数据结构---ArrayList
ArrayList实现的接口
ArrayList的构造方法(3种)
ArrayList常用方法
ArrayList的遍历(打印)
--->for循环+下标、foreach、使用迭代器
ArrayList的扩容
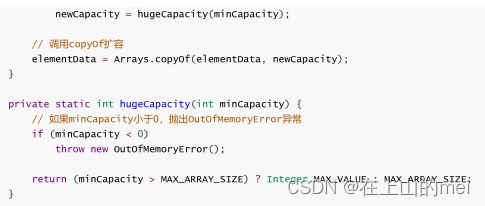
ArrayList源码中扩容方式(可以看看):
做题时间到哈哈哈
class Student {
private String name;
private String classes;
private double score;
public Student(String name, String classes, double score) {
this.name = name;
this.classes = classes;
this.score = score;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getClasses() {
return classes;
}
public void setClasses(String classes) {
this.classes = classes;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", classes='" + classes + '\'' +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList students = new ArrayList<>();
students.add(new Student("bit","102-1",98.9));
students.add(new Student("gaobo","102-2",18.9));
students.add(new Student("zhiqiang","102-1",88.9));
System.out.println(students);
}
} public class TestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "welcome to bit";
String str2 = "come";
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < str1.length(); i++) {
char ch = str1.charAt(i);
if(!str2.contains(ch+"")) {
list.add(ch);
}
}
for (char ch : list) {
System.out.print(ch);
}
}
} public class TestDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList integers = new ArrayList<>();
integers.add(1);
integers.add(2);
integers.add(3);
Collections.sort(integers);
//Collections.reverse(integers);
System.out.println(integers);
}
} 4.扑克牌
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* User: 12629
* Date: 2021/11/29
* Time: 21:02
* Description:
*/
class Card {
private int rank;//数字
private String suit;//花色
public Card(int rank, String suit) {
this.rank = rank;
this.suit = suit;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "[ "+this.suit+":"+this.rank+" ]";
}
}
//没有大小王:1 2 3 。。。。。。10 11 12 13
public class TestDemo3 {
private static final String[] suits = {"♥","♠","♣","♦"};
public static List buyCard() {
ArrayList cards = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 13; j++) {
/*String suit = suits[i];
int rank = j;
Card card = new Card(rank,suit);
cards.add(card);*/
cards.add(new Card(j,suits[i]));
}
}
return cards;
}
private static void swap(List cards,int i,int j) {
//Card tmp = cards[i];
Card tmp = cards.get(i);
//cards[i] = cards[j];
cards.set(i,cards.get(j));
//cards[j] = tmp;
cards.set(j,tmp);
}
public static void shuffle(List cards) {
int size = cards.size();
for (int i = size-1; i > 0 ; i--) {
Random random = new Random();
int rand = random.nextInt(i);
swap(cards,i,rand);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List cards = buyCard();
System.out.println("买牌:"+cards);
shuffle(cards);
System.out.println("洗牌:"+cards);
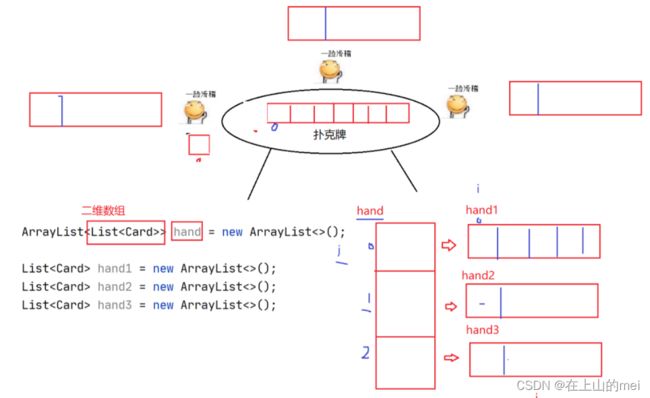
System.out.println("揭牌:3个人每个人轮流揭5张牌");
ArrayList> hand = new ArrayList<>();
List hand1 = new ArrayList<>();
List hand2 = new ArrayList<>();
List hand3 = new ArrayList<>();
hand.add(hand1);
hand.add(hand2);
hand.add(hand3);
//每个人,轮流揭牌
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
Card card = cards.remove(0);
hand.get(j).add(card);
}
}
System.out.println("第1个人的牌:"+hand1);
System.out.println("第2个人的牌:"+hand2);
System.out.println("第3个人的牌:"+hand3);
System.out.println("剩下的牌:"+cards);
}
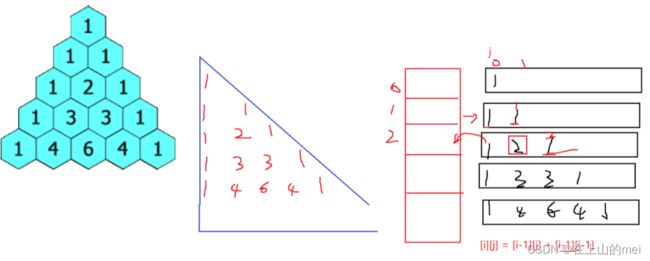
public List> generate(int numRows) {
List> ret = new ArrayList<>();
//第一行:
List list1 = new ArrayList<>();
list1.add(1);
ret.add(list1);//才把第一行的数据存放到了ret当中
for (int i = 1; i < numRows; i++) {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);//每一行的开始都是1
List preRow = ret.get(i-1);//上一行
for (int j = 1; j < i ; j++) {
//中间的情况
int num1 = preRow.get(j)+preRow.get(j-1);
list.add(num1);
}
list.add(1);//每一行的结尾都是1
ret.add(list);
}
return ret;
}
public static void main1(String[] args) {
Card card = new Card(3,"♥");
System.out.println(card);
}
} 5.杨辉三角
杨辉三角
class Solution {
public List> generate(int numRows) {
List> ret=new ArrayList<>();
//第一行
List list1=new ArrayList<>();
list1.add(1);
ret.add(list1);//把第一行的数据存放到ret当中
for(int i=1;i list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);//每一行的开始都是1
