DGL分布式流程
DGL分布式流程
- 官网document
-
- interacting processes
- API
-
- initialize
-
- DistGraphServer
-
- load_partition
- DLpack
- DisGraph
-
- num_nodes(), num_edges()
- g.ndata
- DisTensor
- DisEmbedding
- DisSampling
-
- low-level
- high-level
- 异构
- DGL分布式脚本文件
-
- copy_files.py
- launch.py
-
- DDP Test
- DGL 单机版
-
- data处理部分
- dataloader
-
- sample_frontier
-
- sampling.sample_neighbors
- dataloading.NodeDataLoader
-
- 测试sample_neighbors
- 当传入的图为DistGraph形式
- GraphSAGE model
-
- update_all函数测试
- 内置信息传递API
官网document
dgl distributed training user guide
通过dgl自定义的server来建立DistGraphServer,然后底层使用rpc协议去取其他机器上的图数据形成一个子图,也就是mini-batch。取到数据的机器再利用dataparallel的方式去并行执行,执行的线程称为客户端,通过torch.distributed.launch去建立。
interacting processes
dgl分布式中主要有server、sampler、trainer
-
Server processes run on each machine that stores a graph partition (this includes the graph structure and node/edge features). These servers work together to serve the graph data to trainers. Note that one machine may run multiple server processes simultaneously to parallelize computation as well as network communication.也就是说server不仅管数据,也管通信
-
Sampler processes interact with the servers and sample nodes and edges to generate mini-batches for training.
-
Trainers contain multiple classes to interact with servers. It has DistGraph to get access to partitioned graph data and has DistEmbedding and DistTensor to access the node/edge features/embeddings. It has DistDataLoader to interact with samplers to get mini-batches.
注意DistEmbedding、DisGraph、DisTensor、DisDataLoader等这几个分布式API
API
initialize
this API builds connections with DGL servers and creates sampler processes
这个dgl.distributed.initialize()函数和ddp.initialize_group()函数类似,定义很多通信变量为下面API服务,但是它也有很多不同的地方,特别是在server和client端的定义上
def initialize(ip_config, num_servers=1, num_workers=0,
max_queue_size=MAX_QUEUE_SIZE, net_type='socket',
num_worker_threads=1):
"""Initialize DGL's distributed module
This function initializes DGL's distributed module. It acts differently in server
or client modes. In the server mode, it runs the server code and never returns.
In the client mode, it builds connections with servers for communication and
creates worker processes for distributed sampling. `num_workers` specifies
the number of sampling worker processes per trainer process.
Users also have to provide the number of server processes on each machine in order
to connect to all the server processes in the cluster of machines correctly.
关于socket
Definition:
A socket is one endpoint of a two-way communication link between two programs running on the network. A socket is bound to a port number so that the TCP layer can identify the application that data is destined to be sent to.
由于现在dgl.distributed.initialize()的net_type只支持socket,所以还是很有必要了解一下socket通信模型,参见what is a socket?
首先server需要给出特定的ip跟port来listen
然后client需要知道server的ip跟port,并发出请求在server的socket(即ip跟port)上rendovous,The client also needs to identify itself to the server so it binds to a local port number that it will use during this connection. This is usually assigned by the system.
If everything goes well, the server accepts the connection. Upon acceptance, the server gets a new socket bound to the same local port and also has its remote endpoint set to the address and port of the client. It needs a new socket so that it can continue to listen to the original socket for connection requests while tending to the needs of the connected client.所以接受之后server会获得两个新的socket?
