Linux内核4.14版本——alsa框架分析(3)-PCM设备的创建
目录
1. pcm设备的创建
1.1 snd_pcm_new
1.2 _snd_pcm_new
1.3 snd_pcm_dev_register
ALSA已经为我们实现了功能强劲的PCM中间层,自己的驱动中只要实现一些底层的需要访问硬件的函数即可。
要访问PCM的中间层代码,你首先要包含头文件
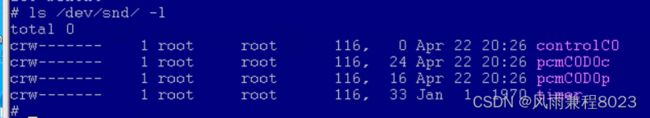
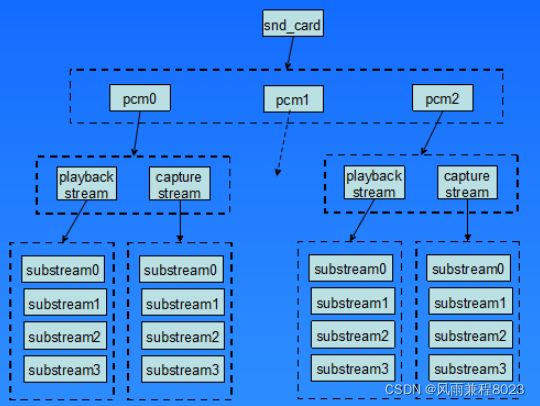
每个声卡最多可以包含4个pcm的实例,每个pcm实例对应一个pcm设备文件。pcm实例数量的这种限制源于linux设备号所占用的位大小,如果以后使用64位的设备号,我们将可以创建更多的pcm实例。不过大多数情况下,在嵌入式设备中,一个pcm实例已经足够了。
一个pcm实例由一个playback stream和一个capture stream组成,这两个stream又分别有一个或多个substreams组成。
下面一张图列出了pcm中间层几个重要的结构,他可以让我们从uml的角度看一看这列结构的关系,理清他们之间的关系,对我们理解pcm中间层的实现方式。
 1. pcm设备的创建
1. pcm设备的创建
snd_pcm_new->_snd_pcm_new->snd_pcm_dev_register->snd_register_device
1.1 snd_pcm_new
/**
* snd_pcm_new - create a new PCM instance
* @card: the card instance
* @id: the id string
* @device: the device index (zero based)
* @playback_count: the number of substreams for playback
* @capture_count: the number of substreams for capture
* @rpcm: the pointer to store the new pcm instance
*
* Creates a new PCM instance.
*
* The pcm operators have to be set afterwards to the new instance
* via snd_pcm_set_ops().
*
* Return: Zero if successful, or a negative error code on failure.
*/
int snd_pcm_new(struct snd_card *card, const char *id, int device,
int playback_count, int capture_count, struct snd_pcm **rpcm)
{
return _snd_pcm_new(card, id, device, playback_count, capture_count,
false, rpcm);
}1.2 _snd_pcm_new
static int _snd_pcm_new(struct snd_card *card, const char *id, int device,
int playback_count, int capture_count, bool internal,
struct snd_pcm **rpcm)
{
struct snd_pcm *pcm;
int err;
static struct snd_device_ops ops = {
.dev_free = snd_pcm_dev_free,
.dev_register = snd_pcm_dev_register,
.dev_disconnect = snd_pcm_dev_disconnect,
};
........
if (id)
strlcpy(pcm->id, id, sizeof(pcm->id));
err = snd_pcm_new_stream(pcm, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK,
playback_count);
if (err < 0)
goto free_pcm;
err = snd_pcm_new_stream(pcm, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE, capture_count);
if (err < 0)
goto free_pcm;
err = snd_device_new(card, SNDRV_DEV_PCM, pcm, &ops);
if (err < 0)
goto free_pcm;
if (rpcm)
*rpcm = pcm;
return 0;
free_pcm:
snd_pcm_free(pcm);
return err;
}
先创建playback和capture两个substream,最终创建pcm设备,ops最终为pcm的ops。
1.3 snd_pcm_dev_register
static int snd_pcm_dev_register(struct snd_device *device)
{
..............
err = snd_pcm_add(pcm);
if (err)
goto unlock;
for (cidx = 0; cidx < 2; cidx++) {
int devtype = -1;
if (pcm->streams[cidx].substream == NULL)
continue;
switch (cidx) {
case SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK:
devtype = SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_PCM_PLAYBACK;
break;
case SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE:
devtype = SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_PCM_CAPTURE;
break;
}
/* register pcm */
err = snd_register_device(devtype, pcm->card, pcm->device,
&snd_pcm_f_ops[cidx], pcm,
.............
}
pcm_call_notify(pcm, n_register);
unlock:
mutex_unlock(®ister_mutex);
return err;
}这里注意snd_pcm_f_ops结构体,如下所示。sound\core\pcm_native.c
/*
* Register section
*/
const struct file_operations snd_pcm_f_ops[2] = {
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.write = snd_pcm_write,
.write_iter = snd_pcm_writev,
.open = snd_pcm_playback_open,
.release = snd_pcm_release,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.poll = snd_pcm_playback_poll,
.unlocked_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl,
.compat_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl_compat,
.mmap = snd_pcm_mmap,
.fasync = snd_pcm_fasync,
.get_unmapped_area = snd_pcm_get_unmapped_area,
},
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = snd_pcm_read,
.read_iter = snd_pcm_readv,
.open = snd_pcm_capture_open,
.release = snd_pcm_release,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.poll = snd_pcm_capture_poll,
.unlocked_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl,
.compat_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl_compat,
.mmap = snd_pcm_mmap,
.fasync = snd_pcm_fasync,
.get_unmapped_area = snd_pcm_get_unmapped_area,
}
};该操作函数集被注册在snd_minors结构体的操作函数集中,所以上层应用最终的open,compat_ioctl等函数,最终都会调用到这里。