Python双人五子棋
优质资源分享
| 学习路线指引(点击解锁) | 知识定位 | 人群定位 |
|---|---|---|
| Python实战微信订餐小程序 | 进阶级 | 本课程是python flask+微信小程序的完美结合,从项目搭建到腾讯云部署上线,打造一个全栈订餐系统。 |
| Python量化交易实战 | 入门级 | 手把手带你打造一个易扩展、更安全、效率更高的量化交易系统 |
这篇文章旨在介绍一个双人的五子棋程序。再次重申,本人不擅长对代码的可读性进行优化,所以可能有些杂乱(在所难免)。
先瞅一眼效果图:
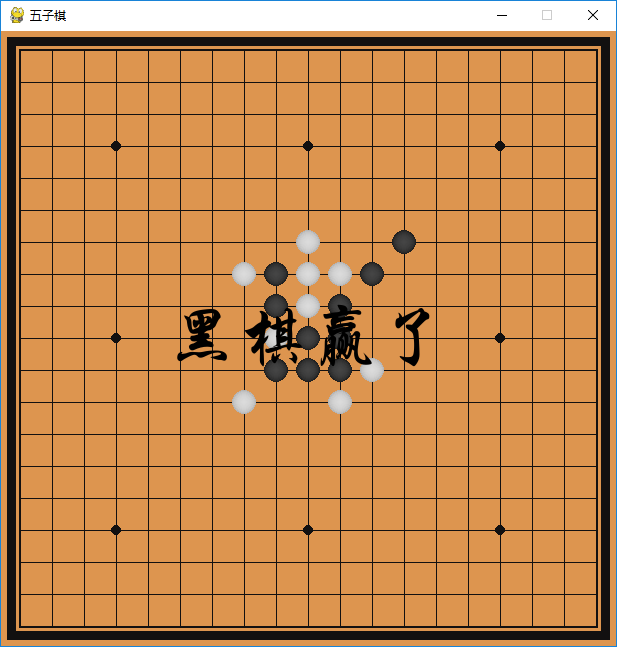
请注意,这个棋子……是这么圆润立体!本程序不需任何素材图片,完全用代码绘制所需的图像,因此这样立体的棋子十分难能可贵。那么,这究竟是如何做到的呢?别急,听我慢慢道来。
首先,一个好的程序必须配有高端大气的文字。对于博大精深的中文,gbk或utf-8的编码声明自然是非常必要的。于是,就有了第一行代码:
#coding:utf-8
然后,当然是模块的导入。本次所需的模块不多,只有sys、pygame和random。其中pygame需要用pip工具进行安装。
import sys
import pygame
import random
接下来,我们定义一个函数:do(),里面输入我们所需要的代码。至于为何要定义函数,这是因为在游戏结束后需要重新运行该程序,因而不可避免地要将全部的程序代码输入一个函数中,并调用这个函数。
def do():
然后,就是最重磅的棋子绘制函数,我们先看黑棋:
def black(x, y):
a = 30
b = 30
c = 30
d = 8
for i in range(50):
pygame.draw.circle(screen, (a, b, c), [19.5 + 32 * x, 19.5 + 32 * y], 111 / d)
a += 0.3
b += 0.3
c += 0.3
d += 0.2
pygame.display.update()
这里的x和y是绘制黑棋的位置,暂且先不管。可以看到,这一个圆润的棋子是有50个同心圆组成。这些同心圆的颜色逐个变浅,相邻两个圆的颜色差值不变。因此,我们只需要使圆的直径(或半径)呈曲线变化,就可以使绘制的棋子边缘非常圆润。作为一个初二的学生,我立马想到了反比例函数。因此,“d=8”“111/d”和“d+=0.2”实际上是使同心圆的半径随循环变量的变化呈一个偏移的反比例函数,这样就可以营造一种圆润的视感。
同理,白棋的绘制也是遵循类似的方式。在此不在赘述,只给出代码:
def white(x, y):
a = 200
b = 200
c = 200
d = 8
for i in range(50):
pygame.draw.circle(screen, (a, b, c), [19.5 + 32 * x, 19.5 + 32 * y], 111 / d)
a += 0.3
b += 0.3
c += 0.3
d += 0.2
pygame.display.update()
接下来,是冗长无味的棋盘绘制:
pygame.init()
screen = pygame.display.set\_mode((615, 615))
pygame.display.set\_caption('五子棋')
screen.fill("#DD954F")
a = pygame.Surface((603, 603), flags=pygame.HWSURFACE)
a.fill(color='#121010')
b = pygame.Surface((585, 585), flags=pygame.HWSURFACE)
b.fill(color="#DD954F")
c = pygame.Surface((579, 579), flags=pygame.HWSURFACE)
c.fill(color='#121010')
d = pygame.Surface((576, 576), flags=pygame.HWSURFACE)
d.fill(color="#DD954F")
e = pygame.Surface((31, 31), flags=pygame.HWSURFACE)
e.fill(color="#DD954F")
screen.blit(a, (6.5, 6.5))
screen.blit(b, (15, 15))
screen.blit(c, (18, 18))
for j in range(18):
for i in range(18):
screen.blit(e, (20 + 32 * i, 20 + 32 * j))
alist = []
for j in range(19):
alistone = []
for i in range(19):
alistone.append(0)
alist.append(alistone)
pygame.draw.circle(screen, '#121010', [307.5, 307.5], 5)
pygame.draw.circle(screen, '#121010', [115.5, 307.5], 5)
pygame.draw.circle(screen, '#121010', [499.5, 307.5], 5)
pygame.draw.circle(screen, '#121010', [115.5, 499.5], 5)
pygame.draw.circle(screen, '#121010', [499.5, 499.5], 5)
pygame.draw.circle(screen, '#121010', [115.5, 115.5], 5)
pygame.draw.circle(screen, '#121010', [499.5, 115.5], 5)
pygame.draw.circle(screen, '#121010', [307.5, 499.5], 5)
pygame.draw.circle(screen, '#121010', [307.5, 115.5], 5)
pygame.display.flip()
可以看到,我们先画了一个花哨的边框,然后画上其中的格子,顺便定义了一个被0填满的19*19的二维列表(在此处似乎很冗余,但到后面,你会发现它异常有用!)。最后,九个平平无奇的点被画上了棋盘。
