Map和Set
Map和Set是集合中的两个接口,Set实现了Collection接口,而Map没有实现。
Map下面又有很多子类,我们主要研究HashMap和TreeMap;Set同样有很多子类,主要研究HashSet和TreeSet。
在理解掌握它们之前,我们要先研究二叉搜索树(又叫二叉排序树),因为TreeMap、TreeSet底层是红黑树,红黑树是一种特殊的二叉搜索树,HashSet、HashMap底层是哈希表,哈希表中也涉及到了红黑树。
一:二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树又叫二叉排序树,它可以是空树,具有以下性质:
(1)若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
(2)若它的右子树不为空,则它右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
(3)它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
下面实现二叉搜索树的增删改查
1.添加操作(建立二叉搜索树)
例如将数组{10,4,29,35,18,27,5,13}建立二叉搜索树
思路见下图:
public class BinarysearchTree {
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int val) {
this.value = val;
}
}
public Node root = null;
//建立二叉搜索树
public boolean buildTree(int value){
Node newnode = new Node(value);
Node cur = root;
Node parent = root;
if(root==null){
root = newnode;
return true;
}
while(cur!=null){
if(newnode.value< cur.value) {
cur = cur.left;
if (cur == null) {
parent.left = newnode;
return true;
}
parent = cur;
}else if (newnode.value> cur.value){
cur = cur.right;
if(cur==null){
parent.right = newnode;
return true;
}
parent = cur;
}else{
break;
}
}
return false;
}
//中序遍历二叉搜索树
public void midsort(Node root){
if(root==null)return;
midsort(root.left);
System.out.print(root.value+" ");
midsort(root.right);
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinarysearchTree tree = new BinarysearchTree();
int[] array = new int[]{10,4,4,29,35,18,27,5,13};
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
tree.buildTree(array[i]);
}
tree.midsort(tree.root);
}
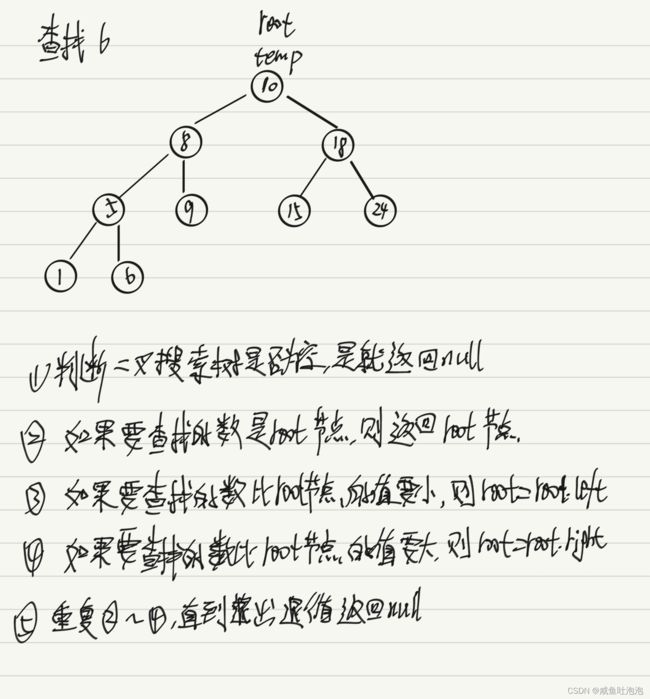
}2.查找操作
思路见下图:
public Node findnode(Node root,int key){
if(root==null)return null;
Node temp = root;
while(temp!=null){
if(temp.value==key)return temp;
else if(key3.删除操作
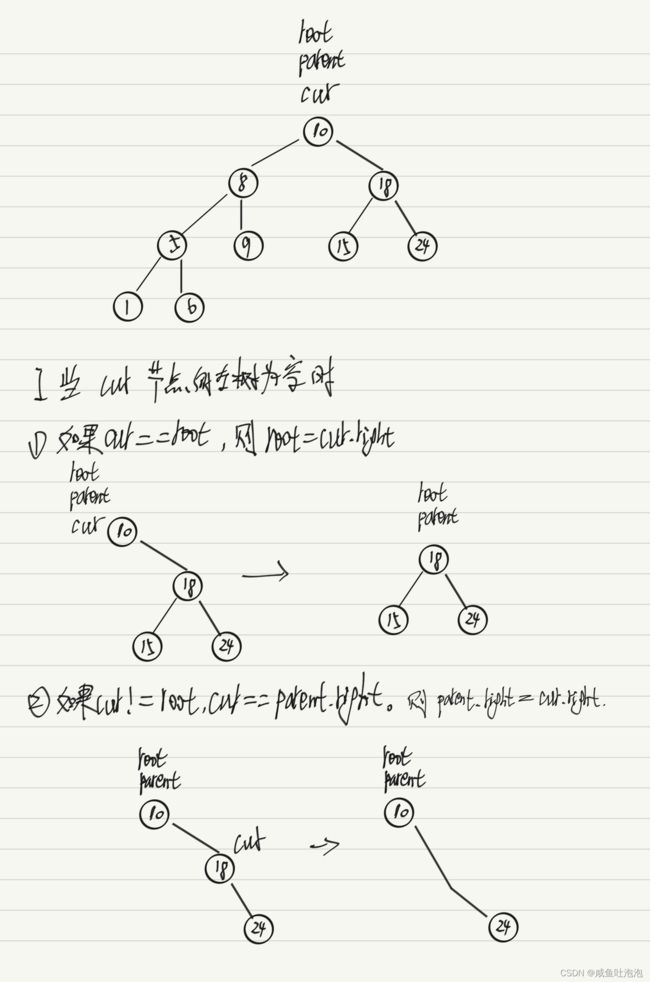
思路见下图
public boolean deletNode(int key){
if(root==null)return false;
Node cur = root;
Node parent = root;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.value==key){//说明找到了要删除的节点,则跳出循环,对cur进行处理
break;
}else if(keypublic class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinarysearchTree tree = new BinarysearchTree();
int[] array = new int[]{10,4,29,35,18,27,5,13};
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
