Android页面跳转(Intent)
Android 意图的使用(Intent)
- 显式四种跳转方式
-
- 一
- 二
- 三
- 四
- 布局+代码
- 效果
- 隐式意图和隐式意图的跳转
- Intent概述
- Action属性
- Data属性
- Category属性
-
- 按home键时启动自己做的应用
- Component属性
- Extra属性(重点)
-
- Bundle
- 传递序列化对象
- Type属性
- Flag属性
- 返回值
显式四种跳转方式
一
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,HomeActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
二
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(MainActivity.this,HomeActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
三
Intent intent = new Intent();
ComponentName componentName = new ComponentName(MainActivity.this,HomeActivity.class);
intent.setComponent(componentName);
startActivity(intent);
四
startActivity(new Intent(MainActivity.this,HomeActivity.class));
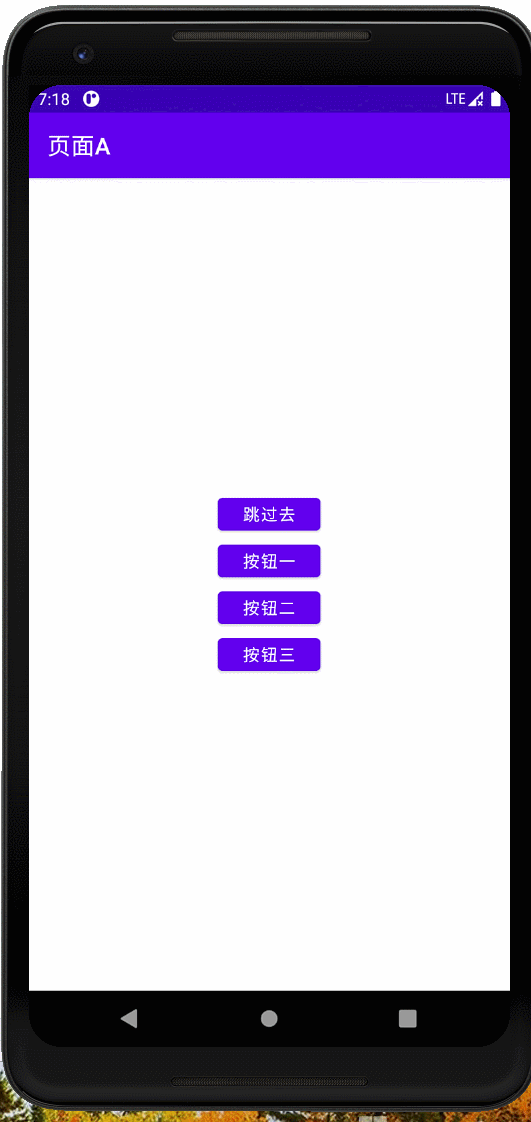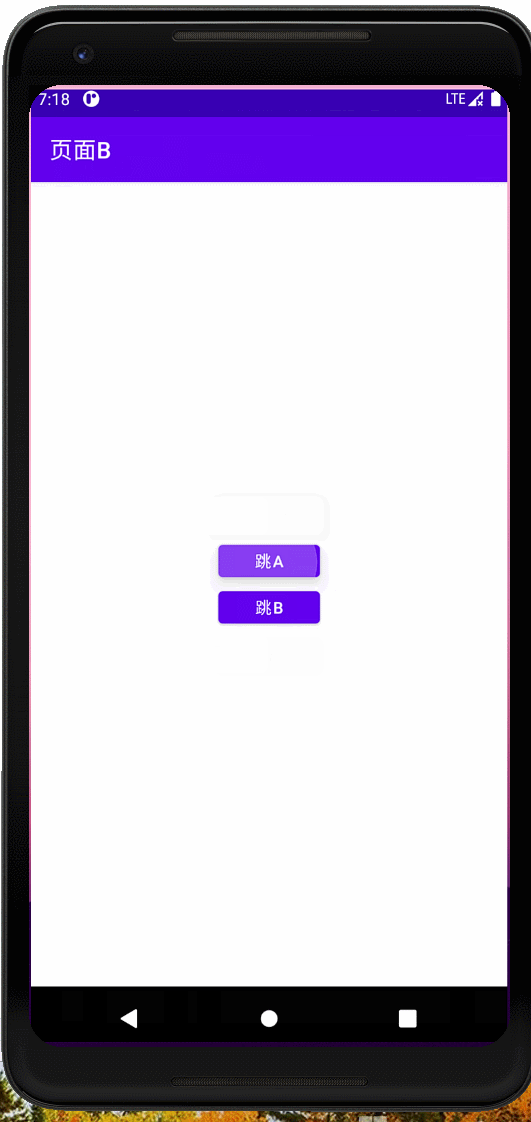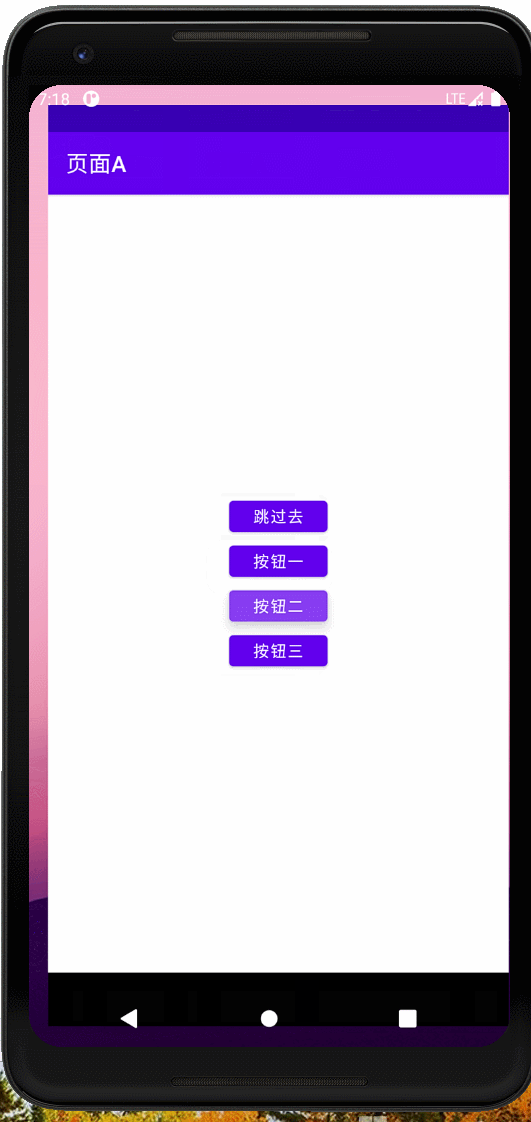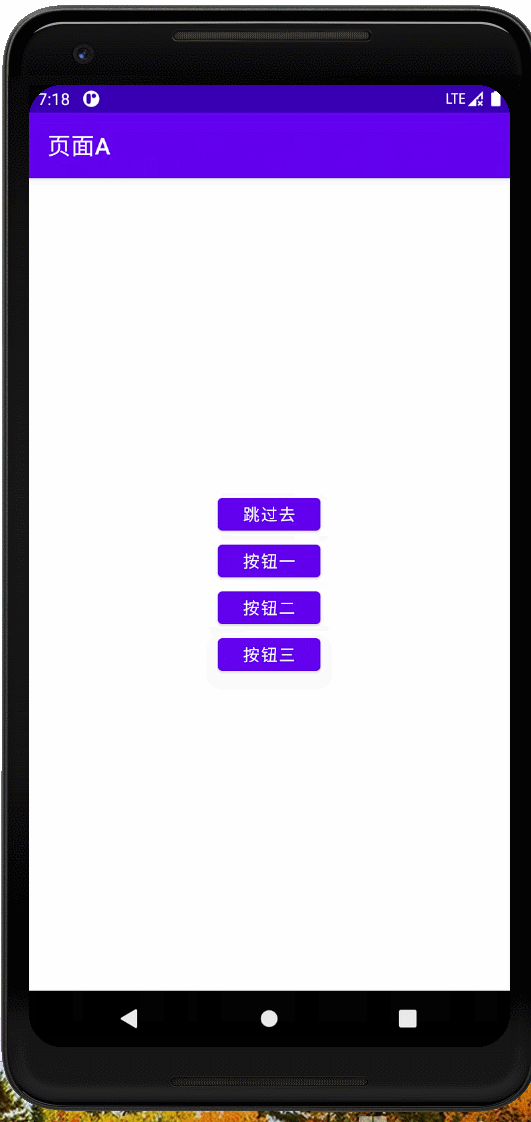
布局+代码
布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center">
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_intentmain"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:text="跳过去"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_intentOne"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:text="按钮一"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_intentTwo"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:text="按钮二"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_intentThree"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:text="按钮三"
/>
</LinearLayout>
代码
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private Button mBtIntent,mBtIntentOne,mBtIntentTwo,mBtIntentThree;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
Log.d("TAG","onCreate");
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initView();
mBtIntent.setOnClickListener(this);
mBtIntentOne.setOnClickListener(this);
mBtIntentTwo.setOnClickListener(this);
mBtIntentThree.setOnClickListener(this);
setTitle("页面A");
}
private void initView(){