至此,我们的五子棋初见雏形。但是,要使用它进行对弈,这还远远不够。
wb = "black"
font1 = pygame.font.SysFont('stxingkai', 70)
while True:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
pygame.quit()
sys.exit()
if event.type == pygame.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:
x, y = pygame.mouse.get\_pos()
x = round((x - 19.5) / 32)
y = round((y - 19.5) / 32)
if x < 0:
x = 0
if x > 18:
x = 18
if y < 0:
y = 0
if y > 18:
y = 18
z = False
if alist[x][y] == 0:
eval(wb + "({},{})".format(x, y))
if wb == "black":
alist[x][y] = 1
wb1 = "黑棋"
wb = "white"
elif wb == "white":
alist[x][y] = 2
wb1 = "白棋"
wb = "black"
这里,就是最核心的对弈程序。首先我们进入主循环,并获取事件。在这里,我们除了对按下关闭按钮进行了几乎每个pygame程序都会进行的处理外,还对按下鼠标事件进行了处理。首先,我们获取鼠标点击的坐标,通过计算来得到对应的格点(这里对不在格点上的点击进行四舍五入,对棋盘之外的点击自动匹配与其最近的格点)。然后,根据此时的先手方和计算得的格点运行black/white函数,绘制所需的棋子。
xx = x
yy = y
while True:
if xx == 0:
break
elif alist[xx][yy] != alist[x][y]:
xx += 1
break
else:
xx -= 1
num = 0
while True:
if xx == 18:
break
elif alist[xx][yy] != alist[x][y]:
break
else:
xx += 1
num += 1
if num >= 5:
pygame.font.init()
text = font1.render("{}赢了".format(wb1), True, (0, 0, 0))
textRect = text.get\_rect()
textRect.center = (307.5, 307.5)
screen.blit(text, textRect)
pygame.display.flip()
while True:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
pygame.quit()
sys.exit()
if event.type == pygame.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:
do()
xx = x
yy = y
while True:
if yy == 0:
break
elif alist[xx][yy] != alist[x][y]:
yy += 1
break
else:
yy -= 1
num = 0
while True:
if yy == 18:
break
elif alist[xx][yy] != alist[x][y]:
break
else:
yy += 1
num += 1
if num >= 5:
pygame.font.init()
text = font1.render("{}赢了".format(wb1), True, (0, 0, 0))
textRect = text.get\_rect()
textRect.center = (307.5, 307.5)
screen.blit(text, textRect)
pygame.display.flip()
while True:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
pygame.quit()
sys.exit()
if event.type == pygame.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:
do()
xx = x
yy = y
while True:
if xx == 0:
break
elif yy == 0:
break
elif alist[xx][yy] != alist[x][y]:
xx += 1
yy += 1
break
else:
xx -= 1
yy -= 1
num = 0
while True:
if xx == 18:
break
elif yy == 18:
break
elif alist[xx][yy] != alist[x][y]:
break
else:
xx += 1
yy += 1
num += 1
if num >= 5:
pygame.font.init()
text = font1.render("{}赢了".format(wb1), True, (0, 0, 0))
textRect = text.get\_rect()
textRect.center = (307.5, 307.5)
screen.blit(text, textRect)
pygame.display.flip()
while True:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
pygame.quit()
sys.exit()
if event.type == pygame.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:
do()
xx = x
yy = y
while True:
if xx == 0:
break
elif yy == 18:
break
elif alist[xx][yy] != alist[x][y]:
xx += 1
yy -= 1
break
else:
