Mac M1芯片安装Anaconda、Jupyter、TensorFlow环境
本文适用于macOS 12+,使用conda自带python3.9
- 电脑环境
- Miniforge
-
- 先配置环境变量
- 给anaconda添加国内镜像源
- macOS中PyCharm配置conda环境的方法
- 安装JupyterLab、JupyterNotebook
-
- 命令
- 配置JupyterLab的默认工作路径
- 安装TensorFlow2.8
-
- 创建虚拟环境
- 安装 Tensorflow dependencies(虚拟环境中执行)
-
- 首次安装
- 升级安装
- 安装 Tensorflow(虚拟环境中执行)
- 安装tensorflow-metal(虚拟环境中执行)
- 安装必须的包(虚拟环境中执行)
- jupyter虚拟环境的配置
- 测试代码
-
- 输出Hello,TensorFlow
- 测试GPU加速功能是否正常
- 测试GPU性能
电脑环境
Miniforge
Anaconda 无法在 M1 上运行, Miniforge 是用来替代它的。
从 https://github.com/conda-forge/miniforge下载 Miniforge3-MacOSX-arm64。如下图:

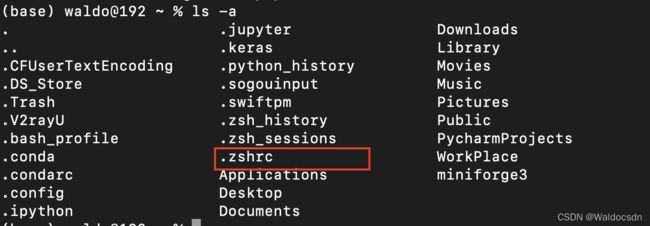
回到终端,用ls -a命令检查是否已有.zshrc文件,如果没有,使用命令touch ~/.zshrc建立文件:
在终端执行以下命令,使用刚刚下载的 文件,安装Miniforge:
bash Miniforge3-MacOSX-arm64.sh
重启终端并检查 Python 安装情况:
先配置环境变量
conda安装的Python、Jupyter都在这个目录下
/Users/waldo/miniforge3/bin,将它添加进环境变量
步骤:
- 终端执行:
touch ~/.bash_profile - 终端执行:
open ~/.bash_profile - 添加环境变量,如下图:

- 终端执行:
source ~/.bash_profile - 终端执行:
open ~/.zshrc - 在首行添加:
source ~/.bash_profile,如下图:
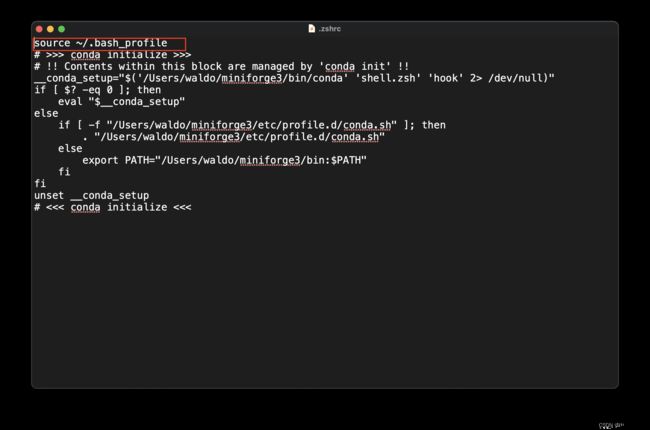
- 终端执行:
source ~/.bash_profile - 终端执行:
source ~/.zshrc
给anaconda添加国内镜像源
若在本文以后的配置中,有些地方网速还是慢,开启“全局模式”可解决
1. 查看镜像源: conda config --show channels
2. 添加(两条命令):
conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/free/
conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main/
3. 再次查看镜像源: conda config --show channels
macOS中PyCharm配置conda环境的方法
我们的目的是在PyCharm使用Anaconda自带的python以及它丰富的第三方库,所以这一步才是最重要的。
选择Python解释器,这一步最为关键,也是最容易出错的。当我们看到上图所示的内容之后,第一反应就是点击 Conda Environment,这是不正确的,也是很多人都会遇到的困惑。正确的选择应该是 System Interpreter。
再按照下图中路径选择python解释器,则可以在pycharm中使用conda的包:
安装JupyterLab、JupyterNotebook
命令
安装jupyter notebook命令:
pip3 install jupyter或者conda install jupyter,按enter等待安装完成
终端输入jupyter notebook,按enter键就会用默认浏览器打开
安装jupyter lab命令:
pip3 install jupyterlab或者conda install jupyterlab
终端输入jupyter lab,按enter键就会用默认浏览器打开
配置JupyterLab的默认工作路径
目的: 自己创建一个文件夹专门放JupyterLab中的文件
创建一个py文件,命令: jupyter notebook --generate-config
![]()
打开这个py文件: open /Users/waldo/.jupyter/jupyter_notebook_config.py
找到下图对应位置修改notebook默认工作目录(去掉注释符),保存:
重新打开后,是空的(处于默认的wpforJupyter文件夹里面):
![]()
安装TensorFlow2.8
Apple Silicon Mac M1 原生支持 TensorFlow 2.8 GPU 加速(tensorflow-metal PluggableDevice)
创建虚拟环境
虚拟环境相当于沙盒,避免不能框架的互相影响,这样甚至可以安装多个不同版本的tensorflow。也方便卸载,直接把虚拟环境删除就行
创建一个 conda 创建虚拟环境,这里使用 python 3.9.7 (TensorFlow 需要)。
创建名为“tf2_8”的虚拟环境:
conda create -n tf2_8 python=3.9.7
激活虚拟环境:
conda activate tf2_8
补充一个知识点,删除上述虚拟环境的命令为:
conda remove -n tf2_8 --all
安装 Tensorflow dependencies(虚拟环境中执行)
首次安装
conda install -c apple tensorflow-deps
注:tensorflow-deps 的版本是基于 TensorFlow 的,因此可以根据自己的需求指定版本安装。如下:
安装指定2.6版本:
conda install -c apple tensorflow-deps==2.6.0
