Java常用类和枚举类型详解(Java必备知识)
Java类包提供了一些常用类供开发人员使用,例如Math类、生成随机数Random类,以及处理日期、时间相关的类。除了类包外,还提供了枚举类型。枚举类型是
目录
-
- 1.0 Java lang包
- 2.0 包装类
-
- 2.1 Integer类
- 2.2 Number类
- 3.0 Math类
-
- 3.1 Math类概述
- 3.2 常用数学运算方法
-
- 3.2.1 实现指数运算
- 3.2.2 取整函数方法
- 3.2.3 取最大值、最小值、绝对值函数方法
- 4.0 Random类
- 4.1 Date类
- 5.0 枚举类型
- 6.0 难点解答
-
- 6.1 注意随机数的取值范围
- 6.2 装箱与拆箱
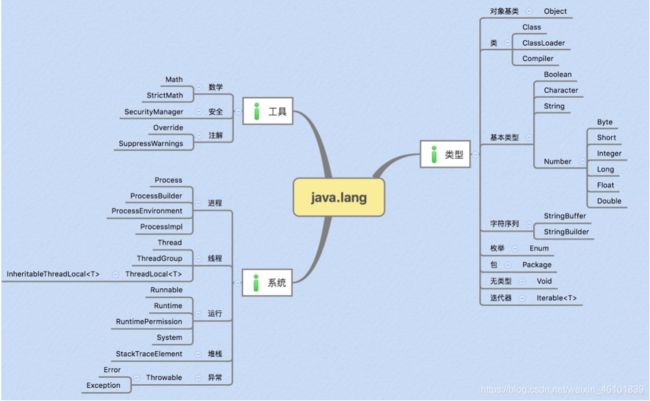
1.0 Java lang包
java.lang包是提供利用java编程语言进行程序设计的基础类,在项目中使用的时候不需要import。
2.0 包装类
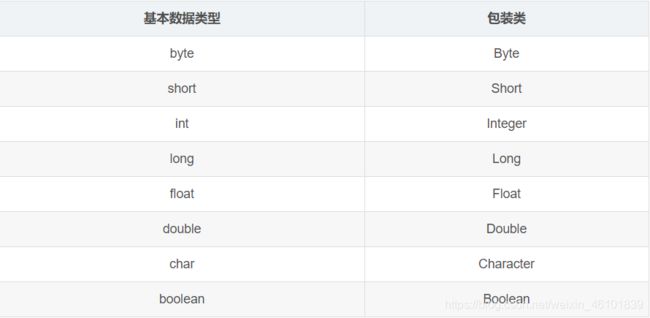
Java是一种面向对象的编程语言,为了能把基本数据类型当做对象处理,Java提供了包装类的概念,包装类分别把Java中8个基本数据类型包装成了相应的类,这样就可以通过对象调用各自包装类中许多实用的方法。
、
2.1 Integer类
java.lang包中的Byte类、Integer类、Short类和Long类,分别是基本数据类型byte、int、short和long的包装类,由于上述四个包装类都是Number类的子类,且都是对整数进行操作,所以上述四个包装类包含的方法也基本相同。下面以Integer类为例
1、构造方法
Integer有两种构造方法。一个int型作为参数,另一个是String作为参数。
Integer number = new Integer(7);
Integer number = new Integer("7");
如果要使用字符传参,一定要保证参数是数字类型,否则会直接报错NumberFormatException。
2、常用方法
//Integer静态方法,直接通过Integer.方法名调用即可
Integer valueOf = Integer.valueOf("222"); // 字符串转Integer类型
int parseInt = Integer.parseInt("222"); // 字符串转int类型
String binaryString = Integer.toBinaryString(123); // int类型转2进制
String aaString = Integer.toHexString(123); // int类型转16进制
String aaa = Integer.toOctalString(123); // int类型转8进制
Integer integer = new Integer(222);
String string = integer.toString(); // 字符串转String类型
int intValue = integer.intValue(); // 返回int类型
boolean equals = integer.equals(valueOf); // 比较此对象与指定对象是否相等
int compareTo = integer.compareTo(valueOf); // 0相等,前者小于后者返回负值,前者大于后者,返回正数
int maxValue = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // 获取Integer类最大值
int minValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE; // 获取Integer类最小值
int size = Integer.SIZE; // 获取Integer类的二进制位数
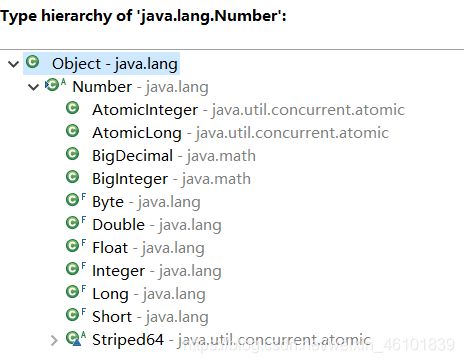
2.2 Number类
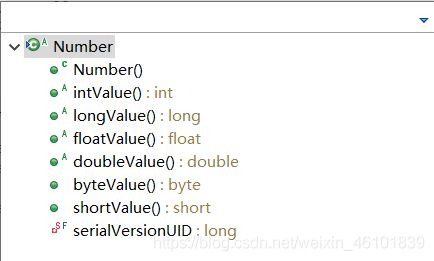
Number类是一个抽象类,他是Byte类、Integer类、Short类、Long类、Flot类和Double类的父类。
要把Number的子类对象转换为对应的基本数据类型,调用对应子类中的方法即可。
3.0 Math类
开发者可以使用加减乘除等运算符可以完成一些简单的数学运算,如果遇到复杂的怎么办呢?Java提供了Math类,Math类中包含许多数学方法,如取最大值、最小值、取绝对值、三角函数、指数函数和取整函数等。除此之外,Math类还提供了一些数学常量,如PI、E等。
3.1 Math类概述
Math类也是lang包的,类中有很多被定义为了静态变量所以直接通过 类名.数学方法 即可使用。
System.out.println(Math.PI); // 表示圆周率PI的值
System.out.println(Math.E); // 表示自然对数底数e的值
3.2 常用数学运算方法
