图片倾斜矫正(hough直线检测,仿射变换)
原理
先用hough直线检测找到图像中最长的直线,以最长的直线为基准。
使用仿射变换对图像进行修改。
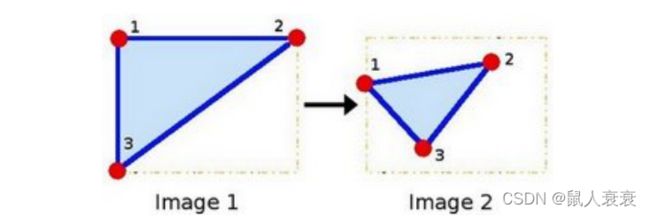
仿射变换中需要有两个三角形,两个三角形的变化决定了图像怎么变化。
我的做法
最长的直线L 就给了两个点(x1,y1),(x2,y2),以下图方式计算即可
具体可对照代码理解
之后就调用函数进行仿射变换即可。
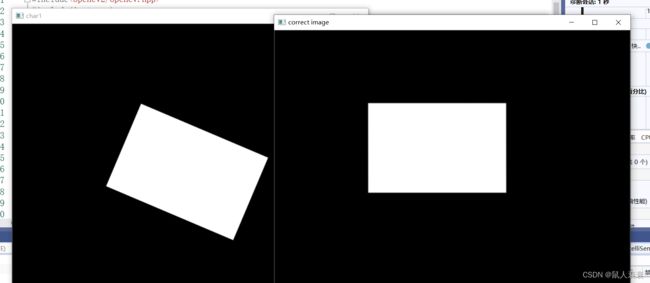
效果
 代码
代码
类的cpp文件
#include "imgprocess.h"
//求两点之间距离的代码
float distance(Vec4i point)
{
float dis = 0;
float a = abs(point[2] - point[0]);
float b = abs(point[3] - point[1]);
dis = sqrt(a * a + b * b);
return dis;
}
Mat imgprocess::Correct(Mat& image)
{
Mat dst = Mat::zeros(image.size(), image.type());;
cvtColor(image, dst, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);//转灰度图
Mat test = Mat::zeros(dst.size(), dst.type());//在test上用白色画检测出来的直线
GaussianBlur(dst,dst,Size(5,5),0,0);//高斯滤波,消除噪点
//把检测位置定位到中心
Canny(dst, dst, 50, 200, 3);//canny 边缘检测
// Probabilistic Line Transform
vector linesP; // will hold the results of the detection
HoughLinesP(dst, linesP, 1, CV_PI / 180, 50, 50, 10); // runs the actual detection
// Draw the lines
/*for (size_t i = 0; i < linesP.size(); i++)
{
Vec4i l = linesP[i];
line(test, Point(l[0], l[1]), Point(l[2], l[3]), Scalar(255), 3, LINE_AA);
cout << i << endl;
cout << linesP[i] << endl;
}*/
//找到最长的直线
float max = 0;
float d;
int index = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < linesP.size(); i++)
{
Vec4i l = linesP[i];
d = distance(l);
if (d > max) {
max = d;
index = i;
}
}
Vec4i l = linesP[index];
line(dst, Point(l[0], l[1]), Point(l[2], l[3]), Scalar(255), 3, LINE_AA);
cout << index << " is the longesst" << endl;
//以最长直线为基准进行放射变换,按照论文的公式
cout << l << endl;
Point2f srcTri[3];
srcTri[0] = Point2f(l[0], l[1]);
srcTri[1] = Point2f(l[2], l[3]);
//假设这个三角形是直角三角形
srcTri[2] = Point2f(l[0],l[3]);
Vec4i l_3 = { l[0],l[1],l[0],l[3] };
float d2 = distance(l_3);
cout << "max dis: " << max << endl;
cout << "d2 test " << d2 << endl;
//求角度
float angle = acos(d2/max);
angle = angle * 180 / CV_PI;
//cout << "angel : " << angle << endl;
//测试angle 72度
//cout << sin((30 * CV_PI)/180) << endl;
Point2f dstTri[3];
//max 就是 index 对应的最长的直线长度*
dstTri[0] = Point2f(l[0], l[1]);
dstTri[1] = Point2f(l[0]+max,l[1] );
//求出三角形转平之后的角的坐标
dstTri[2] = Point2f(l[0]+cos((angle*CV_PI)/180)*d2,l[1]+sin((angle * CV_PI)/180)*d2);
Mat warp_mat = getAffineTransform(srcTri, dstTri); // 获得反射变换矩阵
warpAffine(image, dst, warp_mat, dst.size());
return dst;
} .h
#pragma once
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
class imgprocess
{
public:
Mat Correct(Mat& image);//位置矫正前的图像预处理
};
主函数
#include
#include
#include "imgprocess.h"
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
imgprocess imgP;//类的声明
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
//load pics
string imgPath = "E:\\研究生\\数字图像处理\\c++\\字符识别\\Project1\\char1.png";
Mat srcImg = imread(imgPath);//RGB,JPG,PNG,TIFF格式
if (srcImg.empty()) {
cout << "can't load pic" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
//show pics
std::string winName = "char1";//std:: 标准命名空间
namedWindow(winName, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow(winName, srcImg);
namedWindow("correct image", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
Mat img;
img = imgP.Correct(srcImg);
imshow("correct image", img);
waitKey(0);//wait function
return 0;
}