入门案例
在服务消费者导入依赖
org.springframework.cloud spring-cloud-starter-openfeign
在启动类上添加@EnableFeignClients注解
Feign中已经自动集成了Ribbon负载均衡,因此不需要自己定义RestTemplate了
@SpringCloudApplication
@EnableFeignClients // 开启Feign注解
public class ConsumerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConsumerApplication.class, args);
}
}
编写Feign客户端
@FeignClient(value = "user-service") // 添加FeignClient,指定服务ID
public interface UserClient {
/**
* 声明一个feign的接口,它的实现是服务提供者的controller实现
*/
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
User getById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}
代码中调用,使用userClient访问:
@Autowired // 注入UserClient
private UserClient userClient;
public User getUserById(@PathVariable long id) {
User user = userClient.getById(id);
return user;
}
@FeignClient注解详解
@FeignClient注解只能在Interface接口上使用。Feign会通过动态代理,生成实现类。
FeignClient注解被@Target(ElementType.TYPE)修饰,表示FeignClient注解的作用目标在接口上
@FeignClient ,声明这是一个Feign客户端,同时通过 name / value 属性指定服务名称
接口中定义的方法,完全采用SpringMVC的注解,Feign会根据注解生成URL,并访问获取结果
服务的启动类要有@EnableFeignClients 注解才能使Fegin生效
@FeignClient注解的常用属性如下:
name / value:指定FeignClient的名称,如果项目使用了Ribbon(注册中心),name属性会作为微服务的名称,用于服务发现
url:一般用于调试,可以手动指定@FeignClient调用的地址。默认为空
url可以从配置文件获取,如果有则通过url调用,没有则根据服务名调用。格式为 url = "${xxx.xxx.xxx: }"
configuration:Feign配置类,可以自定义Feign的Encoder、Decoder、LogLevel、Contract,可以为每一个feign client指定不同的配置
fallback:定义容错的处理类,当调用远程接口失败或超时时,会调用对应接口的容错逻辑,fallback指定的类必须实现@FeignClient标记的接口
fallbackFactory:工厂类,用于生成fallback类示例,通过这个属性可以实现每个接口通用的容错逻辑,减少重复的代码
path:定义当前FeignClient的统一前缀,当项目中配置了server.context-path, server.servlet-path时使用
decode404:当发生http 404错误时,如果该字段位true,会调用decoder进行解码,否则抛出FeignException
调用方式:
方式一:接口提供方在注册中心
如果服务提供方已经注册到注册中心了,那么name或者value的值为:服务提供方的服务名称。必须为所有客户端指定一个name或者value
@FeignClient(value="run-product",fallback = ProductClientServiceFallBack.class)
方式二:单独的一个http接口,接口提供方没有注册到注册中心
@FeignClient(name="runClient11111",url="localhost:8001")
此处name的值为:调用客户端的名称
以上两种方式都能正常调用。name可以为注册中心的服务名称,加上url属性时,name的值就与注册中心服务名称无关。
Feign Client的配置
feign配置是在ribbon配置的基础上做了扩展,可以支持服务级超时时间配置,所以,feign配置和ribbon配置的效果是⼀样的。
SpringCloud对配置的优先级顺序如下:
- Feign局部配置 > Feign全局配置 > Ribbon局部配置 > Ribbon全局配置
- 配置文件属性和配置类的优先级顺序为:配置文件属性配置 > 配置类代码配置
feign:
client:
config:
default: # 全部服务配置
connectTimeout: 5000 # 建立连接的超时时长,单位:毫秒。默认为1000
readTimeout: 5000 # 指建立连接后从服务端读取到可用资源所用的超时时间,单位:毫秒。默认为1000
loggerLevel: FULL # 日志级别
errorDecoder: com.example.SimpleErrorDecoder # Feign的错误解码器,相当于代码配置方式中的ErrorDecoder
retryer: com.example.SimpleRetryer # 配置重试,相当于代码配置方式中的Retryer
requestInterceptors: # 配置拦截器,相当于代码配置方式中的RequestInterceptor
- com.example.FooRequestInterceptor
- com.example.BarRequestInterceptor
decode404: false # 是否对404错误解码
encode: com.example.SimpleEncoder
decoder: com.example.SimpleDecoder
