阵的高和宽均为通道数 c c c。
def gram(X):
num_channels,n = X.shape[1],X.numel() // X.shape[1] #//需要整除得到是一个int型,/除号是得到一个float型
X = X.reshape(num_channels,n)
return torch.matmul(X,X.T)/(n*num_channels)
风格损失的平方误差函数的两个格拉姆矩阵输入分别基于合成图像与风格图像的风格层输出,这里假设基于风格图像的格拉姆矩阵gram_Y已经预先计算好了(与训练无关,可以提前计算好)。
def style_loss(Y_hat,gram_Y):
return torch.square(gram(Y_hat)-gram_Y.detach()).mean()
6.3 全变分损失
有时候由于学到的合成图像里面有大量高频噪点,即有特别亮或者特别暗的颗粒像素。一种常见的去噪方法是全变分去噪(total variation denoising):假设 x i , j x_{i, j} xi,j表示坐标 ( i , j ) (i, j) (i,j)处的像素值,降低全变分损失能够尽可能使邻近的像素值相似,从而不具有特别亮或者特别暗的像素。
∑ i , j ∣ x i , j − x i + 1 , j ∣ + ∣ x i , j − x i , j + 1 ∣ \sum_{i, j} \left|x_{i, j} - x_{i+1, j}\right| + \left|x_{i, j} - x_{i, j+1}\right| i,j∑∣xi,j−xi+1,j∣+∣xi,j−xi,j+1∣
def tv_loss(Y_hat):
return 0.5*(torch.abs(Y_hat[:,:,1:,:]-Y_hat[:,:,:-1,:]).mean()+
torch.abs(Y_hat[:,:,:,1:]-Y_hat[:,:,:,:-1]).mean())
6.4 模型损失函数
风格迁移的损失函数是内容损失、风格损失和全变分损失的加权和,通过调节这些权重超参数,可以权衡合成图像在保留内容、迁移风格以及去噪三方面的相对重要性。
content_weight,style_weight,tv_weight = 1,1e3,10
def compute_loss(X,contents_Y_hat,contents_Y,styles_Y_hat,styles_Y_gram):
#X就是合成图片对应的tensor值
# 分别计算内容损失、风格损失和全变分损失
contents_l = [content_loss(Y_hat,Y)*content_weight for Y_hat,Y in zip(contents_Y_hat,contents_Y)]
styles_l = [style_loss(Y_hat,Y)*style_weight for Y_hat,Y in zip(styles_Y_hat,styles_Y_gram)]
tv_l = tv_loss(X)*tv_weight
# 对所有损失求和
l = sum(contents_l+styles_l*10+[tv_l])
return contents_l,styles_l,tv_l,l
7. 初始化合成图像
在风格迁移中合成的图像是训练期间唯一需要更新的变量,因此定义一个简单的模型SynthesizedImage,并将合成的图像像素作为模型参数。模型的前向传播只需返回模型参数(也即是合成的图像像素值)即可。
class SynthesizedImage(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,img_shape):
super(SynthesizedImage,self).__init__()
#weight值就是合成图片对应的tensor值,将这个tensor值作为权重参数进行训练,进行梯度下降,网络训练过程中就是对该合成图片对应的tensor值权重参数不断变化,而不是对预训练网络的权重参数进行训练,使其生成的合成图片得到一个与内容图片相符合,同时与风格图片的风格相同,且合成的图片平滑度比较好,没有较大的噪点
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.rand(*img_shape))
def forward(self):
return self.weight
下面定义get_inits()函数,该函数创建了合成图像的模型实例,并将合成图像初始化为跟内容图像一样,同时将风格图像在各个风格层的格拉姆矩阵styles_Y_gram在训练前预先计算好。
def get_inits(X,device,lr,styles_Y):
gen_img = SynthesizedImage(X.shape).to(device)
gen_img.weight.data.copy_(X.data)
optim = torch.optim.Adam(gen_img.parameters(),lr)
styles_Y_gram = [gram(style_Y) for style_Y in styles_Y]
return gen_img(),optim,styles_Y_gram #gen_img()返回的是self.weight
8. 模型训练
在训练模型进行风格迁移时不断抽取合成图像的内容特征和风格特征,然后与内容图像的内容特征以及风格图像的风格特征计算损失函数,同时计算合成图像的全变分损失,三者损失求和来更新迭代权重参数(也即是更新合成图像的像素值从而达到使合成图像既包含内容图像的内容又包含风格图像的风格,同时使合成图像噪点比较低)。
def train(content_img,contents_Y,styles_Y,device,lr,num_epochs,lr_decay_epoch):
#刚开始将合成图片初始化为内容图片
synthesized_Image,optim,styles_Y_gram = get_inits(content_img,device,lr,styles_Y)
optim_steper = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optim,lr_decay_epoch,0.8)
animator = d2l.torch.Animator(xlabel='epoch',ylabel='loss',
xlim=[10,num_epochs],
legend=['contens_loss','styles_loss','tv_loss'],
ncols=2,figsize=(7,2.5))
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
optim.zero_grad()