tree.buildTree(array[i]);
}
tree.midsort(tree.root);
System.out.println();
tree.deletNode(29);
tree.midsort(tree.root);
}
}4.修改操作
思路:找到要修改的节点,将节点的值修改为新值
//查找二叉搜索树上的某个节点
public Node findnode(Node root,int key){
if(root==null)return null;
Node temp = root;
while(temp!=null){
if(temp.value==key)return temp;
else if(key注意:修改不要改变二叉搜索树的结构
从上面可以看到,二叉搜索树的增删改都要涉及到查找功能,所以二叉搜索树的效率由查找效率表示,查找二叉搜索树的效率最好的时候为logN,也就是二叉搜索树为一颗完全二叉树的情况;效率最差的时候为N,也就是二叉搜索树是但分支树的时候。
二:哈希表
TreeSet、TreeMap底层是一个红黑树(红黑树是一颗近似平衡的二叉搜索树,即在二叉搜索树的基础之上+颜色以及红黑树的性质验证);HashSet、HashMap底层是一个哈希表
1.哈希表的概念
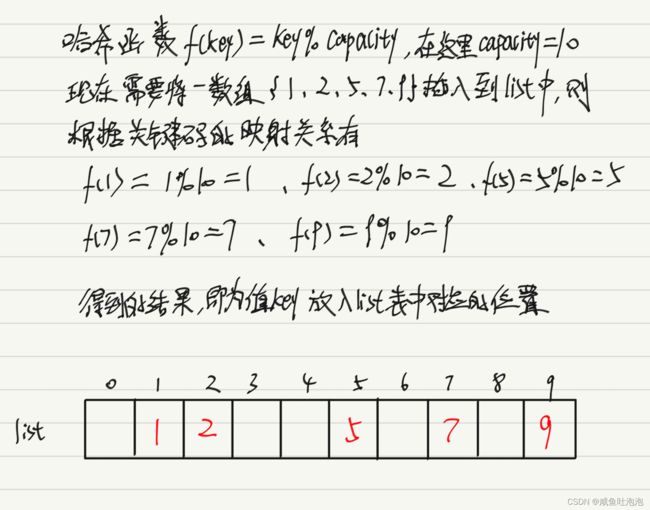
哈希表又叫做散列表,是根据关键码值(key,value)而直接进行访问的数据结构,它通过把关键码值映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度。这个映射函数叫做散列函数,存放记录的数组叫做散列表。给定表list,存在函数f(key),对任意给定的关键字值key,代入函数后若能得到包含该关键字的记录在表中的地址,则称表list为哈希(Hash)表,函数f(key)为哈希(Hash) 函数。
如下图所示:
上面是将元素插入到哈希表中,从哈希表中取数据也是同样的方法,列如要取出数据7,则通过哈希函数计算得到哈希表中下标为7的位置里面的数据也就是我们要取出的数据。
利用哈希表搜索和插入数据不必进行多次关键码的比较,搜索和查找的时间复杂度为O(1)。
2.哈希冲突
从上面数据的插入,会存在这样一个问题。现在我想将数据(key)17也插入到哈希表中,如果通过哈希函数计算,那么就需要将17插入到哈希表中下标为7的位置,但是这个位置已经有数据了。那这样就会造成数据插入冲突。这就是哈希冲突 ,即对于两个数据元素的关键字k1和k2,k1!=k2,但是它们的f(k1)==f(k2),不同关键字通过相同哈希函数计算出的哈希地址相同。
3.避免冲突
从上面的列子可以看出,为了解决17插入的问题,我们可以将数组的长度增长。但是我们知道哈希表底层数组的容量往往是小于实际要存储的关键字数量的,所以不可能遇到问题就对数组扩容。所以冲突的发生是必然的,我们能做的就是尽量降低冲突发生的概率。 降低冲突率主要从以下两个方面出发:
(1)设计一个良好的哈希函数
(2)调节负载因子
常见的哈希函数有:
直接定制法 :取关键字的某个线性函数为散列地址:Hash(key) = A*key+B。
除留余数法:设散列表中允许的地址为m,取一个不大于m,但是接近或者等于m的质数p作为除数,按照哈希函数:Hash(key) = key%p(p<=m),将关键码转换成哈希地址。
负载因子![]() = 填入表中的元素个数/哈希表的长度
= 填入表中的元素个数/哈希表的长度
由于哈希表的长度往往是个定值,所以负载因子与表中的元素个数成正比。要填入的数据越多,负载因子也就越大,就越容易发生冲突。负载因子和冲突率的关系如下图所示:
由于要填入的数据是不确定的,所以为了降低负载因子,我们只能调整哈希表数组的大小。
4.解决哈希冲突
解决哈希冲突有两种方法:闭散列、开散列
(1)闭散列:当发生哈希冲突时,如果哈希表未被装满,说明在哈希表中必然还有空位置,那么可以把key存放到冲突位置中的"下一个"空位置去。
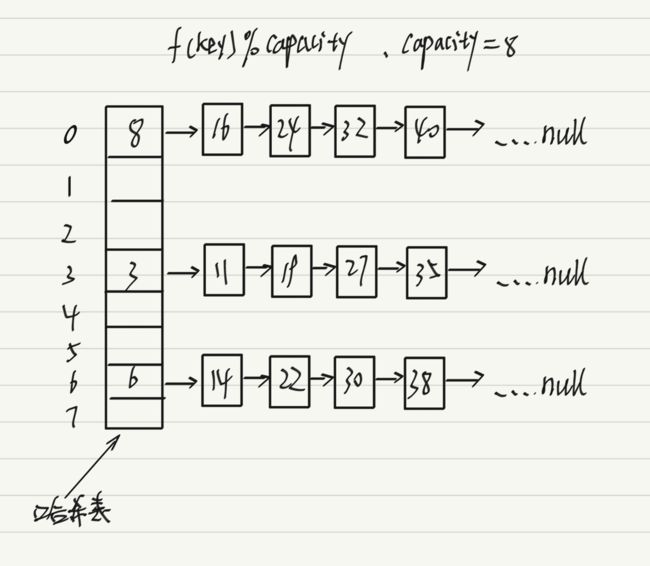
(2)开散列:开散列/哈希桶又叫做链地址法(开链法),首先对关键码集合用散列函数计算散列地址,具有相同地址的关键码归于同一子集合,每个子集合称为一个桶,各个桶中的元素通过一个单链表链接起来,各链表的头结点存储在哈希表中。
当数组的长度>=64并且链表长度>=8时,链表就会变成一颗红黑树
三:模拟实现哈希表的一小部分
哈希表底层是由数组+链表组成的
public class MyHashMap {
public static class Node{
private int key;
private int value;
private Node next;
public Node(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
public Node[] array;//建立一个数组,数组里面存放的类型是Node类型
public int usedSize;//用来记录数组里面的元素个数
public static final double DEFAULT_FACTOR = 0.75;//设定负载因子为0.75