contract: com.example.SimpleContract
serverName: # 单独给某⼀服务配置。serverName是服务名,使⽤的时候要⽤服务名替换掉这个
connectTimeout: 5000
readTimeout: 5000
Feign请求添加headers
方案一:方法上的@RequestMapping注解添加headers信息
@RequestMapping注解的属性中包含一个headers数组,可以在指定的方法上@RequestMapping注解中添加需要的headers,可以是写死的,也可以读取配置=
同理@RequestMapping一组的@PostMapping,@GetMapping注解等均适用
@FeignClient(name = "server",url = "127.0.0.1:8080")
public interface FeignTest {
@RequestMapping(value = "/test",headers = {"app=test-app","token=${test-app.token}"})
String test();
}
方案二:接口上的@RequestMapping注解添加headers信息
如果同一个接口中所有的方法都需要同样的headers,可以在接口上的@RequestMapping注解中添加headers,使整个接口的方法均被添加同样的headers
@FeignClient(name = "server",url = "127.0.0.1:8080")
@RequestMapping(value = "/",headers = {"app=test-app","token=${test-app.token}"})
public interface FeignTest {
@RequestMapping(value = "/test")
String test();
}
方案三:使用@Headers注解添加headers信息(不推荐)
@FeignClient(name = "server",url = "127.0.0.1:8080")
@Headers({"app: test-app","token: ${test-app.token}"})
public interface FeignTest {
@RequestMapping(value = "/test")
String test();
}
查看openfeign官方文档发现其使用的是@Headers来添加headers,测试发现并没有生效,spring cloud使用了自己的SpringMvcContract来解析注解,所以需要自己实现一个Contract来实现对@Headers注解的支持,具体实现参照(https://www.jb51.net/article/252325.htm)
方案四:自定义RequestInterceptor添加headers信息
feign提供了一个拦截器接口RequestInterceptor,实现RequestInterceptor接口就可以实现对feign请求的拦截,接口提供了一个方法apply(),实现apply()方法
实现apply()方法直接添加header会拦截所有的请求都加上headers,如果不是所有的feign请求都需要用到不建议此方法
@Component
public class FeignRequestInterceptor implements RequestInterceptor {
@Value("${test-app.token}")
private String token;
@Override
public void apply(RequestTemplate requestTemplate) {
requestTemplate.header("app","test-app");//静态
requestTemplate.header("token",token);//读配置
}
}
方案五:自定义RequestInterceptor实现添加动态数据到header
以上方案都不适合把动态的数据放入headers中,而通常场景下可能经常需要把计算的签名,用户id等动态信息设置到headers,所以还需要一个更加完善的方案。方案1/2/3均不能设置动态的值,方案4可以设置动态值,但是没做到请求的区分,所以在方案4的基础上进行改进得到了较为完善的方案5。具体实现如下:
在请求调用代码中,获取到HttpServletRequest对象,将需要添加到headers中的值封装成一个map后放入HttpServletRequest的attribute域中
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = Objects.requireNonNull(attributes).getRequest();
String signedMsg = getSignedMsg(reqJson); // 计算签名字符串
Map reqMap = new HashMap<>();
reqMap.put("content-type", "application/json"); //常量字段
reqMap.put("accessKey", accessKey); //常量字段
reqMap.put("signedMsg", signedMsg); //动态计算/获取字段
request.setAttribute("customizedRequestHeader", reqMap);
在自定义RequestInterceptor中获取到HttpServletRequest对象的attribute域中指定的key,将key对应map中的所有参数加入到headers。
@Component
public class FeignRequestInterceptor implements RequestInterceptor {
@Override
public void apply(RequestTemplate requestTemplate) {
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
// 设置自定义header