对于server端的ssh命令,initialize函数会初始化一个DistGraphServer,同时该类是KVServer的一个子类,KVServer听说是一个最基本的数据库,通过key-value的mapping方式进行通信
而每个线程会根据SERVER_ID分为是否是backup_server,一般一台机器上可能有好几个server,但是只有主server,主server才会加载切割。其他backup_server只会加载切割图的book,而这个partition_book在dgl有两种分类,而backup server具体加载哪一种看load_partition_book好像是和切割图的.json文件有关。关于Graph partition book可以参考---------------->dgl docs,主要有两种BasicGraphPartitionBook and RangePartitionBook。
对于主客户端,则加载分割图,并将图拷贝到共享内存中,这个共享内存具体指什么暂时还不清楚,只知道它新建了一个partitionbook,然后将切割图的一些属性(具体就是ndata[‘inner_node’],EID,inner_edge,NID等,inner是一个bool的mask,NID应该是在原始图上的ID)copy到这个shared_memory的partitionbook上,中间的转换还使用了DLpack和dgl自定义的NArray库。感觉应该是告诉不同machine上自己上的数据。
initialize在client端会定义一个全局的SAMPLE_POOL,它是一个DGL自定义的CustomPool类,会根据num_workers(=参数DGL_NUM_SAMPLER)设置进程数,每个进程会执行init_process,每个进程中又会定义num_worker*4的queue,在调用该类submit_task的时候会将相关命令放到队列中,其中submit_task会和DistDataLoader中取下一个batch data的时候互动。因为distdataloader的时候会先取batch data的NodeID,再通过collate_fn(也就是sampler函数)取node特征。
- 是不是每给一个batchID就会向这个queue添加一个task,然后取挨个去处理。因为使用了queue.put()
DistGraphServer
会通过rpc的方式建立KVServer,但是所有的rpc_server都是第一台ip的机器,只是如果有多个server的话,则该机器会开多个端口来作为server。
- 而对于rpc_client而言,
load_partition
在.json文件中,通过node_map和edge_map可以得知切割之后的ID分布,但是这和load_partition之后的inner_node(就是在该partition中的node,参考--------------------->distributed的partition部分)以及edge数量不一致
- 需要再测试一下
DLpack
见链接Github–DLPack。
不论是Pytorch还是DGL,都在各种从dlpack到tensor的相互转换,这个dlpack用处就是在各种框架之间相互共享。
DisGraph
Each machine is responsible for one and only one partition. It loads the partition data (the graph structure and the node data and edge data in the partition) and makes it accessible to all trainers in the cluster.
注意这里DisGraph即有单机版也有分布式版
单机版:测试开发,可以测试下单机版DisGraph
分布式版:DistGraph connects with the servers in the cluster of machines and access them through the network. 说明server之间还是通信来传输图信息的啊
num_nodes(), num_edges()
常用的统计函数,针对DistGraph类
g.ndata
非常重要的属性,会定义一个NodeDataView类,NodeDataView则会在get_data的时候定义一个DistTensor
DisTensor
Currently, DGL does not provide protection for concurrent writes from multiple trainers when a machine runs multiple servers. This may result in data corruption. One way to avoid concurrent writes to the same row of data is to run one server process on a machine.
怎样在一台机器上运行一个server process?
DisEmbedding
Internally, distributed embeddings are built on top of distributed tensors, and, thus, has very similar behaviors to distributed tensors. For example, when embeddings are created, they are sharded and stored across all machines in the cluster. It can be uniquely identified by a name.
embedding所有机器共享的话,如果实现通信?Distensor是不是也是共享?
DisSampling
有两种level,但不论哪种level
low-level
需要自己写代码定义如何sample
dgl.sampling.sample_neighbors()
For the lower-level sampling API, it provides sample_neighbors() for distributed neighborhood sampling on DistGraph.