contents_Y_hat,styles_Y_hat = extract_features(synthesized_Image,content_layers,style_layers)
contents_l,styles_l,tv_l,l = compute_loss(synthesized_Image,contents_Y_hat,contents_Y,styles_Y_hat,styles_Y_gram)
l.backward()
optim.step()
optim_steper.step()
if (epoch+1)%10 == 0:
print(' ')
animator.axes[1].imshow(postprocess(synthesized_Image))
animator.add(epoch+1,[float(sum(contents_l)),float(sum(styles_l)),float(tv_l)])
return synthesized_Image
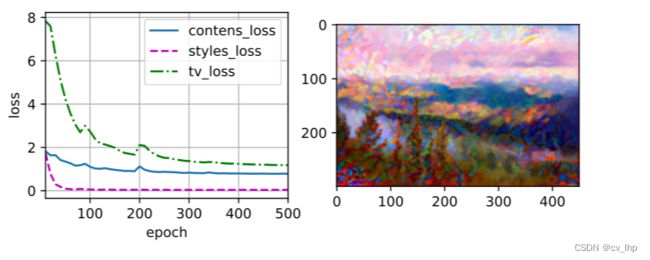
训练模型,首先将内容图像和风格图像的高和宽分别调整为300x450像素,用内容图像来初始化合成图像。模型训练结果如下图所示,可以看到合成图像保留了内容图像的风景和物体,并同时迁移了风格图像的色彩,例如合成图像具有与风格图像中一样的色彩块,其中一些甚至具有画笔笔触的细微纹理。
device,img_shape = d2l.torch.try_gpu(1),(300,450)
net = net.to(device)
content_X,contents_Y = get_contents(img_shape,device)
_,styles_Y = get_styles(img_shape,device)
synthesized_Image = train(content_X,contents_Y,styles_Y,device,lr=0.3,num_epochs=500,lr_decay_epoch=50)
9. 小结
- 风格迁移常用的损失函数由3部分组成:(i)内容损失使合成图像与内容图像在内容特征上接近;(ii)风格损失令合成图像与风格图像在风格特征上接近;(iii)全变分损失则有助于减少合成图像中的噪点。
- 通过预训练的卷积神经网络来抽取图像的特征,并通过损失函数来不断更新模型参数,也即是不断更新合成图像像素值。
- 使用格拉姆矩阵表达风格层输出的风格。
- 在训练模型进行风格迁移时不断抽取合成图像的内容特征和风格特征,然后与内容图像的内容特征以及风格图像的风格特征计算损失函数,同时计算合成图像的全变分损失,三者损失求和来更新迭代权重参数(也即是更新合成图像的像素值从而达到使合成图像既包含内容图像的内容又包含风格图像的风格,同时使合成图像噪点比较低)。
10.全部代码
import torch
import torchvision
import d2l.torch
from torch import nn
d2l.torch.set_figsize()
content_img = d2l.torch.Image.open('../images/rainier.jpg')
d2l.torch.plt.imshow(content_img)
style_img = d2l.torch.Image.open('../images/autumn-oak.jpg')
d2l.torch.plt.imshow(style_img)
rgb_mean = torch.tensor([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
rgb_std = torch.tensor([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
def preprocess(img, img_shape):
transforms = torchvision.transforms.Compose([
torchvision.transforms.Resize(size=img_shape),
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
torchvision.transforms.Normalize(mean=rgb_mean, std=rgb_std)])
return transforms(img).unsqueeze(0)
def postprocess(img):
img = img[0].to(rgb_std.device)
img = img.permute(1, 2, 0) * rgb_std + rgb_mean
img = torch.clamp(img, min=0, max=1)
return torchvision.transforms.ToPILImage()(img.permute(2, 0, 1))
pretrained_net = torchvision.models.vgg19(pretrained=True)
pretrained_net
content_layers = [25]
style_layers = [0, 5, 10, 19, 28]
net = nn.Sequential(*[pretrained_net.features[i] for i in range(max(content_layers + style_layers) + 1)])
def extract_features(X, content_layers, style_layers):
contents = []
styles = []
for i in range(len(net)):
X = net[i](X)
if i in content_layers:
contents.append(X)
if i in style_layers:
styles.append(X)
return contents, styles
def get_contents(img_shape, device):
#content_X为原始内容图片的tensor值,contents_Y为从网络中抽取内容特征的特征图聚合
content_X = preprocess(content_img, img_shape).to(device)
contents_Y, _ = extract_features(content_X, content_layers, style_layers)
return content_X, contents_Y
def get_styles(img_shape, device):
#style_X为原始风格图片的tensor值,styles_Y为从网络中抽取内容特征的特征图聚合
style_X = preprocess(style_img, img_shape).to(device)
_, styles_Y = extract_features(style_X, content_layers, style_layers)
