SpringBoot常用注解
1、@SpringBootApplication
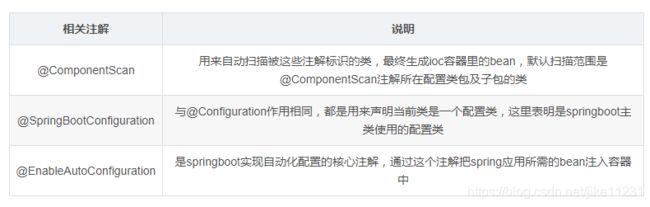
包含@Configuration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponentScan通常用在主类上;
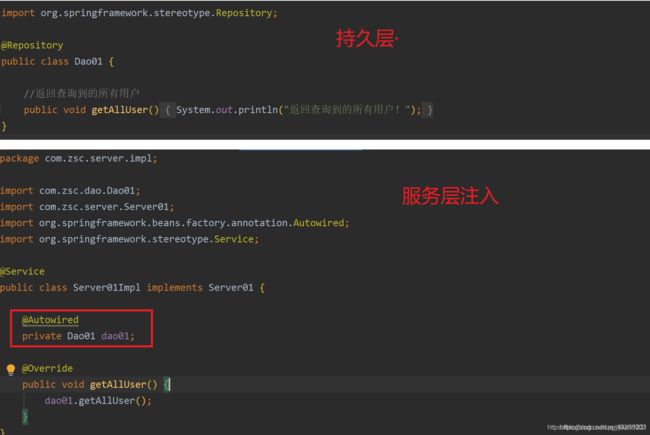
2、@Component、@Service、@Controller、@Repository
这几个注解放在一起是因为功能基本一样的,都是将类注入到spring容器中,只不过它们使用的场景不同,被@Component,@Service,@Controller,@Repository注解标注的类,这些类会被纳入进spring容器中管理。

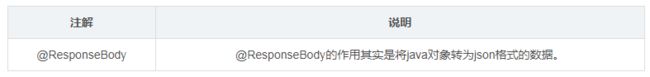
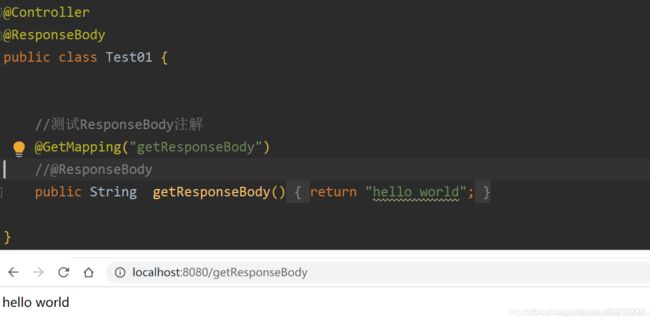
3、@ResponseBody
@ResponseBody可以作用在方法上或类上,表示该方法的返回结果直接写入 HTTP response body 中,而不会被解析为跳转路径,即不会经过视图解析器,返回什么数据即在页面输入什么数据。
测试如下
4、@RestController
该注解是@Controller和@ResponseBody的结合体,一般用于类,作用等于在类上面添加了@ResponseBody和@Controller
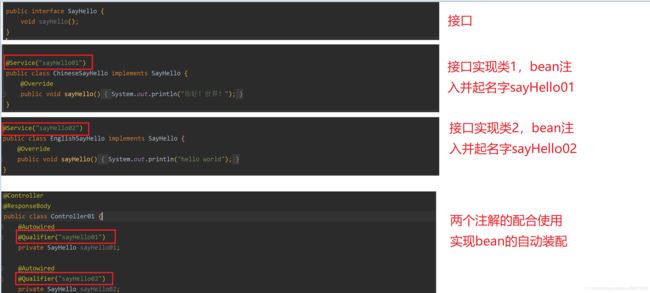
5、@AutoWired、@Qualifier、@Resource
这3个注解都是基于注解方式进行自动装配,在容器里面将查找到的bean返回,一般@AutoWired用得最多,@Qualifier则需要配合@AutoWired使用,@Resource则是可以通过名字进行自动装配