public MyHashMap() {//初始化数组
this.array = new Node[8];
}
public void put(int key,int value){//添加元素
Node node = new Node(key,value);
//根据key找到相应数组中的下标
int index = key% array.length;
Node cur = array[index];
/**
* 遍历cur
* 1.因为Map里面不能放入key相同的数据,如果key相同,那么新插入的key要覆盖掉原来的key,然后返回
* 2.如果1不满足,那么就找到链表的头结点,进行头插法
*/
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.key==key){
cur.value = value;
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
node.next = array[index];
array[index] = node;
usedSize++;
//每插入一个元素就要判断负载因子是否大于默认值,大了,就要扩容
if (loadFactor()>=DEFAULT_FACTOR){
grow();
}
}
/**
* 对数组进行扩容以后,因为array.length变了,所以各个节点的位置也要发生改变,要重新哈希一遍
*/
public void grow(){
Node[] newArray = new Node[2* array.length];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {//遍历原来的数组,将上面的节点全部重新插入到新数组中
Node cur = array[i];//获取原数组中的头结点
while(cur!=null){//原数组中头结点不为空,就说明该链表有数据,那么就要操作这个链表
Node curNext = cur.next;
int index = cur.key% newArray.length;
cur.next = newArray[index];
newArray[index] = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
}
array = newArray;
}
public int get(int key){//根据key,返回对应的value
int index = key% array.length;
Node cur = array[index];
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.key==key){
return cur.value;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return -99;
}
public double loadFactor(){
return usedSize*1.0/ array.length;
}
}public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyHashMap map = new MyHashMap();
map.put(1,2022);
map.put(3,2022);
map.put(9,2022);
System.out.println(map.get(1));
System.out.println();
}
}public class MyHashMap2 {
private static class Node{
public K key;
public V value;
public Node next;
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
private Node[] array = (Node[])new Node[8];
private int usedSize;
private static final double DEFAULT_FACTOR = 0.75;
public void put(K key,V value){
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = hash% array.length;
Node node = new Node<>(key, value);
Node cur = array[index];
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.key.equals(key)){
cur.value = value;
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
node.next = array[index];
array[index] = node;
usedSize++;