mBtIntent = findViewById(R.id.bt_intentmain);
mBtIntentOne = findViewById(R.id.bt_intentOne);
mBtIntentTwo = findViewById(R.id.bt_intentTwo);
mBtIntentThree = findViewById(R.id.bt_intentThree);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()){
case R.id.bt_intentmain:
IntentOne();
break;
case R.id.bt_intentOne:
IntentTwo();
break;
case R.id.bt_intentTwo:
IntentThree();
break;
case R.id.bt_intentThree:
IntentFour();
break;
default:
break;
}
}
private void IntentOne(){
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,HomeActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
private void IntentTwo(){
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(MainActivity.this,HomeActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
private void IntentThree(){
Intent intent = new Intent();
ComponentName componentName = new ComponentName(MainActivity.this,HomeActivity.class);
intent.setComponent(componentName);
startActivity(intent);
}
private void IntentFour(){
startActivity(new Intent(MainActivity.this,HomeActivity.class));
}
}
效果
隐式意图和隐式意图的跳转
隐式意图
没有明确指定组件名的Intent为隐式意图,系统会根据隐式意图中设置的动作(action)、类别(category)、数据UIL等来匹配最合适的组件。
首先在清单文件中使用意图过滤器设置活动的名字
< action android:name=“HomeActivity” />
< category android:name=“android.intent.category.DEFAULT” />
<activity
android:name=".HomeActivity"
android:launchMode="singleInstance" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="HomeActivity" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
跳转
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction("HomeActivity");
startActivity(intent);
Intent概述
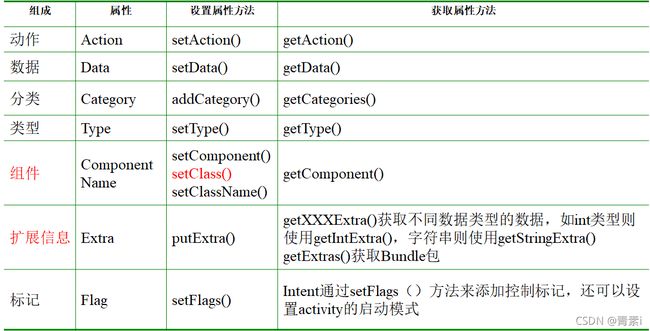
Intent是Android的核心组件,利用消息实现应用程序间的交互机制,这种消息描述了应用中一次操作的动作、数据以及附加数据,系统通过该Intent的描述负责找到对应的组件,并将Intent传递给调用的组件,完成组件的调用。
Intent由动作、数据、分类、类型、组件、扩展信息、标记等内容组成,每个组成都由相应的属性进行表示,并提供设置和获取相应属性的方法。
Action属性
• Action属性用于描述Intent要完成的动作,对要执行的动作进行一个简要描述。Intent类定义了一系列Action属性常量,用来标识一套标准动作,如ACTION_CALL(打电话)等。
• 通常与Data一般匹配使用
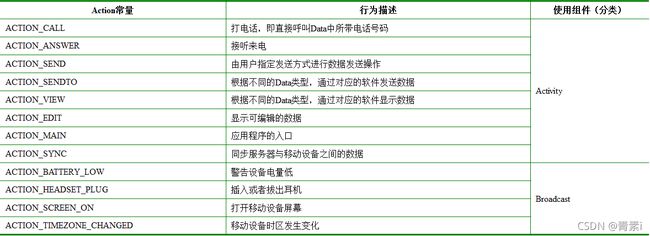
例如 短信发送
一、
Uri uri= Uri.parse(“tel:10086”);