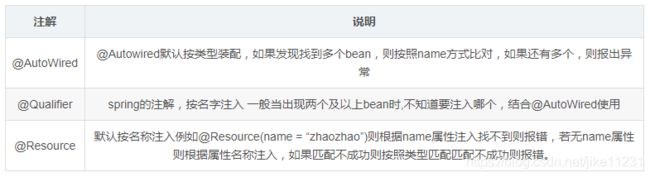
@AutoWired
@Qualifier
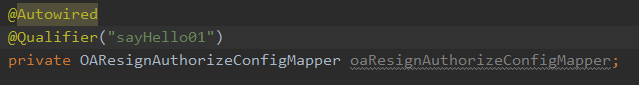
当有一个接口的多个实现类时,只用@AutoWired会报错,因为它有多个接口的实现类,不知道你要找哪一个,这个时候就需要在注入bean的时候起个名字,然后用@Qualifier注解指定哪一个bean(按照名字注入与装配),比如
@Autowired
@Qualifier("sayHello")
@Resource
该注解的使用相当于@AutoWired和@Qualifier配合使用的效果

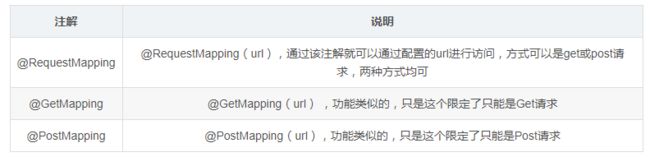
6、@RequestMapping、@GetMapping、@PostMapping
这3个注解功能也是类似的,通过这3个注解来映射请求,也就是通过它来指定控制器可以处理哪些URL请求,用在方法上,可以通过配置的url进行访问
@RequestMapping
发起get请求或者post请求都可以
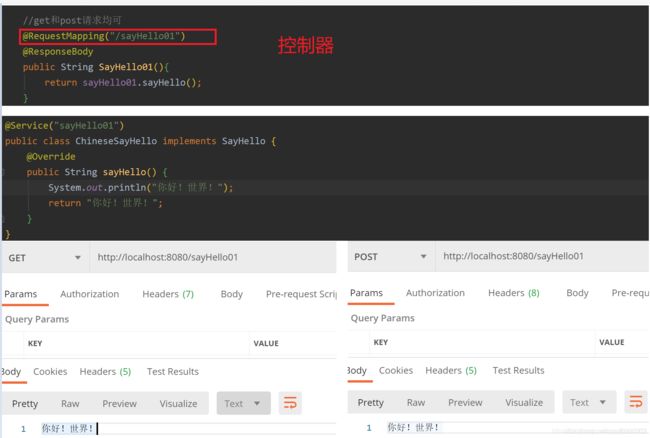
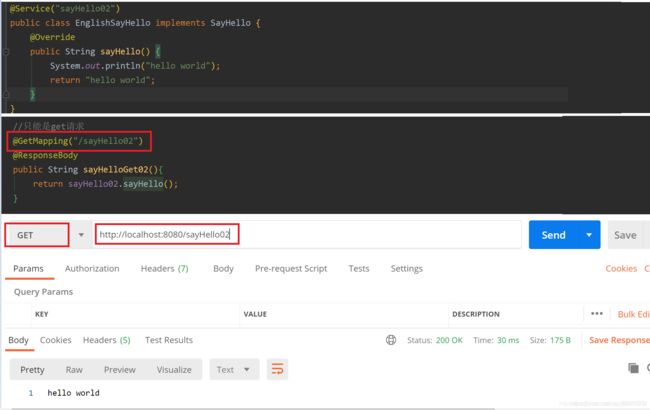
@GetMapping
只能用get请求
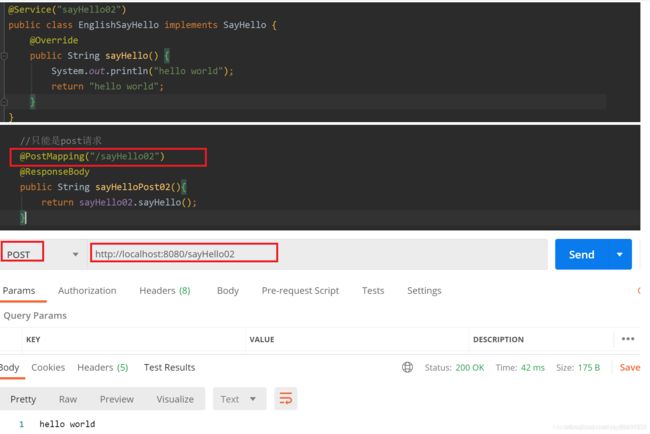
@PostMapping
只能发起post请求
7、@Value、@ConfigurationProperties、@PropertySource
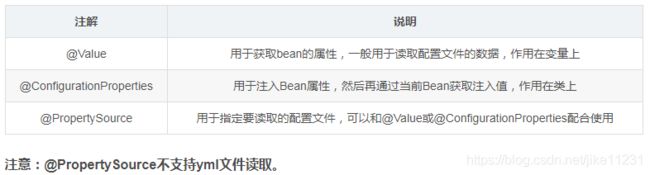
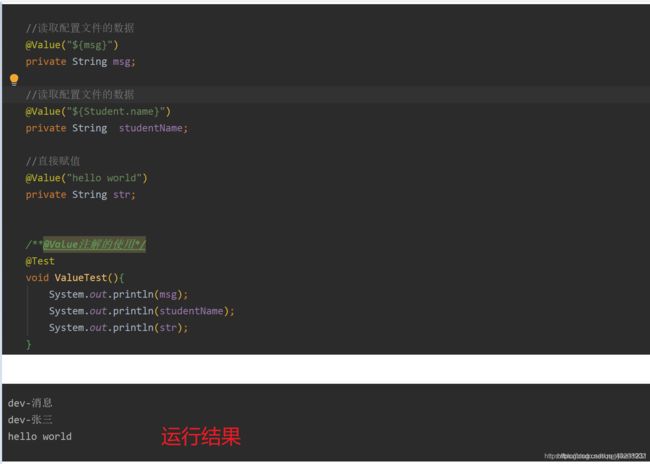
@Value
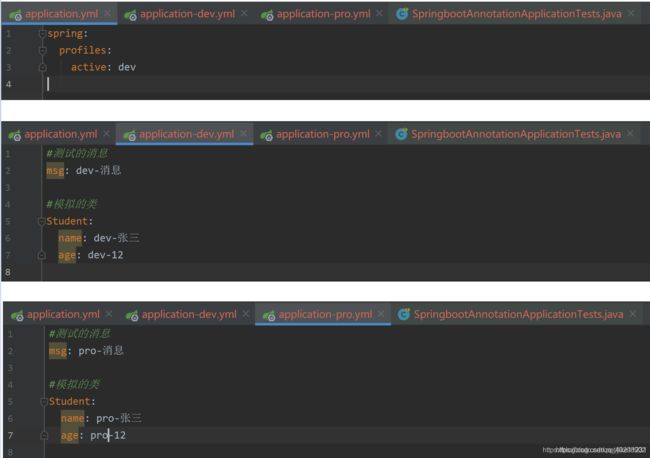
