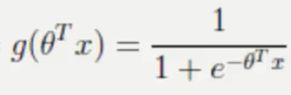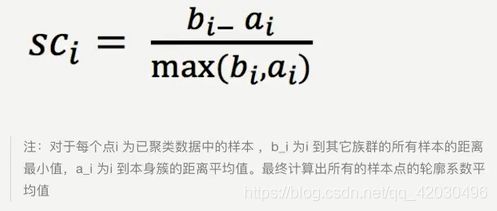黑马程序员3天快速入门python机器学习
目录
1、机器学习概述
1.1 人工智能概述
1.1.2 机器学习、深度学习能做些什么
1.2 什么是机器学习
1.2.1 定义
1.2.3 数据集构成
1.3 机器学习算法分类
1.4 机器学习开发流程
1.5 学习框架和资料介绍
1.5.1 机器学习库与框架
2、特征工程
2.1 数据集
2.1.1 可用数据集
2.1.2 sklearn数据集
2.1.3 数据集的划分
2.2 特征工程介绍
2.2.1 为什么需要特征工程(Feature Engineering)
2.2.2 什么是特征工程
2.2.3 特征工程的位置与数据处理的比较
2.3 特征抽取/特征提取/特征值化
2.3.1 为什么要特征提取?什么是特征提取?
2.3.2 字典特征提取
2.3.3 文本特征提取
2.4 特征预处理
2.4.1 为什么要进行归一化/标准化?
2.4.2 归一化
2.4.3 标准化
2.5 特征降维
2.5.1 降维
2.5.2 降维的两种方式
2.5.3 什么是特征选择
2.5.4 主成分分析(PCA)
3、分类算法
3.2 K-近邻
3.3 模型选择与调优
3.3.1 交叉验证
3.3.2 超参数搜索-网格搜索
3.4 朴素贝叶斯算法
3.4.3 联合概率、条件概率与相互独立
3.4.7 朴素贝叶斯算法总结
3.5 决策树
3.6 集成学习方法之随机森林
3.6.1 集成学习方法
3.6.2 随机森林
4、回归与聚类算法
4.1 线性回归
4.1.2 线性回归的损失和优化原理
4.2 欠拟合与过拟合
4.3 岭回归(带L2正则化的线性回归)
4.4 分类算法——逻辑回归与二分类
4.5 模型保存和加载
4.6 无监督学习-K-means算法
4.6.1 原理
4.6.6 如何去评估聚类的效果——Kmeans性能评估指标
1、机器学习概述
1.1 人工智能概述
- 机器学习、人工智能、深度学习的关系
- 机器学习是人工智能的一个实现途径
- 深度学习是机器学习的一个方法(人工神经网络)发展而来
1.1.2 机器学习、深度学习能做些什么
- 用在挖掘、预测领域:
- 应用场景:店铺销量预测、量化投资、广告推荐、企业客户分类、SQL语句安全检测分类
- 用在图像领域:
- 应用场景:街道交通标志检测、人脸识别等
- 用在自然语言处理领域:
- 应用场景:文本分类、情感分析、自动聊天、文本检测等
1.2 什么是机器学习
1.2.1 定义
机器学习是从数据中自动分析获得模型,并利用模型对未知数据进行预测
从历史数据中获得规律?这些历史数据是怎样的格式?