// 设置request中的attribute到header以便转发到Feign调用的服务
Enumeration reqAttrbuteNames = request.getAttributeNames();
if (reqAttrbuteNames != null) {
while (reqAttrbuteNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = reqAttrbuteNames.nextElement();
if (!"customizedRequestHeader".equalsIgnoreCase(attrName)) {
continue;
}
Map requestHeaderMap = (Map)request.getAttribute(attrName);
for (Map.Entry entry : requestHeaderMap.entrySet()) {
requestTemplate.header(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
break;
}
}
}
}
负载均衡 (Ribbon)
Feign中本身已经集成了Ribbon依赖和自动配置,默认支持Ribbon。
Fegin内置的ribbon默认设置了请求超时时长,默认是1000ms。因为Ribbon内部有重试机制,一旦超时,会自动重新发起请求
可以通过配置来修改:
全局配置 使用 ribbon.=
ribbon:
ReadTimeout: 2500 # 数据通信超时时长,单位:ms。默认为1000
ConnectTimeout: 500 # 连接超时时长,单位:ms。默认为1000
OkToRetryOnAllOperations: false # 是否对所有的异常请求(连接异常和请求异常)都重试。默认为false
MaxAutoRetriesNextServer: 1 # 最多重试多少次连接服务(实例)。默认为1。不包括首次调用
MaxAutoRetries: 0 # 服务的单个实例的重试次数。默认为0。不包括首次调用
NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName: com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule # 切换负载均衡策略为随机
指定服务配置 <服务名称>.ribbon. =
serverName: # 单独给某⼀服务配置。serverName是服务名,使⽤的时候要⽤服务名替换掉这个
ribbon:
connectTimeout: 5000
readTimeout: 5000
容错机制
Hystrix支持
Feign默认也有对Hystix的集成,只不过,默认情况下是关闭的。需要通过下面的参数来开启:
feign:
hystrix:
enabled: true # 开启hystrix熔断机制
hystrix:
command:
default: # 全局默认配置
execution: # 线程隔离相关
timeout:
enabled: true # 是否给方法执行设置超时时间,默认为true。一般不改。
isolation:
strategy: THREAD # 配置请求隔离的方式,这里是默认的线程池方式。还有一种信号量的方式semaphore,
thread:
timeoutlnMilliseconds: 10000 # 方式执行的超时时间,默认为1000毫秒,在实际场景中需要根据情况设置
circuitBreaker: # 服务熔断相关
requestVolumeThreshold: 10 # 触发熔断的最小请求次数,默认20
sleepWindowInMilliseconds: 10000 # 休眠时长,单位毫秒,默认是5000毫秒
errorThresholdPercentage: 50 # 触发熔断的失败请求最小占比,默认50%
serverName: # 单独给某⼀服务配置
execution:
timeout:
enabled: true
isolation:
strategy: THREAD
thread:
timeoutlnMilliseconds: 10000
注意:
Hystix的超时时间应该比Ribbon重试的总时间要大 ,否则Hystrix命令超时后,该命令直接熔断,重试机制就没有任何意义了。
Ribbon:总重试次数 = 访问的服务器数 * 单台服务器最大重试次数
即 总重试次数 = (1+MaxAutoRetriesNextServer)*(1+MaxAutoRetries )
Hystrix超时时间 > (Ribbon超时时间总和)* 重试次数
故 建议hystrix的超时时间为:
( ( 1+MaxAutoRetriesNextServer) * (1+MaxAutoRetries ) ) * (ReadTimeout + connectTimeout)
- MaxAutoRetries:Ribbon配置: 服务的单个实例的重试次数。不包括首次调用
- MaxAutoRetriesNextServer:Ribbon配置: 最多重试多少次连接服务(实例)。不包括首次调用
- ReadTimeout:Ribbon配置: 通信超时时间
- connectTimeout:Ribbon配置: 建立连接超时时间
Sentinel支持
Sentinel 可以通过并发线程数模式的流量控制来提供信号量隔离的功能。并且结合基于响应时间的熔断降级模式,可以在不稳定资源的平均响应时间比较高的时候自动降级,防止过多的慢调用占满并发数,影响整个系统。
依赖
com.alibaba.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel
在配置文件中开启Feign对Sentinel的支持
feign:
sentinel:
enabled: true
Feign开启容错机制支持后的使用方式
Feign 开启 Hystrix 或 Sentinel 容错机制支持后的使用方式均是如下两种:
方案一:直接继承被容错的接口,并为每个方法实现容错方案
方案二:实现FallbackFactory接口