这里用yml配置文件进行演示,propres配置文件也是同样的效果,在application.yml配置文件里设置开发环境的的配置文件(dev),这样用@Value获取到的就是开发环境的配置文件的数据,切换成生产环境(pro)则获取到的是生产环境的数据
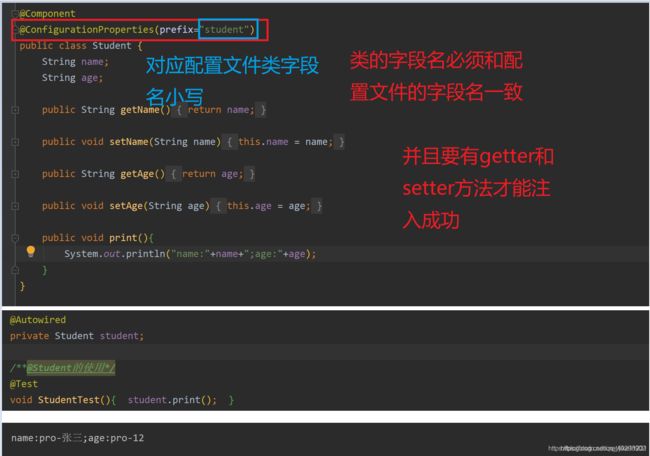
@ConfigurationProperties
该注解可以直接注入整个类的数据,作用于类
配置文件如下,这里使用pro环境
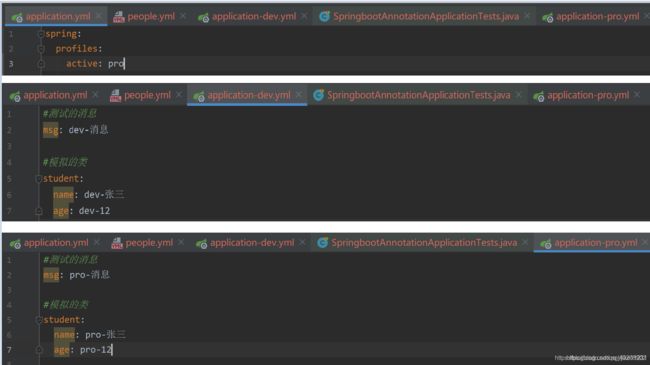
测试
@PropertySource
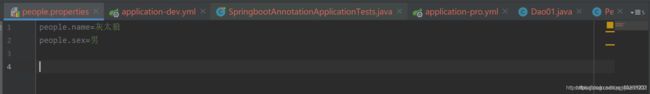
注意:@PropertySource不支持yml文件读取。
配置文件如下:people.properties
测试
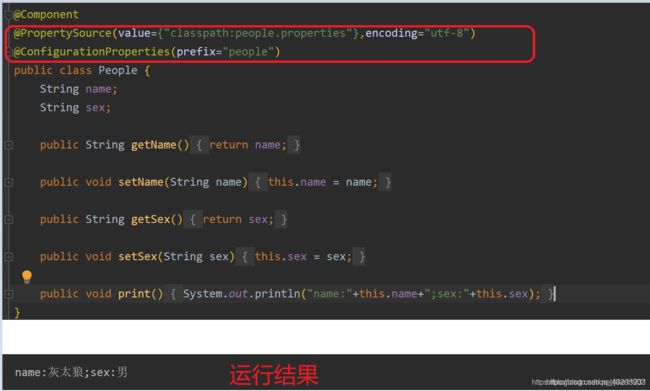
当然@PropertySource还可以和@Value配合使用,即一个一个注入值。
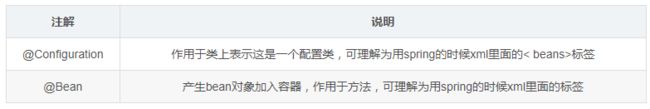
8、@Configuration、@Bean
@Configuration作用于类上面,表明这是一个配置类,@Bean产生一个Bean对象加入Spring IOC容器
注意:@Configuration标注在类上,相当于把该类作为spring的xml配置文件中,作用为:配置spring容器(应用上下文)
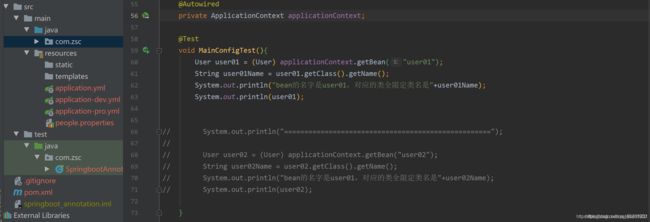
一般这两个注解同时配合使用,新建配置类,将User加入容器,并自定义生命周期
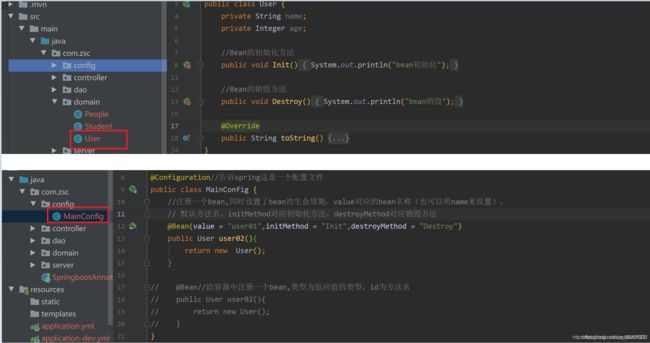
测试
9、@RequestParam、@RequestBody、@PathVariable、@RequestHeader、@CookieValue
这几个注解放在一起主要是经常在控制层用来接收参数的
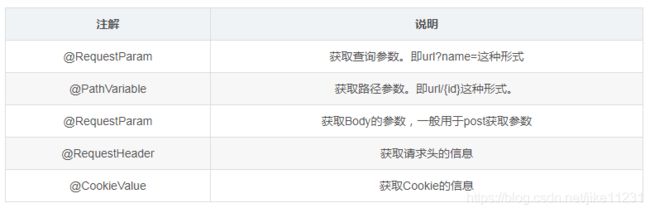