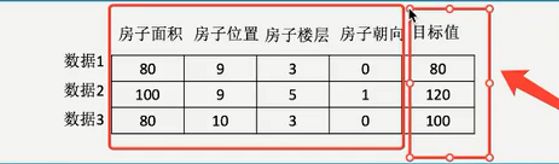
1.2.3 数据集构成
- 结构:特征值+目标值
注:
- 每一行数据可以称之为样本
- 有些数据集可以没有目标值(聚类任务:无监督学习,训练样本的标记信息是未知的,目标是通过对无标记训练样本的学习来揭示数据的内在性质和规律)
1.3 机器学习算法分类
学习目标:
- 说明机器学习算法:监督学习与无监督学习的区别
- 说明监督学习中的分类、回归的特点
- 无应用
- 监督学习:输入数据是由输入特征值+目标值组成
- 回归问题:目标值是连续型数据
- 线性回归、岭回归
- 分类问题:目标值是类别
- KNN、贝叶斯分类、决策树与随机森林、逻辑回归
- 回归问题:目标值是连续型数据
- 无监督学习:无目标值,输入数据由输入特征值所组成
- 聚类任务
- K-means
- 聚类任务
1.4 机器学习开发流程
- 获取数据
- 数据处理
- 特征工程:将数据处理为能被机器学习直接使用的数据
- 选择合适的机器学习算法进行训练的到模型
- 进行模型评估,模型不合格则返回第2步
- 应用
1.5 学习框架和资料介绍
1.5.1 机器学习库与框架
2、特征工程
2.1 数据集
学习目标:
- 知道数据集分为训练集和测试集
- 会使用sklearn数据集
- 无应用
2.1.1 可用数据集
- 公司内部的数据
- 要付费的数据接口
- 学习阶段可用的数据集
- sklearn:数据量小,方便学习
- UCI:收录了360个数据集,覆盖科学、生活、经济等领域,数据量几十万
- kaggle:大数据竞赛平台,80万科学家,真实数据,数据量巨大
- https://www.kaggle.com/datasets
- http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/
- http://scikit-learn.org/stable/datasets/index.html#datasets
2.1.2 sklearn数据集
1 scikit-learn数据集API介绍
- sklearn.datasets
- 加载获取流行数据集
- datasets.load_*()
- 获取小规模数据集,数据包含在dataset里
- datasets.fetch_*(data_home=None,subset='train')
- 获取大规模数据集,需要从网络上下载
- data_home表示数据集下载的目录,默认下载目录是~/scikit_learn_data/
- subset表示,选择加载训练集、测试集还是全部,train、test、all
2 数据集的返回值
- load和fetch返回的数据类型是datasets.base.Bunch(字典格式)
- data:特征数据数组,是[n_samples*n_features]的二维numpy.ndarray数组
- target:标签数组,是n_samples的一维numpy.ndarray数组
- DESCR:数据描述
- feature_names:特征名
- target_names:标签名
2.1.3 数据集的划分
1 数据集划分API
-
def train_test_split(*arrays, test_size=None, train_size=None, random_state=None, shuffle=True, stratify=None): """Split arrays or matrices into random train and test subsets子集合 Quick utility that wraps input validation and ``next(ShuffleSplit().split(X, y))`` and application to input data into a single call for splitting (and optionally subsampling) data in a oneliner. Read more in the :ref:`User Guide`. Parameters ---------- *arrays : sequence of indexables with same length / shape[0] Allowed inputs are lists, numpy arrays, scipy-sparse matrices or pandas dataframes. test_size : float or int, default=None If float, should be between 0.0 and 1.0 and represent the proportion of the dataset to include in the test split. If int, represents the absolute number of test samples. If None, the value is set to the complement of the train size. If ``train_size`` is also None, it will be set to 0.25. train_size : float or int, default=None If float, should be between 0.0 and 1.0 and represent the proportion of the dataset to include in the train split. If int, represents the absolute number of train samples. If None, the value is automatically set to the complement of the test size. random_state : int, RandomState instance or None, default=None Controls the shuffling applied to the data before applying the split. Pass an int for reproducible