b站视频-尚硅谷Web前端axios从入门到源码分析-笔记
目录
- 前言
- 一、课程介绍
- 二、json-server的介绍与服务搭建
- 三、axios的介绍与页面配置
- 四、axios的基本使用
- 五、axios其他方式发送请求
- 六、axios请求响应结果的结构
- 七、axios配置对象详细说明
- 八、axios的默认配置
- 九、axios创建实例对象发送请求
- 十、axios拦截器
- 十一、axios取消请求
- 十二、axios文件结构说明
- 十三、axios的创建过程
- 十四、axios对象创建过程模拟实现
- 十五、axios发送请求过程详解
- 十六、模拟实现axios发送请求
- 十七、axios拦截器工作原理
- 十八、模拟实现axios拦截器功能
- 十九、axios取消请求工作原理
- 二十、模拟实现axios取消请求功能
- 二十一、axios源码分析总结
- 写在后面
前言
在继续学习React-ajax之前,学完了Promise,再来学习axios
看的是b站尚硅谷李强老师的视频:axios从入门到源码分析
上一篇:Promise视频笔记
axios是目前前端最热门的ajax请求库,Vue和React官方都推荐使用axios进行ajax请求
一、课程介绍
内容包括三大部分:
- axios API 怎么安装怎么用
- 源码分析
- 源码仿写
二、json-server的介绍与服务搭建
github—json-server
全局安装json-server:npm install -g json-server
创建json文件,内容是:
{
"posts": [
{ "id": 1, "title": "json-server", "author": "typicode" }
],
"comments": [
{ "id": 1, "body": "some comment", "postId": 1 }
],
"profile": { "name": "typicode" }
}
在该文件目录下运行:json-server --watch db.json
这是对数据的获取
三、axios的介绍与页面配置
github—axios
axios是基于HTTP的客户端,可以在浏览器和node.js两个环境中运行:Promise based HTTP client for the browser and node.js

安装:npm install axios
四、axios的基本使用
<div>
<h2>axios基本使用</h2>
<button> 发送GET请求 </button>
<button> 发送POST请求 </button>
<button> 发送 PUT 请求 </button>
<button> 发送 DELETE 请求 </button>
</div>
// 获取按钮
const btns=document.querySelectorAll('button');
// 第一个按钮 发送GET请求
btns[0].onclick=function(){
// 发送AJAX请求
axios({
// 请求类型
method:'GET',
// URL
url:'http://localhost:3000/posts/2',
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response);
});
}
// 第二个按钮 发送POST请求 添加一篇新的文章
btns[1].onclick=function(){
// 发送AJAX请求
axios({
// 请求类型
method:'POST',
// URL
url:'http://localhost:3000/posts',
// 设置请求体
data:{
title: "今天天气很好",
author: "王五"
}
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response);
});
}
// 第三个按钮 发送PUT请求 更新数据
btns[2].onclick=function(){
// 发送AJAX请求
axios({
// 请求类型
method:'PUT',
// URL
url:'http://localhost:3000/posts/3',
// 设置请求体
data:{
title: "今天天气很好",
author: "赵六"
}
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response);
});
}
// 第四个按钮 发送DELETE请求 删除数据
btns[3].onclick=function(){
// 发送AJAX请求
axios({
// 请求类型
method:'delete', // 大小写都可以
// URL
