Android架构师之插件化深造——VirtualAPK 原理与源码解读
插件化技术最初源于免安装运行 apk 的想法,这个免安装的 apk 可以理解为插件。支持插件化的 app 可以在运行时加载和运行插件,这样便可以将 app 中一些不常用的功能模块做成插件,一方面减小了安装包的大小,另一方面可以实现 app 功能的动态扩展。想要实现插件化,主要是解决下面三个问题:
- 插件中代码的加载和与主工程的互相调用。
- 插件中资源的加载和与主工程的互相访问
- 四大组件生命周期的管理。
背景
小菊发布的插件化框架,提供了四大组件的插件化功能,并且支持大多数的android特性。滴滴的这个框架可以称得上是“麻雀虽小,五脏俱全”,整个core library的代码量比较小,对runtime中一些类的hook也比较少,但却实现了不弱于主流插件化框架的功能,代码也比较清晰易懂。
在插件库的基础上,这个框架还有一个gradle的插件,主要为了解决宿主和插件之间资源冲突的问题,用这个gradle插件打出来的插件不具备在手机上单独运行的功能,必须被宿主加载使用,这意味着这个框架比较适合插件和宿主都是同一公司项目的情况,并且插件和宿主之间比较耦合。
VirtualAPK如何使用
按如下12个步骤可轻松接入VirtualAPK,先整体罗列,然后分步展开:
- 在宿主项目,根目录下的build.gradle文件中添加 classpath ‘com.didi.virtualapk:gradle:0.9.8.6’
- 在宿主项目,app下的build.gradle文件中顶端添加 apply plugin: ‘com.didi.virtualapk.host’
- 在宿主项目,app下的build.gradle文件中底部添加 compile ‘com.didi.virtualapk:core:0.9.8’
- 在宿主项目,Application下的attachBaseContext()方法中添加 PluginManager.getInstance(base).init();
- 在宿主项目,app下的proguard-rules.pro文件中添加混淆规则
- 在模块APK,根目录下的build.gradle文件中添加 classpath ‘com.didi.virtualapk:gradle:0.9.8.6’
- 在模块APK,app下的build.gradle文件中顶端添加 apply plugin: ‘com.didi.virtualapk.plugin’
- 在模块APK,app下的build.gradle文件中底部配置 VirtualAPK
- 在宿主项目,app下的文件中加载模块APK,然后可以跳转模块APK,或者与之通信
- 在宿主项目,app下的AndroidManifest.xml文件中添加读写存储权限
- 构建宿主项目与模块APK
- 将模块APK拷贝至存储设备某个目录,安装运行宿主APK
(1)在宿主项目,根目录下的build.gradle文件中添加 classpath ‘com.didi.virtualapk:gradle:0.9.8.6’
dependencies {
//noinspection GradleDependency
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.1.3'
classpath group: 'org.tmatesoft.svnkit', name: 'svnkit', version: '1.8.11'
classpath 'com.didi.virtualapk:gradle:0.9.8.6'
// NOTE: Do not place your application dependencies here; they belong
// in the individual module build.gradle files
}
(2)在宿主项目,app下的build.gradle文件中顶端添加 apply plugin: ‘com.didi.virtualapk.host’
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
apply plugin: 'com.didi.virtualapk.host'
(3)在宿主项目,app下的build.gradle文件中底部添加 compile ‘com.didi.virtualapk:core:0.9.8’
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.12'
androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test:runner:1.0.2'
androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.0.2'
implementation 'com.android.support:recyclerview-v7:27.1.1'
implementation 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:27.1.1'
implementation(name: 'wifidiagnose-release', ext: 'aar')
implementation 'com.didi.virtualapk:core:0.9.8'
}