output across multiple function calls. See :term:`Glossary `. shuffle : bool, default=True Whether or not to shuffle the data before splitting. If shuffle=False then stratify must be None. stratify : array-like, default=None If not None, data is split in a stratified fashion, using this as the class labels. Read more in the :ref:`User Guide `. Returns ------- splitting : list, length=2 * len(arrays) List containing train-test split of inputs. .. versionadded:: 0.16 If the input is sparse, the output will be a ``scipy.sparse.csr_matrix``. Else, output type is the same as the input type. Examples -------- >>> import numpy as np >>> from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split >>> X, y = np.arange(10).reshape((5, 2)), range(5) >>> X array([[0, 1], [2, 3], [4, 5], [6, 7], [8, 9]]) >>> list(y) [0, 1, 2, 3, 4] >>> X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split( ... X, y, test_size=0.33, random_state=42) ... >>> X_train array([[4, 5], [0, 1], [6, 7]]) >>> y_train [2, 0, 3] >>> X_test array([[2, 3], [8, 9]]) >>> y_test [1, 4] >>> train_test_split(y, shuffle=False) [[0, 1, 2], [3, 4]] """
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# sklearn数据集使用
def datasets_demo():
'''
sklearn数据集使用
# 获取数据集
'''
# 获取小数据集
iris = load_iris()
print("鸢尾花数据集的返回值:\n",iris) #返回值是一个继承自字典的bunch
print("查看数据集描述(鸢尾花的描述):\n",iris["DESCR"]) # iris.DESCR也可以
print("查看特征值:\n", iris.data, iris.data.shape)
print("查看特征值的名字(鸢尾花特征的名字):\n",iris.feature_names)
print("鸢尾花的目标值:\n",iris.target)
print("鸢尾花的目标值的名字:\n", iris.target_names)
# 获取大数据集 subset:train test all 可选,选择要加载的数据集
# 训练集的“训练”,测试集的“测试“,两者的”全部“
#sklearn.datasets.fetch_20newsgroups(data_home=None,subset='train')
# 数据集划分(特征值,目标值,测试集的范围默认25%,随机数种子)
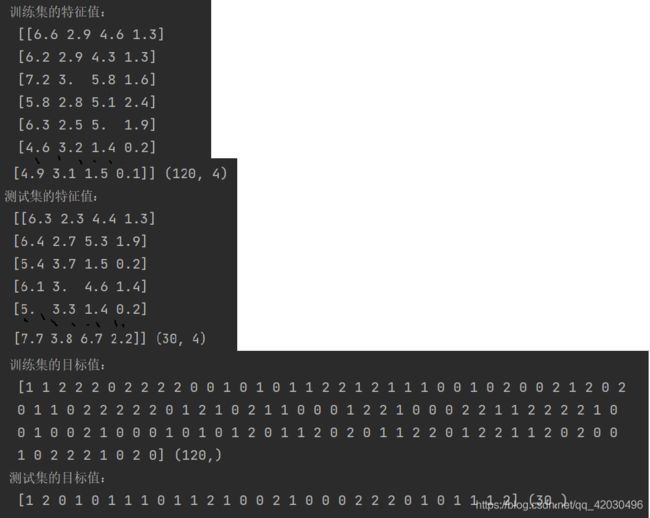
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(iris.data,iris.target,test_size=0.2,random_state=10)
print("训练集的特征值:\n",x_train,x_train.shape)
print("测试集的特征值:\n", x_test, x_test.shape)
print("训练集的目标值:\n", y_train, y_train.shape)
print("测试集的目标值:\n", y_test, y_test.shape)
return None2.2 特征工程介绍
2.2.1 为什么需要特征工程(Feature Engineering)
数据和特征决定了机器学习的上限,而模型和算法只是逼近这个上限而已
2.2.2 什么是特征工程
特征工程是使用专业背景知识和技巧处理数据,使得特征能在机器学习算法上发挥更好的作用的过程。会直接影响机器学习的效果。
2.2.3 特征工程的位置与数据处理的比较
pandas:一个数据读取非常方便以及基本的处理格式的工具。用于数据清洗、数据处理
sklearn:对特征的处理提供了强大的接口。用于特征工程
2.3 特征抽取/特征提取/特征值化
学习目标:
- 应用DictVectorizer实现对类别特征数值化、离散化
- 应用CountVectorizer实现对文本特征数值化
- 应用TfidfVectorizer实现对文本特征数值化
- 说出两种文本特征提取方式的区别
- 无应用
2.3.1 为什么要特征提取?什么是特征提取?
1 用机器学习算法对数据集进行学习,机器学习算法实际上一些统计方法(数学公式),是不能处理字符串、文本、图像的,需要转换为可用于机器学习的数字特征
- 字典特征提取
- 文本特征提取
- 图像特征提取(深度学习)
2 特征提取API
The sklearn.feature_extraction module deals with feature extraction from raw data. It currently includes methods to extract features from text and images.