if(loadFactor()>=DEFAULT_FACTOR){
grow();
}
}
public void grow(){
Node[] newArray = new Node[2* array.length];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
Node cur = array[i];
while(cur!=null){
Node curNext = cur.next;
int hash = cur.key.hashCode();
int index = hash% newArray.length;
cur.next = newArray[index];
newArray[index] = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
}
array = newArray;
}
public V get(K key){
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = hash% array.length;
Node cur = array[index];
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.key.equals(key)){
return cur.value;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
public double loadFactor(){
return usedSize*1.0/ array.length;
}
} 从上面可以看出hashcode在hashMap中的作用主要是为了在哈希表中定位,equals在hashcode中的作用主要是用于比较。如果要使用我们自己定义的类作为HashMap的key或者HashSet的值,必须重写hashcode和equals方法。
例如:
class Cat{
public String name;
public Integer age;
public Cat(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(this==obj)return true;
if(!(obj instanceof Cat)||obj==null)return false;
Cat cat = (Cat)obj;
return this.age==cat.age&&this.name.equals(((Cat) obj).name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return super.hashCode();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat tom = new Cat("Tom", 3);
Cat stive = new Cat("Stive", 3);
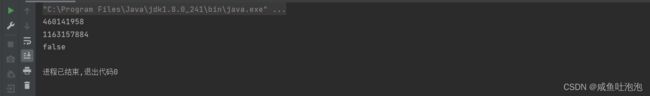
System.out.println(tom.hashCode());
System.out.println(stive.hashCode());
System.out.println(tom.equals(stive));
}
}
四:Map
Map底层存储的是key-value键值对,而且key一定是唯一的,不能重复。
1.Map的常用方法
get(Object key) 得到key对应的value值
getOrDefault(Object key,V defaultValue) 得到key对应的value,key不存在时,返回默认值
put(K key,V value) 添加key及对应的value值
remove(Object key) 删除key对应的映射关系
例如:
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("西华大学",5);
System.out.println(map.get("西华大学"));//结果为5
System.out.println(map.remove("西华大学"));//结果为5
System.out.println(map.get("西华大学"));//结果为null,因为该键值对的映射关系已经没了
}
}
remove(Object key,Object value) 删除map集合中指定的键值对(要求K、V都必须正确)
SetkeySet() 将所有的key都存放在Set集合中
Collectionvalues() 将所有的value都放在一个集合中
Map.Entry是Map内部实现的用来存放键值对映射关系的内部类,该内部类中主要提供了的获取,value的设置以及key的比较方式
方法 解释
getKey() 返回entry中的key
getValue() 返回entry中的value
setValue(V value) 将键值对中的value替换为指定value