(4)在宿主项目,Application下的attachBaseContext()方法中添加 PluginManager.getInstance(base).init();
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) {
super.attachBaseContext(base);
PluginManager.*getInstance*(base).init();
}
(5)在宿主项目,app下的proguard-rules.pro文件中添加混淆规则
**-keep** class com.didi.virtualapk.internal.VAInstrumentation { *; }
**-keep** class com.didi.virtualapk.internal.PluginContentResolver { *; }
**-dontwarn** com.didi.virtualapk.**
**-dontwarn** android.**
**-keep** class android.** { *; }
(6)在模块APK,根目录下的build.gradle文件中添加 classpath ‘com.didi.virtualapk:gradle:0.9.8.6’
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.1.2'
// classpath ('com.tencent.tinker:tinker-patch-gradle-plugin:1.9.1')
// classpath ("com.tinkerpatch.sdk:tinkerpatch-gradle-plugin:${TINKERPATCH_VERSION}") { changing = true }
// NOTE: Do not place your application dependencies here; they belong
// in the individual module build.gradle files
classpath 'com.didi.virtualapk:gradle:0.9.8.6'
}
(7)在模块APK,app下的build.gradle文件中顶端添加 apply plugin: ‘com.didi.virtualapk.plugin’
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
//apply from: 'tinkerpatch.gradle'
apply plugin: 'com.didi.virtualapk.plugin'
(8)在模块APK,app下的build.gradle文件中底部配置VirtualAPK
virtualApk {
// 插件资源表中的packageId,需要确保不同插件有不同的packageId.
// 范围 0x1f - 0x7f
packageId = 0x6f
// 宿主工程application模块的路径,插件的构建需要依赖这个路径
targetHost = 'C:\\AndroidStudioProjects\\SystemDiagnose\\app'
//默认为true,如果插件有引用宿主的类,那么这个选项可以使得插件和宿主保持混淆一致
applyHostMapping = true
}
(9)在宿主项目,app下的文件中加载模块APK,然后可以跳转模块APK,或者与之通信
public class TestActivity extends Activity {
private static final String *TAG* = TestActivity.class.getSimpleName();
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.*activity_main*);
Log.*d*(*TAG*,"onCreate()");
String pluginPath = Environment.*getExternalStorageDirectory*().getAbsolutePath().concat("/plugin.apk");
File plugin = new File(pluginPath);
try {
PluginManager.*getInstance*(getApplicationContext()).loadPlugin(plugin);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.*e*(*TAG*,"error");
e.printStackTrace();
}
findViewById(R.id.*iv_get_plugin*).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Log.*d*(*TAG*,"onCLick");
// Given "com.agg.application" is the package name of plugin APK,
// and there is an activity called `MainActivity`.
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClassName("com.agg.application", "com.agg.application.view.activity.MainActivity");
