自然语言处理——Transformer模型架构
自然语言处理
Transformer
Transformer的优势
- 相比LSTM和GRU模型,Transformer有两个显著的优势:
- Transformer能够利用分布式GPU进行并行训练,提高模型训练效率
- 在分析预测更长文本时,捕捉间隔较长的语义关联效果更好
认识Transformer架构
- Transformer模型的作用:基于seq2seq架构的Transformer模型可以完成NLP领域研究的典型任务,如机器翻译、文本生成等。同时又可以构建预训练语言模型,用于不同任务的迁移学习
- 在接下来的架构分析中,我们将假设使用Transformer模型架构处理从一种语言文本到另一种语言文本的翻译工作,因此很多命名方式遵循NLP中的规则。比如:Embeddding层将称作文本嵌入层,Embedding层产生的张量称为词嵌入张量,它的最后一维将称作词向量等。
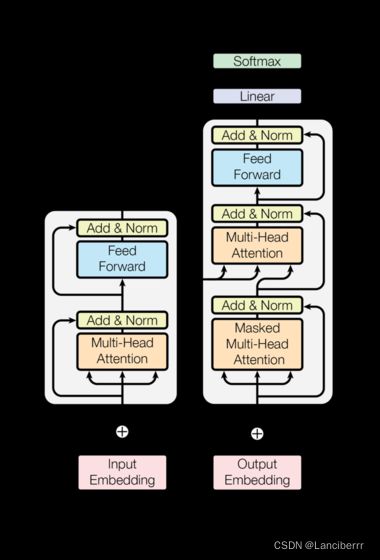
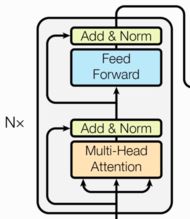
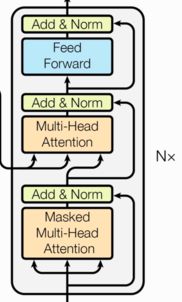
- Transformer总体架构图
- Transformer总体架构分为四个部分:
- 输入部分
- 输出部分
- 编码器部分
- 解码器部分
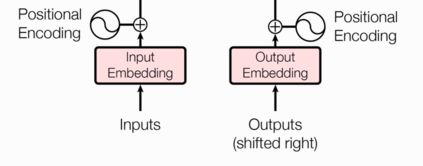
- 输入部分
- 源文本嵌入层以及位置编码器
- 目标文本嵌入层及其位置编码器
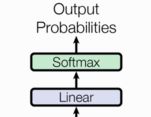
- 输出部分
- 线性层
- softmax层
- 编码器部分
- 由N个编码器层堆叠而成
- 每个编码器层由两个子层连接结构组成
- 第一个子层连接结构包括一个多头自注意力子层和一个规范化层和一个残差连接
- 第二个子层连接结构包括一个前馈全连接子层和规范化层以及一个残差连接
- 解码器部分
- 由N个解码器层堆叠而成
- 每个解码器层有三个子层连接结构组成
- 第一个子层连接结构包括一个多头自注意力子层和规范化层以及一个残差连接
- 第二个子层连接结构包括一个多头注意力子层和规范化层以及一个残差连接
- 第三个子层连接结构包括一个前馈全连接子层和规范化层以及一个残差连接
输入部分实现
- 源文本嵌入层及其位置编码器
- 目标文本嵌入层及其位置编码器
- 文本嵌入层代码分析:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import math
# torch中变量封装函数Variable
from torch.autograd import Variable
# 定义Embeddings类来实现文本嵌入层,这里s说明有两个一模一样的嵌入层,共享参数
# 继承nn.Module,这样就有标准层的一些形式,我们也可以理解为一种模式,自己实现的所有层
class Embeddings(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, vocab):
"""
类初始化函数
:param d_model:词嵌入维度
:param vocab:词表大小
"""
super(Embeddings, self).__init__()
# 调用预定义层获得一个词嵌入对象self.lut
self.lut = nn.Embedding(vocab, d_model)
# 将d_model传入类中
self.d_model = d_model
def forward(self, x):
"""
前向传播逻辑
:param x: 因为Embedding层是首层,所以代表输入给模型的文本通过词汇映射后的张量
:return: 将x传给self.lut冰与根号下self.d_model相乘作为结果返回
"""
return self.lut(x) * math.sqrt(self.d_model)
d_model = 512
vocab = 1000
x = Variable(torch.LongTensor([[100, 2, 421, 508], [491, 998, 1, 221]]))
emb = Embeddings(d_model, vocab)
embr = emb(x)
print('embr:', embr)
print(embr.shape)
embr: tensor([[[ 1.0475e+00, 1.3453e+01, 2.6241e-01, ..., 2.9441e+01,
-2.5215e+01, -4.3535e+00],
[ 2.4608e+01, 7.7417e+00, -1.2245e+01, ..., -1.6638e+01,
-6.3578e+00, 1.4190e+01],
[ 2.2178e+00, 3.4196e+00, -5.1346e+01, ..., -9.3995e+00,
4.1286e+00, 1.1181e+01],
[-8.0681e-01, -3.9530e+01, -5.4157e+01, ..., -2.8879e+00,
-3.0965e+00, -2.6074e+00]],
[[-3.3936e+01, 1.2602e+00, 3.2782e+01, ..., -9.1337e+00,
8.0855e+00, -1.1189e+01],
[ 3.4364e+00, 4.8852e+00, -1.6806e+01, ..., -1.0207e-01,
-2.3943e+01, 2.8694e+01],
[ 4.1119e+01, -1.5948e+01, 1.4040e-02, ..., 9.6460e+00,
-1.1069e+01, 1.1702e+01],
[ 2.8475e+01, 9.4708e+00, 2.6635e+01, ..., 1.7517e+01,
-2.6948e+01, 6.3171e+00]]], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
- 位置编码器的作用:因为在Transformer的编码器结构中,并没有针对词汇位置信息的处理,所以需要在Embedding层后加入位置编码器,将词汇位置不同可能会产生不同语义的信息加入到词嵌入张量中,以弥补位置信息的缺失
# 定义位置编码器类,同样把他看作是一个层,因此会继承nn.Module
class PositionalEncoding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, dropout, max_len=5000):
"""
位置编码器的初始化函数
:param d_model: 词嵌入维度
:param dropout: 置零比率
:param max_len: 每个句子最大长度
"""
super(PositionalEncoding, self).__init__()
# 实例化Dropout层
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=dropout)
# 初始化一个位置编码矩阵,是一个0阵,大小是max_len*d_model
pe = torch.zeros(max_len, d_model)
# 初始化一个绝对位置矩阵
# 首先使用arange方法获得一个连续自然数向量,然后扩展维度变成max_len*1
position = torch.arange(0, max_len).unsqueeze(1)
# 有了绝对位置矩阵、位置编码矩阵,现在需要进行连接。
# 根据他们两个的形状,可以创建一个1*d_model形状的变换矩阵div_term
div_term = torch.exp(torch.arange(0, d_model, 2)*
-(math.log(10000.0) / d_model))
pe[:, 0::2] = torch.sin(position * div_term)
pe[:, 1::2] = torch.cos(position * div_term)
# 此时pe是一个二维矩阵,为得到embedding的输出,需要扩展一个维度
pe = pe.unsqueeze(0)
# 最后把pe位置编码矩阵注册成buffer
# 我们认为buffer是对模型效果有帮助的、但又不是模型结构中超参数或者参数,不需要随着优化步骤迭代
# 注册之后就可以在模型保存后重加载时和模型结构与参数一同被加载
self.register_buffer('pe', pe)
def forward(self, x):
"""
前向函数
:param x:文本序列的词嵌入表示
:return:经处理的x
"""
# 我们默认的max_len太大了,一般不会有句子超过5000词汇。所以需要进行与输入张量的适配
# 最后再使用Variable封装,使其与x的样式相同。
x = x + Variable(self.pe[:, :x.size(1)], requires_grad=False)
# 最后再使用self.dropout对象进行“丢弃”操作,它会使某些数值失效,它的参数p表示失效百分比
return self.dropout(x)