安装指定2.8版本:
conda install -c apple tensorflow-deps==2.8.0
升级安装
如果之前已经安装了 v2.6,想要更新 v2.8 的,可以执行以下命令安装。
# 卸载已安装的 tensorflow-macos 和 tensorflow-metal
python -m pip uninstall tensorflow-macos
python -m pip uninstall tensorflow-metal
# 升级 tensorflow-deps
conda install -c apple tensorflow-deps --force-reinstall
# 后者指向特定的 conda 环境
conda install -c apple tensorflow-deps --force-reinstall -n tf2_8
安装 Tensorflow(虚拟环境中执行)
python -m pip install tensorflow-macos
注: 若这一步出现报错,执行pip3 install torch,再重新执行上面的命令
安装tensorflow-metal(虚拟环境中执行)
python -m pip install tensorflow-metal
安装必须的包(虚拟环境中执行)
pip3 install libjpeg
conda install -y matplotlib jupyterlab
注意: libjpeg 是 matplotlib 需要依赖的库。
jupyter虚拟环境的配置
此时打开jupyter notebook,执行
import tensorflow as tf是不成功的,需要如下配置
打开系统终端,执行以下命令:
1. conda activate tf2_8 //注意替换成自己的虚拟环境名
2. conda install ipykernel //安装ipykernel
3. sudo python -m ipykernel install --name tf2_8 //在ipykernel中安装当前环境
4. conda deactivate
打开jupyter,切换kernel:
![]()
![]()
测试代码
输出Hello,TensorFlow
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"]="0"
tf.compat.v1.disable_eager_execution()
hello=tf.constant('Hello,TensorFlow')
config=tf.compat.v1.ConfigProto()
config.gpu_options.per_process_gpu_memory_fraction = 0.9
sess=tf.compat.v1.Session(config=config)
print(sess.run(hello))
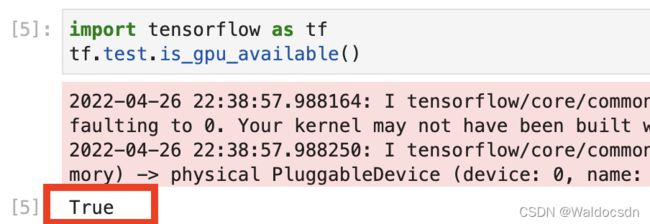
测试GPU加速功能是否正常
import tensorflow as tf
tf.test.is_gpu_available()
测试GPU性能
from tensorflow.keras import layers
from tensorflow.keras import models
import tensorflow as tf
import time
begin_time = time.time()
print(f"Running TensorFlow {tf.__version__} with {len(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU'))} GPUs recognized")
model = models.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', input_shape=(28, 28, 1)))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.Flatten())
model.add(layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax'))
model.summary()
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = mnist.load_data()
train_images = train_images.reshape((60000, 28, 28, 1))
train_images = train_images.astype('float32') / 255
test_images = test_images.reshape((10000, 28, 28, 1))
test_images = test_images.astype('float32') / 255
train_labels = to_categorical(train_labels)
test_labels = to_categorical(test_labels)
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop',
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
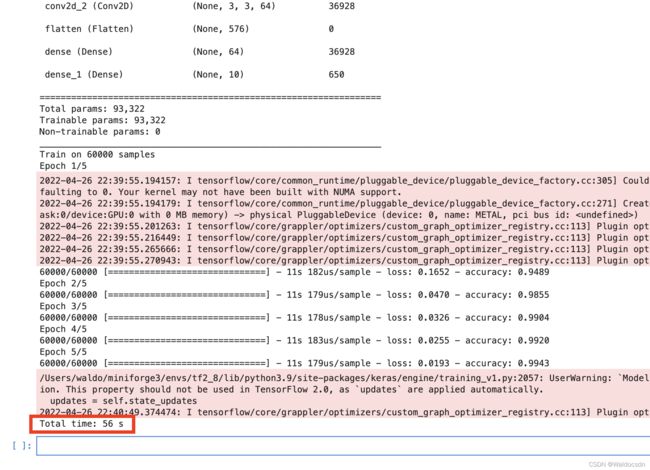
model.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=5, batch_size=64)
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels)
test_acc
end_time = time.time()
print('Total time: {} s'.format(int(end_time-begin_time)))