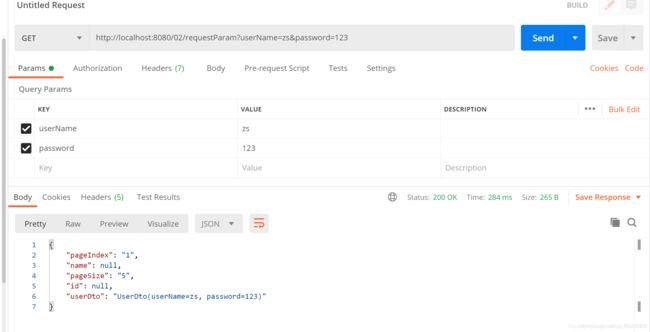
@RequestParam
@RequestParam主要用于接收url?后面的参数,get或post请求,只要后面的url?有参数都可以获取到对应的参数
@RequestParam注解有几个比较重要的属性,required 表示是否必须,默认为 true,必须。defaultValue 可设置请求参数的默认值。value 为接收url的参数名(相当于key值)。
@GetMapping("/requestParam")
@ResponseBody
public Map<String, String> requestParam(
UserDto userDto,//通过一个实体类来接收,字段名必须一致
@RequestParam(value = "id", required = false) String userId,
@RequestParam(value = "name", required = false) String userName,
@RequestParam(value = "pageIndex", required = true, defaultValue = "1") String pageIndex,
@RequestParam(value = "pageSize", required = true, defaultValue = "5") String pageSize) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("userDto",userDto.toString());
map.put("id", userId);
map.put("name", userName);
map.put("pageIndex", pageIndex);
map.put("pageSize", pageSize);
return map;
