【Java】Java 高频面试题英语版(1)
今天分享 Java 高频面试题英语版。音频文件放在下方,点击获取。
【Java】Java 高频面试题英语版(1)
【Java】Java 高频面试题英语版(2)
【Java】Java 高频面试题英语版(3)
【Java】Java 高频面试题英语版(4)
【Java】Java 高频面试题英语版(5)
Java Basic Interview Questions
1. Why is Java a platform independent language?
Java language was developed in such a way that it does not depend on any hardware or software due to the fact that the compiler compiles the code and then converts it to platform-independent byte code which can be run on multiple systems.
- The only condition to run that byte code is for the machine to have a runtime environment (JRE) installed in it.
1、为什么 Java 是平台无关的语言?
Java 语言的开发方式使其不依赖于任何硬件或软件,因为编译器会编译代码,然后将其转换为可以在多个系统上运行的与平台无关的字节码。
- 运行该字节码的唯一条件是机器安装了运行时环境 (JRE)。
2. Why is Java not a pure object oriented language?
Java supports primitive data types - byte, boolean, char, short, int, float, long, and double and hence it is not a pure object oriented language.
2. 为什么 Java 不是纯粹的面向对象语言?
Java 支持原始数据类型 - byte、boolean、char、short、int、float、long 和 double,因此它不是纯面向对象的语言。
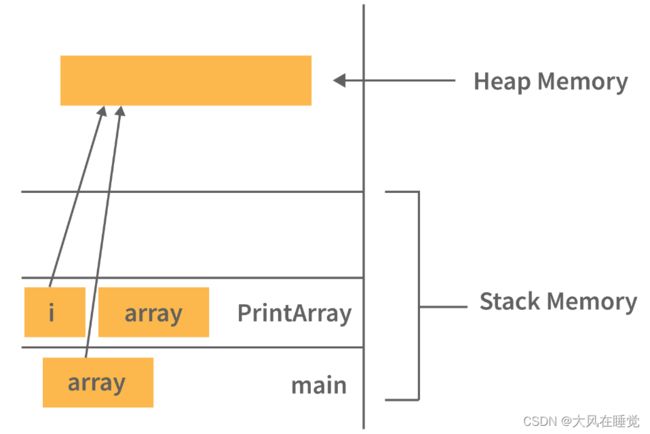
3. Difference between Heap and Stack Memory in java. And how java utilizes this.
Stack memory is the portion of memory that was assigned to every individual program. And it was fixed. On the other hand, Heap memory is the portion that was not allocated to the java program but it will be available for use by the java program when it is required, mostly during the runtime of the program.
3. java中堆内存和栈内存的区别。以及java如何利用它。
堆栈内存是分配给每个单独程序的内存部分。它是固定的。另一方面,堆内存是未分配给 java 程序的部分,但在需要时可供 java 程序使用,主要是在程序运行时。
Java Utilizes this memory as:
- When we write a java program then all the variables, methods, etc are stored in the stack memory.
- And when we create any object in the java program then that object was created in the heap memory. And it was referenced from the stack memory.
Java 将此内存用作:
- 当我们编写一个 java 程序时,所有的变量、方法等都存储在堆栈内存中。
- 当我们在 java 程序中创建任何对象时,该对象就会在堆内存中创建。它是从堆栈内存中引用的。
Example- Consider the below java program:
class Main {
public void printArray(int[] array){
for(int i : array)
System.out.println(i);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = new int[10];
printArray(array);
}
}
For this java program. The stack and heap memory occupied by java is:
Main and PrintArray is the method that will be available in the stack area and as well as the variables declared that will also be in the stack area.
And the Object (Integer Array of size 10) we have created, will be available in the Heap area because that space will be allocated to the program during runtime.
Main 和 PrintArray 是堆栈区域中可用的方法,以及声明的变量也将在堆栈区域中。
我们创建的对象(大小为 10 的整数数组)将在堆区域中可用,因为该空间将在运行时分配给程序。
4. Can java be said to be the complete object-oriented programming language?
It is not wrong if we claim that java is the complete object-oriented programming language. Because Everything in Java is under the classes. And we can access that by creating the objects.
But also if we say that java is not a completely object-oriented programming language because it has the support of primitive data types like int, float, char, boolean, double, etc.
