牛客网刷题 | SQL
文章目录
- 入门
-
-
-
- SQL1 查询所有列
- SQL2 查询多列
- SQL3 查询结果去重
- SQL4 查询结果限制返回行数
- SQL5 将查询后的列重新命名
- SQL6 查找学校是北大的学生信息
- SQL7 查找年龄大于24岁的用户信息
- SQL8 查找某个年龄段的用户信息
- SQL13 查找存在某个集合内的用户信息
- SQL15 查看学校名称中含北京的用户
- SQL17 计算男生人数以及平均GPA
- SQL19 分组过滤练习题 (having用法)
- SQL21 浙江大学用户题目回答情况 (连接两张表)
- SQL22 统计每个学校的答过题的用户的平均答题数 (连接两张表)
- SQL23 统计每个学校各难度的用户平均刷题数 (连接三张表)
- SQL25 查找山东大学或者性别为男生的信息
- SQL26 计算25岁以上和以下的用户数量
- SQL28 计算用户8月每天的练题数量
- SQL29 计算用户的平均次日留存率
- SQL31 提取博客URL中的用户名
- SQL22.两个字段拼成一个+大小写转换
-
-
- Sql进阶
-
-
-
- SQL1 插入记录(一)
- SQL2 插入记录(二)
- SQL3 覆盖插入记录
- SQL5 修改记录
- SQL7 删除记录(二)
- SQL14 SQL类别高难度试卷得分的截断平均值(去掉最高最低分后的平均分)
- SQL16 得分不小于平均分的最低分
- SQL17 平均活跃天数和月活人数
- SQL18 月总刷题数和日均刷题数
- SQL19 未完成试卷数大于1的有效用户
- SQL20 月均完成试卷数不小于3的用户爱作答的类别
- SQL27 每类试卷得分前3名
- SQL28 第二快/慢用时之差大于试卷时长一半的试卷
- SQL29 连续两次作答试卷的最大时间窗
- SQL30 近三个月未完成试卷数为0的用户完成情况
- SQL45 对过长的昵称截取处理
- SQL46 大小写混乱时的筛选统计
-
-
- 大厂面试题
-
-
-
- SQL3 每类视频近一个月的转发量/率
- SQL4 每个创作者每月的涨粉率及截止当前的总粉丝量
- SQL8 每篇文章同一时刻最大在看人数
- SQL9 2021年11月每天新用户的次日留存率
- SQL14 统计2021年10月每个退货率不大于0.5的商品各项指标
- SQL15 某店铺的各商品毛利率及店铺整体毛利率
- SQL16 零食类商品中复购率top3高的商品 (筛选近90天的记录)
- SQL21 每个城市中评分最高的司机信息
- SQL22 国庆期间近7日日均取消订单量
- SQL31 牛客直播开始时各直播间在线人数
-
- 连接
-
- 表1inner join 表2 using(xxx)
- 查询
-
- 查找符合特定要求的数据
-
- 查找某字段不为空的
- 查找某个字段最大值
- 字符匹配
- 字符截取函数
- 多张表关联查询
- 先输出满足A的,在输出满足B的,结果不去重(union all)
- 逆序排序
-
- 插入
-
- 更新
- 替换
- 删除
- 修改表列名等
- 索引
- 日期
-
-
- 求时间差
- 给定日期,求当前月有几天
- 日期转换格式
-
- 汇总合计
- 窗口函数
-
- 累加
- 字符串
- 临时表 with as
入门
SQL1 查询所有列
select 表列名 from 表名
例如:
select
id,device_id,gender,age,university,province
from user_profile
或者
select
*
from user_profile
SQL2 查询多列
select
device_id,gender,age,university
from
user_profile
SQL3 查询结果去重
例.在成绩表中查询有哪些学生修了课程,要求列出学生的学号。
SELECT 学号 FROM 成绩表
结果中有重复的行。
用DISTINCT关键字可以去掉结果中的重复行。
SELECT DISTINCT 学号 FROM 成绩表
SQL4 查询结果限制返回行数
使用LIMIT限制返回行数
①选取前n行
SELECT 数据列 FROM 数据表 LIMIT 0,n
或者
SELECT 数据列 FROM 数据表 LIMIT n
②选取中间任意几行( LIMIT OFFSET)
查询第n到m行
SELECT 数据列 FROM 数据表 LIMIT m-n offset n
选取中间任意几行 ( OFFSET...FETCH)
SELECT 数据列 FROM 数据表 OFFSET n rows FETCH NEXT m-n rows ONLY
SQL5 将查询后的列重新命名
改变列标题(取别名)
语法:列名 | 表达式 [ AS ] 新列名
或:新列名=列名 | 表达式
题目:现在你需要查看2个用户明细设备ID数据,并将列名改为 ‘user_infors_example’,,请你从用户信息表取出相应结果。
SELECT device_id AS user_infos_example
FROM user_profile LIMIT 2
SQL6 查找学校是北大的学生信息
SELECT 列名 FROM 表名 WHERE 条件
题目:现在运营想要筛选出所有北京大学的学生进行用户调研,请你从用户信息表中取出满足条件的数据,结果返回设备id和学校。
SELECT device_id,university FROM user_profile WHERE university= '北京大学'
SQL7 查找年龄大于24岁的用户信息
select device_id,gender,age,university from user_profile where age>=24
SQL8 查找某个年龄段的用户信息
select device_id,gender,age from user_profile where (age>=20 and age<=23)
SQL13 查找存在某个集合内的用户信息
查找学校为北大、复旦和山大的同学信息
select device_id,gender,age,university,gpa from user_profile
where university in('北京大学','复旦大学','山东大学')
SQL15 查看学校名称中含北京的用户
select * from user_profile
where university like '%北京%'
SQL17 计算男生人数以及平均GPA
select count(gender),round(avg(gpa),1)
from user_profile
where gender='male'
SQL19 分组过滤练习题 (having用法)
取出平均发贴数低于5的学校或平均回帖数小于20的学校
select