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
}
(10)在宿主项目,app下的AndroidManifest.xml文件中添加读写存储权限
(11)构建宿主项目与模块APK
宿主的构建和正常apk的构建方式是相同的,可以通过Build > Generate Signed APK的方式,也可以命令:gradlew clean assembleRelease,或者如下图方式,构建完成的apk在app > build > outputs > apk > release目录下。
模块APK构建可以命令:gradlew clean assemblePlugin,也可以如下图方式,构建完成的apk在app > build > outputs > plugin > release目录下。
(12)将模块APK拷贝至存储设备某个目录,安装运行宿主APK
存储设备目录在第9步中使用,至此,接入VirtualAPK大功告成。
备注:
- targetHost配置问题——targetHost可以设置绝对路径或相对路径,它是宿主工程application模块的路径,模块APK的构建需要依赖这个路径。
- 读写存储的权限设置——6.0以上手机需要动态申请,或手动在设置中打开权限。
VirtualAPK原理简析
基本原理
- 合并宿主和插件的ClassLoader 需要注意的是,插件中的类不可以和宿主重复
- 合并插件和宿主的资源 重设插件资源的packageId,将插件资源和宿主资源合并
- 去除插件包对宿主的引用 构建时通过Gradle插件去除插件对宿主的代码以及资源的引用
四大组件的实现原理
- Activity 采用宿主manifest中占坑的方式来绕过系统校验,然后再加载真正的activity;
- Service 动态代理AMS,拦截service相关的请求,将其中转给
Service Runtime去处理,Service Runtime会接管系统的所有操作; - Receiver 将插件中静态注册的receiver重新注册一遍;
- ContentProvider 动态代理IContentProvider,拦截provider相关的请求,将其中转给
Provider Runtime去处理,Provider Runtime会接管系统的所有操作。
整体架构图
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-q87h9Mt9-1657546577936)(https://ewr1.vultrobjects.com/imgur4/000/013/313/907_534_fb0.png)]
VirtualAPK源码分析
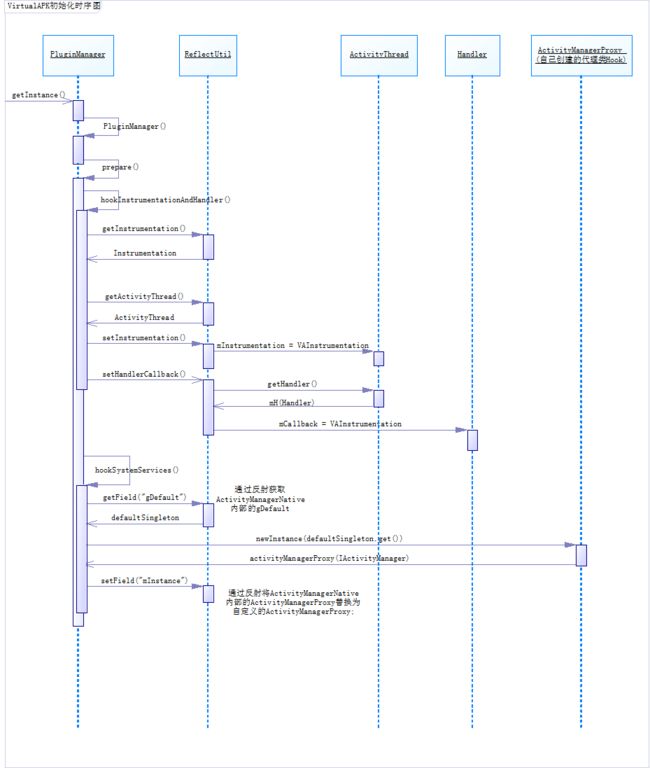
时序图
框架初始化的源码分析
在Application中开始初始化插件框架:PluginManager.getInstance(application).init()
// PluginManager.class
public static PluginManager getInstance(Context base) {
if (sInstance == null) {
synchronized (PluginManager.class) {
if (sInstance == null)
// 首次进来要初始化
sInstance = new PluginManager(base);
}
}
return sInstance;
}
// PluginManager.class
private PluginManager(Context context) {
Context app = context.getApplicationContext();
if (app == null) {
this.mContext = context;
} else {
this.mContext = ((Application)app).getBaseContext();
}
// 这里初始化是核心
prepare();
}
// PluginManager.class
private void prepare() {
Systems.sHostContext = getHostContext();
//利用Hook技术,替换ActivityThread中的Instrumentation对象
this.hookInstrumentationAndHandler();
//利用Hook技术,替换ActivityManagerNative中的gDefault对象中的IActivityManager对象
this.hookSystemServices();
}
// PluginManager.class
private void hookInstrumentationAndHandler() {
try {
Instrumentation baseInstrumentation = ReflectUtil.getInstrumentation(this.mContext);
if (baseInstrumentation.getClass().getName().contains("lbe")) {
// reject executing in paralell space, for example, lbe.