Now for the question: Is java a completely object-oriented programming language? We can say that - Java is not a pure object-oriented programming language, because it has direct access to primitive data types. And these primitive data types don’t directly belong to the Integer classes.
4. java 可以说是完整的面向对象的编程语言吗?
如果我们声称 java 是完整的面向对象的编程语言,那并没有错。因为 Java 中的一切都在类之下。我们可以通过创建对象来访问它。
但是,如果我们说 java 不是一种完全面向对象的编程语言,因为它支持原始数据类型,如 int、float、char、boolean、double 等。
现在的问题是:**Java 是完全面向对象的编程语言吗?**我们可以说——Java 不是一种纯粹的面向对象的编程语言,因为它可以直接访问原始数据类型。而且这些原始数据类型不直接属于 Integer 类。
5. How is Java different from C++?
- C++ is only a compiled language, whereas Java is compiled as well as an interpreted language.
- Java programs are machine-independent whereas a c++ program can run only in the machine in which it is compiled.
- C++ allows users to use pointers in the program. Whereas java doesn’t allow it. Java internally uses pointers.
- C++ supports the concept of Multiple inheritances whereas Java doesn’t support this. And it is due to avoiding the complexity of name ambiguity that causes the diamond problem.
5. Java 与 C++ 有何不同?
- C++ 只是一种编译语言,而 Java 既是编译语言又是解释语言。
- Java 程序与机器无关,而 c++ 程序只能在编译它的机器上运行。
- C++ 允许用户在程序中使用指针。而 java 不允许它。Java 在内部使用指针。
- C++ 支持多重继承的概念,而 Java 不支持这一点。正是由于避免了导致名称歧义复杂性的严重问题。
6. Pointers are used in C/C++. Why does Java not make use of pointers?
Pointers are quite complicated and unsafe to use by beginner programmers. Java focuses on code simplicity, and the usage of pointers can make it challenging. Pointer utilization can also cause potential errors. Moreover, security is also compromised if pointers are used because the users can directly access memory with the help of pointers.
Thus, a certain level of abstraction is furnished by not including pointers in Java. Moreover, the usage of pointers can make the procedure of garbage collection quite slow and erroneous. Java makes use of references as these cannot be manipulated, unlike pointers.
6. C/C++中使用指针。为什么 Java 不使用指针?
指针对于初学者来说非常复杂且不安全。Java 专注于代码的简单性,而指针的使用可能使其具有挑战性。指针的使用也可能导致潜在的错误。此外,如果使用指针,安全性也会受到影响,因为用户可以在指针的帮助下直接访问内存。
因此,通过在 Java 中不包括指针来提供一定程度的抽象。此外,指针的使用会使垃圾收集过程变得非常缓慢和错误。Java 使用引用,因为这些不能被操纵,不像指针。
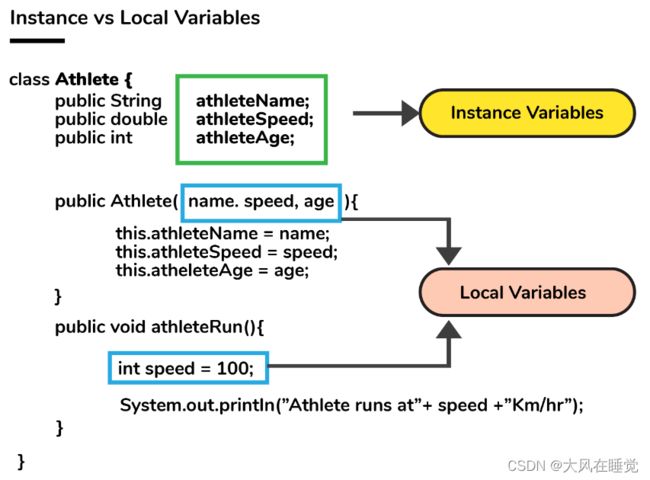
7. What do you understand by an instance variable and a local variable?
Instance variables are those variables that are accessible by all the methods in the class. They are declared outside the methods and inside the class. These variables describe the properties of an object and remain bound to it at any cost.
All the objects of the class will have their copy of the variables for utilization. If any modification is done on these variables, then only that instance will be impacted by it, and all other class instances continue to remain unaffected.
Example:
class Athlete {
public String athleteName;
public double athleteSpeed;
public int athleteAge;
}
7. 你对实例变量和局部变量的理解是什么?