university,
round(avg(question_cnt), 1)as avg_question_cnt,
avg(answer_cnt)as avg_answer_cnt
from user_profile
group by university
having avg(question_cnt)<5 or avg(answer_cnt)<20
having具体用法:
where(数据查询) -> group by(数据编组) -> having(结果过滤) -> order by(排序)
SQL21 浙江大学用户题目回答情况 (连接两张表)
select t1.a,t1.b
from table1 as t1
inner join table2 as t2
on t1.id = t2.id and t2.university='浙江大学'
order by t1.b
SQL22 统计每个学校的答过题的用户的平均答题数 (连接两张表)
表1:学生id 学校名称
表2:学生id 题目标号
计算不同学校,答题总次数除以答过题的不同用户个数
select university,
count(question_id) / count(distinct(qpd.device_id)) as avg_answer_cnt
from 表1as qpd
inner join 表2 as up
on qpd.device_id=up.device_id
group by university
SQL23 统计每个学校各难度的用户平均刷题数 (连接三张表)
表1与表2通过device_id相连,表1与表3通过question_id相连
select
university,
difficult_level,
round(count(qpd.question_id) / count(distinct qpd.device_id), 4) as avg_answer_cnt
from 表1 as qpd
left join 表2 as up
on up.device_id=qpd.device_id
left join 表3 as qd
on qd.question_id=qpd.question_id
group by university, difficult_level
SQL25 查找山东大学或者性别为男生的信息
分别查看学校为山东大学或者性别为男性的用户的device_id、gender、age和gpa数据,请取出相应结果,结果不去重。
select
device_id, gender, age, gpa
from user_profile
where university='山东大学'
union all
select
device_id, gender, age, gpa
from user_profile
where gender='male'
SQL26 计算25岁以上和以下的用户数量
SELECT CASE WHEN age < 25 OR age IS NULL THEN '25岁以下'
WHEN age >= 25 THEN '25岁及以上'
END age_cut,COUNT(*)number
FROM user_profile
GROUP BY age_cut
SQL28 计算用户8月每天的练题数量
select
day(date) as day,
count(question_id) as question_cnt
from question_practice_detail
where month(date)=8 and year(date)=2021
group by date
SQL29 计算用户的平均次日留存率
表头重命名:as
去重:需要按照devece_id,date去重,因为一个人一天可能来多次
子查询必须全部有重命名
select count(date2) / count(date1) as avg_ret
from (
select
distinct qpd.device_id,
qpd.date as date1,
uniq_id_date.date as date2
from question_practice_detail as qpd
left join(
select distinct device_id, date
from question_practice_detail
) as uniq_id_date
on qpd.device_id=uniq_id_date.device_id
and date_add(qpd.date, interval 1 day)=uniq_id_date.date
) as id_last_next_date
SQL31 提取博客URL中的用户名
- 字符截取函数
SQL22.两个字段拼成一个+大小写转换
A列取前2+B列取前3个字符,并且转为大写,拼成C
select cust_id,cust_name,
upper(concat(substring(A,1,2),substring(B,1,3))) as user_login
from Customers
Sql进阶
SQL1 插入记录(一)
用户1001在2021年9月1日晚上10点11分12秒开始作答试卷9001,并在50分钟后提交,得了90分;
用户1002在2021年9月4日上午7点1分2秒开始作答试卷9002,并在10分钟后退出了平台。
INSERT INTO exam_record (id,uid, exam_id, start_time, submit_time, score) VALUES
(null,1001, 9001, '2021-09-01 22:11:12', '2021-09-01 23:01:12', 90),
(null,1002, 9002, '2021-09-04 07:01:02', NULL, NULL);
SQL2 插入记录(二)
已有原始表exam_record,需要备份。新建表exam_record_before_2021用来备份2021年之前的试题作答记录,结构和exam_record表一致,请将2021年之前的已完成了的试题作答纪录导入到该表。
普通插入(全字段):INSERT INTO table_name VALUES (value1, value2, ...)
普通插入(限定字段):INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, ...) VALUES (value1, value2, ...)
多条一次性插入:INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, ...) VALUES (value1_1, value1_2, ...), (value2_1, value2_2, ...), ...