url:'http://localhost:3000/posts/3',
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response);
});
}
五、axios其他方式发送请求
// 获取按钮
const btns=document.querySelectorAll('button');
// 第一个按钮 发送GET请求
btns[0].onclick=function(){
// 与axios()使用方式一样
axios.request({
method:'GET',
url:'http://localhost:3000/comments'
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response);
});
}
// 第二个按钮 发送POST请求 添加一个新的评论
btns[1].onclick=function(){
axios.post('http://localhost:3000/comments',
{
"body": "我是一条评论",
"postId": 2
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response);
});
}
六、axios请求响应结果的结构
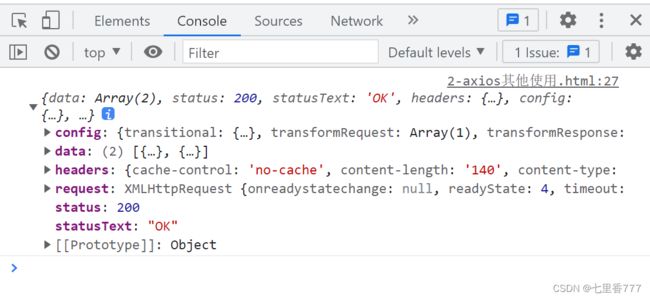
config:配置对象
data:响应体的结果
headers:响应头的信息
request:原生的AJAX请求对象
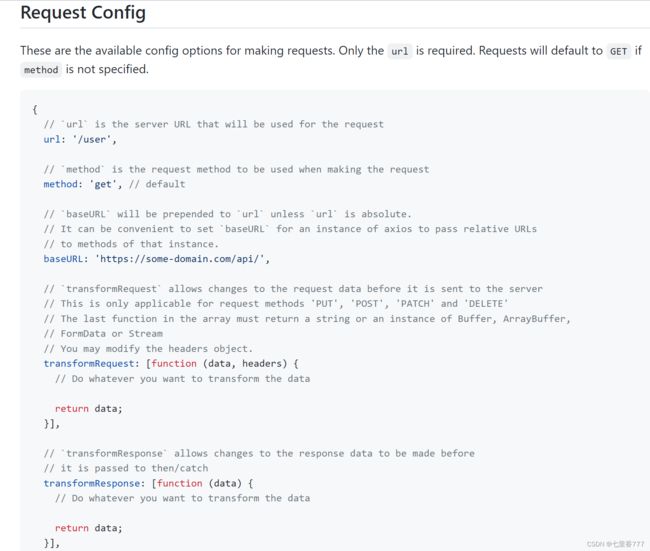
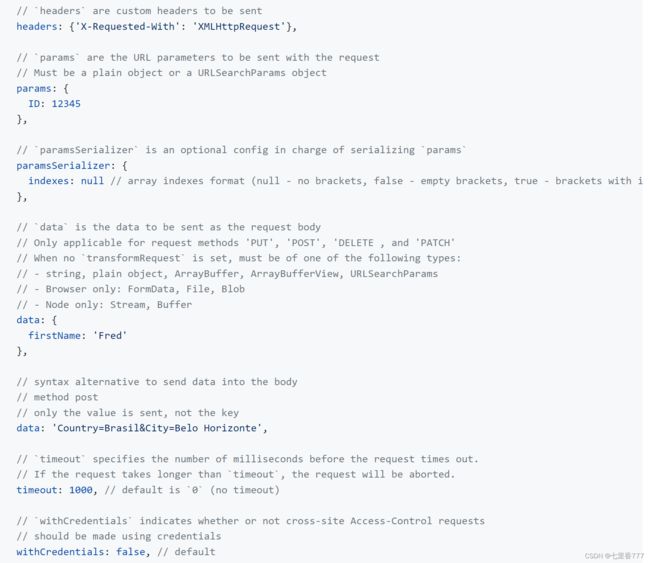
七、axios配置对象详细说明
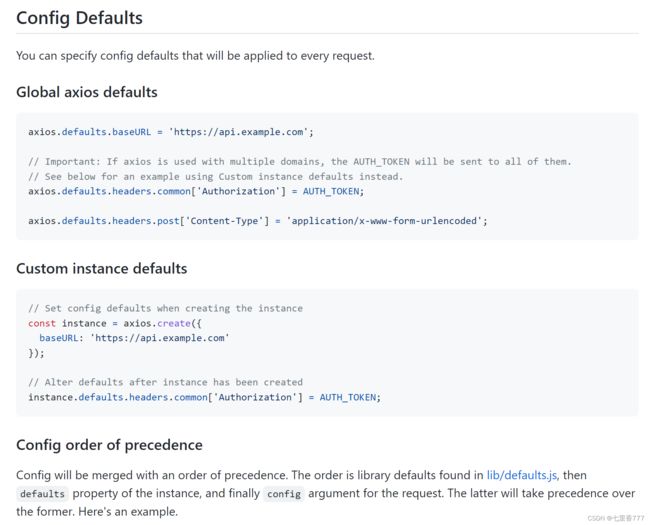
八、axios的默认配置
// 获取按钮
const btns=document.querySelectorAll('button');
//默认配置
axios.defaults.method='GET'; // 设置默认的请求类型为GET
axios.defaults.baseURL='http://localhost:3000'; // 设置基础URL
axios.defaults.params={id:100};
axios.defaults.timeout=3000; // 超时时间
btns[0].onclick=function(){
axios({
url:'/posts',
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response);
});
}
九、axios创建实例对象发送请求
//创建实例对象
const duanzi = axios.create({
baseURL:'http://api.apiopen.top',
timeout:2000
});
// 给另一个协议、域名或端口不同的服务器发请求
const another = axios.create({
baseURL:'http://b.com',
timeout:2000
});
// 这里duanzi与axios对象的功能几近是一样的
// duanzi({
// url:'getJoke',
// }).then(response=>{
// console.log(response);
// });
duanzi.get('/getJoke').then(response=>{
console.log(response);
});
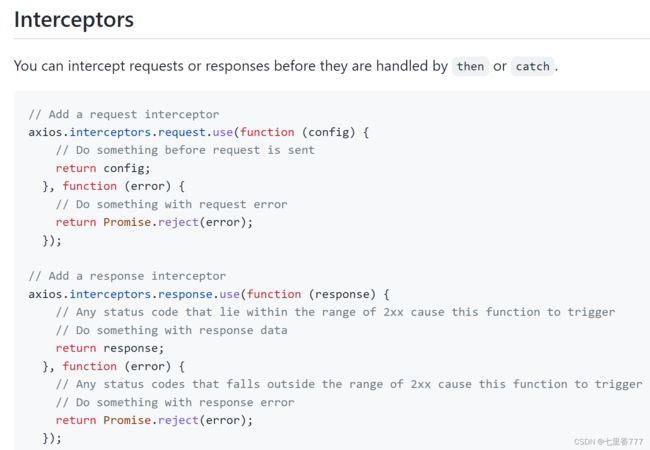
十、axios拦截器
十一、axios取消请求
// 获取按钮
const btns=document.querySelectorAll('button');
// 2. 声明全局变量
let cancel=null;
// 发送请求
btn[0].onclick=function(){
axios({
method:'GET',
url:'http://localhost:3000/posts',
// 1. 添加配置对象的属性
cancelToken:new axios.CancelToken(function(c){
// 3. 将c的值赋给cancel
cancel=c;
})
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response);
})
}
// 取消请求
btn[1].onclick=function(){
cancel();
}
上述方法,每次点击取消请求时,都没什么反应。因为服务器在本都,每次点击取消,请求都已经回来了。
解决方法:
①服务端做延时响应:json-server --watch db.json -d 2000