2.3.2 字典特征提取
作用:对字典数据进行特征值化
1 API
class sklearn.feature_extraction.DictVectorizer(*, dtype=
- 将特征值映射列表转换为向量
- 该转换器将特征名称到特征值的映射列表(类似字典的对象)转换为 Numpy 数组或 scipy.sparse 矩阵,以便与 scikit-learn 估计器一起使用。
- 当特征值是字符串时,此转换器将执行二进制 one-hot(又名 one-of-K)编码:为该特征可以采用的每个可能的字符串值构造一个布尔值特征(为了公平)。例如,可以采用值“ham”和“spam”的特征“f”将成为输出中的两个特征,一个表示“f=ham”,另一个表示“f=spam”。
- 如果特征值是一个序列或一组字符串,则此转换器将迭代这些值并计算每个字符串值的出现次数。
- 但是,请注意,当特征值为字符串类型时,此转换器只会执行二进制 one-hot 编码。
- 如果分类特征表示为数值,例如 int 或字符串的可迭代,则可以使用 DictVectorizer
OneHotEncoder来完成二进制 one-hot 编码。 - 样本(映射)中未出现的特征将在结果数组/矩阵中具有零值。
from sklearn.feature_extraction import DictVectorizer
def dict_demo():
'''
字典特征抽取
:return:
'''
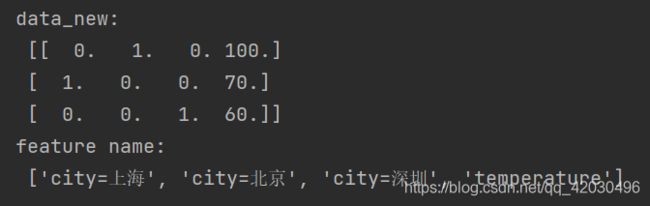
data = [{'city':'北京','temperature':100},{'city':'上海','temperature':70},{'city':'深圳','temperature':60}]
# 1、实例化一个转换器类(是否用稀疏矩阵表示
transfer = DictVectorizer(sparse=False)
# 2、调用fit_transform()方法
data_new = transfer.fit_transform(data)
print("data_new:\n",data_new)
print("feature name:\n",transfer.get_feature_names())2 应用场景:
- 数据集中类别特征比较多
- 将数据集特征转换为字典类型
- 字典特征抽取进行转换
- 本身拿到的数据就是字典类型
2.3.3 文本特征提取
作用:对文本数据进行特征值化
1 API 文本特征抽取:CountVecotrizer统计每个样本特征词出现的次数
class sklearn.feature_extraction.text.CountVectorizer(*, input='content', encoding='utf-8', decode_error='strict', strip_accents=None, lowercase=True, preprocessor=None, tokenizer=None, stop_words=None停用词, token_pattern='(?u)\b\w\w+\b', ngram_range=(1, 1), analyzer='word', max_df=1.0, min_df=1, max_features=None, vocabulary=None, binary=False, dtype=
- 将文本文档集合转换为标记计数矩阵
- 此实现使用 scipy.sparse.csr_matrix 生成计数的稀疏表示。
- 如果您不提供先验字典并且不使用进行某种特征选择的分析器,那么特征的数量将等于通过分析数据找到的词汇量大小。
英文
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