从另一个表导入:INSERT INTO table_name SELECT * FROM table_name2 [WHERE key=value]
insert into exam_record_before_2021
select null,uid, exam_id, start_time, submit_time, score
from exam_record
WHERE YEAR(submit_time) < '2021';
SQL3 覆盖插入记录
- 带更新的插入:REPLACE INTO table_name VALUES (value1, value2, …)
- 原理:先删去重复的,在插入
SQL5 修改记录
请把exam_record表中2021年9月1日之前开始作答的未完成记录全部改为被动完成,即:将完成时间改为’2099-01-01 00:00:00’,分数改为0。
update exam_record
set score = 0, submit_time = '2099-01-01 00:00:00'
where start_time<'2021-09-01' AND submit_time is null;
注意,score = 0, submit_time = '2099-01-01 00:00:00’这里“,”不能换成and
SQL7 删除记录(二)
请删除exam_record表中未完成作答或作答时间小于5分钟整的记录中,开始作答时间最早的3条记录。
DELETE FROM exam_record
WHERE submit_time IS NULL
OR TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE, start_time, submit_time) < 5
order by start_time
limit 3
SQL14 SQL类别高难度试卷得分的截断平均值(去掉最高最低分后的平均分)
select tag, difficulty,
round((sum(score) - max(score) - min(score)) / (count(score) - 2), 1) as clip_avg_score
from exam_record
join examination_info using(exam_id)
where tag="SQL" and difficulty="hard"
SQL16 得分不小于平均分的最低分
两张表,表1有不同用户,做了不同卷子,得到不同分数,因此有user_id, exam_id,score,表2是不同卷子是哪一类的,难度如何,因此表2有exam_id,tag,difficulty
我们现在需要算出tag为sql,且得分大于sql平均分的最低分
select min(score) as min_score_over_avg
from table1
join table2 using(exam_id)
where tag = 'SQL' and score>=(
select avg(score)
from table1
join table2 using(exam_id)
where tag='SQL'
)
思路:先连接两表求出平均分的分数,就是score>的那部分,然后连接两表找到符合tag且求出score>平均分的数据,求最小
SQL17 平均活跃天数和月活人数
exam_record表(uid用户ID, exam_id试卷ID, start_time开始作答时间, submit_time交卷时间, score得分),请计算2021年每个月里试卷作答区用户平均月活跃天数avg_active_days和月度活跃人数mau
也就是说,要先根据月份分组,然后找到每个月份中,不同的人总共活跃的天数(同一个人可能活跃了好几天),再找到有几个活跃的人,求出活跃天数/活跃人数,此处活跃指有submit_time不为null。
select
date_format(start_time, '%Y%m'),
count(submit_time)/count(distinct if(submit_time is null,null,uid)) as avg_active_days,
count(distinct if(submit_time is null,null,uid)) as mau
from exam_record
where year(start_time)=2021
group by date_format(start_time, '%Y%m')
SQL18 月总刷题数和日均刷题数
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/f6b4770f453d4163acc419e3d19e6746?tpId=240&tags=&title=&difficulty=0&judgeStatus=0&rp=0&sourceUrl=%2Fexam%2Foj%3Fpage%3D1%26tab%3DSQL%25E7%25AF%2587%26topicId%3D240
求每个月一共刷了多少题,除以一个月有多少天,再把2021年的总和计算下
select
DATE_FORMAT(submit_time,'%Y%m') as submit_month,
count(*) as month_q_cnt,
round(count(*) / day(last_day(submit_time)) ,3) as avg_day_q_cnt
from practice_record
and year(submit_time) = '2021'
group by DATE_FORMAT(submit_time,'%Y%m')
union all
select
'2021汇总' as submit_month,
count(*) as month_q_cnt,
round(count(*) /31 ,3) as avg_day_q_cnt -- /30 会不通过用例
from practice_record where score is not null
and year(submit_time) = '2021'
order by submit_month ;
简化版本:
SELECT COALESCE (DATE_FORMAT(submit_time, "%Y%m"),"2021汇总") AS submit_month,
COUNT(submit_time) AS month_q_cnt,
ROUND(COUNT(submit_time)/MAX(DAY(last_day(submit_time))),3) AS avg_day_q_cnt
FROM practice_record
WHERE YEAR(submit_time) = 2021
GROUP BY DATE_FORMAT(submit_time, "%Y%m") WITH ROLLUP
- COALESCE
select coalesce(success_cnt, 1) from tableA
表示当success_cnt 为null值的时候,将返回1,否则将返回success_cnt的真实值。
COALESCE是一个函数, (expression_1, expression_2, …,expression_n)依次参考各参数表达式,遇到非null值即停止并返回该值。如果所有的表达式都是空值,最终将返回一个空值。使用COALESCE在于大部分包含空值的表达式最终将返回空值。
SQL19 未完成试卷数大于1的有效用户
关键点:统计作答过的tag集合:
对于每条作答tag,用:连接日期和tag:concat_ws(':', date(start_time), tag)
对于一个人(组内)的多条作答,用;连接去重后的作答记录:
group_concat(distinct concat_ws(':', date(start_time), tag) SEPARATOR ';')
select
uid,
count(start_time)-sum(if(submit_time is null,0,1)) as incomplete_cnt,
sum(if(submit_time is null,0,1)) as complete_cnt,
group_concat(distinct CONCAT(DATE_FORMAT(start_time, '%Y-%m-%d'),':',tag) separator ';') as detail
from exam_record
inner join examination_info using(exam_id)
where year(start_time)=2021
group by uid
having incomplete_cnt>1 and incomplete_cnt<5 and complete_cnt>1
SQL20 月均完成试卷数不小于3的用户爱作答的类别
- 统计一共有几个月:count(distinct DATE_FORMAT(start_time, “%Y%m”))
- 统计月均完成数:
having count(exam_id) / count(distinct DATE_FORMAT(start_time, "%Y%m")) >= 3
首先,找出月均完成试卷数不小于3的用户,就是where括号里面的那段
其次,根据用户id筛选出数据,然后根据tag分组,求出不同tag的个数
select tag, count(tag) as tag_cnt
from exam_record
join examination_info using(exam_id)
where uid in (
select uid
from exam_record
where submit_time is not null
group by uid
having count(exam_id) / count(distinct DATE_FORMAT(start_time, "%Y%m")) >= 3
)
group by tag
order by tag_cnt desc
SQL27 每类试卷得分前3名
求:找到每类试卷得分的前3名,如果两人最大分数相同,选择最小分数大者,如果还相同,选择uid大者。
SELECT tag,uid,ranking
FROM (
SELECT b.tag,a.uid,
ROW_NUMBER()OVER(PARTITION BY tag ORDER BY max(a.score) DESC,min(a.score) DESC,a.uid DESC) ranking
/*先按照最高分,再按照最低分排,最后按照uid排序 */
FROM exam_record a
LEFT JOIN examination_info b ON a.exam_id=b.exam_id
GROUP BY b.tag,a.uid)t1
WHERE ranking<=3
SQL28 第二快/慢用时之差大于试卷时长一半的试卷
怎么找第二和倒数第二,分别按照逆序和正序排序,然后给第二的赋值正数,倒数第二的赋负数,这样加起来刚好为0的就是第二和倒数第二的
select distinct exam_id, duration, release_time
from
(select exam_id as exam_id, duration, release_time,
sum(case when rank1 = 2 then costtime when rank2 = 2 then -costtime else 0 end) as sub
from (
select e_i.exam_id, duration, release_time,
timestampdiff(minute, start_time, submit_time) as costtime,
row_number() over(partition by e_r.exam_id order by timestampdiff(minute, start_time, submit_time) desc) rank1,
row_number() over(partition by e_r.exam_id order by timestampdiff(minute, start_time, submit_time) asc) rank2
from exam_record e_r join examination_info e_i
on e_r.exam_id = e_i.exam_id
where submit_time is not null
) table1
group by exam_id
) table2
where sub * 2 >= duration
order by exam_id desc
SQL29 连续两次作答试卷的最大时间窗
- 窗口函数lead()、lag()
同一次查询中取出同一字段的前N行的数据(Lag)和后N行的数据(Lead)作为独立的列。
lag(exp_str,offset,defval) over(partion by ..order by …)
lead(exp_str,offset,defval) over(partion by ..order by …)
exp_str是字段名
Offset是偏移量,即是上1个或上N个的值,假设当前行在表中排在第5行,则offset 为3,则表示我们所要找的数据行就是表中的第2行(即5-3=2)。可以省略Offset,不屑默认为1
- 思路
首先,得到不同用户,下一次答题时间,用lead窗口函数
SELECT uid, exam_id, start_time,
lead(start_time) over(
PARTITION BY uid ORDER BY start_time) as next_start_time -- 将连续的下次作答时间拼上
FROM exam_record
WHERE YEAR(start_time)=2021
统计最早一次作答和最晚一次作答的相差天数:DATEDIFF(max(start_time), min(start_time))+1 as diff_days
统计两次作答的最大时间窗:max(DATEDIFF(next_start_time, start_time))+1 as days_window
时间差函数,tiamediff
最后,总体代码如下
SELECT uid, days_window, ROUND(days_window * exam_cnt / diff_days, 2) as avg_exam_cnt
FROM (
SELECT uid,
count(start_time) as exam_cnt, -- 此人作答的总试卷数
DATEDIFF(max(start_time), min(start_time))+1 as diff_days, -- 最早一次作答和最晚一次作答的相差天数
max(DATEDIFF(next_start_time, start_time))+1 as days_window -- 两次作答的最大时间窗
FROM (
SELECT uid, exam_id, start_time,
lead(start_time) over(