所以DisGraph是整张图而DisSampling是采样为minibatch
high-level
经典算法NodeDataLoader和EdgeDataLoader
异构
关于异构图的描述
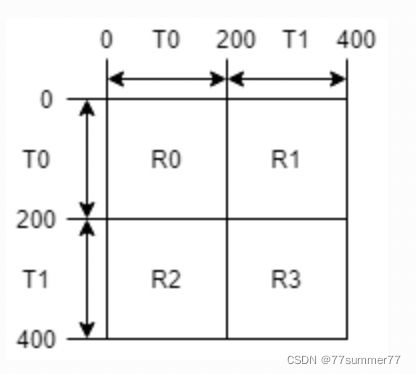
Below is an example adjancency matrix of a heterogeneous graph showing the homogeneous ID assignment. Here, the graph has two types of nodes (T0 and T1 ), and four types of edges (R0, R1, R2, R3 ). There are a total of 400 nodes in the graph and each type has 200 nodes. Nodes of T0 have IDs in [0,200), while nodes of T1 have IDs in [200, 400). In this example, if we use a tuple to identify the nodes, nodes of T0 are identified as (T0, type-wise ID), where type-wise ID falls in [0, 200); nodes of T1 are identified as (T1, type-wise ID), where type-wise ID also falls in [0, 200).
DGL分布式脚本文件
copy_files.py
复制切割图和training脚本到指定机器上(via ip_config)
但是需要每台机器之间ssh无密访问
- 这种方式是不是不需要NFS?
在使用copy_files.py的时候发现需要.npy文件,但是之前切割的图里面并没有.npy文件,于是在使用partition_graph的时候,将reshuffle改成false,发现.npy文件出来了,可见下面
Ifreshuffle=False, node IDs and edge IDs of a partition do not fall into contiguous
ID ranges. In this case, DGL stores node/edge mappings (from
node/edge IDs to partition IDs) in separate files (node_map.npy and edge_map.npy).
The node/edge mappings are stored in numpy files.
launch.py
具体请参考我的博客
默认端口号是30050,当出现端口占用的时候需要kill掉相关进程
在我的设定里有两台机器,launch.py会原创创建两个server,两个client,通过ssh去启动。两个server分别是两台机器,而在client端则是ip_config.txt的第一个ip为master,调用了pytorch DDP,也即第一个ip为MASTER_ADDR。关于threading.Thread()以及start(),join()的用法可以参考------------------->Python Thread.join()详解
第一个server的cmd
‘cd /home/user/gnn-tutorial/graphsage/experimental; (export PATH=$PATH:/home/user/anaconda3/bin; (export DGL_ROLE=server DGL_NUM_SAMPLER=0 OMP_NUM_THREADS=1 DGL_NUM_CLIENT=2 DGL_CONF_PATH=2part_data/reddit.json DGL_IP_CONFIG=ip_config.txt DGL_NUM_SERVER=1 DGL_GRAPH_FORMAT=csc DGL_SERVER_ID=0; /home/user/anaconda3/envs/torch/bin/python train_dist_noprof.py --graph_name reddit --ip_config ip_config.txt --num_gpus 1 --local_rank 0 --num_epochs 3 --batch_size 1000))’
第二个server
‘cd /home/user/gnn-tutorial/graphsage/experimental; (export PATH=$PATH:/home/user/anaconda3/bin; (export DGL_ROLE=server DGL_NUM_SAMPLER=0 OMP_NUM_THREADS=1 DGL_NUM_CLIENT=2 DGL_CONF_PATH=2part_data/reddit.json DGL_IP_CONFIG=ip_config.txt DGL_NUM_SERVER=1 DGL_GRAPH_FORMAT=csc DGL_SERVER_ID=1; /home/user/anaconda3/envs/torch/bin/python train_dist_noprof.py --graph_name reddit --ip_config ip_config.txt --num_gpus 1 --local_rank 0 --num_epochs 3 --batch_size 1000))’
第一个client
