链表经典面试题
目录
- 1.删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
- 2.反转单链表
- 3. 链表的中间节点
- 4.链表中倒数第k个节点
- 5.合并两个有序链表
- 6.链表的回文结构
- 7.链表分割
- 8. 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。
- 9.环形链表
- 10.环形链表II
1.删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
OJ链接
删除节点的核心是:需要找到这个节点的前一个节点是谁
思路:
定义两个变量prev,cur,prev从head开始,cur从head.next开始prev代表cur的前驱,头节点留在最后处理 ,cur遍历整个链表如果cur.value==key,就让pre.next=cur.next,之后cur=cur.next,否则pre=cur,cur=cur.next
时间复杂度O(N)
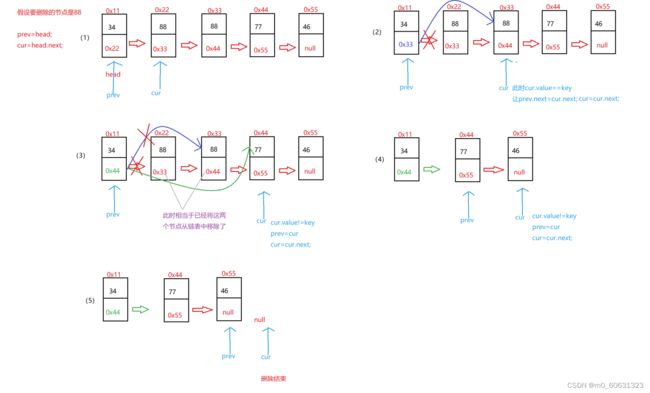
经过上面的删除后,因为cur是从head.next开始遍历的,所以最后需要检查头节点是否是要删除的节点,如果是head=head.next即可
⭐️
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode pre=head;
ListNode cur=head.next;
while (cur!=null){
if(cur.val==val){
pre.next=cur.next;
cur=cur.next;
}else {
pre=cur;
cur=cur.next;
}
}
if(head.val==val){
head=head.next;
}
return head;
}
2.反转单链表
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
if(head.next==null){
return head;
}
ListNode pre=null;
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode curNext=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=curNext;
}
return pre;
}
3. 链表的中间节点
OJ链接
思路:快慢指针
两个指针都从链表头开始,慢指针一次走一步,快指针一次走两步,当快指针走到链表结尾的时侯,慢指针正好处在链表的中间节点
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
if(head.next==null){
return head;
}
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
【注意】:
循环的终止条件 fast!=null&&fast.next!=null 顺序不能颠倒,否则会出现空指针异常。
4.链表中倒数第k个节点
OJ链接
思路:快慢指针
先让快指针走k步,再让两个指针一起走,当快指针走到尾时,慢指针走到倒数第k个节点
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
if(head==null||k<=0){
return null;
}
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head;
while(k!=0){
if(fast!=null){
fast=fast.next;
} else{
return null;
}
k--;
}
while(fast!=null){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
5.合并两个有序链表
OJ链接
ListNode dum = new ListNode();
cur = dum;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if(l1.val < l2.val) {
cur.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}
else {
cur.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = l1 != null ? l1 : l2;
return dum.next;
}
6.链表的回文结构
OJ链接
思路:
判断回文链表其实是找到链表的中点和翻转链表这两道题的组合
1.找到链表的中间节点
2.翻转中间节点及其后面的节点
3.比较头节点到中间节点和翻转后的后半段链表,只要发现不相等的节点直接返回false,全都相等返回true
源码:
public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode A) {
if(A==null||A.next==null){
return false;
}
ListNode slow=A;
ListNode fast=A;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
}
ListNode reversed=reverse(slow);
while(reversed!=null&&slow!=null){
if(reversed.val!=A.val){
return false;
}else {
reversed=reversed.next;
A=A.next;
}
}
return true;
}
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head){
if(head==null){
return null;
}
if(head.next==null){
return head;
}
ListNode pre=null;
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode next=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=next;
}
return pre;
}
7.链表分割
源码:
public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x) {
if(pHead==null) return null;
ListNode s1=null;
ListNode e1=null;
ListNode s2=null;
ListNode e2=null;
ListNode cur =pHead;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val<x){
if(s1==null){
s1=cur;
e1=cur;
}else {
e1.next=cur;
e1=e1.next;
}
}else {
if(s2==null){
s2=cur;
e2=cur;
}else {
e2.next=cur;
e2=e2.next;
}
}
cur=cur.next;
}
if(s1==null){
e2.next=null;
return s2;
}
e1.next=s2;
if(s2!=null){
e2.next=null;
}
return s1;
}
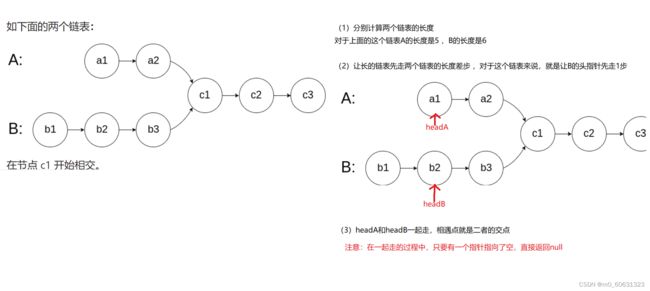
8. 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。
OJ链接
思路:
源码:
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA==null||headB==null){
return null;
}
int len1=0;
int len2=0;
ListNode cur1=headA;
ListNode cur2=headB;
while(cur1!=null){
len1++;
cur1=cur1.next;
}
while(cur2!=null){
len2++;
cur2=cur2.next;
}
cur1=headA;
cur2=headB;
int len=len1-len2;
if(len<0){
cur1=headB; //让cur1永远指向较长的那个链表
cur2=headA; //让cur2永远指向较短的那个链表
len =len2-len1;
}
while(len>0){
cur1=cur1.next;
len--;
}
while(cur1!=cur2){
if(cur1==null||cur2==null){
return null;
}
cur1=cur1.next;
cur2=cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}
9.环形链表
OJ链接
思路:
快慢指针
快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,如果二者相遇,证明链表中存在环。
有的同学可能会有这样的疑问,快指针一次走3、4步不可以吗??
答案是:不一定。

快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,是不会出现错过的情况的。
源码:
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null){
return false;
}
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
if(slow==fast){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
10.环形链表II
OJ链接
思路:

结论:一个指针从链表头开始走,另一个指针从相遇点开始走,二者将在入口点相遇
源码:
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null)return null;
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if(fast==slow){
break;
}
}
if(fast==null||fast.next==null){
return null;
}
while(head!=fast){
head=head.next;
fast=fast.next;
}
return head;
}