d_model = 512
dropout = 0.1
max_len = 60
x = embr
pe = PositionalEncoding(d_model, dropout, max_len)
pe_result = pe(x)
print(pe_result)
print(pe_result.shape)
tensor([[[-22.2443, 10.4765, 20.9230, ..., 33.3853, -27.4162, 0.0000],
[-68.9479, -9.0789, -6.3897, ..., -24.0922, -36.7171, 19.2992],
[ -0.0000, 3.4948, 9.5748, ..., -15.5479, 3.4603, -26.1024],
[ -0.0000, 19.4465, 23.6037, ..., 46.6244, -23.6807, -18.3327]],
[[-13.3040, -34.6103, -13.8357, ..., 0.8803, -30.2061, -39.2501],
[-24.4327, -19.0099, -5.7386, ..., 22.1442, 9.0043, -15.2990],
[-23.6487, -5.3476, -4.4221, ..., -36.6264, 3.3799, -12.9731],
[-28.2970, 11.3006, -7.0964, ..., -8.5298, -15.7532, 28.2575]]],
grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
- 下面是nn.Dropout演示
m = nn.Dropout(p = 0.2)
input = torch.rand(4,5)
output = m(input)
output
Out[6]:
tensor([[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.9010, 0.6331, 0.0000],
[0.3987, 0.6336, 0.6971, 0.4122, 0.1316],
[0.0000, 0.9154, 1.1348, 0.0000, 0.9654],
[0.8678, 0.2157, 0.7471, 1.1321, 0.0000]])
- torch.unsqueeze()演示
x = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4])
torch.unsqueeze(x, 0)
Out[8]: tensor([[1, 2, 3, 4]])
torch.unsqueeze(x, 1)
Out[9]:
tensor([[1],
[2],
[3],
[4]])
- 绘制词汇向量中特征的分布曲线
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 创建画布
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))
# 实例化对象
pe = PositionalEncoding(20, 0)
# 向pe传入被Variable封装的tensor,这样pe会直接执行forward函数
# 且这个tensor里数值都是0,被处理后相当于位置编码张量
y = pe(Variable(torch.zeros(1, 100, 20)))
# 定义画布横纵坐标
plt.plot(np.arange(100), y[0, :, 4:8].data.numpy())
# 在画布上填写维度提示信息
plt.legend(['dim %d' % p for p in [4, 5, 6, 7]])
plt.show()
编码器部分实现
- 由N个编码器层堆叠而成,每个编码器层内部相同
- 每个编码器层由两个子层连接结构组成
- 第一个子层连接结构包括一个多头自注意力子层和一个规范化层和一个残差连接
- 第二个子层连接结构包括一个前馈全连接子层和规范化层以及一个残差连接
掩码张量
-
掩代表遮掩,码就是我们张量中的数值,它的尺寸不定,里面一般只有1和0的元素,代表位置被遮掩或者不被遮掩,至于是0位置被遮掩还是1位置被遮掩可以自定义,因此它的作用就是让另外一个张量中的一些数值被遮掩,也可以说被替换,它的表现形式是一个张量。
-
在transformer中,掩码张量的主要作用在应用attention时,有一些生成的attention张量中的值计算有可能已知了未来信息而得到的,未来信息被看到是因为训练时会把整个输出结果都一次性进行Embedding,但是理论上解码器的的输出却不是一次就能产生最终结果的,而是一次次通过上一次结果综合得出的,因此,未来的信息可能被提前利用。所以,我们会进行遮掩。(防止非因果)
def subsequent_mask(size):
"""
生成向后的掩码张量
:param size: 掩码张量后两个维度大小
:return: 新的张量
"""
# 首先定义掩码张量的形状
attn_shape = (1, size, size)
# 使用np.ones方法向这个形状中加入1元素,形成上三角阵。
# 为节省空间,再使其中的数据类型变成无符号八位整形unit8
subsequent_mask = np.triu(np.ones(attn_shape), k=1).astype('uint8')
# 最后将numpy类型转为tensor,并做一个1-的操作。
# 这其实进行了三角阵的反转,每个元素都会被1减。
return torch.from_numpy(1 - subsequent_mask)
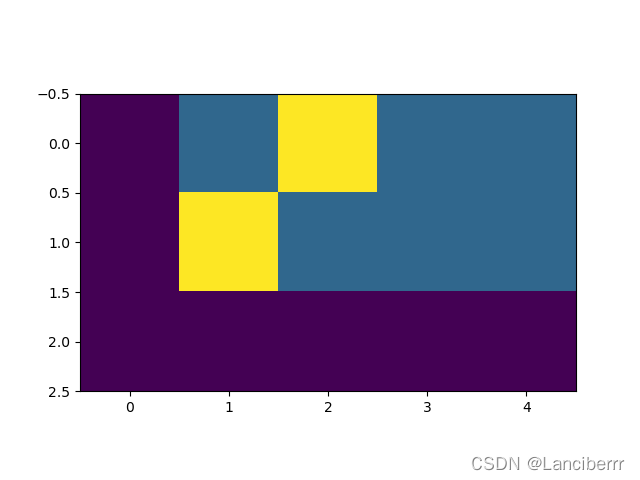
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
plt.imshow(subsequent_mask(20)[0])
plt.show()
- numpy.triu演示
np.triu([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9],[10,11,12]],k=-1)
Out[3]:
array([[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6],
[ 0, 8, 9],
[ 0, 0, 12]])
np.triu([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9],[10,11,12]],k=0)
Out[4]:
array([[1, 2, 3],
[0, 5, 6],
[0, 0, 9],
[0, 0, 0]])
np.triu([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9],[10,11,12]],k=1)
Out[5]:
array([[0, 2, 3],
[0, 0, 6],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]])
- 通过观察可视化方阵,黄色是1的部分,代表被遮掩,紫色代表没有被遮掩的信息,横坐标代表目标词汇的位置,纵坐标代表可查看的位置。
- 我们在第二个位置能看到位置1的词,这样就说明信息变成因果的了。
注意力机制
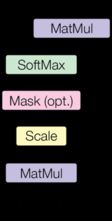
- 注意力机制的解释不再赘述了,我们在这里使用的计算规则如下:
A t t e n t i o n ( Q , K , V ) = s o f t m a x ( Q k T d k ) V Attention(Q,K,V)=softmax(\frac{Qk^T}{\sqrt{d_k}})V Attention(Q,K,V)=softmax(dkQkT)V
- 比喻解释方法:
假如我们有一个问题: 给出一段文本,使用一些关键词对它进行描述
为了方便统一正确答案,这道题可能预先已经给大家写出了一些关键词作为提示.其中这些给出的提示就可以看作是key,
而整个的文本信息就相当于是query,value的含义则更抽象,可以比作是你看到这段文本信息后,脑子里浮现的答案信息,
这里我们又假设大家最开始都不是很聪明,第一次看到这段文本后脑子里基本上浮现的信息就只有提示这些信息,
因此key与value基本是相同的,但是随着我们对这个问题的深入理解,通过我们的思考脑子里想起来的东西原来越多,
并且能够开始对我们query也就是这段文本,提取关键信息进行表示. 这就是注意力作用的过程, 通过这个过程,
我们最终脑子里的value发生了变化,
根据提示key生成了query的关键词表示方法,也就是另外一种特征表示方法.
刚刚我们说到key和value一般情况下默认是相同,与query是不同的,这种是我们一般的注意力输入形式,
但有一种特殊情况,就是我们query与key和value相同,这种情况我们称为自注意力机制,就如同我们的刚刚的例子,
使用一般注意力机制,是使用不同于给定文本的关键词表示它. 而自注意力机制,
需要用给定文本自身来表达自己,也就是说你需要从给定文本中抽取关键词来表述它, 相当于对文本自身的一次特征提取.