PARTITION BY uid ORDER BY start_time) as next_start_time -- 将连续的下次作答时间拼上
FROM exam_record
WHERE YEAR(start_time)=2021
) as t_exam_record_lead
GROUP BY uid
) as t_exam_record_stat
WHERE diff_days > 1
ORDER BY days_window DESC, avg_exam_cnt DESC;
SQL30 近三个月未完成试卷数为0的用户完成情况
SELECT uid, COUNT(score) as exam_complete_cnt -- 此人完成的总试卷数
FROM (
SELECT uid, score,
DENSE_RANK() OVER(
PARTITION BY uid
ORDER BY DATE_FORMAT(start_time, "%Y%m") DESC
) as start_month_rank -- 按作答月份降序编号
FROM exam_record
) as t_exam_record_month_rank
WHERE start_month_rank <= 3
GROUP BY uid
HAVING COUNT(1) = COUNT(score) -- 都完成了
ORDER BY exam_complete_cnt DESC, uid DESC;
SQL45 对过长的昵称截取处理
输出昵称字符数大于10的用户信息,对于字符数大于13的用户昵称输出前10个字符然后加上三个点号:『…』
- 统计英文字符串个数:
lenghth - 统计有中文的,一个中文占好几个字符:
char_lenghth
select uid, if(CHAR_LENGTH(nick_name)>13,
concat(substr(nick_name,1,10),'...'),
nick_name)
from user_info
where CHAR_LENGTH(nick_name)>=10
SQL46 大小写混乱时的筛选统计
有两张表,一张叫试卷信息表examination_info(exam_id试卷ID, tag试卷类别, difficulty试卷难度, duration考试时长, release_time发布时间)
一张叫试卷作答信息表exam_record(uid用户ID, exam_id试卷ID, start_time开始作答时间, submit_time交卷时间, score得分)
试卷的类别tag可能出现大小写混乱的情况,请先筛选出试卷作答数小于3的类别tag,统计将其转换为大写后对应的原本试卷作答数。
如果转换后tag并没有发生变化,不输出该条结果。
- 思路
首先,统计每类试卷的作答数(区分大小写),生成临时表 t_tag_count,利用with as
其次,对表t_tag_count进行自连接,假设取出的两条记录分别为a和b:t_tag_count as a JOIN t_tag_count as b
最后,选出满足题目条件的结果:
a.tag转大写后和b.tag一样:ON UPPER(a.tag) = b.tag
a.tag转换后必须发生变化:a.tag != b.tag
a的试卷作答数小于3:a.answer_cnt < 3
WITH t_tag_count as (
SELECT tag, COUNT(uid) as answer_cnt
FROM exam_record
LEFT JOIN examination_info USING(exam_id)
GROUP BY tag
)
SELECT a.tag, b.answer_cnt
FROM t_tag_count as a
JOIN t_tag_count as b
ON UPPER(a.tag) = b.tag and a.tag != b.tag and a.answer_cnt < 3;
最后这样也可以
SELECT a.tag, b.answer_cnt
FROM t_tag_count as a, t_tag_count as b
where UPPER(a.tag) = b.tag and a.tag != b.tag and a.answer_cnt < 3
- 补充:自连接
比如说表a有两列,分别是分类和分数,即分类为A,分数为30,分类为B,分数为20。
那么通过自连接,也就是
select *
from a,a
就会得到,四列,四行分别是分类1为A,分数1为30,分类2为A,分数2为30;分类1为A,分数1为30,分类2为B,分数2为20…
即做了笛卡尔乘积
大厂面试题
SQL3 每类视频近一个月的转发量/率
SELECT
b.tag,
SUM(if_retweet) retweet_cnt,
ROUND(SUM(if_retweet)/COUNT(*), 3) retweet_rate
FROM tb_user_video_log a
LEFT JOIN tb_video_info b
ON a.video_id = b.video_id
WHERE DATEDIFF(DATE((select max(start_time) FROM tb_user_video_log)), DATE(a.start_time)) <= 29
GROUP BY b.tag
ORDER BY retweet_rate desc
SQL4 每个创作者每月的涨粉率及截止当前的总粉丝量
SELECT author,DATE_FORMAT(DATE(end_time),'%Y-%m') AS month,
round(SUM(case when if_follow=1 then 1
when if_follow=2 then -1
else 0
end)/ COUNT(author), 3),
sum(SUM(case when if_follow=1 then 1
when if_follow=2 then -1
else 0
end)) over(partition by author order by DATE_FORMAT(DATE(end_time),'%Y-%m'))
total_fans
FROM tb_user_video_log JOIN tb_video_info USING(video_id)
WHERE YEAR(end_time)=2021
GROUP BY author,month
ORDER BY author,total_fans
SQL8 每篇文章同一时刻最大在看人数
SELECT
artical_id,
MAX(instant_viewer_cnt) max_uv
FROM (
SELECT
artical_id,
SUM(diff) OVER(PARTITION BY artical_id ORDER BY dt, diff DESC) instant_viewer_cnt
FROM (
SELECT
artical_id, in_time dt, 1 diff
FROM tb_user_log
WHERE artical_id != 0
UNION ALL
SELECT
artical_id, out_time dt, -1 diff
FROM tb_user_log
WHERE artical_id != 0) t1
) t2
GROUP BY 1
ORDER BY 2 DESC
SQL9 2021年11月每天新用户的次日留存率
-
先得到新用户表
用户最早登录的时间,就是改天的新用户,所以我们查询各个用户min登录的时间 -
用户第二天仍活跃?