Math类中的数学方法较多,如取最大值、取最小值、取绝对值、三角函数、指数函数和取整函数等。
3.2.1 实现指数运算
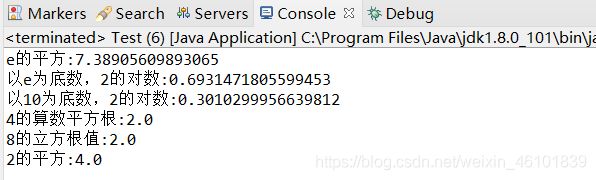
System.out.println("e的平方:" + Math.exp(2)); // 取e的2平方
System.out.println("以e为底数,2的对数:" + Math.log(2)); // 取以e为底2的对数
System.out.println("以10为底数,2的对数:" + Math.log10(2)); // 取以10为底2的对数
System.out.println("4的算数平方根:"+Math.sqrt(4)); // 取4的算术平方根
System.out.println("8的立方根值:"+Math.cbrt(8)); // 取8的立方根
System.out.println("2的平方:"+Math.pow(2, 2)); // 取2的平方
3.2.2 取整函数方法
// 返回第一个大于或等于参数的整数 (向上取整)
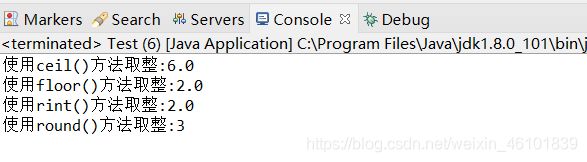
System.out.println("使用ceil()方法取整:"+Math.ceil(5.1));
// 返回第一个小于或等于参数的整数 (向下取整)
System.out.println("使用floor()方法取整:"+Math.floor(2.5));
// 返回与参数最接近的整数 (5舍6入)
System.out.println("使用rint()方法取整:"+Math.rint(2.5));
// 将参数加上0.5后返回最接近的整数,并将结果强制转换为整型 (4舍5入)
System.out.println("使用round()方法取整:"+Math.round(2.5));
3.2.3 取最大值、最小值、绝对值函数方法
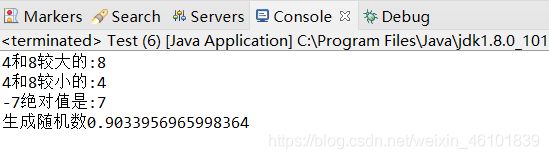
System.out.println("4和8较大的:"+Math.max(4, 8));
System.out.println("4和8较小的:"+Math.min(4, 8));
System.out.println("-7绝对值是:"+Math.abs(-7));
System.out.println("生成随机数"+Math.random());
4.0 Random类
通过实例化Random类对象可以创建一个随机数生成器。
Random random = new Random();
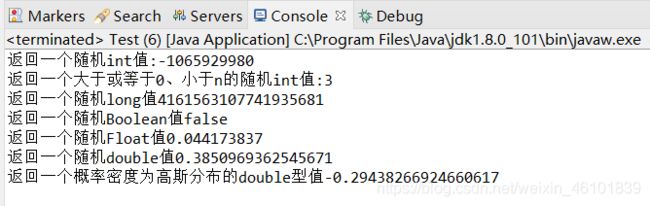
System.out.println("返回一个随机int值:"+ random.nextInt());
System.out.println("返回一个大于或等于0、小于n的随机int值:"+ random.nextInt(22));
System.out.println("返回一个随机long值"+random.nextLong());
System.out.println("返回一个随机Boolean值"+random.nextBoolean());
System.out.println("返回一个随机Float值"+random.nextFloat());
System.out.println("返回一个随机double值"+random.nextDouble());
System.out.println("返回一个概率密度为高斯分布的double型值"+random.nextGaussian());
4.1 Date类
Java的Java.util包中提供了Date类来操作日期和时间。使用Date需要先创建Date类对象。
// 主要用来获取系统当前时间距基准时间(1970年1月1日)的毫秒数
long currentTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
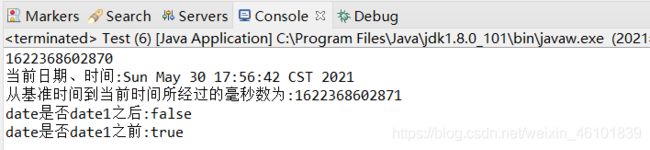
System.out.println(currentTimeMillis);
Date date = new Date(); // 创建现在的日期
long time = date.getTime(); // 获取毫秒数
System.out.println("当前日期、时间:" + date);
System.out.println("从基准时间到当前时间所经过的毫秒数为:" + time);
Date date2 = new Date();
System.out.println("date是否date1之后:" + date.after(date2));
System.out.println("date是否date1之前:" + date.before(date2));
在程序中直接输出Date对象,显示的是"Sun May 30 17:56:42 CST 2021",那么如何将日期显示为"2020-01-01 14:22:43"这样的格式呢?