- 注意力机制是注意力计算规则能够应用的深度学习网络的载体,除了注意力计算规则外,还包括一些必要的全连接层和相关张量处理,使其与应用网络融为一体。使子注意力计算规则的注意力机制称为自注意力机制。
def attention(query, key, value, mask=None, dropout=None):
"""
注意力机制的实现,输入分别是query,key,value,mask,dropout
:param query: Q
:param key: K
:param value: V
:param mask: 掩码张量
:param dropout: nn.Dropout层的实例化对象,默认为None
:return: 返回公式运行的结果和注意力张量
"""
# 首先取query的最后一维的大小,一般就等于词嵌入维度,命名为d_k
d_k = query.size(-1)
# 根据注意力公式进行计算
scores = torch.matmul(query, key.transpose(-2, -1)) / math.sqrt(d_k)
# 判断是否使用掩码张量
if mask is not None:
# 使用tensor的masked_fill方法,将掩码张量和scores张量每个位置一一比较,如果掩码张量处于0
# 则对应的scores张量用-1e9来替换
scores = scores.masked_fill(mask == 0, -1e9)
# 对scores最后一维进行softmax操作
p_attn = F.softmax(scores, dim=-1)
# 之后判断是否使用dropout进行随机置零
if dropout is not None:
# 将p_attn传入dropout进行丢弃处理
p_attn = dropout(p_attn)
# 最后根据公式将p_attn与V相乘。
return torch.matmul(p_attn, value), p_attn
query = key = value = pe_result # pe_result是位置编码器处理后的结果
attn, p_attn = attention(query, key, value)
print('attn:', attn)
print('p_attn:', p_attn)
attn: tensor([[[ 0.0000, 36.8924, -15.7834, ..., 1.8793, 0.0000, -32.0809],
[-10.6699, 0.0000, 31.8204, ..., 0.0000, -13.3163, 0.0000],
[ 23.5323, 26.1211, -2.1896, ..., -23.2017, 12.3768, -13.9006],
[-31.7782, 3.9544, 23.4522, ..., -33.6694, 12.3344, -4.3606]],
[[ 11.8964, 0.0000, -12.1055, ..., -13.3012, 0.0000, -6.2498],
[ 34.3945, -5.7067, 10.1474, ..., -0.5229, -5.6711, -3.6539],
[ 8.8495, -34.1951, 24.3367, ..., 10.1538, 25.2722, 1.9425],
[ 2.3051, -54.2162, -1.6515, ..., 16.5660, 10.4399, -5.8726]]],
grad_fn=<UnsafeViewBackward>)
p_attn: tensor([[[1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1.]],
[[1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1.]]], grad_fn=<SoftmaxBackward>)
- 调用带有mask的输入参数
query = key = value = pe_result
mask = Variable(torch.zeros(2, 4, 4))
attn, p_attn = attention(query, key, value, mask)
print('attn:', attn)
print('p_attn:', p_attn)
attn: tensor([[[ 7.4030, -6.0119, -1.7209, ..., -12.0667, -18.5379, 14.4942],
[ 7.4030, -6.0119, -1.7209, ..., -12.0667, -18.5379, 14.4942],
[ 7.4030, -6.0119, -1.7209, ..., -12.0667, -18.5379, 14.4942],
[ 7.4030, -6.0119, -1.7209, ..., -12.0667, -18.5379, 14.4942]],
[[ -4.6481, 28.7028, 16.4447, ..., -10.4067, -15.2942, 11.3513],
[ -4.6481, 28.7028, 16.4447, ..., -10.4067, -15.2942, 11.3513],
[ -4.6481, 28.7028, 16.4447, ..., -10.4067, -15.2942, 11.3513],
[ -4.6481, 28.7028, 16.4447, ..., -10.4067, -15.2942, 11.3513]]],
grad_fn=<UnsafeViewBackward>)
p_attn: tensor([[[0.2500, 0.2500, 0.2500, 0.2500],
[0.2500, 0.2500, 0.2500, 0.2500],
[0.2500, 0.2500, 0.2500, 0.2500],
[0.2500, 0.2500, 0.2500, 0.2500]],
[[0.2500, 0.2500, 0.2500, 0.2500],
[0.2500, 0.2500, 0.2500, 0.2500],
[0.2500, 0.2500, 0.2500, 0.2500],
[0.2500, 0.2500, 0.2500, 0.2500]]], grad_fn=<SoftmaxBackward>)
- tensor.masked_fill演示:
input = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5))
input
Out[4]:
tensor([[ 1.3062, -0.4590, 1.1816, 0.0947, -0.5350],
[-0.7377, -2.3147, -1.3210, -0.9536, 0.4579],
[ 1.6539, 1.0782, 0.6475, -0.2675, 1.2919],
[-0.7665, -0.1977, -0.5126, -0.2222, -1.4385],
[ 1.2670, 0.5111, 0.9820, 0.8215, -0.9060]])
mask = Variable(torch.zeros(5, 5))
mask
Out[6]:
tensor([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]])
input.masked_fill(mask==0, -1e9)
Out[7]:
tensor([[-1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09],
[-1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09],
[-1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09],
[-1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09],
[-1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09, -1.0000e+09]])
多头注意力机制
- 从多头注意力的结构图中,貌似这个所谓的多个头就是指多组线性变换层,其实并不是,只有使用了一组线性变化层,即三个变换张量对Q,K,V分别进行线性变换,这些变换不会改变原有张量的尺寸,因此每个变换矩阵都是方阵,得到输出结果后,多头的作用才开始显现,每个头开始从词义层面分割输出的张量,也就是每个头都想获得一组Q,K,V进行注意力机制的计算,但是句子中的每个词的表示只获得一部分,也就是只分割了最后一维的词嵌入向量. 这就是所谓的多头,将每个头的获得的输入送到注意力机制中, 就形成多头注意力机制。
- 多头注意力机制的作用:能使每个注意力机制去优化每次词汇的不同特征部分,从而均衡同一种注意力机制可能产生的偏差,让词义拥有来自更多元的表达,实验表明可以提升模型效果。
# 深度拷贝
import copy
# 克隆函数
def clones(module, N):
"""
用于生成相同网络层的克隆函数
:param module:要克隆的目标网络层
:param N:需要克隆的数量
:return:存入nn.ModuleList列表
"""
return nn.ModuleList([copy.deepcopy(module) for _ in range(N)])
# 使用一个类来实现多头注意力机制处理
class MultiHeadedAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, head, embedding_dim, dropout=0.1):
"""
类初始化函数
:param head:头数
:param embedding_dim:词嵌入维度
:param dropout: 置零比率
"""
super(MultiHeadedAttention, self).__init__()
# 在函数中,先使用一个测试中常用的assert语句判断h能否被d_model整除
# 这是因为我们之后要给每个头分配等量的词特征,也就是embedding_dim/head个
assert embedding_dim % head == 0
# 得到每个头获得分割词向量维度d_k
self.d_k = embedding_dim // head
# 传入头数
self.head = head
# 获得线性层对象,通过nn的Linear实例化。它内部变换矩阵是embedding_dim x embedding_dim
# 需要四个,因为QKV各需要一个,最后拼接的矩阵还要一个
self.linears = clones(nn.Linear(embedding_dim, embedding_dim), 4)
# self.attn为None,他代表最后得到的注意力张量,现在还没有结果所以为None
self.attn = None
# 最后一个self.dropout对象,通过nn中的Dropout实例化而来
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=dropout)
def forward(self, query, key, value, mask=None):
"""
前向逻辑函数
:param query:Q
:param key:K
:param value:B
:param mask:可能需要的掩码张量
:return:多头注意力结构的输出
"""
# 如果存在掩码张量
if mask is not None:
# 扩展维度,代表多头中的第n头
mask = mask.unsqueeze(1)
# 接着获得一个batch_size变量,他是query尺寸的第一个数字,代表有多少样本
batch_size = query.size(0)