返回用户id,前面几行是登入时间,后几行是登出时间
-- 用户活跃表
select uid , date(in_time) dt
from tb_user_log
union
select uid , date(out_time)
from tb_user_log
得到用户活跃表后,再用新用户表最早登录时间+1,和用户表中登入时间,登出时间比对,找出最早登录时间+1的数据
- 整体代码如下
select t1.dt,round(count(t2.uid)/count(t1.uid),2) uv_rate
from (select uid
,min(date(in_time)) dt
from tb_user_log
group by uid) as t1 -- 每天新用户表
left join (select uid , date(in_time) dt
from tb_user_log
union
select uid , date(out_time)
from tb_user_log) as t2 -- 用户活跃表
on t1.uid=t2.uid
and t1.dt=date_sub(t2.dt,INTERVAL 1 day) -- date_sub表示减去
where date_format(t1.dt,'%Y-%m') = '2021-11'
group by t1.dt
order by t1.dt
- 一般求次日留存率的时候
用户id,时间
然后left join 上次一日时间,没有其他乱七八糟的列,不然没法join匹配
SQL14 统计2021年10月每个退货率不大于0.5的商品各项指标
select product_id,
round(sum(if_click)/count(1),3) ctr,
round(sum(if_cart)/sum(if_click),3) cart_rate,
round(sum(if_payment)/sum(if_cart),3) payment_rate,
round(sum(if_refund)/sum(if_payment),3) refund_rate
from tb_user_event
where DATE_FORMAT(event_time,'%Y-%m') = '2021-10'
group by product_id
having refund_rate <= 0.5
order by product_id
SQL15 某店铺的各商品毛利率及店铺整体毛利率
- 求整体:
WITH ROLLUP,并且命名IFNULL(product_id, ‘店铺汇总’) - 把19变为19%,
CONCAT(xx, "%")
SELECT product_id, CONCAT(profit_rate, "%") as profit_rate
FROM (
SELECT IFNULL(product_id, '店铺汇总') as product_id,
ROUND(100 * (1 - SUM(in_price*cnt) / SUM(price*cnt)), 1) as profit_rate
FROM (
SELECT product_id, price, cnt, in_price
FROM tb_order_detail
JOIN tb_product_info USING(product_id)
JOIN tb_order_overall USING(order_id)
WHERE shop_id = 901 and DATE(event_time) >= "2021-10-01"
) as t_product_in_each_order
GROUP BY product_id
WITH ROLLUP
HAVING profit_rate > 24.9 OR product_id IS NULL
ORDER BY product_id
) as t1;
SQL16 零食类商品中复购率top3高的商品 (筛选近90天的记录)
筛选近90天的记录:
计算最小允许日期:DATE_SUB(MAX(event_time), INTERVAL 89 DAY)
筛选:event_time >= (SELECT ... FROM tb_order_overall)
SQL21 每个城市中评分最高的司机信息
SELECT city, driver_id, avg_grade, avg_order_num, avg_mileage
FROM (
SELECT city, driver_id, ROUND(avg_grade, 1) as avg_grade,
ROUND(order_num / work_days, 1) as avg_order_num,
ROUND(toal_mileage / work_days, 3) as avg_mileage,
RANK() over(PARTITION BY city ORDER BY avg_grade DESC) as rk
FROM (
SELECT driver_id, city, AVG(grade) as avg_grade,
COUNT(DISTINCT DATE(order_time)) as work_days,
COUNT(order_time) as order_num,
SUM(mileage) as toal_mileage
FROM tb_get_car_record
JOIN tb_get_car_order USING(order_id)
GROUP BY driver_id, city
) as t_driver_info
) as t_driver_rk
WHERE rk = 1
ORDER BY avg_order_num;
SQL22 国庆期间近7日日均取消订单量
- 难点:求包含自己在内的前7天数据:
sum(finish_num)over(order by dt rows 6 preceding)
select dt,
ROUND(finish_num/7,2) finish_num_7d,
ROUND(cancel_num/7,2) cancel_num_7d
from(select dt,
sum(finish_num)over(order by dt rows 6 preceding) as finish_num,
sum(cancel_num)over(order by dt rows 6 preceding) as cancel_num
from(select date(order_time) dt,
sum(if (start_time is not null,1,0)) as finish_num,
sum(if (start_time is null,1,0)) as cancel_num
from tb_get_car_order
group by date(order_time)
) t
) a
where dt between '2021-10-01' and '2021-10-03'
SQL31 牛客直播开始时各直播间在线人数