}
运行
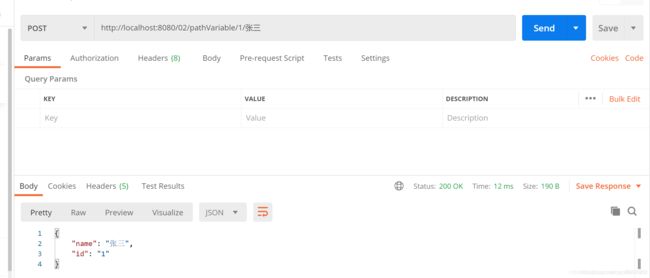
@PathVariable
该注解主要用于获取路径参数,像url/{id}/{name}这种形式的参数都可以,get获取post请求均可
示例代码如下:
@PostMapping("/pathVariable/{id}/{name}")
@ResponseBody
public Map<String, String> pathVariable(
@PathVariable(name = "id") String userId,
@PathVariable(name = "name") String userName) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("id", userId);
map.put("name", userName);
return map;
}
运行结果
@RequestBody
该注解用于获取请求体数据(body),get没有请求体,故而一般用于post请求
示例代码如下:
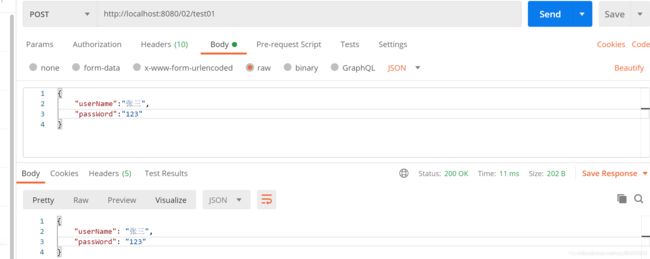
@PostMapping("/test01")
@ResponseBody
public UserDto test01(@RequestBody UserDto userDto) {
return userDto;
}
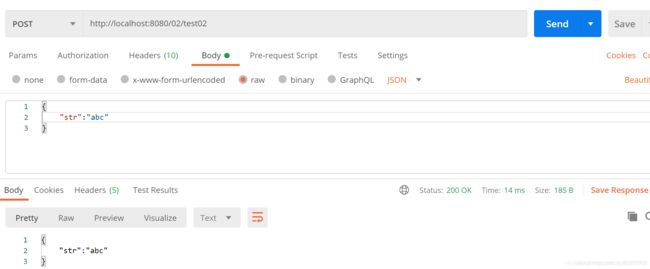
@PostMapping("/test02")
@ResponseBody
public String test02(@RequestBody String str) {
return str;
}
运行结果
注意,如果要传多个参数过去只能将其封装成一个类,如果是出现了多个@RequestBody注解访问的时候会报400错误,例如下面这种代码就是错误的