# 多头处理环节
# 首先利用zip将输入QKV与三个线性层组到一起,然后使用for循环,将输入QKV分别传到线性层中,
# 做完线性变换后,开始为每个头分割输入,这里使用view方法对线性变换的结果进行维度重塑,多加了一个维度h,代表头数,
# 这样就意味着每个头可以获得一部分词特征组成的句子,其中的-1代表自适应维度,
# 计算机会根据这种变换自动计算这里的值.然后对第二维和第三维进行转置操作,
# 为了让代表句子长度维度和词向量维度能够相邻,这样注意力机制才能找到词义与句子位置的关系,
# 从attention函数中可以看到,利用的是原始输入的倒数第一和第二维.这样我们就得到了每个头的输入.
query, key, value = \
[model(x).view(batch_size, -1, self.head, self.d_k).transpose(1, 2)
for model, x in zip(self.linears, (query, key, value))]
# 得到了每个头的输入后,接下来就是传入attention中
# 直接调用前面的attention函数
x, self.attn = attention(query, key, value, mask, self.dropout)
# 通过多头注意力计算后,我们就得到了每个头计算结果组成的4维张量,我们需要将其转换为输入的形状以方便后续的计算,
# 因此这里开始进行第一步处理环节的逆操作,先对第二和第三维进行转置,然后使用contiguous方法,
# 这个方法的作用就是能够让转置后的张量应用view方法,否则将无法直接使用,
# 所以,下一步就是使用view重塑形状,变成和输入形状相同.
x = x.transpose(1, 2).contiguous().view(batch_size, -1, self.head*self.d_k)
# 最后使用线性列表中最后一个线性层对输入进行线性变换得到最终的多头注意力结构的输出
return self.linears[-1](x)
# 实例化参数
head = 8
embedding_dim = 512
dropout = 0.2
# 输入参数
query = key = value = pe_result
mask = Variable(torch.zeros(2, 4, 4))
mha = MultiHeadedAttention(head, embedding_dim, dropout)
mha_result = mha(query, key, value, mask)
print(mha_result)
print(mha_result.shape)
tensor([[[ 3.8827, 0.8817, 1.7978, ..., -0.1673, 0.2704, -1.8327],
[ 3.6428, 2.3661, -0.3085, ..., -2.9801, -4.5386, 2.0246],
[ 5.8768, 0.9758, 3.5753, ..., 0.7436, -6.6801, 0.3069],
[ 3.6071, 0.6004, 0.5129, ..., -1.8717, -2.9086, 3.4700]],
[[-3.3070, 2.1144, 4.9284, ..., -2.3153, 1.5112, 6.1881],
[-1.2763, 0.9109, 6.8544, ..., -1.9582, -1.5882, 3.5471],
[-0.1433, 0.8745, 1.5774, ..., -0.0952, 0.7166, 5.9290],
[-1.0488, 0.0909, 0.5606, ..., 0.6372, 0.5663, 4.5667]]],
grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
- torch.transpose演示:
import torch
x = torch.randn(2,3)
x
Out[5]:
tensor([[ 0.3885, 0.5783, 0.0216],
[-0.5455, -0.1933, 0.1021]])
torch.transpose(x, 0, 1)
Out[6]:
tensor([[ 0.3885, -0.5455],
[ 0.5783, -0.1933],
[ 0.0216, 0.1021]])
前馈全连接层
- 在Transformer中前馈全连接层就是具有两层线性层的全连接网络
- 考虑注意力机制可能对复杂过程的拟合程度不够,通过增加两层网络来增强模型的能力。
# 通过类PositionwiseFeedForward来实现前馈全连接层
class PositionwiseFeedForward(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, d_ff, dropout=0.1):
"""
初始化函数
:param d_model:第一个线性层输入维度,也就是第二个线性层输出维度
:param d_ff: 第二个线性层输入维度
:param dropout:置零比率
"""
super(PositionwiseFeedForward, self).__init__()
# 首先按照预期使用了nn实例化了两个线性层对象
self.w1 = nn.Linear(d_model, d_ff)
self.w2 = nn.Linear(d_ff, d_model)
# 实例化dropout
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, x):
"""
前向逻辑函数
:param x: 来自上一层的输出
:return: 经过两个线性层,先经过第一个,并使用relu函数激活,然后经过丢弃,进入第二个线性层
"""
return self.w2(self.dropout(F.relu(self.w1(x))))
d_model = 512
d_ff = 64
dropout = 0.2
x = mha_result
ff = PositionwiseFeedForward(d_model, d_ff, dropout)
ff_result = ff(x)
print(ff_result)
print(ff_result.shape)
tensor([[[ 0.2639, -0.9054, 1.4258, ..., -0.1676, 1.1199, 0.1611],
[-1.3599, 0.4144, 2.0401, ..., -0.6439, 1.4871, -0.2984],
[-1.2093, 0.2571, 2.5868, ..., -0.1841, 2.3364, -0.4500],
[-0.3950, -0.7321, 1.8540, ..., -0.6394, 1.8761, 0.5336]],
[[-0.6994, -0.4020, 0.0253, ..., 0.7228, -0.0081, -0.3397],
[ 0.7661, -0.3339, 0.4593, ..., -0.8447, -0.2167, 0.5297],
[ 0.8368, 0.0181, -0.4963, ..., 0.6193, 0.5291, 0.4029],
[ 0.0500, 0.1160, 0.6328, ..., 0.3166, 1.8558, 0.2115]]],
grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
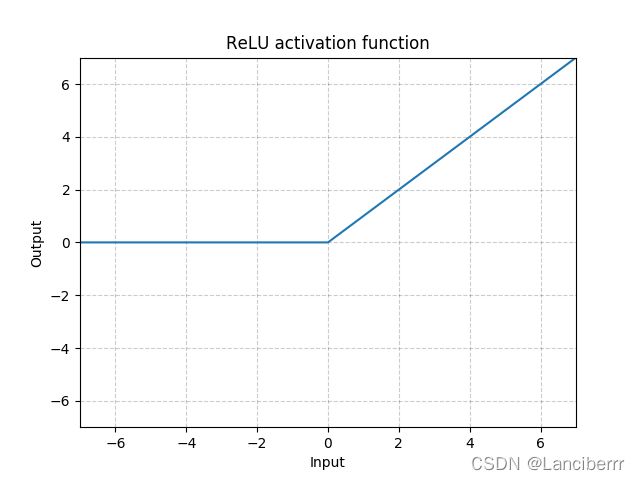
- relu函数公式:
R e L U ( x ) = m a x ( 0 , x ) ReLU(x)=max(0,x) ReLU(x)=max(0,x)
- relu函数图象:
规范化层
- 是所有深层网络模型都需要的标准网络层,因为随着网络层数的增加,通过多层计算后的参数可能会出现过大或过小的情况,这就会导致学习过程出现异常,模型可能收敛的非常慢。因此一定层数后接规范化层进行数值的规范化是其特征数值在合理范围之内。
# 通过LayerNorm实现规范化层的类
class LayerNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, features, eps=1e-6):
"""
初始化函数
:param features:词嵌入维度
:param eps:在规范化公式的分母出现,防止分母为零
"""
super(LayerNorm, self).__init__()
# 初始化两个张量,一个全为1一个全为0
# 最后使用nn.parameter封装,代表他们是模型的参数
self.a2 = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(features))
self.b2 = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(features))
# 把eps传进类中
self.eps = eps
def forward(self, x):
"""
前向函数
:param x:来自上一层的输出
:return:规范化后的参数
"""
mean = x.mean(-1, keepdim=True)
std = x.std(-1, keepdim=True)
return self.a2 * (x - mean) / (std + self.eps) + self.b2
features = d_model
eps = 1e-6
# 输入x来自前馈全连接层的输出
x = ff_result
ln = LayerNorm(features, eps)
ln_result = ln(x)
print(ln_result)
print(ln_result.shape)
tensor([[[-0.1806, -0.7587, 0.3926, ..., 0.0025, 1.3156, 0.5026],
[-0.0182, -0.1753, -0.0330, ..., 0.6421, 1.4776, 0.5200],
[ 0.6778, -0.9311, 1.1786, ..., 0.4126, 0.0035, 0.4120],
[-0.6313, -0.5981, 0.5563, ..., -0.6654, 0.8282, -0.5216]],
[[ 0.4320, -0.8349, -1.0383, ..., 0.8928, -0.3223, -0.2585],
[ 0.3029, -0.1326, 0.0427, ..., 2.1079, -1.1085, -0.0591],
[ 0.7906, 0.4954, 0.1452, ..., 2.1114, -0.9033, -0.1630],
[ 0.6392, -0.7169, -0.3528, ..., 1.5880, -1.7807, -0.2537]]],
grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
- 可以发现张量的形状没有改变,这是因为使用了keepdim=True参数。
子层连接结构
- 输入到每个子层以及规范化层的过程中,还使用了残差链接(跳跃连接),因此我们把这一部分结构整体叫做子层连接结构(代表子层及其连接结构),在每个解码器层中,都有两个子层,这两个子层加上周围的连接结构就形成了两个子层连接结构。
- 子层连接结构的代码分析:
# 使用SubLayerConnection来实现子层连接结构的类
class SubLayerConnection(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, size, dropout=0.1):
"""
初始化函数
:param size:词嵌入维度大小
:param dropout:置零比率
"""
super(SubLayerConnection, self).__init__()
# 实例化规范化对象self.norm
self.norm = LayerNorm(size)
# 又使用nn中预定义的dropout实例化一个dropout对象
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, x, subLayer):
"""
前向逻辑函数
:param x: 接受上一层的输入
:param subLayer: 子层参数
:return:最终子层连接输出
"""
# 先规范化,然后将结果传入子层处理,再对子层进行dropout操作。随机停止一些网络中神经元的作用,防止过拟合,
# 因为存在跳跃连接,所以将输入x与dropout后的子层输出结果相加作为最终子层连接输出
return x + self.dropout(subLayer(self.norm(x)))
size = 512
dropout = 0.2