def count_demo():
"""
文本特征抽取:CountVecotrizer统计每个样本特征词出现的次数
"""
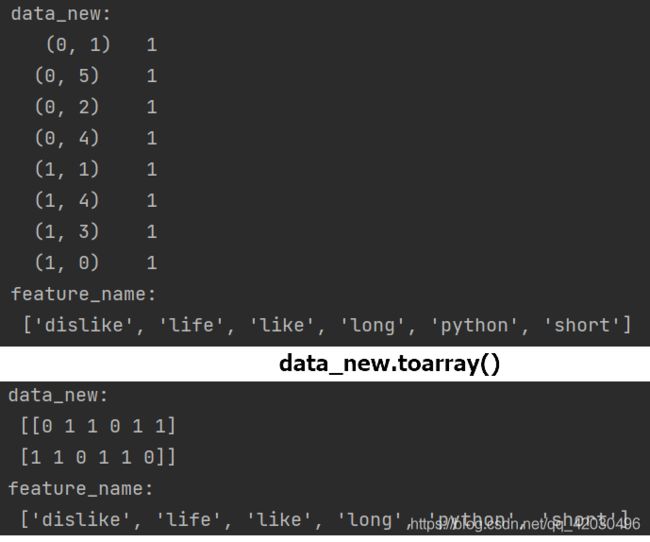
data = ["life is short, I like python","life is too long, i dislike python"]
# 1、实例化一个转换器类
transfer = CountVectorizer(stop_words=["is","too"])
# 2、调用fit_transform,用toarray()来显示二维数组
data_new = transfer.fit_transform(data)
print("data_new:\n",data_new.toarray())
print("feature_name:\n",transfer.get_feature_names())
return None中文
def count_chinese_demo():
"""
文本特征抽取:CountVecotrizer统计每个样本特征词出现的次数
不手动空格的话,需要jieba分词先处理才能得到单词
"""
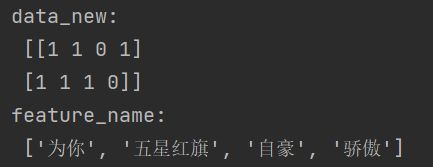
data = ["五星红旗 我 为你 骄傲","五星红旗 我 为你 自豪"]
# 1、实例化一个转换器类
transfer = CountVectorizer()
# 2、调用fit_transform,用toarray()来显示数组
data_new = transfer.fit_transform(data)
print("data_new:\n",data_new.toarray())
print("feature_name:\n",transfer.get_feature_names())
return None中文jieba分词
import jieba
def count_chinese_demo2():
'''
中文文本特征抽取,自动分词
:return:
'''
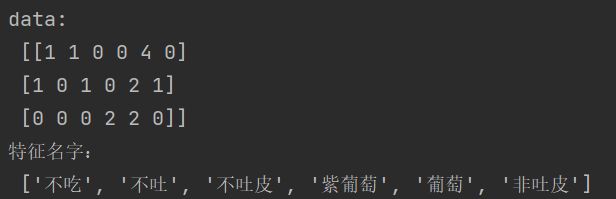
data = ["吃葡萄不吐葡萄皮,不吃葡萄倒吐葡萄皮",
"若要不吃葡萄非吐皮,就得先吃葡萄不吐皮",
"青葡萄,紫葡萄,青葡萄没紫葡萄紫"]
data_new = []
for sent in data:
# list()强转为列表形式
# “ ”.join()强转为字符串格式,其中空格是分词符号
data_new.append(" ".join(jieba.cut(sent)))
# 实例化一个转换器类
transfer = CountVectorizer()
# 调用fit_transform
data_final = transfer.fit_transform(data_new)
print(type(data_final))
print("data:\n", data_final.toarray())
print("特征名字:\n", transfer.get_feature_names())
return None2 API tfidf的方法进行文本特征抽取,关键词:在某个类别的文章中,出现的次数很多,但是在其他类别中
2.4 特征预处理
通过一些转换函数将特征数据转换成更加适合算法模型的特征数据
1 包含内容
- 数值型数据的无量纲化:
- 归一化
- 标准化
2 特征预处理API
The sklearn.preprocessing module includes scaling, centering, normalization, binarization methods.缩放、居中、归一化、二值化
2.4.1 为什么要进行归一化/标准化?