为了解决这个问题,Java的java.txt包中提供了DateFormat类,DateFormat类的作用是按照指定格式对日期或者时间进行格式化。
要自定义日期时间格式,首先要创建DateFormat类对象,由于DateFormat类是抽象类,因此需要使用DateFormate类的静态方法getInstance()创建DateFormat类对象。
Date date = new Date(); // 创建现在的日期
DateFormat df1 = DateFormat.getInstance(); // DateFormat抽象类需要getInstance实例化
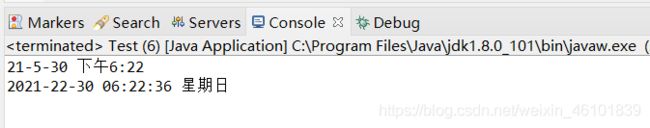
String format = df1.format(date); // java默认的格式化方式
System.out.println(format);
// SimpleDateFormat是DateFormat的子类,SimpleDateFormat参数可以设置格式,还可以设置时间的区域
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss EE",Locale.CHINA);
String format2 = simpleDateFormat.format(date);
System.out.println(format2);
Date date2 = simpleDateFormat.parse(format2); // 将格式化后的日期,转换成date类型
Calendar calendar = simpleDateFormat.getCalendar(); // 获取与此日期/时间格式器关联的日历
DateFormat dateInstance = DateFormat.getDateInstance(); // 获取日期格式器
DateFormat dateTimeInstance = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(); // 获取日期/时间格式器
DateFormat timeInstance = DateFormat.getTimeInstance(); // 获取时间格式器
5.0 枚举类型
枚举类型常被用于设置常量,传统常量在实际开发中习惯的定义在接口中。
public interface Constants {
public static final int a = 1;
public static final int b = 1;
}
由于枚举类型要一种数据类型,而且被视为一些列具有名称的常量集合,所以被赋予了在程序编译时检查数据类型的功能,使得使用枚举类型定义的常量逐渐取代了传统常量。
public enum Enumtest {
a,
b
}
其中enum是定义枚举类的关键字,在程序可以通过Enumtest.a的方式使用枚举类型的常量。
使用代码示例:
public interface Constants {
public static final int Constants_A = 1;
public static final int Constants_B = 12;
}
public class Test {
enum Enumtest {
Constants_A,Constants_B
}
// 接口中常量用法
public static void doint(int c) {
switch (c) {
case Constants.Constants_A:
System.out.println(Constants.Constants_A);
break;
case Constants.Constants_B:
System.out.println(Constants.Constants_B);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
// 枚举用法
public static void doint2(Enumtest c) {
switch (c) {
case Constants_A:
System.out.println(c.Constants_A);
break;
case Constants_B:
System.out.println(c.Constants_B);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
doint(1); // 使用接口中定义的常量
doint2(Enumtest.Constants_A); // 使用枚举类型的常量
}
}
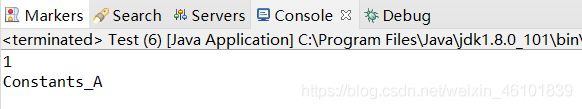

综上所述,枚举类型在程序编译时具有检查数据类型的功能。
6.0 难点解答
6.1 注意随机数的取值范围
random.nextInt(100);取不到100这个值,他的取值范围是大于或等于0,然后小于100。
6.2 装箱与拆箱
装箱是指将基本数据类型赋值给封装类对象,例如int转为Integer对象。
int a = 2;
Integer integer = new Integer(a);
拆箱是将封装类对象赋值给基本数据类型,例如Integer转为int。
int integer = new Integer(2);