C++快速入门(上)
必须了解的C++头文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS//避免我们在编译老的用C语言的开源项目如lua源包的时候,可能因为一些老的.c文件使用了strcpy,scanf等不安全的函数,而报警告和错误,而导致无法编译通过。
#include 条件编译

以#if开头以#endif结尾就构成一个条件编译
如果这个是0表示这里面的就跳过(不编译)
输入输出
std::cout << " 标准名字空间 " << std::endl;
Endl 相当于换行符
- 也可在开头声明
using std::count;
using std::endl;
- 还可以整体引入:
using namespace std;
输入:
- cin >>
输出:
- cout <<
- Puts();
文件输出与写入
#include 引用变量、引用形参
引用变量.
- 引用变量是其他变量的别名。如同- -个人的外号或小名。
- 既然是引用, 定义引用变量时就必须指明其引用的是哪个变量。
int a =3;
int &r=a;
- 引用变量“从一而终”,一旦定义就不能再弓|用其他变量
int &er=a;
int&r=b;
- 引用变量和被弓|用的变量类型必须匹配。
double d;
int&r=d;
- 对弓|用变量的操作就是对它引|用的变量的操作。
int a =3, &r=a;
cout<<a<< '\t' < <endl;
r=5;
cout<<a<< '\t' < <endl;
函数的值形参
C函数的形参 都是值参数,形参作为函数的局部变量有自 己单独的内存块,当函数调用时,实参将值拷贝(赋值给)形参。对形参的修改不会影响实参。
#include #include void swap(int *x, int *y) {
int t = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = t;
}
#include //x和y作为引用变量
void swap(int &x, int &y) {
int t = x;
x = y;
y = t;
}
#include 函数的默认形参
函数的形参可以有默认值。
void print(char ch, int n =1);
●默认形参必须在非默认形参右边,即一律靠右
add(x=1,y, z=3); //false
add(y, x=1,z=3); //true
看两个例子:
#include #include 函数重载
●C+ +允许同意作用域里有同名的函数,只要它们的形参不同。如:
int add(int X, int y);
double add(double x, double y);
●函数名和形参列表构造了函数的签名。
●函数重载不能根据返回类型区分函数。如
int add(int X, int y);
double add(int X, int y);
#include 函数模板
- 通用算法:函数模板。也称为泛型算法
int add(int x,int y) {
return x + y;
}
double add (double x,double y ) {
return x + y;
}
- 用template关键字增加一个模板头,将数据类型变成类型模板参数。
template<typename T>
T add(Tx, Ty) {
return x + y;
}
#include 模板参数自动推断
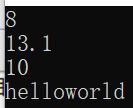
cout << add(5,3) << endl;
cout << add(5.3,7.8) << endl;
#include #include string
- string是一个用户定义类型,表示的是符串。
string s = "hello", s2("world");
- 用成员访问运算符访问string类的成员。
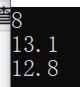
cout << s.size() << endl;
string s3 = s.substr(1,3);
cout << s3 << endl;
- 用运算符对string对象进行运算,如+、[]
#include vector
- 向量,类似于数组,但可以动态增长。
头文件< vector> - 是一个类模板,实例化产生一个类,如vector产生一个数据元素是int的vector< int>类(向量)
- 同样,可以通过vector < int>类对象去访问其成员,如成员函数。
- 同样可以用运算符进行一些运算。
#include