head = 8
d_model = 512
# 令x为位置编码器的输出
x = pe_result
mask = Variable(torch.zeros(2, 4, 4))
# 假设子层中装的是多头注意力层,实例化类
self_attn = MultiHeadedAttention(head, d_model)
# 使用lambda表达式获取一个函数类型子层
sublayer = lambda x : self_attn(x, x, x, mask)
# 调用
sc = SubLayerConnection(size, dropout)
sc_result = sc(x, sublayer)
print(sc_result)
print(sc_result.shape)
tensor([[[-3.1186e+01, -2.2072e+01, -3.3177e+01, ..., 2.1531e+01,
2.8843e+01, 1.6473e+01],
[-1.0114e+01, 1.4173e+01, 1.0516e+01, ..., -2.4289e+01,
7.9229e+00, 1.1578e+00],
[-4.9469e+00, 1.2722e+01, 4.3186e+01, ..., -3.2159e-01,
-1.0617e+00, -1.2537e+01],
[-1.1592e+01, -2.1211e+01, 1.2908e+01, ..., 4.7250e+00,
2.4243e+01, -3.1078e+01]],
[[ 8.7191e+00, 8.4207e+00, -1.8972e-01, ..., 2.9479e+01,
5.7478e-02, 3.2309e+01],
[ 1.7719e+01, -2.6291e+01, -3.9933e+01, ..., 6.9330e+00,
1.3092e-01, -1.4262e+01],
[ 3.7918e-01, 7.2478e+01, 1.4829e+01, ..., 1.4887e+01,
1.3645e+01, 4.0244e+00],
[ 4.1714e+00, 2.4918e+01, 2.8290e+01, ..., -4.7075e+00,
-1.3270e+01, -5.8517e+00]]], grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
编码器层
- 作为编码器的组成单元,每个编码器层完成一次对输入的特征提取过程,即编码过程。
# 使用EncoderLayer类实现编码器层
class EncoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, size, self_attn, feed_forward, dropout):
"""
初始化函数
:param size:词嵌入维度大小,也是编码器层大小
:param self_attn: 多头注意力子层实例化对象,并且是自注意力机制
:param feed_forward:传入前馈全连接层实例化对象
:param dropout:置零比率
"""
super(EncoderLayer, self).__init__()
# 首先将self_attn和feed_forward传入
self.self_attn = self_attn
self.feed_forward = feed_forward
# 编码器层有两个子层连接结构,所以克隆
self.sublayer = clones(SubLayerConnection(size, dropout=dropout), 2)
# 传入size
self.size = size
def forward(self, x, mask):
"""
前向函数
:param x:上一层的输出
:param mask: 掩码张量
:return: 该层输出
"""
# 根据结构图的流程,先通过第一个子层连接结构,包含多头自注意力子层,
# 然后通过第二个子层连接结构,包含前馈全连接层
x = self.sublayer[0](x, lambda x: self.self_attn(x, x, x, mask))
return self.sublayer[1](x, self.feed_forward)
size = 512
head = 8
d_model = 512
d_ff = 64
x = pe_result
dropout = 0.2
self_attn = MultiHeadedAttention(head, d_model)
ff = PositionwiseFeedForward(d_model, d_ff, dropout)
mask = Variable(torch.zeros(2, 4, 4))
el = EncoderLayer(size, self_attn, ff, dropout)
el_result = el(x, mask)
print(el_result)
print(el_result.shape)
tensor([[[ 7.4170e+00, 1.5941e+01, 1.8582e+01, ..., -1.6513e+01,
-7.5697e+00, 2.9006e+00],
[ 3.4636e+01, -4.8907e+00, 9.3721e+00, ..., 2.8848e+01,
1.0291e-01, 5.9421e+00],
[-2.4890e-02, -1.7333e+01, -1.3641e+01, ..., 3.3901e+01,
2.9555e+00, -2.8404e+01],
[-3.6117e+01, 2.6905e+01, 7.3604e+00, ..., -1.7876e+01,
-2.0849e+01, 1.0163e+01]],
[[ 1.2192e+01, 1.5942e+00, 2.0299e+01, ..., 1.7000e+01,
2.6857e+01, -1.3472e+01],
[ 8.1772e+00, 1.8628e+01, 7.7557e+00, ..., 3.6955e-01,
3.9174e-01, 5.0197e+01],
[-4.2689e+00, -1.3987e-01, 3.5203e+00, ..., 3.0674e+01,
-3.4167e+00, 4.6212e+01],
[ 2.5148e+01, 2.3866e+01, -2.3203e+01, ..., -2.3726e+01,
3.1312e+00, 3.5690e+01]]], grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
编码器
- 编码器用于对输入进行指定的特征提取过程,也称为编码,由N个编码器层堆叠而成。
# 使用Encoder类来实现编码器
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, layer, N):
"""
初始化函数
:param layer:编码器层
:param N: 编码器层个数
"""
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
# 克隆编码器层
self.layers = clones(layer, N)
# 再初始化一个规范化层,用在编码器的最后面
self.norm = LayerNorm(layer.size)
def forward(self, x, mask):
"""
前向函数
:param x:上一层输出
:param mask: 掩码张量
:return: 该层输出
"""
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer(x, mask)
# 先经过N个编码器层,然后再经过一个规范化层
return self.norm(x)
# 第一个实例化参数layer是一个编码器层的实例化对象,因此需要传入编码器层的参数
# 又因为编码器层中子层不共享,所以需要深度拷贝各个对象
size = 512
head = 8
d_model = 512
d_ff = 64
dropout = 0.2
c = copy.deepcopy
attn = MultiHeadedAttention(head, d_model)
ff = PositionwiseFeedForward(d_model, d_ff, dropout)
layer = EncoderLayer(size, c(attn), c(ff), dropout)
N = 8
mask = Variable(torch.zeros(2, 4, 4))
en = Encoder(layer, N)
en_result = en(x, mask)
print(en_result)
print(en_result.shape)
tensor([[[-0.8795, -0.5701, 0.3524, ..., -0.5187, 0.0935, -0.1045],
[-0.0314, -1.9219, 0.0855, ..., -0.4812, -2.3182, 2.0296],
[-0.8030, 0.2809, 0.0362, ..., -1.3277, -0.0855, -0.2862],
[-1.1773, 1.4952, 0.4564, ..., -0.8603, -1.5427, 0.1344]],
[[ 0.1343, -1.6148, 0.3878, ..., -0.0367, -0.9784, -0.0809],
[-0.2819, 0.0378, 0.4739, ..., -1.6151, -0.3725, 0.7180],
[-0.1348, -0.8308, 0.6970, ..., 2.7181, -0.6818, -0.9665],
[-0.6819, 2.8685, -1.3610, ..., 0.9373, -0.2219, 0.1585]]],
grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
解码器部分实现
- 解码器部分:
- 由N个解码器层堆叠而成,每个解码器层有三个子层连接结构组成
- 第一个子层连接结构包括一个多头自注意力子层和规范化层以及一个残差连接
- 第二个子层连接结构包括一个多头注意力子层和规范化层以及一个残差连接
- 第三个子层连接结构包括一个前馈全连接子层和规范化层以及一个残差连接
- 由N个解码器层堆叠而成,每个解码器层有三个子层连接结构组成
解码器层中的各个部分,由于高度封包,可以直接拿来构建解码器层
解码器层
- 作为解码器的组成单元,每个解码器层根据给定的输入向目标方向进行特征提取操作,即解码过程。
# 使用DecoderLayer来实现解码器层
class DecoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, size, self_attn, src_attn, feed_forward, dropout):
"""
初始化函数
:param size:词嵌入维度大小,解码器层尺寸
:param self_attn:多头自注意力对象,也就是这个注意力机制需要Q=K=V
:param src_attn:多头注意力对象,Q!=K=V
:param feed_forward:前馈全连接层对象
:param dropout:置零比率
"""
super(DecoderLayer, self).__init__()
self.size = size
self.self_attn = self_attn
self.src_attn = src_attn
self.feed_forward = feed_forward
# 按照结构图克隆三个子层连接对象
self.sublayer = clones(SubLayerConnection(size, dropout), 3)
def forward(self, x, memory, source_mask, target_mask):
"""
前向函数
:param x:上一层的输出
:param memory: 来自编码器层的语义存储变量
:param source_mask: 源数据掩码张量
:param target_mask: 目标数据掩码张量
:return: 该层输出
"""
m = memory
# 将x传入第一个子层结构,因为是自注意力机制,所以Q,K,V都是x
# 最后一个参数是目标数据掩码张量,这时要对目标数据进行遮掩,因为此时模型可能还没有生成任何目标数据
# 比如在解码器准备生成第一个字符或词汇时,已经传入了第一个字符以便计算损失
# 但并不希望再生成第一个字符时模型利用这个信息,所以将其遮掩,同样在生成第二个字符或词汇时
# 模型只能使用第一个字符或词汇信息,第二个字符以及之后的信息都不允许被使用
x = self.sublayer[0](x, lambda x: self.self_attn(x, x, x, target_mask))