方案一:直接继承被容错的接口,并为每个方法实现容错方案
定义一个类,作为fallback的处理类 。直接继承被容错的接口,并为每个方法实现容错方案
@Component
public class UserClientFallback implements UserClient {
@Override
public User getById(Long id) {
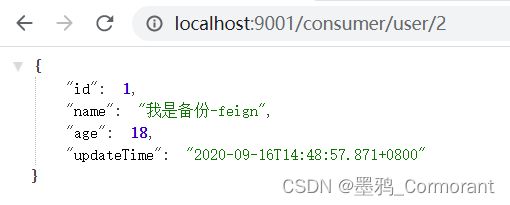
return new User(1L, "我是备份-feign", 18, new Date());
}
}
在 @FeignClient 注解中使用 fallback 属性指定自定义的容错处理类
@FeignClient(value = "user-service",fallback = UserClientFallback.class)
public interface UserClient {
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
User getById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}
测试验证
方案二:实现FallbackFactory接口。可以拿到具体的服务错误信息,便于后期排查问题
@FeignClient(value="34-SPRINGCLOUD-SERVICE-GOODS", fallbackFactory = GoodsRemoteClientFallBackFactory.class)
public interface GoodsRemoteClient {
@RequestMapping("/service/goods")
public ResultObject goods();
}
@Component public class GoodsRemoteClientFallBackFactory implements FallbackFactory{ @Override public GoodsRemoteClient create(Throwable throwable) { return new GoodsRemoteClient() { @Override public ResultObject goods() { String message = throwable.getMessage(); // message即为错误信息 System.out.println("feign远程调用异常:" + message); return new ResultObject(); } }; } }
请求压缩feign.compression
Spring Cloud Feign 支持对请求和响应进行GZIP压缩,以减少通信过程中的性能损耗。通过下面的参数即可开启请求与响应的压缩功能:
feign:
compression:
request:
enabled: true
response:
enabled: true
也可以对请求的数据类型,以及触发压缩的大小下限进行设置,只有超过这个大小的请求才会对其进行压缩:
feign:
compression:
request:
enabled: true
mime-types: text/xml,application/xml,application/json
min-request-size: 2048
日志级别
通过logging.level.xx=debug来设置日志级别。然而这个对Fegin客户端而言不会产生效果。因为@FeignClient注解修改的客户端在被代理时,都会创建一个新的Fegin.Logger实例,所以需要额外指定这个日志的级别才可以。
Feign支持4种日志级别:
- NONE:不记录任何日志信息,这是默认值。
- BASIC:仅记录请求的方法,URL以及响应状态码和执行时间
- HEADERS:在BASIC的基础上,额外记录了请求和响应的头信息
- FULL:记录所有请求和响应的明细,包括头信息、请求体、元数据。
全局配置
方式一:配置文件属性实现
feign:
client:
config:
default: # 将调用的微服务名称设置为default即为配置成全局
loggerLevel: FULL
方式一:代码实现
//在启动类上为@EnableFeignClients注解添加defaultConfiguration配置 @EnableFeignClients(defaultConfiguration = FeignConfig.class)
细粒度(指定服务配置)
方式一:配置文件实现
feign:
client:
config:
server-1: # 想要调用的微服务名称
loggerLevel: FULL
方式二:代码实现
1)编写配置类,定义日志级别
@Configuration
public class FeignConfig {
@Bean
Logger.Level level(){
return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
}
2)在FeignClient中指定配置类:(可以省略)
@FeignClient(value = "user-service", configuration = FeignConfig.class)
// 添加FeignClient,指定服务ID
public interface UserClient {
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
User getById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}
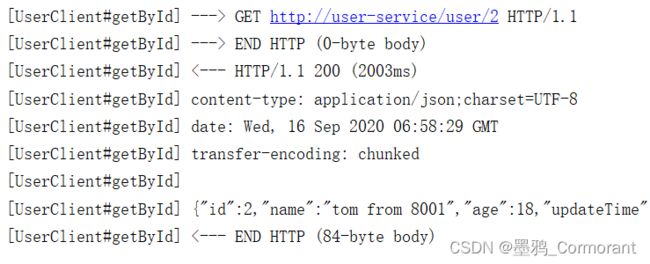
Feign每次访问的日志示例:
到此这篇关于SpringCloud超详细讲解Feign声明式服务调用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringCloud Feign内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!