Intent intent= new Intent(Intent.ACTION_CALL, uri);
//intent.setData(uri));//设置数据
startActivity(intent);
二、
Manifest里需要添加CALL_PHONE权限
三、
危险权限需要动态申请。
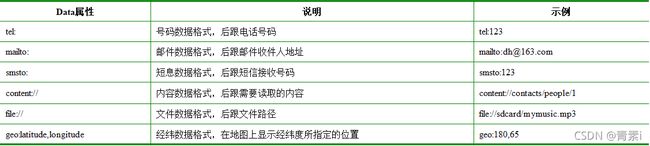
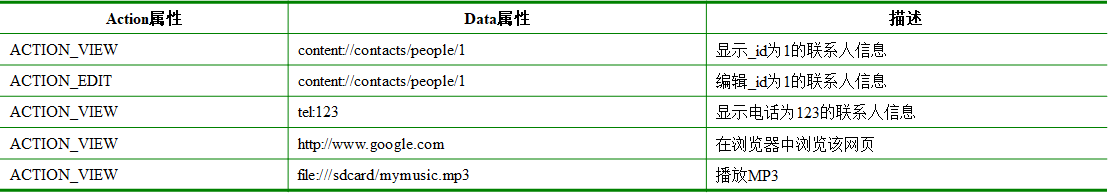
Data属性
Action和Data一般匹配使用,不同的Action由不同的Data数据指定
Category属性
• Category属性指明一个执行Action的分类
• Intent中定义了一系列Category属性常量

按home键时启动自己做的应用
<intent-filter>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.HOME"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN"/>
</intent-filter>
Component属性
一、Component属性用于指明Intent的目标组件的类名称。
二、通常Android会根据Intent中包含的其他属性的信息,比如Action、Data/Type、Category进行查找,最终找到一个与之匹配的目标组件。但是,如果指定了Component这个属性,Intent则会直接根据组件名查找到相应的组件,而不再执行上述查找过程。指定Component属性后,Intent的其他属性都是可选的。
三、根据Intent寻找目标组件时所采用的方式不同,可以将Intent分为两类:
显式Intent,这种方式通过直接指定组件名称Component来实现;
Intent intent = new Intent();
ComponentName name = new ComponentName(IntentActivity.this,MainActivity.class);
intent.setComponent(name);
startActivity(intent);
**隐式Intent,**这种方式通过Intent Filter过滤实现,过滤时通常根据Action、Data和Category属性进行匹配查找。
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClassName(IntentActivity.this,"com.ugrow.day02.MainActivity");
显式Intent通过**setComponent()、setClassName()或setClass()**设置组件名
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(IntentActivity.this,MainActivity.class);
Extra属性(重点)
通过使用Intent对象的putExtra()方法来添加附加信息、和信息传递
信息添加 方式类似于键值对
Intent intent= new Intent();
intent.putExtra("name","zhangsan");
信息取出 另一个页面
通过使用Intent对象的getXXXExtra()方法可以获取附加信息。
例如,将上面代码存入Intent对象中的人名获取出来,
因存入的是字符串,所以可以使用getStringExtra()方法获取数据
Intent intent = getIntent();
String name=intent.getStringExtra("name");
Bundle
打包 当一个页面的数据会向多个页面传递的时候并且不是每个页面都会用到这些数据
比如A页面传到B页面 B页面不需要用数据 但需要将数据传递给C页面
进行多次使用 如果数据过多那么将会导致每一个页面都有大量的get方法 页面不整洁
因此使用Bundle打包
存
Intent intent = new Intent();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("user",user.getText().toString());
bundle.putString("pwd",pwd.getText().toString());
intent.putExtras(bundle);
取