# 第二个子层,Q是x,K、V是编码器输出memory
# 同样传入source_mask,但是进行源数据遮掩的原因并非抑制信息泄露,而是遮蔽对结果没用的字符产生的注意力
# 以此提升模型的训练速度和效果
x = self.sublayer[1](x, lambda x: self.src_attn(x, m, m, source_mask))
# 最后一个子层是前馈全连接子层,经过它的处理可以返回结果,这就是解码器层结构
return self.sublayer[2](x, self.feed_forward)
# 类的实例化和解码器层相似,相比多出了src_attn,但是和self_attn是同一个类
head = 8
size = 512
d_model = 512
d_ff = 64
dropout = 0.2
self_attn = src_attn = MultiHeadedAttention(head, d_model, dropout)
# 输入参数
x = pe_result
memory = en_result
# 实际中source_mask和target_mask并不相同,这里为了方便计算令他们都为mask
mask = Variable(torch.zeros(2, 4, 4))
source_mask = target_mask = mask
dl = DecoderLayer(size, self_attn, src_attn, ff, dropout)
dl_result = dl(x, memory, source_mask, target_mask)
print(dl_result)
print(dl_result.shape)
tensor([[[ 2.1147e+01, 1.6479e+01, 9.4290e+00, ..., 1.8446e+01,
1.3847e+01, -2.9132e-01],
[ 6.1785e+01, -1.3439e-01, 2.7719e+01, ..., 4.2643e+00,
-3.1923e+00, 1.5193e+01],
[ 1.1567e-01, -2.2752e+00, -3.0115e+00, ..., -4.2799e-02,
6.6788e-01, 1.9187e+01],
[-7.5411e+00, 2.7842e+01, 1.9881e+01, ..., -1.5528e+01,
-1.7467e+01, 2.2129e+00]],
[[ 4.0937e+01, -2.5544e+01, 9.6575e-01, ..., 1.6179e+01,
-3.6202e+01, 8.6853e-01],
[-2.9447e+01, -1.9267e-01, 9.2034e+00, ..., -5.7855e-01,
-4.0574e+00, 3.9218e+00],
[ 4.8806e+01, -2.3486e+01, 1.7252e+00, ..., -1.6863e+01,
4.4038e+01, 4.3910e+00],
[ 9.2087e+00, 3.2539e+01, 1.8254e+00, ..., 1.0750e+01,
-2.5536e+01, -1.8611e+00]]], grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
解码器
- 根据编码器的结果以及上一次预测的结果,对下一次可能出现的“值”进行特征表示
# 使用Decoder类来实现解码器
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, layer, N):
"""
初始化函数
:param layer:解码器层
:param N: 解码器层个数
"""
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
# 首先使用clones方法克隆,然后实例化一个规范化层
# 因为数据走过了所有的解码器层后最后要做规范化处理
self.layers = clones(layer, N)
self.norm = LayerNorm(layer.size)
def forward(self, x, memory, source_mask, target_mask):
"""
前向函数
:param x: 目标数据的嵌入表示
:param memory: 编码器层输出
:param source_mask: 源数据掩码张量
:param target_mask: 目标数据掩码张量
:return: 最后的结果
"""
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer(x, memory, source_mask, target_mask)
return self.norm(x)
head = 8
size = 512
d_model = 512
d_ff = 64
dropout = 0.2
c = copy.deepcopy
attn = MultiHeadedAttention(head, d_model)
ff = PositionwiseFeedForward(d_model, d_ff, dropout)
layer = DecoderLayer(d_model, c(attn), c(attn), c(ff), dropout)
N = 8
# 输入参数
x = pe_result
memory = en_result
mask = Variable(torch.zeros(2, 4, 4))
source_mask = target_mask = mask
# 调用
de = Decoder(layer, N)
de_result = de(x, memory, source_mask, target_mask)
print(de_result)
print(de_result.shape)
tensor([[[ 0.2125, -1.4147, 0.5227, ..., -0.8351, -0.3715, 0.1323],
[-0.7358, 1.0274, -0.0511, ..., -0.0509, -0.8549, 2.1251],
[-0.7232, -1.2185, 0.8387, ..., -0.2914, 0.4274, -0.2495],
[-1.2537, 1.3698, 1.4753, ..., -1.2799, 0.2767, 0.3558]],
[[-0.6735, -0.0877, -1.5933, ..., -0.6598, -0.3713, 1.8445],
[ 0.5413, 1.2925, 0.8028, ..., 0.9578, 0.6427, -0.8177],
[-0.1011, -0.3633, 0.1055, ..., 0.2356, 2.4622, -0.8856],
[ 0.1805, 1.9676, -1.2283, ..., -1.2129, -1.7658, -0.2285]]],
grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
输出部分实现
- 输出部分包含:线性层和softmax层
- 线性层作用:通过对上一步的线性变换得到指定维度的输出,也就是转换维度的作用
- softmax层的作用:是最后一维的向量中的数字缩放到0-1的概率值域内,并满足其和为1
# 将输出部分线性层和softmax层一起实现,因为二者的共同目标是生成最后的结构
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, vocab_size):
"""
初始化函数
:param d_model:词嵌入维度
:param vocab_size: 词表大小
"""
super(Generator, self).__init__()
# 首先就是使用nn中预定义线性层进行实例化,得到一个对象
# 这个线性层参数有两个,分别就是初始化函数传入的两个参数
self.project = nn.Linear(d_model, vocab_size)
def forward(self, x):
"""
前向函数
:param x:上一层输出
:return: 输出部分输出结果
"""
# 在函数中,首先使用self.project进行线性变换
# 然后使用以实现的log_softmax进行softmax处理
return F.log_softmax(self.project(x), dim=-1)
d_model = 512
vocab_size = 1000 # 词表大小为1000
# 输入参数是上一层网络的输出,我们使用来自解码器层的输出
x = de_result
gen = Generator(d_model, vocab_size)
gen_result = gen(x)
print(gen_result)
print(gen_result.shape)
tensor([[[-7.0432, -7.7691, -7.0721, ..., -7.3606, -7.1644, -6.9683],
[-7.8082, -5.9213, -7.0725, ..., -7.5524, -7.5166, -6.7249],
[-6.7795, -6.9403, -7.6747, ..., -6.4746, -8.2363, -7.1984],
[-7.3819, -7.9958, -6.3010, ..., -6.3719, -7.4321, -7.9810]],
[[-7.0343, -6.8098, -6.8961, ..., -6.8777, -7.3052, -7.8133],
[-6.8705, -7.1945, -6.7892, ..., -8.7885, -7.4094, -7.9331],
[-7.2495, -7.0787, -6.1185, ..., -6.5705, -6.6412, -7.0614],
[-6.8558, -7.7336, -7.7825, ..., -6.6516, -6.8140, -7.6276]]],
grad_fn=<LogSoftmaxBackward>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 1000])
模型构建
-
通过前面的部分,我们已经完成了所有组成部分的实现,接下来就来实现完整的编码器-解码器结构。
-
Transformer总体框架图:
# 使用EncoderDecoder类来实现编码器解码器结构
class EncoderDecoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, encoder, decoder, source_embed, target_embed, generator):
"""
初始化函数
:param encoder:编码器对象
:param decoder: 解码器对象
:param source_embed: 源数据嵌入函数
:param target_embed: 目标数据嵌入函数
:param generator: 输出部分的类别生成器对象
"""
super(EncoderDecoder, self).__init__()
# 传参
self.encoder = encoder
self.decoder = decoder
self.src_embed = source_embed
self.tgt_embed = target_embed
self.generator = generator
def forward(self, source, target, source_mask, target_mask):
"""
前向函数
:param source:源数据
:param target: 目标数据
:param source_mask: 源数据掩码张量
:param target_mask: 目标数据掩码张量
:return: 系统输出结果
"""
# 在函数中,将source、source_mask传入编码函数,得到结果后
# 与其他参数一同传入解码函数
return self.decode(self.encode(source, source_mask), source_mask, target, target_mask)
def encode(self, source, source_mask):
"""
编码函数
:param source:源数据
:param source_mask:源数据掩码张量
:return:传入解码器并返回其结果
"""
return self.encoder(self.src_embed(source), source_mask)
def decode(self, memory, source_mask, target, target_mask):
"""
解码函数
