2022年第十三届蓝桥杯省赛B组C++所有题解
- 写在前面
- 填空题
-
- 试题 A: 九进制转十进制
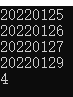
- 试题 B: 顺子日期
- 编程题
-
- 试题 C: 刷题统计
- 试题 D: 修剪灌木
- 试题 E: X 进制减法
- 试题 F: 统计子矩阵
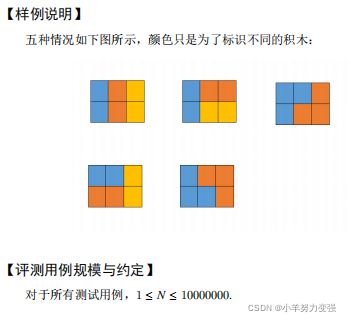
- 试题 G: 积木画
- 试题 H: 扫雷
- 试题 I: 李白打酒加强版
- 试题 J: 砍竹子
- 写到最后
写在前面
刚打完蓝桥杯省赛B组,小还差得远呢,这跟题解中的代码除了第一题,其他的都是看y总直播时候写的
看完本篇文章觉得不错的话记得点赞,收藏⭐,还有问题也可以评论留言
填空题
试题 A: 九进制转十进制

这道题是填空题,我们只需要算2×90+2×91+2×93,最后等于1478。
#include试题 B: 顺子日期

这题题意有点问题![]()
所以很给人误解,到底012算还是不算,在这我们不纠结题意,只看怎么解决。
#include 如果012不算,那就加一个限制条件
if (check(str)&&str[i] != 0)
#include 编程题
试题 C: 刷题统计
#include 试题 D: 修剪灌木

这题其实是一道数学题,多写几个样例就会发现前n/2个数中第i个数=2(n-i),然后是一个对称的。
3 4 2 4
4 6 4 4 6
5 8 6 4 6 8
6 10 8 6 6 8 10
#include 试题 E: X 进制减法
#include 试题 F: 统计子矩阵
#include 试题 G: 积木画
#include 试题 H: 扫雷
#include 试题 I: 李白打酒加强版
#include 试题 J: 砍竹子
#include 优先队列解法,时间复杂度 O(6nlogn)
#include 写到最后
最后看到这了,如果觉得自己有收获的话,可以给博主点个关注哦
觉得本篇文章不错的话记得点赞,收藏⭐,还有问题也可以评论留言
你的支持将是我继续创作的最大动力❤️❤️❤️
由于作者水平有限,如有错误和不准确之处在所难免,本人也很想知道这些错误,恳望读者批评指正!