select a.course_id,
b.course_name,
count(distinct user_id) online_num
from attend_tb a
left join course_tb b
on a.course_id = b.course_id
where '19:00' between DATE_FORMAT(in_datetime,'%H:%i') and DATE_FORMAT(out_datetime,'%H:%i')
group by a.course_id,b.course_name
order by a.course_id
连接
表1inner join 表2 using(xxx)
查询
查找符合特定要求的数据
SELECT 列表达式
FROM <表名>
WHERE <条件表达式>
查找某字段不为空的
select * from 表名 where 字段名1 is null
AND 字段名2 is not null
查找某个字段最大值
select max(字段) form <表名> where <条件表达式>
或者
select 字段
from 表
where 条件
order by 字段 desc limit 1
如果想要返回的是最大值的这一行
select * form 表
where 字段 in (select max(字段) form 表 where 条件)
字符匹配
一般形式为:
列名 [NOT ] LIKE
匹配串中可包含如下四种通配符:
_:匹配任意一个字符;
%:匹配0个或多个字符;
[ ]:匹配[ ]中的任意一个字符(若要比较的字符是连续的,则可以用连字符“-”表 达 );
[^ ]:不匹配[ ]中的任意一个字符。
例23.查询学生表中姓‘张’的学生的详细信息。
SELECT * FROM 学生表 WHERE 姓名 LIKE ‘张%’
例24.查询姓“张”且名字是3个字的学生姓名。
SELECT * FROM 学生表 WHERE 姓名 LIKE '张__’
如果把姓名列的类型改为nchar(20),在SQL Server 2012中执行没有结果。原因是姓名列的类型是char(20),当姓名少于20个汉字时,系统在存储这些数据时自动在后边补空格,空格作为一个字符,也参加LIKE的比较。可以用rtrim()去掉右空格。
SELECT * FROM 学生表 WHERE rtrim(姓名) LIKE ‘张__’
例25.查询学生表中姓‘张’、姓‘李’和姓‘刘’的学生的情况。
SELECT * FROM 学生表 WHERE 姓名 LIKE '[张李刘]%’
例26.查询学生表表中名字的第2个字为“小”或“大”的学生的姓名和学号。
SELECT 姓名,学号 FROM 学生表 WHERE 姓名 LIKE ‘_[小大]%’
例27.查询学生表中所有不姓“刘”的学生。
SELECT 姓名 FROM 学生 WHERE 姓名 NOT LIKE '刘%’
例28.从学生表表中查询学号的最后一位不是2、3、5的学生信息。
SELECT * FROM 学生表 WHERE 学号 LIKE ‘%[^235]’
字符截取函数
- substring
substring(列名, start, end)
start从1开始,而不是0
- substring_index
substring_index(字符串,“截取数据依据的字符”,截取字符的位置N)
例如,//以第二个逗号为分割截取
SELECT SUBSTRING_INDEX(‘15,151,152,16’, ’ , ’ , 2); //结果是15,151
//从后面开始算第一个逗号
SELECT SUBSTRING_INDEX(‘15,151,152,16’, ’ , ’ , -1); //结果是16
多张表关联查询
现有A\B\C 三张表,现在要查询并展示A表和C表中的某些字段,但是A、C两表没有相同字段,无法关联,此时有B表恰好有两个字段,一个字段和A表一个字段相同,一个字段和C表一个字段相同,我们称B表为“中间表”,因此通过B表把A、C表关联起来
方法一(推荐):
SELECT A1,A2,C1,C2 --展示A表中的A1\A2字段和C表中的C1\C2
FROM B --中间表
INNER JOIN A ON A.A1 = B.B1 --A表中的与B表中相同的字段
INNER JOIN C ON C.C1 = B.B1 --C表中的与B表中相同的字段
where xxxxx ---条件你自己按照需求来加,没有条件就不写where了
方法二(有点笨,但也好用,写子查询)
原理:两两关联,在关联第三张表
select C.C1,C.C2,D.* --打印出C表的C1,C2字段和D表中的select 后面的字段,即A1,A2,A3,B1,B2,B3
from C, (select A1,A2,A3,B1,B2,B3 from A,B ) D --先把A,B两张表关联起来,命名为D表,再与C表关联,注意,A,B表关联时一定要记得打印出B表中与C表相同的字段
where xxxxx ---条件你自己按照需求来加,没有条件就不写where了
先输出满足A的,在输出满足B的,结果不去重(union all)
select * from table
where 条件A
union all
select * from table
where 条件B
join---连接表,对列操作
union--连接表,对行操作。
union--将两个表做行拼接,同时自动删除重复的行。
union all---将两个表做行拼接,保留重复的行。
逆序排序
order by xxx desc
插入
插入记录的方式汇总:
普通插入(全字段):INSERT INTO table_name VALUES (value1, value2, ...)
普通插入(限定字段):INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, ...) VALUES (value1, value2, ...)
多条一次性插入:INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, ...) VALUES (value1_1, value1_2, ...), (value2_1, value2_2, ...), ...
从另一个表导入:INSERT INTO table_name SELECT * FROM table_name2 [WHERE key=value]
带更新的插入:REPLACE INTO table_name VALUES (value1, value2, ...) (注意这种原理是检测到主键或唯一性索引键重复就删除原记录后重新插入)
更新
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2, ...
WHERE condition;
请注意
更新表中的记录时要小心!
要注意SQL UPDATE 语句中的 WHERE 子句!
WHERE子句指定哪些记录需要更新。如果省略WHERE子句,所有记录都将更新!