②在发送请求时,看上个请求是否还在继续发送,若还在继续,就把它取消
// 发送请求
btn[0].onclick=function(){
// 检测上一次的请求是否已经完成
if(cancel!==null){
// 取消上一次的请求
cancel();
}
axios({
method:'GET',
url:'http://localhost:3000/posts',
// 1. 添加配置对象的属性
cancelToken:new axios.CancelToken(function(c){
// 3. 将c的值赋给cancel
cancel=c;
})
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response);
// 将cancel值复原
cancel=null;
})
}
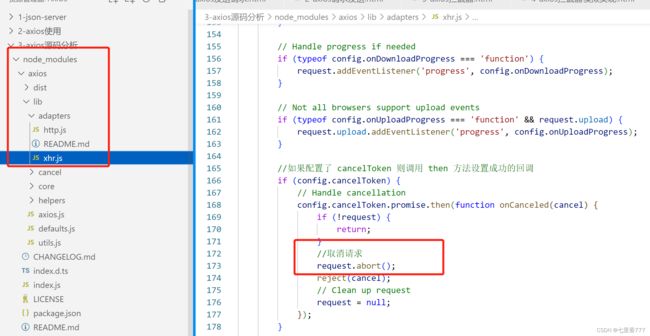
十二、axios文件结构说明
十三、axios的创建过程
分析源码:
axios既可以当函数使用,又可以调用方法
axios();
axios.get();
axios,post();
十四、axios对象创建过程模拟实现
//构造函数
function Axios(config){
//初始化
this.defaults = config;//为了创建 default 默认属性
this.intercepters = {
request: {},
response: {}
}
}
//原型添加相关的方法
Axios.prototype.request = function(config){
console.log('发送 AJAX 请求 请求的类型为 '+ config.method);
}
Axios.prototype.get = function(config){
return this.request({method: 'GET'});
}
Axios.prototype.post = function(config){
return this.request({method: 'POST'});
}
//声明函数
function createInstance(config){
//实例化一个对象
let context = new Axios(config);// context.get() context.post() 但是不能当做函数使用 context() X
//创建请求函数
let instance = Axios.prototype.request.bind(context);// instance 是一个函数 并且可以 instance({}) 此时 instance 不能 instance.get X
//将 Axios.prototype 对象中的方法添加到instance函数对象中
Object.keys(Axios.prototype).forEach(key => {
instance[key] = Axios.prototype[key].bind(context);// this.default this.interceptors
});
//为 instance 函数对象添加属性 default 与 interceptors
Object.keys(context).forEach(key => {
instance[key] = context[key];
});
return instance;
}
let axios = createInstance();
//发送请求
// axios({method:'POST'});
axios.get({});
axios.post({});
十五、axios发送请求过程详解
request–>dispatch–>xhr
十六、模拟实现axios发送请求
//1. 声明构造函数
function Axios(config){
this.config = config;
}
Axios.prototype.request = function(config){
//发送请求
//创建一个 promise 对象
let promise = Promise.resolve(config);
//声明一个数组
let chains = [dispatchRequest, undefined];// undefined 占位
//调用 then 方法指定回调
let result = promise.then(chains[0], chains[1]);
//返回 promise 的结果
return result;
}
//2. dispatchRequest 函数
function dispatchRequest(config){
//调用适配器发送请求
return xhrAdapter(config).then(response => {
//响应的结果进行转换处理
//....