xx -= 1
yy += 1
num = 0
while True:
if xx == 18:
break
elif yy == 0:
break
elif alist[xx][yy] != alist[x][y]:
break
else:
xx += 1
yy -= 1
num += 1
if num >= 5:
pygame.font.init()
text = font1.render("{}赢了".format(wb1), True, (0, 0, 0))
textRect = text.get\_rect()
textRect.center = (307.5, 307.5)
screen.blit(text, textRect)
pygame.display.flip()
while True:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
pygame.quit()
sys.exit()
if event.type == pygame.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:
do()
这是冗长的胜负判断,具体内容我自己也难以解释(这个程序编了有一段时间了)。主要思路,是向各个方向寻找同色棋子的连接,并判断是否满五个棋。当然,不得不承认,这一段确实不太高明,似乎有别人发布过比我更好的方案,感兴趣的可以上网找找。
do()
这是程序的收尾,也就是对do()函数的运行。至此,整个程序完全结束。
完整代码:
#coding:utf-8
import sys
import pygame
import random
def do():
def black(x, y):
a = 20
b = 20
c = 20
d = 0
for i in range(50):
pygame.draw.circle(screen, (a, b, c), [19.5 + 32 * x, 19.5 + 32 * y], (10/(d-5)+10)*1.6)
a += 1
b += 1
c += 1
d += 0.08
pygame.display.update()
def white(x, y):
a = 170
b = 170
c = 170
d = 0
for i in range(50):
pygame.draw.circle(screen, (a, b, c), [19.5 + 32 * x, 19.5 + 32 * y], (10/(d-5)+10)*1.6)
a += 1
b += 1
c += 1
d += 0.08
pygame.display.update()
pygame.init()
screen = pygame.display.set\_mode((615, 615))
pygame.display.set\_caption('五子棋')
screen.fill("#DD954F")
a = pygame.Surface((603, 603), flags=pygame.HWSURFACE)
a.fill(color='#121010')
b = pygame.Surface((585, 585), flags=pygame.HWSURFACE)
b.fill(color="#DD954F")
c = pygame.Surface((579, 579), flags=pygame.HWSURFACE)
c.fill(color='#121010')
d = pygame.Surface((576, 576), flags=pygame.HWSURFACE)
d.fill(color="#DD954F")
e = pygame.Surface((31, 31), flags=pygame.HWSURFACE)
e.fill(color="#DD954F")
screen.blit(a, (6.5, 6.5))
screen.blit(b, (15, 15))
screen.blit(c, (18, 18))
for j in range(18):
for i in range(18):
screen.blit(e, (20 + 32 * i, 20 + 32 * j))
alist = []
for j in range(19):
alistone = []
for i in range(19):
alistone.append(0)
alist.append(alistone)
pygame.draw.circle(screen, '#121010', [307.5, 307.5], 5)
pygame.draw.circle(screen, '#121010', [115.5, 307.5], 5)
pygame.draw.circle(screen, '#121010', [499.5, 307.5], 5)
pygame.draw.circle(screen, '#121010', [115.5, 499.5], 5)
pygame.draw.circle(screen, '#121010', [499.5, 499.5], 5)
pygame.draw.circle(screen, '#121010', [115.5, 115.5], 5)
pygame.draw.circle(screen, '#121010', [499.5, 115.5], 5)
pygame.draw.circle(screen, '#121010', [307.5, 499.5], 5)
pygame.draw.circle(screen, '#121010', [307.5, 115.5], 5)
pygame.display.flip()
wb = "black"
font1 = pygame.font.SysFont('stxingkai', 70)
while True:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
pygame.quit()
sys.exit()
if event.type == pygame.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:
x, y = pygame.mouse.get\_pos()
x = round((x - 19.5) / 32)