特征的单位或者大小相差较大,或者某特征的方差相比其他特征大出几个数量级,容易影响(支配)目标结果,使得一些算法无法学习到其他特征。特征具有相近的尺度,可以帮助梯度下降算法更快的收敛
2.4.2 归一化
1 定义:通过对原始数据进行变换把数据映射到(默认[0,1])之间
2 公式: 根据最值求得,容易受异常值的影响,鲁棒性较差,只适合传统精确小数据场景。
根据最值求得,容易受异常值的影响,鲁棒性较差,只适合传统精确小数据场景。
2.4.3 标准化
1 定义:通过对原始数据进行变换把数据变换到均值为0,标准差为1范围内
2 公式: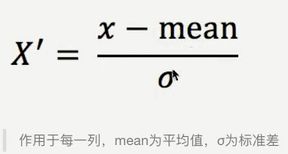 由于具有一定的数据量,少量异常点对平均值和标准差的影响并不大,所以比较稳定
由于具有一定的数据量,少量异常点对平均值和标准差的影响并不大,所以比较稳定
3 总结:在已有样本足够多的情况下比较稳定,适合现代嘈杂大数据场景。
2.5 特征降维
2.5.1 降维
维数:数组嵌套的层数
0维:标量
1维:向量
2维:矩阵
- 降维的对象是:二维数组,降低的是特征数(列数)
- 降维是指在某些限定条件下,降低随机变量(特征)个数,得到一组“不相关”主变量的过程
因为进行训练的时候,是使用特征进行学习。如果特征本身存在问题或者特征之间相关性较强,可能会出现数据冗余,对算法预测影响较大
2.5.2 降维的两种方式
- 特征选择
- 主成分分析(可以理解为一种特征提取的方式)
2.5.3 什么是特征选择
1 定义:数据中包含冗余或相关变量(或称特征、属性、指标等),旨在从原有特征中找出主要特征
2 方法:
- Filter(过滤式):主要探究特征本身特点、特征之间和目标值之间的关联
- 方差选择法:低方差特征过滤
- 相关系数:衡量特征之间的相关程度
- Embedded(嵌入式):算法自动选择特征(特征与目标值之间的关联)
- 决策树:信息熵、信息增益
- 正则化:L1、L2
- 深度学习:卷积等
3 过滤式
3.1 低方差特征过滤:删除一些低方差特征(特征大多样本的值比较相近)
class sklearn.feature_selection.VarianceThreshold(threshold=0.0)
- 删除所有低方差特征的特征选择器。
- 这种特征选择算法只看特征(X),而不是期望的输出(y),因此可以用于无监督学习。
3.2 相关系数:反映变量之间相关关系密切程度的统计指标
scipy.stats.pearsonr( x , y )
- 用于检验非相关性的 Pearson 相关系数和 p 值。
- Pearson 相关系数[1]衡量两个数据集之间的线性关系。p 值的计算依赖于每个数据集呈正态分布的假设。(有关 输入的非正态性对相关系数分布的影响的讨论,请参见 Kowalski [3]。)与其他相关系数一样,该系数在 -1 和 +1 之间变化,其中 0 表示没有相关性。-1 或 +1 的相关性意味着精确的线性关系。正相关意味着随着 x 的增加,y 也会增加。负相关意味着随着 x 增加,y 减少。
