ArrayList与顺序表
目录
1.List接口
2.ArrayList与顺序表
2.1 线性表
2.2 顺序表
2.3 ArrayList说明
2.3.1 ArrayList简介
2.3.2 ArrayList使用
2.3.3 ArrayList的扩容机制
2.3.4 ArrayList的遍历
1.List接口
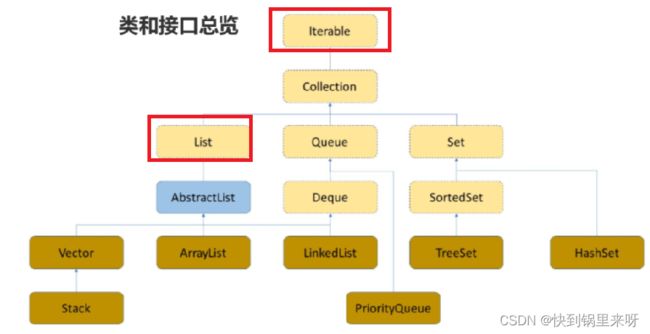
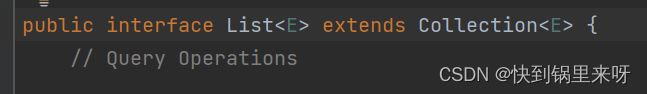
List是一个接口,它继承于Collection接口
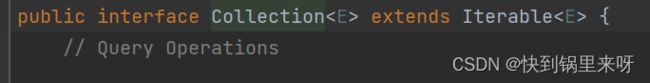
而Collection接口也继承于Iterable接口
2.ArrayList与顺序表
2.1 线性表
线性表(linear list)是数据结构的一种,表示n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列
它表示的数据元素之间的关系是一对一,也就是除第一个和最后一个元素外,其他数据元素都是首尾相接的(循环链表除外)
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,在物理上不一定是连续的,在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储
2.2 顺序表
顺序表是一段物理地址连续的存储单元,依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般是在数组存储,完成增删查改
接口的模拟实现
先写一个顺序表数组结构
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;//记录当前数组中放了几个数据
public static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
public MyArrayList() {
this.elem = new int[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];
}(1)打印顺序表display()
public void display() {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}(2)新增元素,默认在数组最后新增add(int data)
先判断是否需要扩容isFull()
//判断是否需要扩容
public boolean isFull() {
return usedSize == elem.length;
} public void add(int data) {
try {
if (isFull()) {
elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem,2*elem.length);
}
}catch (NegativeArraySizeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
elem[usedSize] = data;
usedSize++;
}(3)在pos位置新增元素add(int pos,int data)
先检查pos合法性
private void checkAddPos(int pos) {
if (pos < 0 || pos > usedSize) {
throw new PosIndexNotLegalException("pos位置不合法");
}
}写一个异常类,不合法时调用
public class PosIndexNotLegalException extends RuntimeException{
public PosIndexNotLegalException() {
}
public PosIndexNotLegalException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
在pos位置新增元素,把pos后面元素全部向后挪一个,然后放入新增元素
public void add(int pos, int data) {
try {
checkAddPos(pos);
if (isFull()) {
elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem,2*elem.length);
}
for (int i = usedSize -1; i >= pos; i--) {
elem[i+1] = elem[i];
}
elem[pos] = data;
usedSize++;
}catch (PosIndexNotLegalException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}(4)判定是否包含某个元素contains()
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {
if (elem[i] == toFind) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}(5)查找某个元素对应的位置indexOf()
public int indexOf(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {
if (elem[i] == toFind) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}(6)获取pos位置的元素get()
获取pos位置的数据检查合法性
private void checkGetPos(int pos) {
if (pos < 0 || pos >= usedSize) {
throw new PosIndexNotLegalException("pos位置不合法");
}
} public int get(int pos) {
int reVal = -1;
try {
checkAddPos(pos);
reVal = elem[pos];
}catch (PosIndexNotLegalException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return reVal;
}(7)给pos位置的元素设为value set()
public void set(int pos, int value) {
checkGetPos(pos);
elem[pos] = value;
}(8)删除第一次出现的关键字key remove()
public void remove(int key) {
int index = indexOf(key);
if (index == -1) {
System.out.println("没有要删除的数字");
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < usedSize-1; i++) {
elem[i] = elem[i+1];
}
usedSize--;
}(9) 获取顺序表长度 size()
public int size() {
return usedSize;
}(10)清空顺序表clear()
public void clear() {
usedSize = 0;
}
2.3 ArrayList说明
2.3.1 ArrayList简介
注意:
(1)ArrayList实现了Cloeable接口,说明可以ArrayList可以clone
(2)ArrayList实现了Serializable接口,说明可以ArrayList支持序列化
(3)ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,说明可以ArrayList支持随机访问
(4)ArrayList底层是一段连续空间,可以动态扩容
(5)ArrayList不是线程安全的,在单线程下可以使用,在多线程中可以选择Vector或者 CopyOnWriteArrayList
2.3.2 ArrayList使用
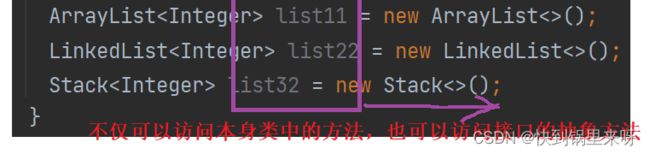
ArrayList构造 (1)无参构造(2)利用其他Collection(3)指定初始容量
ArrayList arrayList2 = new ArrayList<>(15);
ArrayList arrayList3 = new ArrayList<>(arrayList);
LinkedList list = new LinkedList<>();
ArrayList arrayList4 = new ArrayList<>(list);
2.3.3 ArrayList的扩容机制
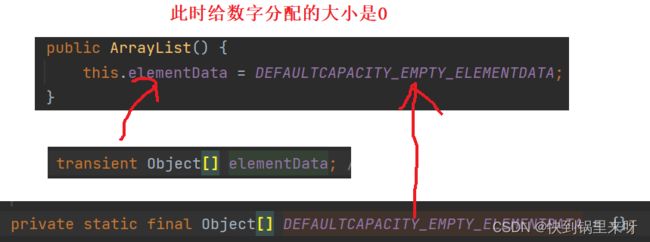
1.
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); 2.调用add后
arrayList.add(1);3.当10个放慢之后,就需要扩容,扩容采取的是1.5倍扩容
2.3.4 ArrayList的遍历
ArrayList遍历(1)下标+for循环(2)for-each(3)使用迭代器
System.out.println("====1.for循环+下标=====");
for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(arrayList.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("=====2.for-each======");
for (int x: arrayList) {
System.out.print(x + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("====3.使用迭代器=======");
Iterator it = arrayList.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(it.next() + " ");
}