:param memory:编码器输出
:param source_mask: 源数据掩码张量
:param target: 目标数据
:param target_mask: 目标数据掩码张量
:return: 传给解码器并返回结果
"""
return self.decoder(self.tgt_embed(target), memory, source_mask, target_mask)
# 实例化参数
vocab_size = 1000
d_model = 512
encoder = en
decoder = de
source_embed = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, d_model)
target_embed = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, d_model)
generator = gen
# 输入参数
# 假设源数据与目标数据相同(实际并不应该相同)
source = target = Variable(torch.LongTensor([[100, 2, 421, 508], [491, 998, 1, 221]]))
# 假设src_mask和tgt_mask相同,实际也不应该相同
source_mask = target_mask = Variable(torch.zeros(2, 4, 4))
# 调用
ed = EncoderDecoder(encoder, decoder, source_embed, target_embed, generator)
ed_result = ed(source, target, source_mask, target_mask)
print(ed_result)
print(ed_result.shape)
tensor([[[-0.5290, 1.3234, -0.7010, ..., 0.5768, 1.4987, -0.9065],
[-0.0638, 1.1969, -0.2659, ..., 0.4419, 1.2238, -0.5434],
[ 0.2999, 1.1867, -0.0706, ..., 0.7312, 1.5966, 0.2390],
[ 0.1703, 1.3818, -0.5551, ..., 0.4527, 1.5705, -0.5760]],
[[ 0.6157, 2.0974, -1.0643, ..., 0.0168, -1.0754, 0.3824],
[-0.2670, 0.7706, -1.5718, ..., -0.6183, -0.3329, 0.5041],
[ 0.5773, 1.5314, -1.3135, ..., -0.8947, -0.7935, 0.3938],
[ 0.1317, 1.1800, -0.4429, ..., -0.0225, -0.2128, -0.2042]]],
grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
- 接着将利用以上的结构来构建用于训练的模型
def make_model(source_vocab, target_vocab, N=6,
d_model=512, d_ff=2048, head=8, dropout=0.1):
"""
模型构建函数
:param source_vocab:源数据特征(词汇)总数
:param target_vocab:目标数据特征(词汇)总数
:param N: 编码器和解码器堆叠数
:param d_model: 词向量映射维度
:param d_ff: 前馈全连接网络中变换矩阵的维度
:param head: 多头注意力结构中的多头数,
:param dropout:置零比率
:return:模型的输出
"""
# 首先得到一个深度拷贝命令,接下来很多结构都需要进行深度拷贝,来保证他们彼此之间相互独立,互不干扰
c = copy.deepcopy
# 实例化了很多多头注意力类,得到对象attn
attn = MultiHeadedAttention(head, d_model)
# 然后实例化前馈全连接类,得到对象ff
ff = PositionwiseFeedForward(d_model, d_ff, dropout)
# 实例化位置编码类,得到对象position
position = PositionalEncoding(d_model, dropout)
# 根据结构图,最外层是EncoderDecoder,在其中
# 分别有编码器层、解码器层、源数据Embedding层和位置编码组成的有序结构
# 目标数据Embedding层和位置编码组成的有序结构,以及类别生成器层
# 在编码器层中有attention子层以及前馈全连接子层
# 在解码器层中有两个attention子层以及前馈全连接层
model = EncoderDecoder(
Encoder(EncoderLayer(d_model, c(attn), c(ff), dropout), N),
Decoder(DecoderLayer(d_model, c(attn), c(attn),
c(ff), dropout), N),
nn.Sequential(Embeddings(d_model, source_vocab), c(position)),
nn.Sequential(Embeddings(d_model, target_vocab), c(position)),
Generator(d_model, target_vocab)
)
# 模型结构完成后,接下来就是初始化模型参数,比如线性层中的变换矩阵
# 这里一旦判断参数维度大于1,则会将其初始化为一个服从均匀分布的矩阵
for p in model.parameters():
if p.dim() > 1:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(p)
return model
# 输入参数
source_vocab = 11
target_vocab = 11
N = 6
# 其他参数都是用默认值
# 调用
if __name__ == '__main__':
res = make_model(source_vocab, target_vocab, N)
print(res)
#下面是输出的结果,也就是根据Transformer结构图构建的整体模型的结构
EncoderDecoder(
(encoder): Encoder(
(layers): ModuleList(
(0): EncoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(1): EncoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(2): EncoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(3): EncoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(4): EncoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(5): EncoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
)
(norm): LayerNorm()
)
(decoder): Decoder(
(layers): ModuleList(
(0): DecoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(src_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(2): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(1): DecoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(src_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(2): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(2): DecoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(src_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(2): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(3): DecoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(src_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(2): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(4): DecoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(src_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(2): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(5): DecoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(src_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(2): SubLayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
)
(norm): LayerNorm()
)
(src_embed): Sequential(
(0): Embeddings(
(lut): Embedding(11, 512)
)
(1): PositionalEncoding(
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
(tgt_embed): Sequential(
(0): Embeddings(
(lut): Embedding(11, 512)
)
(1): PositionalEncoding(
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
(generator): Generator(
(project): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=11, bias=True)
)
)
模型的基本测试以及运行
通过一个小的copy任务,来对模型进行测试
- 任务描述:针对数字序列进行学习,学习的最终目标是使输出和输入的序列相同。如输入[1,5,8,9,3],输出应该也是[1,5,8,9,3]
- 任务意义:copy任务在模型基础测试中具有重要意义,因为copy操作对于模型来讲是一条明显规律,因此模型能否在短时间内小数据集中学会它,可以帮助我们断定模型的所有过程是否正常,是否已具备学习能力。
- 使用copy任务测试模型的四步:
- 构建数据集生成器
- 获得Transformer模型及其优化器和损失函数
- 运行模型进行训练和评估
- 使用模型进行贪婪解码(贪心算法)
构建数据集生成器
# 构建数据集生成器
from pyitcast.transformer_utils import Batch
from pyitcast.transformer_utils import get_std_opt
from pyitcast.transformer_utils import LabelSmoothing
from pyitcast.transformer_utils import SimpleLossCompute
from pyitcast.transformer_utils import run_epoch
from pyitcast.transformer_utils import greedy_decode
def data_generator(V, batch, num_batch):
"""
该函数用于随机生成copy任务的数据
:param V: 随机生成的数字最大值加一
:param batch: 每次输送给模型更新一次参数的数据量
:param num_batch: 一共输送多少次完成一轮
:return: 使用了yield,是一个生成器,封装了这一个批次的数据
"""