return response;
}, error => {
throw error;
});
}
//3. adapter 适配器
function xhrAdapter(config){
console.log('xhrAdapter 函数执行');
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//发送 AJAX 请求
let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
//初始化
xhr.open(config.method, config.url);
//发送
xhr.send();
//绑定事件
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
//判断成功的条件
if(xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300){
//成功的状态
resolve({
//配置对象
config: config,
//响应体
data: xhr.response,
//响应头
headers: xhr.getAllResponseHeaders(), //字符串 parseHeaders
// xhr 请求对象
request: xhr,
//响应状态码
status: xhr.status,
//响应状态字符串
statusText: xhr.statusText
});
}else{
//失败的状态
reject(new Error('请求失败 失败的状态码为' + xhr.status));
}
}
}
});
}
//4. 创建 axios 函数
let axios = Axios.prototype.request.bind(null);
axios({
method:'GET',
url:'http://localhost:3000/posts'
}).then(response => {
console.log(response);
});
十七、axios拦截器工作原理
// 设置请求拦截器
// config:配置对象,在请求拦截器中我们可以对config进行调整、修改
axios.interceptors.request.use(function (config) {
console.log('请求拦截器 成功 - 1号')
// 修改config中的参数
config.params={a:100}
config.timeout=2000
return config;
//throw '参数出了问题'
}, function (error) {
console.log('请求拦截器 失败 - 1号')
return Promise.reject(error);
});
axios.interceptors.request.use(function (config) {
console.log('请求拦截器 成功 - 2号')
// return config;
throw '参数出了问题'
}, function (error) {
console.log('请求拦截器 失败 - 2号')
return Promise.reject(error);
});
// 设置响应拦截器
// response 我们可以对响应结果做一些处理
axios.interceptors.response.use(function (response) {
console.log('响应拦截器 成功 - 1号')
// 我们可以对响应结果做一些处理
return response.data;
// return response;
}, function (error) {
console.log('响应拦截器 失败 - 1号')
});
axios.interceptors.response.use(function (response) {
console.log('响应拦截器 成功 - 2号')
return response;
}, function (error) {
console.log('响应拦截器 失败 - 2号')
});
// 发送请求
axios({
method:'GET',
url:'http://localhost:3000/posts'
}).then(response=>{
console.log('自定义回调处理成功的结果');
// console.log(response);
}).catch(response=>{
console.log('自定义失败回调');
// console.log(response);
});
运行结果:

node_modules/axios/lib/core/Axios.js文件中:

十八、模拟实现axios拦截器功能
//构造函数
function Axios(config){
this.config = config;
this.interceptors = {
request: new InterceptorManager(),
response: new InterceptorManager(),
}
}
//发送请求 难点与重点
Axios.prototype.request = function(config){
//创建一个 promise 对象
let promise = Promise.resolve(config);
//创建一个数组
const chains = [dispatchRequest, undefined];
//处理拦截器
//请求拦截器 将请求拦截器的回调 压入到 chains 的前面 request.handles = []
// console.log( this.interceptors.request.handlers);
this.interceptors.request.handlers.forEach(item => {
chains.unshift(item.fulfilled, item.rejected);
});
//响应拦截器
this.interceptors.response.handlers.forEach(item => {
chains.push(item.fulfilled, item.rejected);
});
// console.log(chains);
//遍历
while(chains.length > 0){
promise = promise.then(chains.shift(), chains.shift());
}
return promise;
}
//发送请求
function dispatchRequest(config){
//返回一个promise 队形
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve({
status: 200,
statusText: 'OK'
});
});
}
//创建实例
let context = new Axios({});
//创建axios函数
let axios = Axios.prototype.request.bind(context);
//将 context 属性 config interceptors 添加至 axios 函数对象身上
Object.keys(context).forEach(key => {
axios[key] = context[key];
});
// console.dir(axios);
//拦截器管理器构造函数
function InterceptorManager(){
this.handlers = [];