System.exit(0);
}
/*
* 创建Instrumentation的代理类VAInstrumentation;
* (将Instrumentation作为参数传入,这样可以在调用系统逻辑之前进行预处理)
*/
final VAInstrumentation instrumentation = new VAInstrumentation(this, baseInstrumentation);
Object activityThread = ReflectUtil.getActivityThread(this.mContext);
ReflectUtil.setInstrumentation(activityThread, instrumentation);
ReflectUtil.setHandlerCallback(this.mContext, instrumentation);
this.mInstrumentation = instrumentation;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// PluginManager.class
private void hookSystemServices() {
try {
/*
* 通过反射获取持有 ActivityManagerProxy(AMP) 对象的单例对象 Singleton ;
* (这部分可以看:[源码分析 — Binder机制(二)之IActivityManager]
* (https://blog.csdn.net/love667767/article/details/79653077))
*/
Singleton<IActivityManager> defaultSingleton = (Singleton<IActivityManager>)
ReflectUtil.getField(ActivityManagerNative.class, null, "gDefault");
/*
* 自己创建一个AMP代理类,将系统原有的AMP作为一个参数传入;
* 好处:
* 在调用系统AMP之前会先调用我们自己创建的AMP,然后进行一些预处理,
* 最后调用系统的AMP,我们的代理类,其实质就是系统AMP的代理);
*/
IActivityManager activityManagerProxy =
ActivityManagerProxy.newInstance(this, defaultSingleton.get());
/*
* Hook IActivityManager from ActivityManagerNative
* 这里创建了自己的 AMP 类后,当然要将它设置回 Singleton 单例了,
* 这样子我们自己实现的 AMP 才能生效;
*/
ReflectUtil.setField(defaultSingleton.getClass().getSuperclass(),
defaultSingleton, "mInstance", activityManagerProxy);
if (defaultSingleton.get() == activityManagerProxy) {
this.mActivityManager = activityManagerProxy;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637383940414243444546474849505152535455565758596061626364656667686970717273747576777879808182838485868788
插件的加载
加载插件的示例代码
在底座(宿主)Apk中加载插件的代码片段:
// 加载plugin.apk插件包
private void loadPlugin() {
PluginManager pluginManager = PluginManager.getInstance(this);
// 指明被加载的插件所在路径
File apk = new File(getExternalStorageDirectory(), "app-release.apk");
if (apk.exists()) {
try {
// 加载插件Apk
pluginManager.loadPlugin(apk);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}1234567891011121314
插件初始化源码分析
/**
* PluginManager.class
*
* 加载插件Apk包,然后调用插件Apk的Application;
* 注意:加载的文件必须以.apk为后缀;
*/
public void loadPlugin(File apk) throws Exception {
if (null == apk) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("error : apk is null.");
}
if (!apk.exists()) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(apk.getAbsolutePath());
}
// 1.加载插件Apk,然后解析其文件结构
LoadedPlugin plugin = LoadedPlugin.create(this, this.mContext, apk);
if (null != plugin) {
this.mPlugins.put(plugin.getPackageName(), plugin);
// 2.调用插件里面的Application(插件内的Application已经被插件框架托管)
plugin.invokeApplication();
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't load plugin which is invalid: " + apk.getAbsolutePath());
}
}123456789101112131415161718192021222324
// LoadedPlugin.class
public static LoadedPlugin create(PluginManager pluginManager, Context host, File apk) throws Exception {
return new LoadedPlugin(pluginManager, host, apk);
}
LoadedPlugin(PluginManager pluginManager, Context context, File apk)
throws PackageParser.PackageParserException {
this.mPluginManager = pluginManager;
this.mHostContext = context;
this.mLocation = apk.getAbsolutePath();
/*
* 1.关键:通过系统的PackageParser.parsePackage()方法去解析Apk文件;
* 参考:[PackageManagerService(一)之启动流程](https://blog.csdn.net/love667767/article/details/79595237)
*
* 说明:由于系统版本的适配问题,这里框架做了一层封装,根据版本的不同做了不同的处理;
*/
this.mPackage = PackageParserCompat.parsePackage(context, apk, PackageParser.PARSE_MUST_BE_APK);
this.mPackage.applicationInfo.metaData = this.mPackage.mAppMetaData;
this.mPackageInfo = new PackageInfo();
this.mPackageInfo.applicationInfo = this.mPackage.applicationInfo;
// ...