Bundle extras = getIntent().getExtras();
String user = extras.getString("user");
String pwd = extras.getString("pwd");
传递序列化对象
Javabean对象序列化后可以直接使用Extra方法传递对象
一、Javabean对象需要实现Serializable接口
CommentBean implements Serializable
二、传数据
intent.putExtra("bean",commentBean);
三、取数据
CommentBean commentBean = new CommentBean();
Intent intent=getIntent();
commentBean = (CommentBean) intent.getSerializableExtra("bean");
Type属性
Intent intent = new Intent();
Uri uri = Uri.parse("file:///data/vivo.mp4");
intent.setAction(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
intent.setDataAndType(uri,"video/*");
startActivity(intent);
Flag属性
Flag属性用来设定Activity的启动模式,与清单文件中的设置launchMode属性值相同
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP);
Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP = singleTask
Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP = singleTop
Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK = singleInstance
返回值
一、A页面传值给B页面
startActivity() (putExtra,Bundle)
二、B页面传值给A页面
startActivityForRestult()
setResult(resultCode,Intent)
onActivityResult
A页面跳转B页面 如果转账成功则返回过江 失败则返回有鬼
页面A
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,HomeActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("money","转账100元");
//有返回值的跳转
/*
* 第一个参数Intent对象
* 第二个参数 RequestCode
*/
startActivityForResult(intent,REQUSET_CODE);
@Override
//第一个参数 是不是我要的返回结果 第二个参数 是谁返回给我的 第三个参数 返回的附加信息
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) {
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
if(requestCode == REQUSET_CODE && resultCode == HomeActivity.RESULT_CODE){
String msg = data.getStringExtra("msg");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,msg,Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
页面B
Intent intent = new Intent();
Intent getIn = getIntent();
String money = getIn.getStringExtra("money");
if(TextUtils.isEmpty(money)){
intent.putExtra("msg","有鬼!");
}else{
intent.putExtra("msg","过江!");
}
setResult(RESULT_CODE,intent);
//关闭页面
finish();