@PostMapping("/requestBody")
@ResponseBody
public Map<String,String> requestBody(
@RequestBody(required = true) String id,
@RequestBody(required = true) String name,
@RequestBody(required = false) String sex,
@RequestBody(required = false) String age
){
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("id","id");
map.put("name","name");
return map;
}
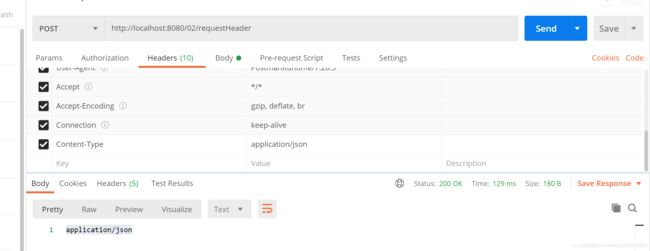
@RequestHeader
示例代码如下
@PostMapping("/requestHeader")
@ResponseBody
public String requestBody03(@RequestHeader(name = "Content-Type") String contentType){
return contentType;
}
运行结果
@CookieValue
由于postman模拟cookie本人不会弄,只能用别人的代码
@GetMapping("/demo3")
public void demo3(@RequestHeader(name = "myHeader") String myHeader,
@CookieValue(name = "myCookie") String myCookie) {
System.out.println("myHeader=" + myHeader);
System.out.println("myCookie=" + myCookie);
}
原文链接
链接: 菜鸟的springboot常用注解总结