SpringBoot--@Async注解使用 及线程池简单配置
文章目录
- 环境配置
- 相关依赖
- 具体使用
- demo
环境配置
IDEA:IntelliJ IDEA 2020.1 (Community Edition)
SpringBoot:SpringBoot2.3.2
相关依赖
spring-context-5.2.8.RELEASE.jar -->
org.springframework.boot:spring-boot:2.3.2.RELEASE -->
org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter:2.3.2.RELEASE
只需引入任何一个起步依赖
针对Web应用,可以引入spring-boot-starter-web,具体如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
具体使用
1、@EnableAsync注解添加
启动类(或配置类)加上 @EnableAsync注解,主要是为了扫描范围包下的所有 @Async注解
2、@Async注解添加
执行异步操作的处理类 方法或类(建议加在方法上)加上 @Async注解,对具体的方法开启异步处理
3、线程池配置
Spring会扫描当前应用上下文中是否有下述关联的线程池Bean对象
{@link org.springframework.core.task.TaskExecutor}
{@link java.util.concurrent.Executor}
若都不存在,则默认采用SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor进行异步处理
在日常使用中,可在配置文件中自定义TaskExecutionProperties相关配置进行定制化使用:
spring.task.execution.threadNamePrefix=lj-customize-pool-task
spring.task.execution.pool.core-size=2
spring.task.execution.pool.max-size=10
spring.task.execution.pool.queue-capacity=10
spring.task.execution.pool.keep-alive=10s
demo
主要涉及三个类和一个配置文件:
1、SpringBoot启动类(DemoApplication.java)
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
@EnableAsync
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.example.demo"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
2、对外接口类(AsyncTestController.java)
package com.example.demo.interfaces.controller;
import com.example.demo.service.AsyncOperationService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.util.StopWatch;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class AsyncTestController {
@Autowired
private AsyncOperationService asyncService;
@GetMapping("/task")
public String doTask() {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch("异步处理测试");
stopWatch.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 21; i++) {
log.info("当前为第【{}】次循环", i + 1);
// 调用异步方法
asyncService.asyncEvent();
}
stopWatch.stop();
log.info("异步处理完成,共花费【{}】ms", stopWatch.getTotalTimeMillis());
return "done";
}
}
3、异步处理类(AsyncOperationService.java)
package com.example.demo.service;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Slf4j
@Service
public class AsyncOperationService {
@Async
public void asyncEvent() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("async event invoked -> thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("asyncEvent内部花费时间为:{}", System.currentTimeMillis() - start);
}
}
4、配置文件(application.properties)
spring.task.execution.threadNamePrefix=zc-customize-pool-task
spring.task.execution.pool.core-size=2
spring.task.execution.pool.max-size=10
spring.task.execution.pool.queue-capacity=10
spring.task.execution.pool.keep-alive=10s
测试案例1:
1、当循环次数为21次时(即异步处理的请求数为21),处理请求数21> 最大线程数10 + 队列深度10,最后一个请求被丢弃,具体效果如下:
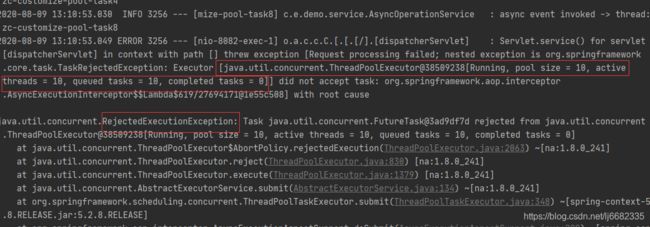
测试案例2:
1、当循环次数为20次时(即异步处理的请求数为20),处理请求数20 = 最大线程数10 + 队列深度10,所有请求都能被正常处理,具体效果如下:

PS:线程池的底层机制待后续剖析。