‘cd /home/user/gnn-tutorial/graphsage/experimental; (export PATH=$PATH:/home/user/anaconda3/bin; (export DGL_DIST_MODE=distributed DGL_ROLE=client DGL_NUM_SAMPLER=0 DGL_NUM_CLIENT=2 DGL_CONF_PATH=2part_data/reddit.json DGL_IP_CONFIG=ip_config.txt DGL_NUM_SERVER=1 DGL_GRAPH_FORMAT=csc OMP_NUM_THREADS=10 ; /home/user/anaconda3/envs/torch/bin/python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=1 --nnodes=2 --node_rank=0 --master_addr=192.168.1.7 --master_port=1234 train_dist_noprof.py --graph_name reddit --ip_config ip_config.txt --num_gpus 1 --local_rank 0 --num_epochs 3 --batch_size 1000))’
第二个client
‘cd /home/user/gnn-tutorial/graphsage/experimental; (export PATH=$PATH:/home/user/anaconda3/bin; (export DGL_DIST_MODE=distributed DGL_ROLE=client DGL_NUM_SAMPLER=0 DGL_NUM_CLIENT=2 DGL_CONF_PATH=2part_data/reddit.json DGL_IP_CONFIG=ip_config.txt DGL_NUM_SERVER=1 DGL_GRAPH_FORMAT=csc OMP_NUM_THREADS=10 ; /home/user/anaconda3/envs/torch/bin/python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=1 --nnodes=2 --node_rank=0 --master_addr=192.168.1.7 --master_port=1234 train_dist_noprof.py --graph_name reddit --ip_config ip_config.txt --num_gpus 1 --local_rank 0 --num_epochs 3 --batch_size 1000))’
‘cd /home/user/gnn-tutorial/graphsage/experimental; (export PATH=$PATH:/home/user/anaconda3/bin; (export DGL_DIST_MODE=distributed DGL_ROLE=client DGL_NUM_SAMPLER=0 DGL_NUM_CLIENT=2 DGL_CONF_PATH=2part_data/reddit.json DGL_IP_CONFIG=ip_config.txt DGL_NUM_SERVER=1 DGL_GRAPH_FORMAT=csc OMP_NUM_THREADS=10 ; /home/user/anaconda3/envs/torch/bin/python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=1 --nnodes=2 --node_rank=1 --master_addr=192.168.1.7 --master_port=1234 train_dist_noprof.py --graph_name reddit --ip_config ip_config.txt --num_gpus 1 --local_rank 0 --num_epochs 3 --batch_size 1000))’
DDP Test
再试一下DDP test
还是和之前的一样参考----------------->Pytorch DDP
os.enviorn的作用
export 的作用
为什么export master-addr没有用
为什么export一次之后就一直是这个值
代码在为建立通信之前会在init_group处等待
init_group中的参数值需要系统提供哪些??
还有一个关于pytorch DDP启动文件的issue------------->alternative api for torch.distributed.launch,还是要多关注pytorch和dgl上的discusion。
DGL 单机版
dgl单机版主要参照graphSAGE
data处理部分
- 读取graph dataset
- 直接将feature和lable直接load进cuda中
- 根据train_mask,valid_mask, test_mask(均为bool值变量,True表示属于)将数据集分为train、valid、test数据集用于各种作用
dataloader
sample_frontier
frontier函数中主要调用sampler函数,因为图的相邻结点在DGL中被描述成frontier
当使用单机版时,采用in_subgraph或者sampling.sample_neighbors函数(根据是否采用fanouts判断)
sampling.sample_neighbors
这个函数比较,比in_subgraph功能强大的多
源码里给的example也非常清晰
Examples
--------
Assume that you have the following graph
>>> g = dgl.graph(([0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2], [1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0]))
And the weights
>>> g.edata['prob'] = torch.FloatTensor([0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1.])
