BUUCTF:喵喵喵
BUUCTF:喵喵喵
-
- 1.LSB隐写
- 2.png的图片需要修复
-
-
-
- 1.修复图片的文件头部(删除fffe)
- 2.使用png一键脚本修复png的高宽问题
-
-
- 3.二维码处理
-
-
-
- 代码如下
-
-
- 4.处理flag.rar
-
-
-
- 1.扫描二维码下载百度云盘的文件(flag.rar)
- 2.拿到rar文件后,解压开来(推荐使用winrar解压,不然可能隐藏的ntfs扫描不出来)
- 3.使用NSE工具扫描,扫描结果是flag.txt:flag.pyc,如图:
- 4.勾选然后导出pyc格式文件即可。
-
-
- 5.反汇编pyc代码
-
-
-
- 1.安装uncompyle库
- 2.使用uncomply6去反汇编pyc
- 3.反汇编出来的代码如下:
- 4.分析一下代码的情况
- 5.进一步分析encode()函数如何加密:
- 6.根据上一步进行倒退代码处理ciphertext,就是步骤反着来,解密代码:
- 7.运行上面的解密代码
-
-
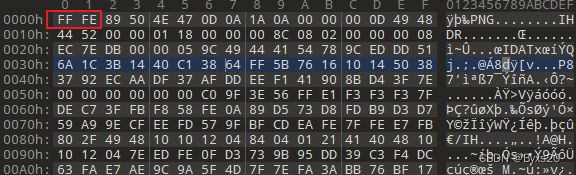
1.LSB隐写
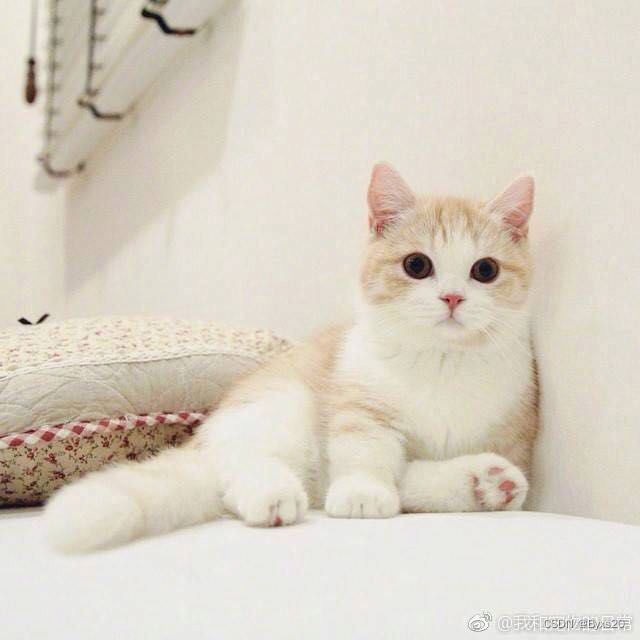
使用Stegsolve去**BGR**通道拿到一张png(有问题的)的图片,保存二进制文件即可。
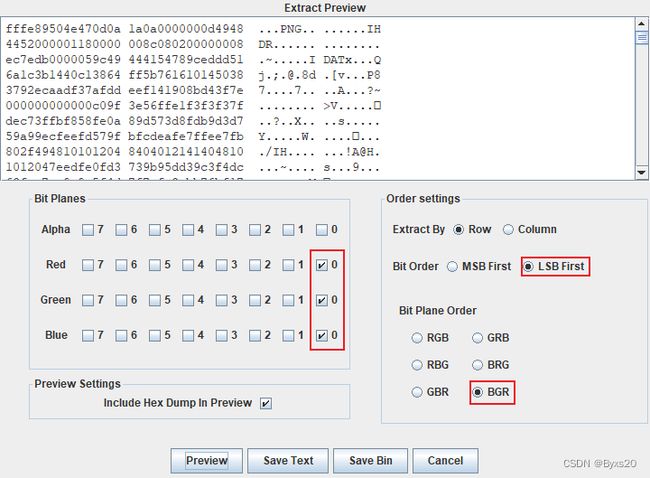
2.png的图片需要修复
1.修复图片的文件头部(删除fffe)
2.使用png一键脚本修复png的高宽问题
经过上一步的修复,现在图片可以查看了,如图:
由于图片的是一张二维码的上部分,加上图片是png格式,所以很正常就想到了是png高宽问题。
这个步骤我使用的是github开源项目链接:
https://github.com/Southseast/PNG_Height_Steganography
这地方比较简单,跳过了,不会使用的看他的使用文档即可食用!