- p 值粗略地表示不相关系统产生的数据集的概率,该数据集的 Pearson 相关性至少与从这些数据集计算出的数据集一样极端。
特征之间相关性较高:
- 选取其中一个
- 加权求和
- 主成分分析
2.5.4 主成分分析(PCA)
定义:高维数据转化为低维数据的过程,在此过程中可能会舍弃原有数据、创造新的变量
作用:是数据维数压缩,尽可能降低原数据的维数(复杂度),损失少量信息
PCA技术对数据进行降维处理,可以进行重要性排序,根据需要取前面最重要的部分,同时最大程度保持了原有数据的信息。PCA技术完全无参数限制,计算过程中不需要认为设定参数或根据经验模型对计算进行干预,最后的结果只与数据相关。但是如果用户对观测对象有一定的先验知识,掌握了数据的一些特征,却无法通过参数化等方法对处理过程进行干预,可能会得不到预期的效果,效率也不高。
应用:回归分析、聚类分析
3、分类算法
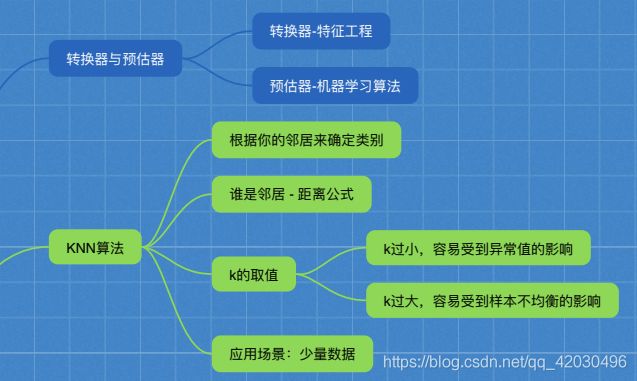
3.2 K-近邻
定义:如果一个样本在特征空间中的k个最相似(即特征空间中最邻近)的样本中的大多数属于某一个类别,则该样本也属于这个类别
应用场景:少量数据
3.3 模型选择与调优
3.3.1 交叉验证
将拿到的训练数据分为训练和验证集。
3.3.2 超参数搜索-网格搜索
通常情况下,有很多参数需要手动指定(如KNN中的K值),手动过程繁杂,所以需要对模型预设集中超参数组合。每组超参数都采用交叉验证来进行评估。最后选出最优参数组合建立模型。
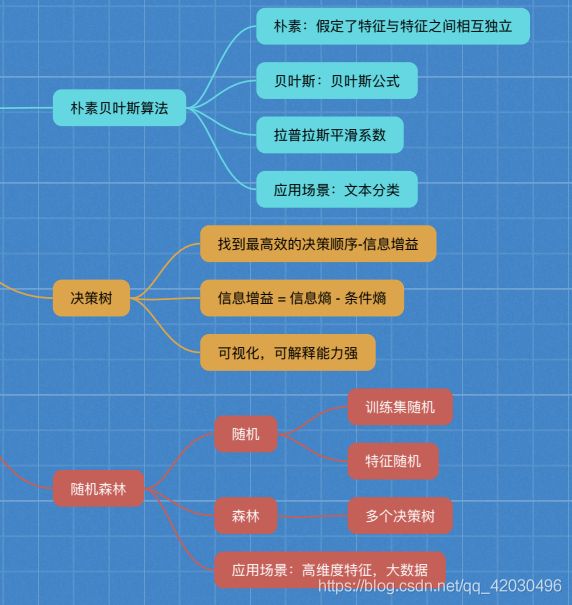
3.4 朴素贝叶斯算法
3.4.3 联合概率、条件概率与相互独立
3.4.7 朴素贝叶斯算法总结
- 优点:
- 朴素贝叶斯模型发源于古典数学理论,有稳定的分类效率
- 对缺失数据不太敏感,算法也比较简单,常用于文本分类
- 分类准确度高,速度快
- 缺点:
- 由于使用了样本属性独立性假设,所以如果特征属性有关联时效果不好
3.5 决策树
如何高效的进行决策?特征的先后顺序很重要
1 决策树的划分依据之一——信息增益(知道某个特征后,不确定性的减少程度)
3.6 集成学习方法之随机森林
3.6.1 集成学习方法
集成学习通过建立几个模型组合来解决单一预测问题。工作原理是生成多个分类器/模型,各自独立的学习和做出预测。这些预测最后结合成组合预测,因此优于任何一个单分类做出的预测。
3.6.2 随机森林
- 随机:
- 特征随机:从M个特征中随机抽取m个特征建立决策树,M >> m,有降维的效果
- 训练集随机:N个样本中随机有放回的抽样N个
- 森林:包含多个决策树的分类器,并且其输出的类别是由个别树输出的类别的众数决定的。
