用Linux / C实现基于自动扩/减容线程池+epoll反应堆检测沉寂用户模型的服务器框架(含源码)
用Linux/ C实现基于自动扩/减容线程池+epoll反应堆模型的服务器框架
- 前言
- 服务器端源码
- 客户端源码
- 自定义库 helper.c 和 helper.h
-
- helper.c
- helper.h
- Makefile文件
- 使用
前言
这个基于线程池和epoll反应堆的服务器大概有以下几个特点吧,简要说一下:
- 综合了线程池和epoll反应堆的优点,这个一个月后做详细说明。
- 线程池实现了根据客户端的数目(任务数量)实现自动扩容和瘦身。
- epoll反应堆额外实现了检测沉寂用户的功能,若一个客户端连接在60秒内没有发送任何消息,服务器会主动断开连接。
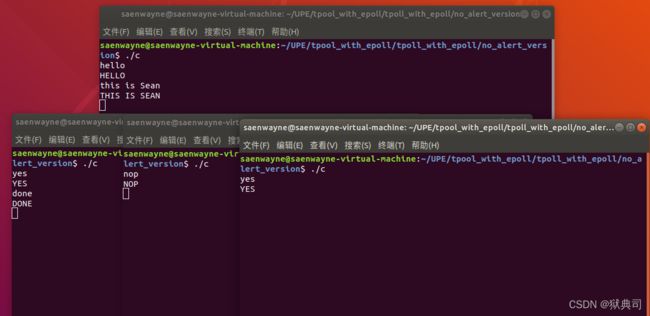
注意:该源码的线程回调函数只是提供了最基础的大小写转换以测试C/S双端的联通性,可以在线程回调函数do_rw()上做自定义的拓展。
转发必须注明出处!
由于作者本人最近在忙期末复习(KPI压力,害),目前暂时不对该代码的各类结构体、函数单独拎出来做分析了,这项工作等到这个月考完试之后在完成!
代码的大部分内容都有比较详细的注释,这一个月内如果有读者有看不懂源码的地方可以在评论区提问,我看到会回复!如有误也欢迎批评指正!
服务器端源码
文件名:server.c
#include 客户端源码
文件名:client.c
/* client.c */
#include 自定义库 helper.c 和 helper.h
helper.c
#include helper.h
#ifndef __HELPER_H_
#define __HELPER_H_
void perr_exit(const char *s);
int Accept(int fd, struct sockaddr *sa, socklen_t *salenptr);
int Bind(int fd, const struct sockaddr *sa, socklen_t salen);
int Connect(int fd, const struct sockaddr *sa, socklen_t salen);
int Listen(int fd, int backlog);
int Socket(int family, int type, int protocol);
ssize_t Read(int fd, void *ptr, size_t nbytes);
ssize_t Write(int fd, const void *ptr, size_t nbytes);
int Close(int fd);
ssize_t Readn(int fd, void *vptr, size_t n);
ssize_t Writen(int fd, const void *vptr, size_t n);
ssize_t my_read(int fd, char *ptr);
ssize_t Readline(int fd, void *vptr, size_t maxlen);
#endif
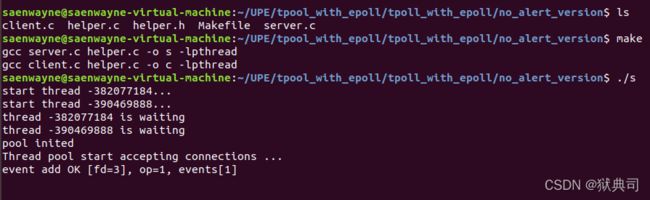
Makefile文件
all: s c
.PHONY: all
s: server.c helper.c
gcc server.c helper.c -o s -lpthread
c: client.c helper.c
gcc client.c helper.c -o c -lpthread
使用
注意:该服务器框架模拟的是多用户高并发的情况,所以你在多开客户机连接的时候可能会出现某个连接没有响应的情况,这是因为线程池的自动扩容瘦身算法,这个算法需要基于不同的场景去定制才能达到比较好的效果,所以如果遇到上述情况,继续开客户端连接就好了。