Set>entrySet() 返回所有的key-value映射关系
例如:
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("西华大学",5);
map.put("成都理工大学",4);
map.put("西南交通大学",3);
map.put("四川大学",2);
map.put("电子科技大学",1);//添加key及对应的value值
Set> set = map.entrySet();
System.out.println(set);
for (Map.Entry entry:
set) {
System.out.println("key:"+entry.getKey()+"\t"+"value:"+entry.getValue());
}
}
}
结果:
//[四川大学=2, 成都理工大学=4, 电子科技大学=1, 西华大学=5, 西南交通大学=3]
//key:四川大学 value:2
//key:成都理工大学 value:4
//key:电子科技大学 value:1
//key:西华大学 value:5
//key:西南交通大学 value:3
boolean containsKey(Object key) 判断是否包含key
boolean containsValue(Object value) 判断是否包含value
2.Map的注意事项
(1)Map是一个接口,不能直接实例化对象,如果要实例化对象只能实例化其实现类TreeMap或者HashMap
(2)Map中存放键值对的key是唯一的,value是可以重复的
(3)Map中value可以全部分离出来,存储到Collection的任何一个子集合中
(4)Map中的key可以全部分离出来,存储到Set中来进行访问
(5)Map中键值对的key不能直接修改,value可以修改,如果要修改key,只能现将key删除掉,然后再来进行重新插入
五:Set
Set底层是一个Map实现的,因为Map中key是唯一的,所以Set里面的元素不能重复。
1.Set的常用方法
add(E e) 添加元素,重复元素不会被添加成功
clear() 清空集合
contains(Object o) 判断集合是否包含O
Iterator iterator 返回迭代器
remove(Object o) 删除集合中的o
size() 返回set中元素的个数
isEmpty() 检测set是否为空
toArray() 将set中的元素转换成数组返回
containsAll(Collection c) 判断集合是否包含集合c中的全部元素
addAll(Collection c) 将集合c中的元素添加到set中 2.Set的注意事项
(1)Set是继承自Collection的一个接口类
(2)Set中只存储了key,并且要求key一定要唯一
(3)Set底层是使用Map来实现的,其使用key与Object的一个默认对象作为键值对插入到Map中
(4)Set最大的功能就是对集合中的元素进行去重
(5)Set中不能插入null的key
六:TreeSet与HashSet的区别,TreeMap与HashMap的区别
TreeMap比HashMap多了一个排序功能,同样TreeSet比HashSet多了排序功能,因为TreeMap、TreeSet分别实现了sortedMap接口和sortedSet接口。
1.TreeMap与HashMap的区别
Map底层结构 TreeMap HashMap
底层结构 红黑树 哈希桶
插入/删除/查找时间复杂度 O(logN) O(1)
是否有序 关于key有序 无序
线程是否安全 不安全 不安全
插入/删除/查找的区别 需要进行元素比较 通过哈希函数计算哈希地址
比较与重写 key必须能够比较,否者会抛出类型转换异常 自定义类型需要重写equals和hashCode方法
应用场景 需要key有序场景下 key是否有序不关心,只需要更高的时间性能 2.TreeSet与HashSet的区别
Set底层结构 TreeSet HashSet
底层结构 红黑树 哈希桶
插入/删除/查找时间复杂度 O(logN) O(1)
是否有序 关于key有序 不一定有序
线程是否安全 不安全 不安全
插入/删除/查找的区别 按照红黑树的特性来进行插入和删除 1.先计算key哈希地址2.然后进行直接插入和删除
比较与重写 key必须能够比较,否者会抛出类型转换异常 自定义类型需要重写equals和hashCode方法
应用场景 需要key有序场景下 key是否有序不关心,只需要更高的时间性能 七:应用Map和Set练习
力扣
解法一:利用异或的性质
相同的数异或得到0,不同的数异或得到异或得到1,0异或上任何数都等于这个数本身
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int temp = 0;
for(int i = 0;i解法二:利用Set来做
创建一个Set集合,遍历数组,将数组里面的数字添加进集合中,判断添加的数据在set中是否存在,存在,则删除集合中相应的数据,不存在则添加数据。将set集合转化为数组,因为只有一个只出现一次的数,所以只需要返回数组0下标的数即可。
