UVa 10316 - Airline Hub
题目:给出地球上的n个机场的经度和纬度,想在这里面确定一个HUB使得他到其他机场的最大距离最小。
分析:计算几何、大地坐标系。因为数据不大直接枚举即可,比较时利用圆心角可以提高计算效率,并控制精度。
利用公式可直接解得两点的空间圆心角:acos(cos(lat1)*cos(lat2)*cos(lon1-lon2)+sin(lat1)*sin(lat2));
因为又是大地坐标,所以再推一遍吧,推导过程如下:
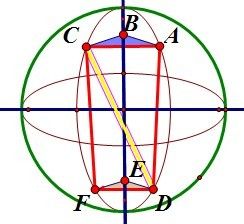
如图,C,D为已知两点则有如下推导:
AB = r*cos(lat1);DE = r*cos(lat2);BE = r*sin(lat1) + r*sin(lat2);
AD*AD = BE*BE + (AB-DE)*(AB-DE) = 2*r*r - 2*r*r*sin(lat1)*sin(lat2) - 2*r*r*cos(lat1)*cos(lat2);
AC*AC = 2*AB*AB - 2*AB*AB*cos(lon1-lon2) = 2*r*r*cos(lat1)*cos(lat1)*(1-cos(lon1-lon2));
DF*DF = 2*DE*DE - 2*DE*DE*cos(lon1-lon2) = 2*r*r*cos(lat2)*cos(lat2)*(1-cos(lon1-lon2));
AC*DF = 2*r*r*cos(lat1)*cos(lat2)*(1-cos(lon1-lon2));
由托勒密定理有 AC*DF + AD*AD = CD*CD 整理有:
CD = r*sqrt(2-2*(cos(lat1)*cos(lat2)*cos(lon1-lon2)+sin(lat1)*sin(lat2)));
设圆心角为α则:
cos(0.5*α) = 0.5*CD/r = sqrt(0.5-0.5*(cos(lat1)*cos(lat2)*cos(lon1-lon2)+sin(lat1)*sin(lat2)));
cos(0.5*α)*cos(0.5*α) = 0.5 - 0.5*(cos(lat1)*cos(lat2)*cos(lon1-lon2)+sin(lat1)*sin(lat2));
cosα = 1 - 2*cos(0.5*α)*cos(0.5*α) = cos(lat1)*cos(lat2)*cos(lon1-lon2)+sin(lat1)*sin(lat2);
圆心角为:acos(cos(lat1)*cos(lat2)*cos(lon1-lon2)+sin(lat1)*sin(lat2));
注意:精度控制。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
double dis[1005][1005];
double lat[1005];
double lon[1005];
double dist( double l1, double d1, double l2, double d2 )
{
double p = acos(-1.0);
l1 *= p/180.0; d1 *= p/180.0;
l2 *= p/180.0; d2 *= p/180.0;
return acos(cos(l1)*cos(l2)*cos(d1-d2)+sin(l1)*sin(l2));
}
int main()
{
int n;
while ( ~scanf("%d",&n) ) {
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i )
scanf("%lf%lf",&lat[i],&lon[i]);
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i )
for ( int j = i ; j < n ; ++ j )
dis[i][j] = dis[j][i] = dist( lat[i], lon[i], lat[j], lon[j] );
double min = 1e20;
int spa = 0;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) {
double max = 0.0;
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j )
if ( max+1e-6 < dis[i][j] )
max = dis[i][j];
if ( min+1e-6 > max ) {
min = max;
spa = i;
}
}
printf("%.2lf %.2lf\n",lat[spa],lon[spa]);
}
return 0;
}