// 插件包的管理对象
this.mPackageManager = new PluginPackageManager();
// 插件包的Context
this.mPluginContext = new PluginContext(this);
this.mNativeLibDir = context.getDir(Constants.NATIVE_DIR, Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
// 资源获取
this.mResources = createResources(context, apk);
this.mAssets = this.mResources.getAssets();
// 创建插件的ClassLoader
this.mClassLoader = createClassLoader(context, apk, this.mNativeLibDir, context.getClassLoader());
// 将插件中Lib库的依赖包拷贝到底座(宿主)中;
tryToCopyNativeLib(apk);
/*
* 2.下面这部分跟PackageManagerService(PMS)逻辑类似,就是将插件清单文件解析出来的信息存入到
* mInstrumentationInfos、mActivityInfos、mServiceInfos、mProviderInfos、mReceiverInfos字段中;
*/
// Cache instrumentations
Map<ComponentName, InstrumentationInfo> instrumentations = new HashMap<ComponentName, InstrumentationInfo>();
for (PackageParser.Instrumentation instrumentation : this.mPackage.instrumentation) {
instrumentations.put(instrumentation.getComponentName(), instrumentation.info);
}
this.mInstrumentationInfos = Collections.unmodifiableMap(instrumentations);
this.mPackageInfo.instrumentation = instrumentations.values().toArray(new InstrumentationInfo[instrumentations.size()]);
// Cache activities
Map<ComponentName, ActivityInfo> activityInfos = new HashMap<ComponentName, ActivityInfo>();
for (PackageParser.Activity activity : this.mPackage.activities) {
activityInfos.put(activity.getComponentName(), activity.info);
}
this.mActivityInfos = Collections.unmodifiableMap(activityInfos);
this.mPackageInfo.activities = activityInfos.values().toArray(new ActivityInfo[activityInfos.size()]);
// Cache services
Map<ComponentName, ServiceInfo> serviceInfos = new HashMap<ComponentName, ServiceInfo>();
for (PackageParser.Service service : this.mPackage.services) {
serviceInfos.put(service.getComponentName(), service.info);
}
this.mServiceInfos = Collections.unmodifiableMap(serviceInfos);
this.mPackageInfo.services = serviceInfos.values().toArray(new ServiceInfo[serviceInfos.size()]);
// Cache providers
Map<String, ProviderInfo> providers = new HashMap<String, ProviderInfo>();
Map<ComponentName, ProviderInfo> providerInfos = new HashMap<ComponentName, ProviderInfo>();
for (PackageParser.Provider provider : this.mPackage.providers) {
providers.put(provider.info.authority, provider.info);
providerInfos.put(provider.getComponentName(), provider.info);
}
this.mProviders = Collections.unmodifiableMap(providers);
this.mProviderInfos = Collections.unmodifiableMap(providerInfos);
this.mPackageInfo.providers = providerInfos.values().toArray(new ProviderInfo[providerInfos.size()]);
// Register broadcast receivers dynamically
Map<ComponentName, ActivityInfo> receivers = new HashMap<ComponentName, ActivityInfo>();
for (PackageParser.Activity receiver : this.mPackage.receivers) {
receivers.put(receiver.getComponentName(), receiver.info);
try {
BroadcastReceiver br = BroadcastReceiver.class.cast(getClassLoader().loadClass(receiver.getComponentName().getClassName()).newInstance());
for (PackageParser.ActivityIntentInfo aii : receiver.intents) {
// 这里将插件清单文件中的静态广播动态注册到底座(宿主)中;
this.mHostContext.registerReceiver(br, aii);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
this.mReceiverInfos = Collections.unmodifiableMap(receivers);
this.mPackageInfo.receivers = receivers.values().toArray(new ActivityInfo[receivers.size()]);
}
文末
文章看过千百遍,不如源码走一遍。
Android架构师之路
一则,提升阅读源码的能力;
二则,在阅读源码的过程中学会思考,理解其实现原理;
更多Android架构师技术知识学习;插件化技术解析。可以领取这份铺路架构师的知识资料,根据架构学习思路导图整理。