To sample one inbound edge for node 0 and node 1:
>>> sg = dgl.sampling.sample_neighbors(g, [0, 1], 1)
>>> sg.edges(order='eid')
(tensor([1, 0]), tensor([0, 1]))
>>> sg.edata[dgl.EID]
tensor([2, 0])
To sample one inbound edge for node 0 and node 1 with probability in edge feature
``prob``:
>>> sg = dgl.sampling.sample_neighbors(g, [0, 1], 1, prob='prob')
>>> sg.edges(order='eid')
(tensor([2, 1]), tensor([0, 1]))
With ``fanout`` greater than the number of actual neighbors and without replacement,
DGL will take all neighbors instead:
>>> sg = dgl.sampling.sample_neighbors(g, [0, 1], 3)
>>> sg.edges(order='eid')
(tensor([1, 2, 0, 1]), tensor([0, 0, 1, 1]))
"""
可以看出EID就是边在原始图中的ID号,而这种采样默认会把子图node和edge的feature信息从原图中一起copy下来
dataloading.NodeDataLoader
这个函数最有意思的是可以使用pytorch的ddp进行分布式训练,且更改use_ddp=true即可,会直接调用ddp的相关API,通过set_epoch来让每个复制的dataset有不同的ordering在每个epoch期间
If you are using PyTorch's distributed training (e.g. when using
:mod:`torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel`), you can train the model by turning
on the `use_ddp` option:
>>> sampler = dgl.dataloading.MultiLayerNeighborSampler([15, 10, 5])
>>> dataloader = dgl.dataloading.NodeDataLoader(
... g, train_nid, sampler, use_ddp=True,
... batch_size=1024, shuffle=True, drop_last=False, num_workers=4)
>>> for epoch in range(start_epoch, n_epochs):
... dataloader.set_epoch(epoch)
... for input_nodes, output_nodes, blocks in dataloader:
... train_on(input_nodes, output_nodes, blocks)
对于num_work以及devices的设置
**Tips for selecting the proper device**
* If the input graph :attr:`g` is on GPU, the output device :attr:`device` must be the same GPU
and :attr:`num_workers` must be zero. In this case, the sampling and subgraph construction
will take place on the GPU. This is the recommended setting when using a single-GPU and
the whole graph fits in GPU memory.
* If the input graph :attr:`g` is on CPU while the output device :attr:`device` is GPU, then
depending on the value of :attr:`num_workers`:
- If :attr:`num_workers` is set to 0, the sampling will happen on the CPU, and then the
subgraphs will be constructed directly on the GPU. This is the recommend setting in
multi-GPU configurations.
- Otherwise, if :attr:`num_workers` is greater than 0, both the sampling and subgraph
construction will take place on the CPU. This is the recommended setting when using a
single-GPU and the whole graph does not fit in GPU memory.
总体最简单的调用为
- 1.首先NodeDataloader确认不为DistGraph后,将collator指定为_NodeCollator类,并将batch_size个node ID传给这个类(形式为items的列表,里面为一个个的tensor),_NodeCollator类是NodeCollator类的子类,只是多实现了_pop_blocks_storage函数,具体不太清楚,NodeCollator返回两个tensor和一个由两个子图组成的东东,应该是input_nodes(即src_node)和output_node(即dst_node),以及两层子图(与GraphSAGE的层数有关,blocks)。
*NodeCollator类,是Collator的子类,里面定义了collate函数,这个collate函数就是上述_NodeCollator的接受值,它将列表items转成一整个tensor,并调用block_sampler中获得子图。然后通过NID(其实就是_ID标识从两个block中获得input和output的ID标识)- block_sampler定义成了MultilayerNeighborSampler,这是BlockSampler的子类,它的主要定义了一些构建可能性矩阵的方法,大概意思就是可以从不固定的degree中获得固定邻居数的子图
- 将dataloader初始化为DataLoader类,DataLoader类实现dataloader的有两种,分别是_SingleProcessDataLoaderIter和_MultiProcessDataLoaderIter两种(具体根据num_worker是否等于0进行switch),两种都是_BaseDataLoaderIter