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
Set set = new HashSet();
for(int i = 0;i 138. 复制带随机指针的链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
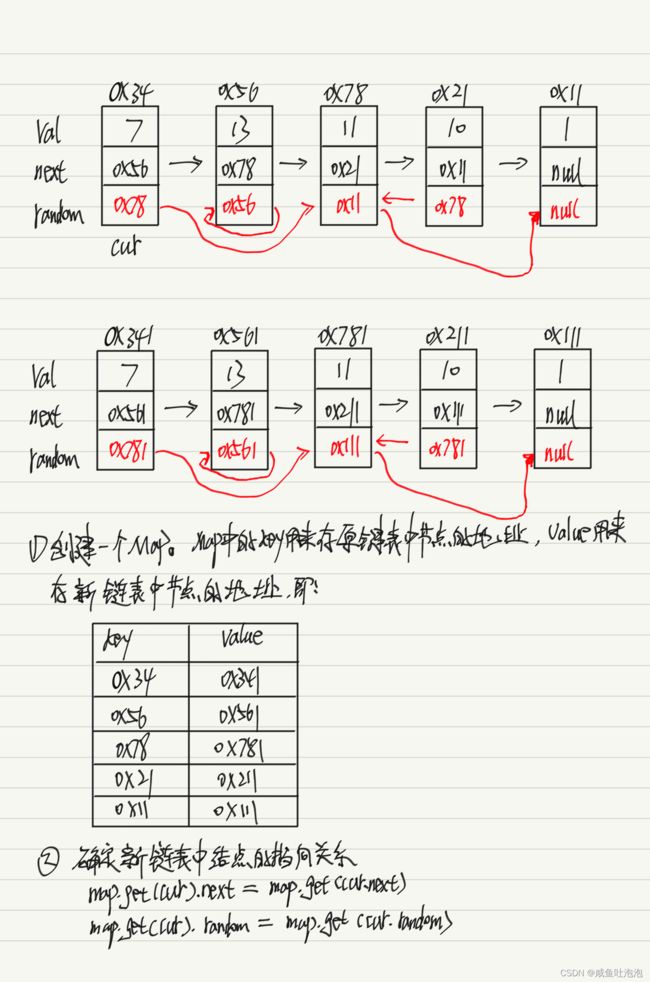
思路:利用Map的性质解
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head==null)return head;
Map map = new HashMap();
Node cur = head;
while(cur!=null){
Node node = new Node(cur.val);
map.put(cur,node);
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
while(cur!=null){
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
} 771. 宝石与石头 - 力扣(LeetCode)
思路:创建一个Set数组,将宝石中的字符加入集合,然后遍历石头字符串,当石头字符出现在集合中,count就加一,最终返回count
class Solution {
public int numJewelsInStones(String jewels, String stones) {
Set set = new HashSet<>();
for(int i = 0;i 旧键盘 (20)__牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
思路:
1.将str1、str2转化为大写字符串,创建两个集合Set1、Set2
2.将str2中的字符串加入set2中,遍历str1,将没有出现在set2中的字符且set1中也没有的字符打印输出
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void checkBad(String str1,String str2){
Set set1 = new HashSet<>();
Set set2 = new HashSet<>();
str1 = str1.toUpperCase();
str2 = str2.toUpperCase();
for(int i = 0;i 692. 前K个高频单词 - 力扣(LeetCode)
思路如下:
class Solution {
public List topKFrequent(String[] words, int k) {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
if(map.containsKey(words[i])){
map.put(words[i],map.get(words[i])+1);
}else{
map.put(words[i],1);
}
}
PriorityQueue> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(k, new Comparator>() {
@Override
public int compare(Map.Entry o1, Map.Entry o2) {
if(o1.getValue().compareTo(o2.getValue())==0){//如果有两个单词出现的次数一样,那么就按照字典顺序排序
return o2.getKey().compareTo(o1.getKey());
}
return o1.getValue().compareTo(o2.getValue());
}
});
for (Map.Entry entry:
map.entrySet()) {
if(queue.size() top = queue.peek();
Integer val = top.getValue();
if(val< entry.getValue()){//如果堆顶元素的value比当前元素的value小,就进行向上调整
queue.poll();
queue.offer(entry);
}else if(val == entry.getValue()){//如果堆顶元素的value和当前元素的value相等,就按照字典顺序比较
String key = top.getKey();
if(key.compareTo(entry.getKey())>0){
queue.poll();
queue.offer(entry);
}
}
}
}
List list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
list.add(queue.poll().getKey());
}
Collections.reverse(list);
return list;
}
}