实例变量是类中所有方法都可以访问的变量。它们在方法外部和类内部声明。这些变量描述了一个对象的属性,并且不惜一切代价保持与它的绑定。
该类的所有对象都将拥有它们的变量副本以供使用。如果对这些变量进行任何修改,那么只有该实例会受到影响,所有其他类实例继续保持不受影响。
Local variables are those variables present within a block, function, or constructor and can be accessed only inside them. The utilization of the variable is restricted to the block scope. Whenever a local variable is declared inside a method, the other class methods don’t have any knowledge about the local variable.
Example:
public void athlete() {
String athleteName;
double athleteSpeed;
int athleteAge;
}
局部变量是存在于块、函数或构造函数中的那些变量,并且只能在它们内部访问。变量的使用仅限于块范围。每当在方法中声明局部变量时,其他类方法对局部变量一无所知。
例子:
public void athlete() {
String athleteName;
double athleteSpeed;
int athleteAge;
}
8. What are the default values assigned to variables and instances in java?
- There are no default values assigned to the variables in java. We need to initialize the value before using it. Otherwise, it will throw a compilation error of " Variable might not be initialized ".
- But for instance, if we create the object, then the default value will be initialized by the default constructor depending on the data type.
- If it is a reference, then it will be assigned to null.
- If it is numeric, then it will assign to 0.
- If it is a boolean, then it will be assigned to false. Etc.
8. java 中变量和实例的默认值是什么?
- java 中的变量没有默认值。我们需要在使用它之前初始化该值。否则会抛出编译错误” 变量可能未初始化 “。
- 但是例如,如果我们创建对象,则默认值将由默认构造函数根据数据类型进行初始化。
- 如果它是一个引用,那么它将被分配给 null。
- 如果它是数字,那么它将分配为 0。
- 如果它是一个布尔值,那么它将被赋值为 false。等等。
9. What do you mean by data encapsulation?
- Data Encapsulation is an Object-Oriented Programming concept of hiding the data attributes and their behaviours in a single unit.
- It helps developers to follow modularity while developing software by ensuring that each object is independent of other objects by having its own methods, attributes, and functionalities.
- It is used for the security of the private properties of an object and hence serves the purpose of data hiding.
9. 数据封装是什么意思?
- 数据封装是一种面向对象的编程概念,将数据属性及其行为隐藏在一个单元中。
- 它通过拥有自己的方法、属性和功能来确保每个对象独立于其他对象,从而帮助开发人员在开发软件时遵循模块化。
- 它用于保护对象的私有属性,因此用于数据隐藏的目的。
10. Tell us something about JIT compiler.
- JIT stands for Just-In-Time and it is used for improving the performance during run time. It does the task of compiling parts of byte code having similar functionality at the same time thereby reducing the amount of compilation time for the code to run.
- The compiler is nothing but a translator of source code to machine-executable code. But what is special about the JIT compiler? Let us see how it works:
- First, the Java source code (.java) conversion to byte code (.class) occurs with the help of the javac compiler.
- Then, the .class files are loaded at run time by JVM and with the help of an interpreter, these are converted to machine understandable code.
- JIT compiler is a part of JVM. When the JIT compiler is enabled, the JVM analyzes the method calls in the .class files and compiles them to get more efficient and native code. It also ensures that the prioritized method calls are optimized.
- Once the above step is done, the JVM executes the optimized code directly instead of interpreting the code again. This increases the performance and speed of the execution.
10. 告诉我们一些关于 JIT 编译器的事情。
- JIT 代表 Just-In-Time,它用于提高运行时的性能。它的任务是同时编译具有相似功能的部分字节码,从而减少代码运行的编译时间。
- 编译器只不过是将源代码翻译成机器可执行代码。但是 JIT 编译器有什么特别之处呢?让我们看看它是如何工作的:
- 首先,在 javac 编译器的帮助下,Java 源代码 (.java) 转换为字节码 (.class)。
- 然后,JVM 在运行时加载 .class 文件,并在解释器的帮助下,将这些文件转换为机器可理解的代码。
- JIT 编译器是 JVM 的一部分。启用 JIT 编译器后,JVM 会分析 .class 文件中的方法调用并对其进行编译以获得更高效的原生代码。它还确保优化优先级的方法调用。
- 完成上述步骤后,JVM 会直接执行优化后的代码,而不是再次解释代码。这提高了执行的性能和速度。
11. Can you tell the difference between equals() method and equality operator (==) in Java?
| equals() | == |
|---|---|
| This is a method defined in the Object class. | It is a binary operator in Java. |
| This method is used for checking the equality of contents between two objects as per the specified business logic. | This operator is used for comparing addresses (or references), i.e checks if both the objects are pointing to the same memory location. |
Note:
- In the cases where the equals method is not overridden in a class, then the class uses the default implementation of the equals method that is closest to the parent class.