- _MultiProcessDataloaderIter实现太复杂了,_SingleProcessDataloaderIter还稍微能看懂,主要介绍下这个。_SingleProcessDataloaderIter通过父类调用_next_index()函数,父类又会调用DataLoader类的._index_sampler函数,因为DataLoader的auto_collation为true(由batch_sampler是否为空确定,batch_sampler为BatchSampler类,主要是生成batch_size大小的基本sampler的iter),这样就得到了一个batchsize的index,然后再通过_SingleProcessDataLoader的_dataset_fetcher函数来取index中的信息,这个函数又是_DatasetKind类的create_fetcher方法,这个方法又由两个类构成utils.fetch._MapDatasetFetcher和_utils.fetch._IterableDatasetFetcher,第二个类没有看,第一个类应该和multilayersampler类有关,因为定义了概率矩阵有关的一些运算。
- _MapDatasetFetcher是_BaseDataFetcher的子类,可以从dataset取出batch_size大小的index数据,即一个for循环得到input_node的tensor的list。而这个取出数据的dataset其实是在Dataloader中将dataset定义为了一个DataSet类,其实这里面装的全是index,即一个map,注释中这样写道
- _MultiProcessDataloaderIter实现太复杂了,_SingleProcessDataloaderIter还稍微能看懂,主要介绍下这个。_SingleProcessDataloaderIter通过父类调用_next_index()函数,父类又会调用DataLoader类的._index_sampler函数,因为DataLoader的auto_collation为true(由batch_sampler是否为空确定,batch_sampler为BatchSampler类,主要是生成batch_size大小的基本sampler的iter),这样就得到了一个batchsize的index,然后再通过_SingleProcessDataLoader的_dataset_fetcher函数来取index中的信息,这个函数又是_DatasetKind类的create_fetcher方法,这个方法又由两个类构成utils.fetch._MapDatasetFetcher和_utils.fetch._IterableDatasetFetcher,第二个类没有看,第一个类应该和multilayersampler类有关,因为定义了概率矩阵有关的一些运算。
r"""An abstract class representing a :class:`Dataset`.
All datasets that represent a map from keys to data samples should subclass
it. All subclasses should overwrite :meth:`__getitem__`, supporting fetching a
data sample for a given key. Subclasses could also optionally overwrite
:meth:`__len__`, which is expected to return the size of the dataset by many
:class:`~torch.utils.data.Sampler` implementations and the default options
of :class:`~torch.utils.data.DataLoader`.
.. note::
:class:`~torch.utils.data.DataLoader` by default constructs a index
sampler that yields integral indices. To make it work with a map-style
dataset with non-integral indices/keys, a custom sampler must be provided.
"""
测试sample_neighbors
g = dgl.graph(([0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2], [1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0]))
g.edata['prob'] = torch.FloatTensor([0., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1.])
sg = dgl.sampling.sample_neighbors(g, [0, 1], 1)
print(sg.edges(order='eid'))
print(sg.edata[dgl.EID])
输出结果
(tensor([1, 0]), tensor([0, 1]))
tensor([2, 0])
而且每次结果都不一样,这段代码中我没有添加边的因素,说明这种sample方式是随机的,eid表示还是根据原边的形式,而EID则是eid在原边中的ID。
当传入的图为DistGraph形式
多机版时使用distributed.graph_services.py中的sampler_neighbors函数,使用issue_remote_req来访问其他机器上的子图信息,local_access访问本机上子图信息(所有图均为DistGraph形式)。
GraphSAGE model
将block(即图)和src_feature传给SAGE
然后利用graph.num_dst_nodes()取出node中前k个node,这些为dst_node并取出dst_feature.
接下来就是把src_feature进行aggregate了,选择最简单的“mean”的方法,这里可以看到DGL在这块儿进行了优化,即进行一个判断,判断经过DNN处理后的feature维度是否减小,如果减小了就先aggregate在DNN,反则反之。
update_all函数测试
内置信息传递API
参照DGL的用户手册-------------------->Build in function and API calls
,这里面讲到了很多信息传递的API,想message函数(针对边),reduce函数(针对node)以及updateall函数,以及一些在dgl中常见的u_add_v以及apply_edge函数,注意在dgl中u一般指src_node,v一般指dst_node。