# 使用for循环遍历num_batch
for i in range(num_batch):
# 在循环中使用np的random.randint方法随机生成[1,V)的整数
# 分布在(batch, 10)形状的矩阵中,然后再把numpy形式转为tensor
data = torch.from_numpy(np.random.randint(1, V, size=(batch, 10)))
# 接着使数据矩阵中第一列数字都为1,这一列也就成了起始标志列
data[:, 0] = 1
# 因为是copy任务,所有source和target完全相同,且数据样本作用变量不需要求梯度
# 因此requires_grad设置为false
source = Variable(data, requires_grad=False)
target = Variable(data, requires_grad=False)
# 使用Batch对source和target进行对应批次的掩码张量生成,最后使用yield返回
yield Batch(source, target)
# 输入参数
V = 11
# 每次给模型20个数据进行参数更新
batch = 20
# 连续30次后完成一轮数据的遍历
num_batch = 30
if __name__ == '__main__':
res = data_generator(V, batch, num_batch)
print(res)
# 打印的值是一个生成器对象
<generator object data_generator at 0x000002246AEC0048>
获得Transformer模型及其优化器和损失函数
# 优化器工具包,获得标准的针对Transformer模型的优化器。基于Adam优化器,使其对序列到序列的任务更有效
from pyitcast.transformer_utils import get_std_opt
# 标签平滑工具包,小幅度的改变原有标签值的值域。因为在理论上即使人工标注数据也并非完全正确,会受外界因素的影响而产生微小偏差
# 因此使用标签平滑来弥补这种偏差,减少模型对某一条规律的绝对认知,以防止过拟合。
from pyitcast.transformer_utils import LabelSmoothing
# 损失计算工具包,对标签平滑后的结果进行损失计算
# 计算方法可以认为是交叉熵损失函数
from pyitcast.transformer_utils import SimpleLossCompute
# 使用make_model获得model
model = make_model(V, V, N=2)
# 使用get_std_opt获得模型优化器
model_optimizer = get_std_opt(model)
# 使用LabelSmoothing获得标签平滑对象
criterion = LabelSmoothing(size=V, padding_idx=0, smoothing=0.0)
# 使用SimpleLossCompute获得利用标签平滑结果的损失方法
loss = SimpleLossCompute(model.generator, criterion, model_optimizer)
# 标签平滑的示例
from pyitcast.transformer_utils import LabelSmoothing
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 实例化一个crit对象
# 第一个参数size代表目标数据词汇总数,也是模型最后一层得到张量的最后一位大小
# 第二个参数表示要将那些tensor中的数字替换成0,padding_idx=0表示不替换
# 第三个参数smoothing表示标签平滑程度,如原来标签的表示值为1,则平滑后值域为[1-smoothing, 1+smoothing]
crit = LabelSmoothing(size=5, padding_idx=0, smoothing=0.5)
# 假定一个任意模型最后输出预测结果和真实结果
predict = Variable(torch.FloatTensor([[0, 0.2, 0.7, 0.1, 0],
[0, 0.2, 0.7, 0.1, 0],
[0, 0.2, 0.7, 0.1, 0]]))
# 标签的表示值为0,1,2
target = Variable(torch.LongTensor([2, 1, 0]))
# 将predict,target传入对象中
crit(predict, target)
# 绘制标签平滑图像
plt.imshow(crit.true_dist)
plt.show()
- 标签平滑图像分析:
- 黄色小方块相对于横坐标横跨的值域就是标签平滑后的正向平滑值域,我们可以看到大致是[0.5, 2.5]
- 相对于纵坐标横跨的值域就是标签平滑后的负向平滑值域,大概是[-0.5, 1.5],总的值域空间由原来的[0, 2]变成了[-0.5, 2.5]
运行模型进行训练和评估
def run(model, loss, epochs=10):
"""
模型训练函数
:param model:将要训练的模型
:param loss: 使用的损失计算方法
:param epochs: 模型训练的轮数
:return: None
"""
# 遍历轮数
for epoch in range(epochs):
# 模型将使用训练模式,更新参数
model.train()
# 训练时,batch_size是20
run_epoch(data_generator(V, 8, 20), model, loss)
# 模型使用评估模式,参数将不会变化
model.eval()
# 评估时,batch_size是5
run_epoch(data_generator(V, 8, 5), model, loss)
# 输入参数
# 进行10轮训练
epochs = 10
# model和loss都是来自上一步的结果
if __name__ == "__main__":
run(model, loss, epochs)
- 下面是模型输出的结果
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 3.302241 Tokens per Sec: 252.420868
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 2.987622 Tokens per Sec: 217.120758
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 2.766058 Tokens per Sec: 267.363037
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 2.168147 Tokens per Sec: 244.734985
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 2.337734 Tokens per Sec: 246.812286
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 1.936902 Tokens per Sec: 132.341949
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 2.062047 Tokens per Sec: 120.521790
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 1.798232 Tokens per Sec: 199.703339
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 2.122241 Tokens per Sec: 238.259140
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 1.724725 Tokens per Sec: 204.511581
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 1.867638 Tokens per Sec: 264.441101
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 1.734602 Tokens per Sec: 261.093506
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 1.822722 Tokens per Sec: 266.885162
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 1.476067 Tokens per Sec: 211.708862
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 1.648540 Tokens per Sec: 230.646805
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 1.533393 Tokens per Sec: 275.542633
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 1.596259 Tokens per Sec: 293.466034
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 1.366808 Tokens per Sec: 304.611206
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 1.517554 Tokens per Sec: 287.046936
Epoch Step: 1 Loss: 1.203983 Tokens per Sec: 268.373901
- 可见,损失正在下降,模型的训练是有效的
使用模型进行贪婪解码
- 只需要重写run函数即可
def run(model, loss, epochs=10):
"""
模型训练函数
:param model:将要训练的模型
:param loss: 使用的损失计算方法
:param epochs: 模型训练的轮数
:return: None
"""
# 遍历轮数
for epoch in range(epochs):
# 模型将使用训练模式,更新参数
model.train()
# 训练时,batch_size是20
run_epoch(data_generator(V, 8, 20), model, loss)
# 模型使用评估模式,参数将不会变化
model.eval()
# 评估时,batch_size是5
run_epoch(data_generator(V, 8, 5), model, loss)
# 模型进入测试模式
model.eval()
# 假定的输入张量
source = Variable(torch.LongTensor([[1, 3, 2, 5, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]]))
# 定义源数据掩码张量,因为元素都是1,我们用1代表不遮掩
# 因此相当于对于源码没有任何遮掩
source_mask = Variable(torch.ones(1, 1, 10))
# 最后将model,src,src_mask,解码的最大长度限制max_len,默认为10
# 以及起始标志数,用1
result = greedy_decode(model, source, source_mask, max_len=10, start_symbol=1)
print(result)
# 输入参数
# 进行50轮训练
epochs = 50
# model和loss都是来自上一步的结果
if __name__ == '__main__':
run(model, loss, epochs)
# 提高了训练轮数后,输出结果达到了预期
tensor([[ 1, 3, 2, 5, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]])
解决问题
-
IndexError: scatter_(): Expected dtype int64 for index.
- 使用
scatter_()函数张量数据类型不匹配。在要修改的数据加上.long(),转为int64类型。可以用.dtype属性查看其数据类型。
- 使用
-
IndexError: invalid index of a 0-dim tensor.
- 不应使用
loss.data[0]的写法,应该换为loss.item()
- 不应使用