3.二维码处理
经过上一步的处理,二维码已经拿到,如图:
仔细观察的话可以发现二维码的颜色有很大问题的,他的3个定位标志的颜色不对劲
如果看不出来的话,你们可以看一下正常的二维码,如图:
原理:让二维码的黑色变白色,白色变黑色,也就是每个像素点255的变成0,0的变成255,即可让二维码恢复正常的样貌。
代码如下
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread("1.png")
img = np.where(img == 0, 255, 0)
img = img.astype(np.uint8)
cv2.imshow("image", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
4.处理flag.rar
1.扫描二维码下载百度云盘的文件(flag.rar)
2.拿到rar文件后,解压开来(推荐使用winrar解压,不然可能隐藏的ntfs扫描不出来)
3.使用NSE工具扫描,扫描结果是flag.txt:flag.pyc,如图:
![]()
4.勾选然后导出pyc格式文件即可。
pyc格式是由py文件经过编译后二进制文件
5.反汇编pyc代码
1.安装uncompyle库
pip install uncompyle
2.使用uncomply6去反汇编pyc
uncompyle6 xxx.pyc > main.py
3.反汇编出来的代码如下:
import base64
def encode():
flag = '*************'
ciphertext = []
for i in range(len(flag)):
s = chr(i ^ ord(flag[i]))
if i % 2 == 0:
s = ord(s) + 10
else:
s = ord(s) - 10
ciphertext.append(str(s))
return ciphertext[::-1]
ciphertext = [
'96', '65', '93', '123', '91', '97', '22', '93', '70', '102', '94', '132', '46', '112', '64', '97', '88', '80', '82', '137', '90', '109', '99', '112']
4.分析一下代码的情况
encode() --> 根据名称能推理出来是个加密函数
ciphertext --> 由encode()加密出来的
5.进一步分析encode()函数如何加密:
def encode():
flag = '*************'
ciphertext = []
for i in range(len(flag)):
# 1.索引i 异或(^) flag第i个的元素的ascii的十进制数
# 然后再转成ascii
s = chr(i ^ ord(flag[i]))
# 2.如果i能被二整除就给ascii转换为十进制再 + 10,否则 - 10
if i % 2 == 0:
s = ord(s) + 10
else:
s = ord(s) - 10
ciphertext.append(str(s)) # 3.把处理好的数据加入到列表中
return ciphertext[::-1] # 4.对加密好ciphertext的进行倒序
6.根据上一步进行倒退代码处理ciphertext,就是步骤反着来,解密代码:
# 密文
ciphertext = [
'96', '65', '93', '123', '91', '97', '22', '93', '70', '102', '94', '132', '46', '112', '64', '97', '88', '80', '82', '137', '90', '109', '99', '112']
# 1.先对密文进行倒序
ciphertext = ciphertext[::-1]
for i in range(len(ciphertext)):
# 2.如果i能被二整除就给十进制数 - 10,否则 + 10.(和加密的关系反过来)
if i % 2 == 0:
s = int(ciphertext[i]) - 10
else:
s = int(ciphertext[i]) + 10
# 3.异或然后再转换为ascii就得出明文
plantext.append(chr(int(i ^ s)))
# 4.打印flag
print("".join(plantext))
7.运行上面的解密代码
获得flag:flag{Y@e_Cl3veR_C1Ever!}