替换
根据已有值替换:
UPDATE table_name
SET column1=replace(column1, '查找内容', '替换成内容')
where 条件
删除
根据条件删除:
DELETE FROM tb_name
where 条件
order by
limit n
全部删除(表清空,包含自增计数器重置):TRUNCATE tb_name
彻底删除表 drop table if exists 表;
delete是把目录撕了,truncate是把书的内容撕下来烧了,drop是把书烧了。
修改表列名等
alter table 表名 add 新增列 varchar(15) after 某列;
增加列在某列之后,限制长度15
alter table 增加的表格 add 增加列的名称 数据类型 位置(after level 在level 之后)
alter table 表名 change 原列名 修改列名 修改数据类型;
更换列的名称及数据类型
alter table user_info modify achievement int(11) default 0;
更改数据类型
alter table 表名 modify 修改列名称 数据类型 默认值等
索引
什么是索引?
索引是与表相关联的数据结构,它基于一个或多个列(索引键)中的值提供对表中行的快速访问。
假设您的数据库中有一个customers表,并且您想使用以下语句找出名字是以字母A开头的所有客户。
示例
SELECT cust_id, cust_name, address FROM customers
WHERE cust_name LIKE 'A%';
为了找到这样的客户,服务器必须在customers表中逐行扫描并检查名字列的内容。尽管对于只有几行的表来说,它可以正常工作,但是请想象一下,如果该表包含一百万行,那么回答查询可能需要花费多长时间。在这种情况下,您可以通过将索引应用于表来加快处理速度。
- 创建索引
您可以使用以下CREATE INDEX语句创建索引:
CREATE INDEX index_name ON table_name (column_name);
例如,要在客户表的name列上创建索引,可以使用:
示例
CREATE INDEX cust_name_idx ON customers (cust_name);
-- 普通索引
CREATE INDEX idx_duration ON examination_info(duration);
-- 唯一索引
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX uniq_idx_exam_id ON examination_info(exam_id);
-- 全文索引
CREATE FULLTEXT INDEX full_idx_tag ON examination_info(tag);
日期
求时间差
timestampdiff (interval, time_start, time_end)可计算time_start-time_end的时间差,单位以指定的interval为准,常用可选:
SECOND 秒
MINUTE 分钟(返回秒数差除以60的整数部分)
HOUR 小时(返回秒数差除以3600的整数部分)
DAY 天数(返回秒数差除以3600*24的整数部分)
MONTH 月数
YEAR 年数
例如,求开始到结束经历了几分钟,TIMESTAMPDIFF(minute, start_time, submit_time)
给定日期,求当前月有几天
day(last_day(给定的日期))
比如给定了2021-08-02我就知道8月最后一天是31号,那么就是31天
日期转换格式
仅取年月:date_format(submit_time, ‘%Y%m’)
汇总合计
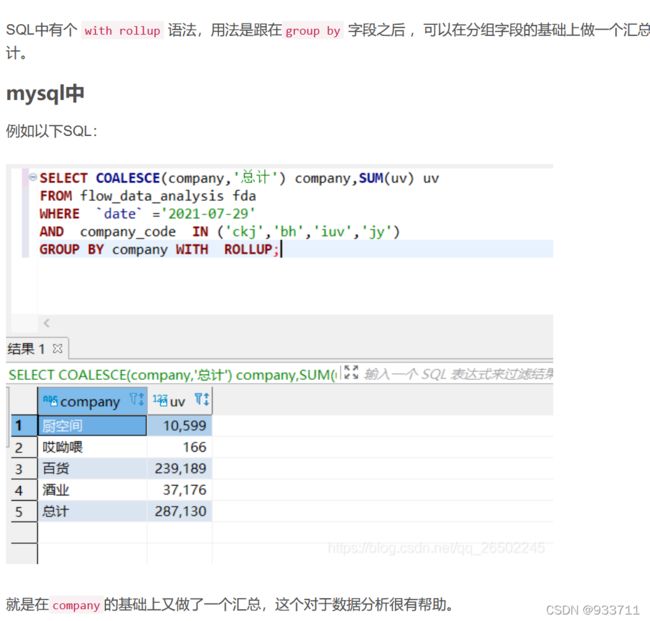 比如说,你已经通过group by计算出1,2,3月的数据,你想最后一行输出第一季度合计数量,命名为“Q1合计”,用coalesce
比如说,你已经通过group by计算出1,2,3月的数据,你想最后一行输出第一季度合计数量,命名为“Q1合计”,用coalesce
select
coalesce(month,'Q1合计') ,
count(deal) #计算每一月数据
from table
group by month
窗口函数
通俗易懂的学会SQL窗口函数:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/92654574
<窗口函数> over (partition by <用于分组的列名>
order by <用于排序的列名> rows N preceding)
滚动前N个,即求包含自己在内共N+1个数
累加
字符串
- 查询字符串个数:
char_length - 截取字符串:
substr(xxx,begin,end),注意sql下标从1开始
如SUBSTR(‘0123456789101112’, 1, 10)返回的就是0到9共10个数字 - 拼接字符串:
concat(str1,str2) - 大小写转换:
upper(str)转为大写,lower(str)转为小写
临时表 with as
可以将需要频繁调用的sql片段加个别名,用with as声明下这是个临时表,后续直接调用这张临时表就行,这样可以减少调用次数,优化效率