- Object class is considered as the parent class of all the java classes. The implementation of the equals method in the Object class uses the == operator to compare two objects. This default implementation can be overridden as per the business logic.
11. 你能分辨出 Java 中 equals() 方法和相等运算符 (==) 的区别吗?
| equals() | == |
|---|---|
| 这是在 Object 类中定义的方法。 | 它是 Java 中的二元运算符。 |
| 此方法用于根据指定的业务逻辑检查两个对象之间的内容是否相等。 | 该运算符用于比较地址(或引用),即检查两个对象是否指向相同的内存位置。 |
笔记:
- 在类中未重写 equals 方法的情况下,该类使用最接近父类的 equals 方法的默认实现。
- 对象类被认为是所有 java 类的父类。Object 类中 equals 方法的实现使用 == 运算符来比较两个对象。可以根据业务逻辑覆盖此默认实现。
12. How is an infinite loop declared in Java?
Infinite loops are those loops that run infinitely without any breaking conditions. Some examples of consciously declaring infinite loop is:
12. Java 中如何声明无限循环?
无限循环是那些在没有任何中断条件的情况下无限运行的循环。有意识地声明无限循环的一些例子是:
- Using For Loop:
for (;;)
{
// Business logic
// Any break logic
}
- Using while loop:
while(true){
// Business logic
// Any break logic
}
- Using do-while loop:
do{
// Business logic
// Any break logic
}while(true);
13. Briefly explain the concept of constructor overloading
Constructor overloading is the process of creating multiple constructors in the class consisting of the same name with a difference in the constructor parameters. Depending upon the number of parameters and their corresponding types, distinguishing of the different types of constructors is done by the compiler.
13. 简述构造函数重载的概念
构造函数重载是在类中创建多个同名但构造函数参数不同的构造函数的过程。根据参数的数量及其对应的类型,不同类型的构造函数的区分由编译器完成。
class Hospital {
int variable1, variable2;
double variable3;
public Hospital(int doctors, int nurses) {
variable1 = doctors;
variable2 = nurses;
}
public Hospital(int doctors) {
variable1 = doctors;
}
public Hospital(double salaries) {
variable3 = salaries
}
}
14. Define Copy constructor in java.
Copy Constructor is the constructor used when we want to initialize the value to the new object from the old object of the same class.
14. 在 java 中定义 Copy Constructor。
Copy Constructor 是当我们想将值从同一个类的旧对象初始化到新对象时使用的构造函数。
class InterviewBit{
String department;
String service;
InterviewBit(InterviewBit ib){
this.departments = ib.departments;
this.services = ib.services;
}
}
Here we are initializing the new object value from the old object value in the constructor. Although, this can also be achieved with the help of object cloning.
在这里,我们从构造函数中的旧对象值初始化新对象值。虽然,这也可以在对象克隆的帮助下实现。
15. Can the main method be Overloaded?
Yes, It is possible to overload the main method. We can create as many overloaded main methods we want. However, JVM has a predefined calling method that JVM will only call the main method with the definition of -
15. main 方法可以重载吗?
是的,可以重载 main 方法。我们可以创建任意数量的重载 main 方法。但是,JVM 有一个预定义的调用方法,JVM 只会调用具有以下定义的 main 方法 -
public static void main(string[] args)
Consider the below code snippets:
考虑以下代码片段:
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println(" Main Method");
}
public static void main(int[] args){
System.out.println("Overloaded Integer array Main Method");
}
public static void main(char[] args){
System.out.println("Overloaded Character array Main Method");
}
public static int main(double[] args){
System.out.println("Overloaded Double array Main Method");
}
public static void main(float args){
System.out.println("Overloaded float Main Method");
}
}