y = round((y - 19.5) / 32)
if x < 0:
x = 0
if x > 18:
x = 18
if y < 0:
y = 0
if y > 18:
y = 18
z = False
if alist[x][y] == 0:
eval(wb + "({},{})".format(x, y))
if wb == "black":
alist[x][y] = 1
wb1 = "黑棋"
wb = "white"
elif wb == "white":
alist[x][y] = 2
wb1 = "白棋"
wb = "black"
xx = x
yy = y
while True:
if xx == 0:
break
elif alist[xx][yy] != alist[x][y]:
xx += 1
break
else:
xx -= 1
num = 0
while True:
if xx == 18:
break
elif alist[xx][yy] != alist[x][y]:
break
else:
xx += 1
num += 1
if num >= 5:
pygame.font.init()
text = font1.render("{}赢了".format(wb1), True, (0, 0, 0))
textRect = text.get\_rect()
textRect.center = (307.5, 307.5)
screen.blit(text, textRect)
pygame.display.flip()
while True:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
pygame.quit()
sys.exit()
if event.type == pygame.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:
do()
xx = x
yy = y
while True:
if yy == 0:
break
elif alist[xx][yy] != alist[x][y]:
yy += 1
break
else:
yy -= 1
num = 0
while True:
if yy == 18:
break
elif alist[xx][yy] != alist[x][y]:
break
else:
yy += 1
num += 1
if num >= 5:
pygame.font.init()
text = font1.render("{}赢了".format(wb1), True, (0, 0, 0))
textRect = text.get\_rect()
textRect.center = (307.5, 307.5)
screen.blit(text, textRect)
pygame.display.flip()
while True:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
pygame.quit()
sys.exit()
if event.type == pygame.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:
do()
xx = x
yy = y
while True:
if xx == 0:
break
elif yy == 0:
break
elif alist[xx][yy] != alist[x][y]:
xx += 1
yy += 1
break
else:
xx -= 1
yy -= 1
num = 0
while True:
if xx == 18:
break
elif yy == 18:
break
elif alist[xx][yy] != alist[x][y]:
break
else:
xx += 1
yy += 1
num += 1
if num >= 5:
pygame.font.init()
text = font1.render("{}赢了".format(wb1), True, (0, 0, 0))
textRect = text.get\_rect()
textRect.center = (307.5, 307.5)
screen.blit(text, textRect)
pygame.display.flip()
while True:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
pygame.quit()
sys.exit()
if event.type == pygame.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:
do()
xx = x
yy = y
while True:
if xx == 0:
break
elif yy == 18:
break
elif alist[xx][yy] != alist[x][y]:
xx += 1
yy -= 1
break
else:
xx -= 1
yy += 1
num = 0
while True:
if xx == 18:
break
elif yy == 0:
break
elif alist[xx][yy] != alist[x][y]:
break
else:
xx += 1
yy -= 1
num += 1
if num >= 5:
pygame.font.init()
text = font1.render("{}赢了".format(wb1), True, (0, 0, 0))
textRect = text.get\_rect()
textRect.center = (307.5, 307.5)
screen.blit(text, textRect)
pygame.display.flip()
while True:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
pygame.quit()
sys.exit()
if event.type == pygame.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:
do()
do()