Springboot 缓存的使用
目录
一、通过LinkedHashMap实现本地缓存
(1)服务层如下:
(2)表现层如下:
(3)测试效果如下:
二、通过springboot的默认缓存方案
(1)首先配置文件添加:
(2)启动了开启缓存
(3)服务层添加注解如下:
(4)测试一下:
三、使用Redis缓存
(1)添加依赖
(2)配置yml
(3)使用方法还是用默认的实验来测试
四、个人最喜欢的方案——jetCache同时实现远程和本地缓存
一、通过LinkedHashMap实现本地缓存
(1)服务层如下:
package com.wxl.redistest.service.impl;
import com.wxl.redistest.pojo.Person;
import com.wxl.redistest.service.CacheTestOne;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.HashMap;
@Service
public class CacheTestOneImpl implements CacheTestOne {
private final HashMap hashMap=new HashMap<>();
@Override
public void putCache(Integer id,Person person) {
hashMap.put(id,person);
}
@Override
public Person gainCache(Integer id) {
return hashMap.get(id);
}
}
(2)表现层如下:
package com.wxl.redistest.controller;
import com.wxl.redistest.pojo.Person;
import com.wxl.redistest.service.impl.CacheTestOneImpl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/testOne")
public class CacheTestControllerOne {
@Autowired
private CacheTestOneImpl cacheTestOne;
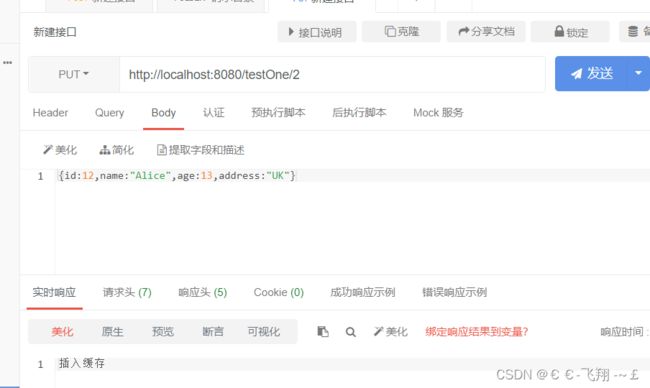
@PutMapping("/{id}")
public String test1(@PathVariable Integer id, @RequestBody Person person){
cacheTestOne.putCache(id,person);
return "插入缓存";
}
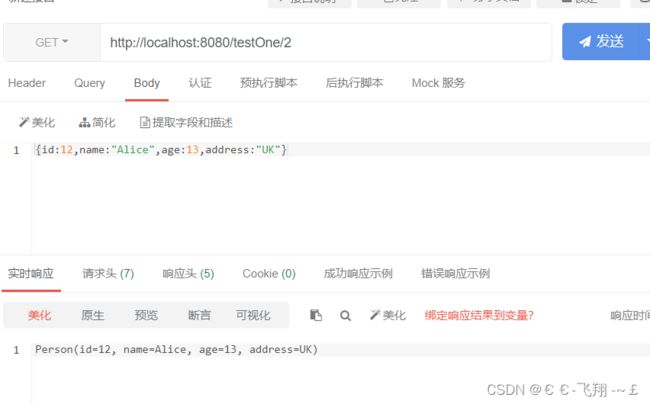
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String test2(@PathVariable Integer id){
Person person=cacheTestOne.gainCache(id);
return person.toString();
}
}
(3)测试效果如下:
可以看到变量实现了缓存功能。但这个情况存在一个弊端,就是可能消耗过多的内存空间,并且服务器重启也会导致缓存清空。
二、通过springboot的默认缓存方案
@EnableCache和@Cacheable两个注解实现
(1)首先配置文件添加:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-cache
(2)启动了开启缓存
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching//开启缓存
public class CacheApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CacheApplication.class, args);
}
}(3)服务层添加注解如下:
package com.wxl.cache.service;
import com.wxl.cache.dao.TestDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class TestService {
@Autowired
private TestDao testDao;
@Cacheable(value="cacheSpace",key="#id")
public String gainCache(Integer id){
return testDao.putData();//如果执行,就会打印信息,方便查看缓存是否生效
}
}
有@Cacheable注解,value为自定义名称的缓存空间,key为变量名,使用后效果:
服务器会先访问缓存里的变量名,如果该变量名不存在,才会执行数据库操作层的操作,否则直接返回缓存里的数据,减小后台压力。
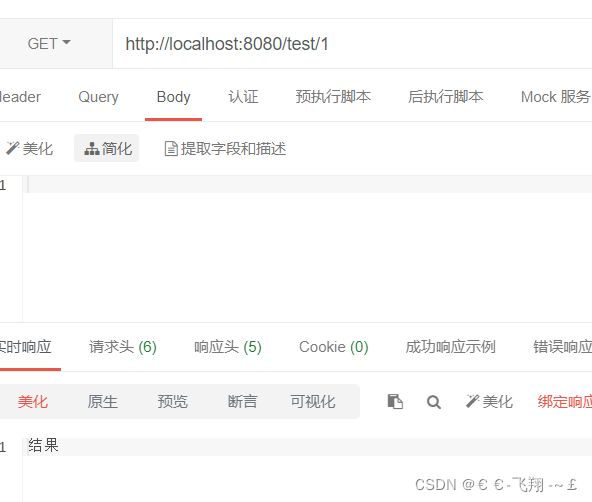
(4)测试一下:
第一次访问:(此时缓存了没有该数据)
从控制台可以看到,此时调用了数据库操作层。再次多次访问该链接,可以看到该条信息不会再打印,但返回结果仍然正确,这就是缓存在起作用。
@Cacheable不仅会往缓存里放入数据,还会往外读取数据。
@CachePut仅会往缓存里放入数据。若要再获取缓存数据必须采用spring容器配合@Cacheable注解的方法去获取。
三、使用Redis缓存
(1)添加依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
(2)配置yml
spring:
cache:
type: redis
# redis:
# time-to-live: 10s #设置缓存存在时间
# key-prefix: wxl_ #设置key的前缀
# cache-null-values: false #是否缓存空值
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
(3)使用方法还是用默认的实验来测试
效果和默认的效果一样。
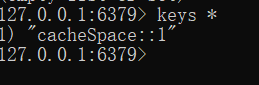
再查看redis服务器,
可以看到缓存已新增!
四、个人最喜欢的方案——jetCache同时实现远程和本地缓存
我写的使用链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_50909707/article/details/123295265