List preRow=ret.get(i-1);
for(int j=1;j ArrayList的模拟实现(可以看看)
import java.util.*;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* User: GB
* Date: 2021/11/26
* Time: 13:31
* Description:
*/
class MyArrayList {
private Object[] array;
private int size;
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
//构造方法
public MyArrayList() {
this.array = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
public MyArrayList(int initCapacity) {
if (initCapacity > 0) {
array = new Object[initCapacity];
} else if (initCapacity == 0) {
array = new Object[0];
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("初始容量为负数");
}
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return 0 == size;
}
// 尾插
public boolean add(E e) {
//容量变为size + 1 后是否需要扩容,注意第一次size为0的时候
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1);
array[size++] = e;
return true;
}
/**
* 存放元素之前,确定内部的容量
* @param minCapacity
*/
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
//1、先计算
int capacity = calculateCapacity(array, minCapacity);
//2、确保该容量是否可以分配
ensureExplicitCapacity(capacity);
}
//默认容量
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
//1、说明调用了不带参数的构造方法
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
//此时默认容量分配10
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
//2、给了参数,返回,你指定的参数
return minCapacity;
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
//计算出来的容量大就要扩容,否则什么都不做
if (minCapacity - array.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
// 扩容
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
private void grow(int initCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = array.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
//当第一次newCapacity==0的时候,大小为给定的容量
if (newCapacity < initCapacity) {
newCapacity = initCapacity;
}
if (newCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) {
newCapacity = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
array = Arrays.copyOf(array, newCapacity);
}
// 为指定位置插入元素e
public void add(int index, E e) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1);
// 将index及其以后的元素统一往后搬移一个位置
for (int i = size - 1; i >= index; i--) {
array[i + 1] = array[i];
}
array[index] = e;
size++;
}
// 检测插入时下标是否异常
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index <0 || index > size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("add下标越界");
}
}
// 删除index位置上元素
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
E e = (E) array[index];
// 将index之后的元素统一往前搬移一个位置
for (int i = index; i < size-1; ++i) {
array[i] = array[i+1];
}
array[size] = null;
size--;
return e;
}
// 检测下标是否异常
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("下标越界");
}
}
// 获取o第一次出现的位置
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (null == o) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (array[i] == null) {
return i;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (array[i].equals(o)) {
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
// 如果o存在,则删除
public boolean remove(Object o) {
int index = indexOf(o);
if (index == -1) {
return false;
}
remove(index);
return true;
}
// 获取index位置上的元素
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return (E) array[index];
}
// 将index位置上元素设置为e
public E set(int index, E e) {
rangeCheck(index);
array[index] = e;
return e;
}
// 清空
public void clear() {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
array[i] = null;
}
size = 0;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String s = "[";
if (size > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
s += array[i];
s += ", ";
}
s += array[size - 1];
}
s += "]";
return s;
}
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList arrayList = new MyArrayList<>();
arrayList.add(1);
arrayList.add(2);
arrayList.add(3);
arrayList.add(4);
System.out.println(arrayList.size());//4
System.out.println(arrayList);
arrayList.add(0,999999);
arrayList.add(0);
System.out.println(arrayList);
System.out.println(arrayList.indexOf(0));
arrayList.remove(0);
System.out.println(arrayList);
arrayList.clear();
System.out.println(arrayList);
}
}