}
InterceptorManager.prototype.use = function(fulfilled, rejected){
this.handlers.push({
fulfilled,
rejected
})
}
//以下为功能测试代码
// 设置请求拦截器 config 配置对象
axios.interceptors.request.use(function one(config) {
console.log('请求拦截器 成功 - 1号');
return config;
}, function one(error) {
console.log('请求拦截器 失败 - 1号');
return Promise.reject(error);
});
axios.interceptors.request.use(function two(config) {
console.log('请求拦截器 成功 - 2号');
return config;
}, function two(error) {
console.log('请求拦截器 失败 - 2号');
return Promise.reject(error);
});
// 设置响应拦截器
axios.interceptors.response.use(function (response) {
console.log('响应拦截器 成功 1号');
return response;
}, function (error) {
console.log('响应拦截器 失败 1号')
return Promise.reject(error);
});
axios.interceptors.response.use(function (response) {
console.log('响应拦截器 成功 2号')
return response;
}, function (error) {
console.log('响应拦截器 失败 2号')
return Promise.reject(error);
});
// console.dir(axios);
//发送请求
axios({
method: 'GET',
url: 'http://localhost:3000/posts'
}).then(response => {
console.log(response);
});
十九、axios取消请求工作原理
二十、模拟实现axios取消请求功能
//构造函数
function Axios(config){
this.config = config;
}
//原型 request 方法
Axios.prototype.request = function(config){
return dispatchRequest(config);
}
//dispatchRequest 函数
function dispatchRequest(config){
return xhrAdapter(config);
}
//xhrAdapter
function xhrAdapter(config){
//发送 AJAX 请求
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//实例化对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
//初始化
xhr.open(config.method, config.url);
//发送
xhr.send();
//处理结果
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
//判断结果
if(xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300){
//设置为成功的状态
resolve({
status: xhr.status,
statusText: xhr.statusText
});
}else{
reject(new Error('请求失败'));
}
}
}
//关于取消请求的处理
if(config.cancelToken){
//对 cancelToken 对象身上的 promise 对象指定成功的回调
config.cancelToken.promise.then(value => {
xhr.abort();
//将整体结果设置为失败
reject(new Error('请求已经被取消'))
});
}
})
}
//创建 axios 函数
const context = new Axios({});
const axios = Axios.prototype.request.bind(context);
// console.dir(axios);
//CancelToken 构造函数
function CancelToken(executor){
//声明一个变量
var resolvePromise;
//为实例对象添加属性
this.promise = new Promise((resolve) => {
//将 resolve 赋值给 resolvePromise
resolvePromise = resolve
});
//调用 executor 函数
executor(function(){
//执行 resolvePromise 函数
resolvePromise();
});
}
//获取按钮 以上为模拟实现的代码
const btns = document.querySelectorAll('button');
//2.声明全局变量
let cancel = null;
//发送请求
btns[0].onclick = function(){
//检测上一次的请求是否已经完成
if(cancel !== null){
//取消上一次的请求
cancel();
}
//创建 cancelToken 的值
let cancelToken = new CancelToken(function(c){
cancel = c;
});
axios({
method: 'GET',
url: 'http://localhost:3000/posts',
//1. 添加配置对象的属性
cancelToken: cancelToken
}).then(response => {
console.log(response);
//将 cancel 的值初始化
cancel = null;
})
}
//绑定第二个事件取消请求
btns[1].onclick = function(){
cancel();
}
二十一、axios源码分析总结
axios与Axios的关系:
- 从语法上来说,axios不是Axios的实例
- 从功能上来说,axios是Axios的实例
- axios是Axios.prototype.request函数bind()返回的函数
- axios作为对象有Axios原型对象上的所有方法,有Axios对象上所有属性
instance与axios的区别:
- 相同点:都既可以当函数用,又可以当对象去用,而且都有默认配置和拦截器的属性
- 不同点:默认配置很可能不一样,instance没有axios后续添加的一些方法
axios运行的整体流程:
axios的请求/响应拦截器是什么:
axios 的请求/响应数据转换器是什么:
response 的整体结构:
error 的整体结构:
如何取消未完成的请求:
写在后面
看完了这21个视频,完结撒花,强哥还是很强的哈。关于源码分析,也就是12~21,没认真看,如果以后有需要再认真学习一下吧。学完了Promise与axios,继续去学习React了