- 总结
- 有极好的准确率,可解释能力强
- 能够有效运行在大数据集上,处理具有高维特征的输入样本,而且不需要降维
- 能够评估各个特征在分类问题上的重要性
4、回归与聚类算法
4.1 线性回归
- 应用场景:回归问题,目标值是连续型数据
- 定义:是利用回归方程对一个或多个自变量和因变量之间关系进行建模的一种分析方式,找到特征值和目标值的关系,以便预测
4.1.2 线性回归的损失和优化原理
- 目标:求模型参数(使预测准确的模型参数)
- 损失函数:衡量真实和预测的误差(最小二乘法)
- 优化损失:
- 正规方程:直接求解权重值,仅用于线性回归,特征过多过复杂时,求解速度因为矩阵求逆而变得很慢且得不到结果
- 梯度下降:手动指定学习率,不断更新W值,面对训练数据规模十分庞大的任务,能够找到较好的结果(需要计算所有样本的值才能得出梯度,计算量大)
- 随机梯度下降:一次迭代只考虑一个训练样本。高效、容易实现,但是需要许多超参数:如正则项参数、迭代数,而且对特征标准化敏感
- 随机平均梯度:应用于岭回归、逻辑回归中,是因为收敛速度慢而提出的
- 回归性能评估:均方误差评价机制
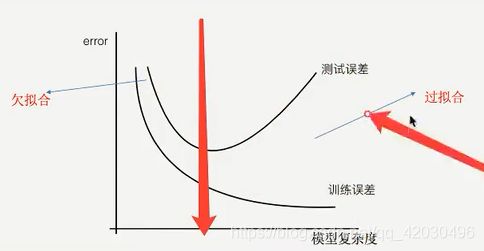
4.2 欠拟合与过拟合
| 解决高方差/过拟合 | 解决高偏差/欠拟合 |
| 获得更多的训练实例 | 尝试增加多项式特征 |
| 尝试减少特征数量 | 尝试获得更多的特征 |
| 尝试增加正则化程度λ | 尝试减少正则化程度λ |
4.3 岭回归(带L2正则化的线性回归)
L2正则化:损失函数+λ惩罚项,削弱某个特征的影响,参数越小(惩罚项系数=正则化力度)说明模型越简单越不容易产生过拟合
4.4 分类算法——逻辑回归与二分类
4.5 模型保存和加载
训练好或计算好一个模型之后,主要是保存算法参数
4.6 无监督学习-K-means算法
4.6.1 原理
- 随机设置K个(超参数:看需求、网格搜索选择合适的K)特征空间内的点作为初始聚类中心
- 对于其他每个点计算到K个中心的距离,未知的点选择最近的一个聚类中心点作为标记类别
- 接着对着标记的聚类中心,平均值重新计算每个聚类新的中心点
- 如果计算得到的新中心点与原中心点一样,那么结束,否则重新进行第二步
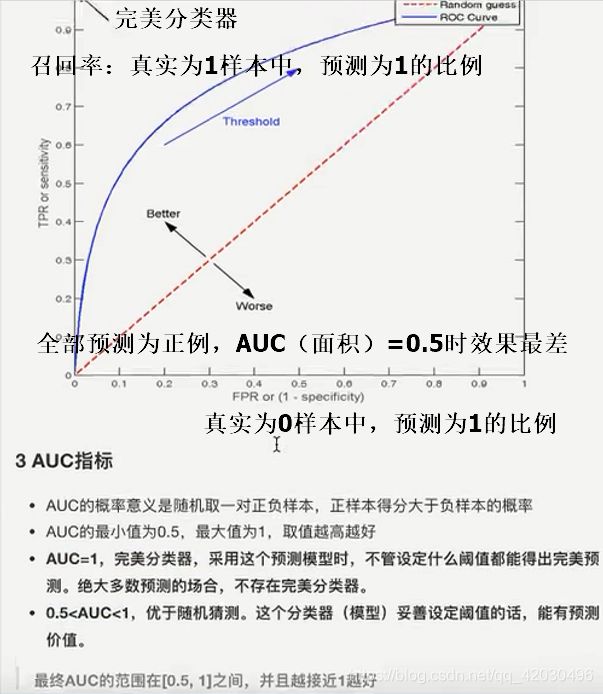
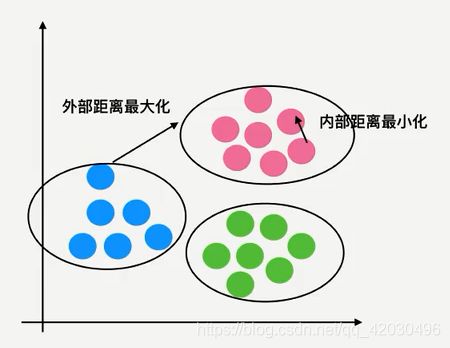
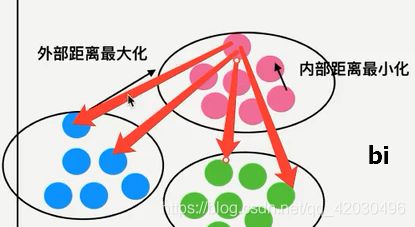
4.6.6 如何去评估聚类的效果——Kmeans性能评估指标
1 轮廓系数
2 总结
- 特点:采用迭代式算法,直观易懂并且非常实用
- 缺点:容易收敛到局部最优解(多次聚类可避免此问题)
- 应用场景:没有目标值、分类问题
- 注意:聚类一般再分类之前