return style_X, styles_Y
def content_loss(Y_hat, Y):
return torch.square(Y_hat - Y.detach()).mean()
def gram(X):
num_channels, n = X.shape[1], X.numel() // X.shape[1] #//需要整除得到是一个int型,/除号是得到一个float型
X = X.reshape(num_channels, n)
return torch.matmul(X, X.T) / (n * num_channels)
def style_loss(Y_hat, gram_Y):
return torch.square(gram(Y_hat) - gram_Y.detach()).mean()
def tv_loss(Y_hat):
return 0.5 * (torch.abs(Y_hat[:, :, 1:, :] - Y_hat[:, :, :-1, :]).mean() +
torch.abs(Y_hat[:, :, :, 1:] - Y_hat[:, :, :, :-1]).mean())
content_weight, style_weight, tv_weight = 1, 1e3, 10
def compute_loss(X, contents_Y_hat, contents_Y, styles_Y_hat, styles_Y_gram):
#X就是合成图片对应的tensor值
# 分别计算内容损失、风格损失和全变分损失
contents_l = [content_loss(Y_hat, Y) * content_weight for Y_hat, Y in zip(contents_Y_hat, contents_Y)]
styles_l = [style_loss(Y_hat, Y) * style_weight for Y_hat, Y in zip(styles_Y_hat, styles_Y_gram)]
tv_l = tv_loss(X) * tv_weight
# 对所有损失求和
l = sum(contents_l + styles_l * 10 + [tv_l])
return contents_l, styles_l, tv_l, l
class SynthesizedImage(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, img_shape):
super(SynthesizedImage, self).__init__()
#weight值就是合成图片对应的tensor值,将这个tensor值作为权重参数进行训练,进行梯度下降,网络训练过程中就是对该合成图片对应的tensor值权重参数不断变化,而不是对预训练网络的权重参数进行训练,使其生成的合成图片得到一个与内容图片相符合,同时与风格图片的风格相同,且合成的图片平滑度比较好,没有较大的噪点
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.rand(*img_shape))
def forward(self):
return self.weight
def get_inits(X, device, lr, styles_Y):
gen_img = SynthesizedImage(X.shape).to(device)
gen_img.weight.data.copy_(X.data)
optim = torch.optim.Adam(gen_img.parameters(), lr)
styles_Y_gram = [gram(style_Y) for style_Y in styles_Y]
return gen_img(), optim, styles_Y_gram #gen_img()返回的是self.weight
def train(content_img, contents_Y, styles_Y, device, lr, num_epochs, lr_decay_epoch):
#刚开始将合成图片初始化为内容图片
synthesized_Image, optim, styles_Y_gram = get_inits(content_img, device, lr, styles_Y)
optim_steper = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optim, lr_decay_epoch, 0.8)
animator = d2l.torch.Animator(xlabel='epoch', ylabel='loss',
xlim=[10, num_epochs],
legend=['contens_loss', 'styles_loss', 'tv_loss'],
ncols=2, figsize=(7, 2.5))
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
optim.zero_grad()
contents_Y_hat, styles_Y_hat = extract_features(synthesized_Image, content_layers, style_layers)
contents_l, styles_l, tv_l, l = compute_loss(synthesized_Image, contents_Y_hat, contents_Y, styles_Y_hat,
styles_Y_gram)
l.backward()
optim.step()
optim_steper.step()
if (epoch + 1) % 10 == 0:
print(' ')
animator.axes[1].imshow(postprocess(synthesized_Image))
animator.add(epoch + 1, [float(sum(contents_l)), float(sum(styles_l)), float(tv_l)])
return synthesized_Image
device, img_shape = d2l.torch.try_gpu(1), (300, 450)
net = net.to(device)
content_X, contents_Y = get_contents(img_shape, device)
_, styles_Y = get_styles(img_shape, device)
synthesized_Image = train(content_X, contents_Y, styles_Y, device, lr=0.3, num_epochs=500, lr_decay_epoch=50)